Drivers Ed Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pls don't use this as your only form of study :)
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
1
New cards
(Zone Control) 6 zones that surround your vehicle
Left front, front, right front, left rear, rear, right rear
2
New cards
Primary reason we use push-pull steering with the 8&4 or 9&3 hand position?
So that if airbags are deployed the drivers hands are not pushed back into their face
3
New cards
A red icon appears on the instrument cluster and stays on while driving, what is needed?
This means there's a safety issue or something is seriously wrong with your car. Safely pull over, turn off the engine, and call a repair service, auto shop, or refer to your owner’s manual to determine the problem and if your car needs a tow, etc.
4
New cards
Reference point
A reference point is a place on the car that you see in relationship to a place on the ground.
5
New cards
5 standard reference points
Front limit, Rear limit, Right side limit, 3 feet away from right edge, Left side limit
6
New cards
Front Limit
Corner post/side mirrors (Line up 3-6 inch line/curb to front of car)
7
New cards
Rear Limit
Middle of side rear window/1 foot behind door post (Line up 3-6 inch line/curb to rear of car)
8
New cards
Right Side Limit
Center of the hood (Line up 3-6 inch line/curb to the right side of the car)
9
New cards
3 Feet Away from the Right Edge
Middle of the right half of hood (Line up 3 ft line/curb to the right side of the car)
10
New cards
Left Side Limit
1 Foot inside left front corner of hood (Line up 3-6 inch curb to the left side of the car)
11
New cards
What does it mean to keep your vehicle “in balance”
To keep your vehicle “in balance” means to use smooth, precise steering, braking, and accelerating actions
12
New cards
How to keep your vehicle in balance throughout curves and turns
You keep your vehicle in balance throughout curves and turns by maintaining a constant speed
13
New cards
When parking and securing your vehicle, you need to apply the brake firmly until which two items have been taken care of? Then turn off the headlights and engine
Put vehicle in park and put e-brake on
14
New cards
Target
A stationary object that’s as far ahead as you can see, above the center of your intended lane
15
New cards
Zone Control =
Space Management
16
New cards
Turn off high beams and fog lights when
Following another car within 350 ft in front of you, an oncoming vehicle is within 500 ft
17
New cards
3 categories of road signs
Regulatory, Warning, Guidance
18
New cards
Warning signs
Yellow/Orange and black, warn you to slow down and be prepared to stop if necessary; a special situation or hazard is ahead, change in attention, speed, position is needed
19
New cards
Regulatory signs
White and black, instructing and reinforcing traffic laws and regulations
20
New cards
Guidance signs
Green/blue/brown, directional and mileage information to specific destinations
21
New cards
Open zone
Zone is open for you to travel in, more than 4 seconds of space
22
New cards
Closed zone
Zone you are unable to travel in because of LOS or POT obstruction
23
New cards
Unstable Zone
Zone that has potential for danger or hazard is present in that zone
24
New cards
Legal stop
Stop made at the stop line, crosswalk, implied crosswalk, or curb line as required by law
25
New cards
Safety stop
Moving your car forward until you have an unobstructed view of approaching traffic
26
New cards
How many LP’s are there
5
27
New cards
Where is lane position 1
The middle of the lane (basic position)
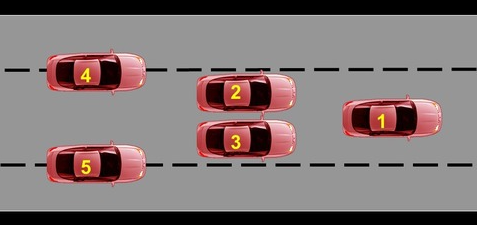
28
New cards
Where is lane position 2
The left of the lane, not passing lane line
