Humans as Primates - Primate Evolution
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are phylogenetic trees?
A diagram which shows the evolutionary relationship between a number of organisms derived by a common ancestor.
how to properly write binomial system
Homo sapiens The genus is captalised while the species is not. It is underlined.
What is primates
primate is a taxonomic order which classifies humans, apes, monkeys and some other related animals
What are the characteristics of Primates
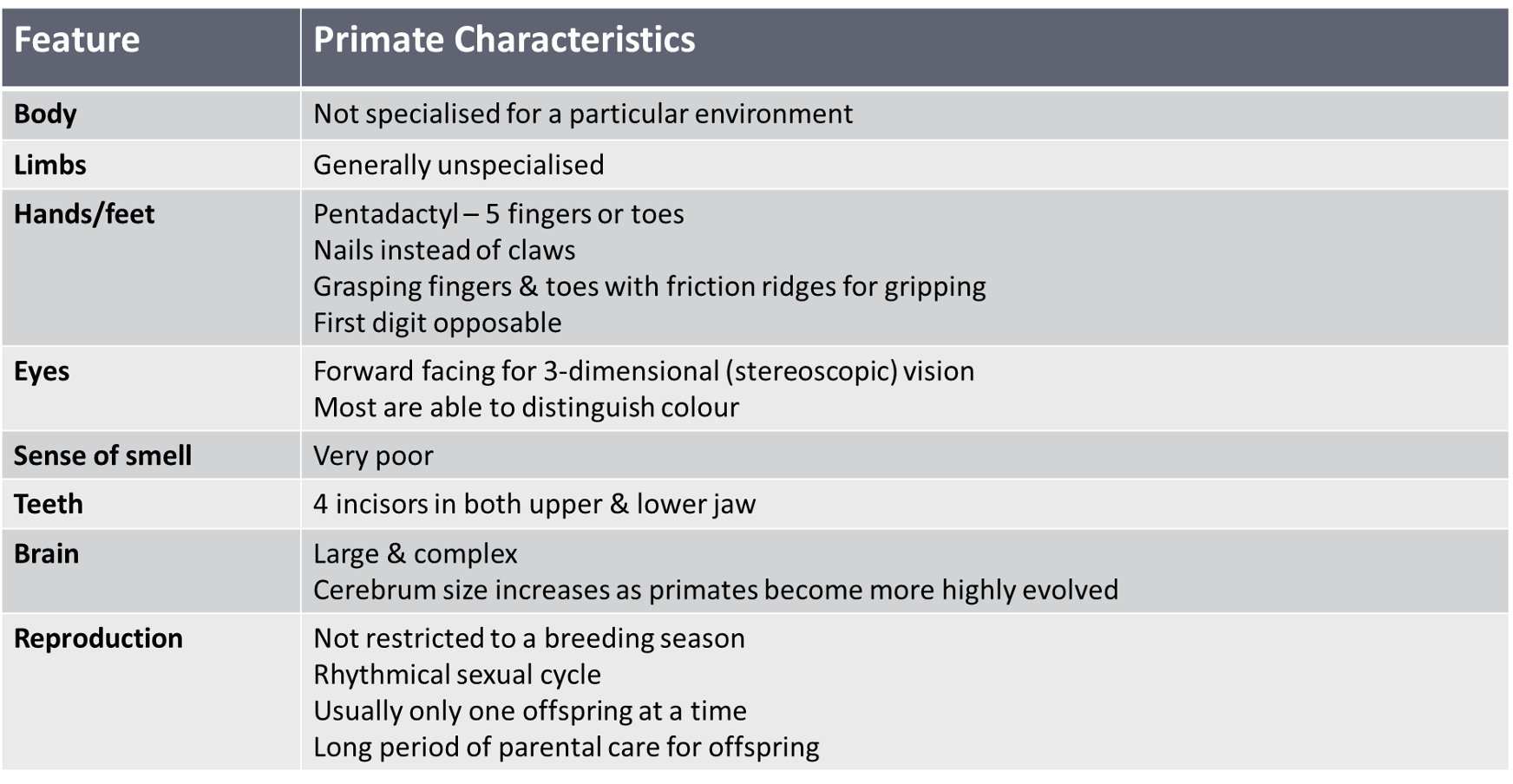
Characteristics and Trends of Brain in Primates as go from low to high order
Characteristic | Trend |
Size | Increasing size of brain relative to size of body |
Convolutions | Gradual increase in the number of folds in the surface of the cerebrum |
Cerebral Cortex | Cerebral cortex making up an increasingly large proportion of the brain (higher functions) |
Frontal lobe | Has greatest enlargement in surface area, compared with other apes (responsible for higher functioning: thinking, reasoning, planning & processing) |
Dental characteristics and trends in primates:
Dental arcade - the shape of the tooth row - evolved differently. Humans - parabolic shape. Apes - U pattern.
Diastema - a gap in a row of teeth, usually referring to gap next to canine teeth in primates. Allows teeth to interlock. Not present in modern humans.
for humans, trend towards smaller molars & decrease in robustness of teeth.
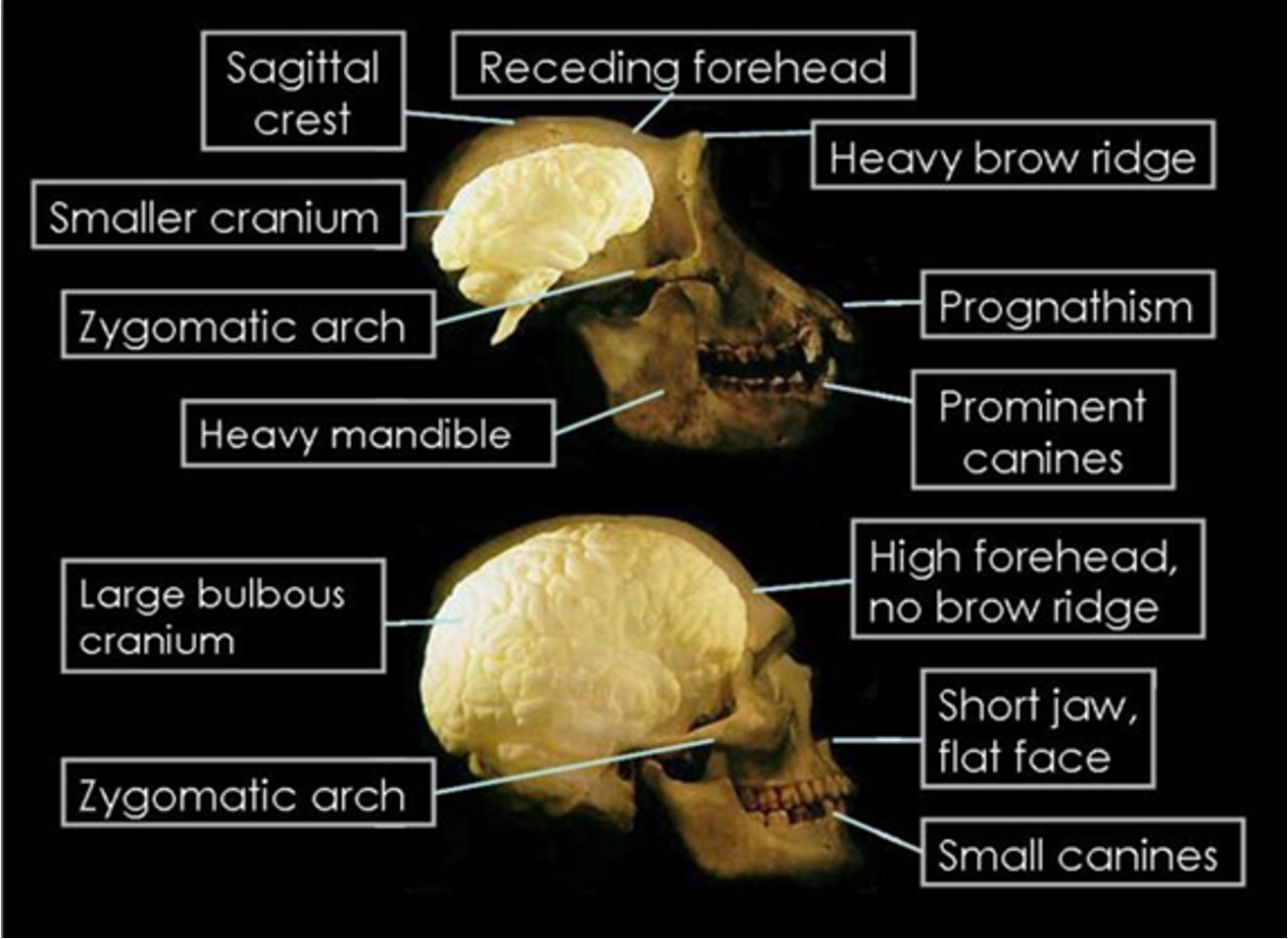
differences in head in general between humans and lower order primates
apes have prominent brow ridges whereas humans have reduced brow ridges
Characteristics and Trends of sight and smell in Primates as go from low to high order
Characteristic | Trend |
Eyes | Increasing efficiency in vision Eyes becoming gradually more forward facing, to give stereoscopic vision |
Eye Socket | Eyes gradually becoming enclosed in a protective bony socket |
Visual area of brain | Increasing proportion of the cerebrum devoted to vision |
Smell | Sense of smell reduced with gradual reduction in length of the snout |
Trends of mobility of digits in primates
Characteristic | Trend |
Mobility | Increasing mobility & ability to move digits independently of one another |
Opposability | First digit opposable & increasing length results in increased effectiveness of opposability |
Claws/nails | Primitive primates retain claws on some digits; higher primates have nails on all digits |
Types of grips:
Precision grip: one of the hallmarks of human beings, but is not unique to humans. Amount of contact between index finger & thumb is unique and enables humans to handle small or delicate objects effectively
•Such as used for holding a pencil or needle when sewing.
Power grip - happens when thumb & fingers apply force against the palm
features that allow for brachiation (arm swinging in monkeys) - NOT IN TEST
shoulders - short/reduced clavicle, high shoulder blades, mobile shoulder joint
arms - longer arms/smaller arm to leg ratio, flexible elbow joint
hands - long, curved fingers, short thumbs, robust but flexible wrist joint
How:
- adapted for swinging in trees
hands adapted to grasp branches
provide strength to support the weight of the hominin in trees
creates energy efficent pattern of movement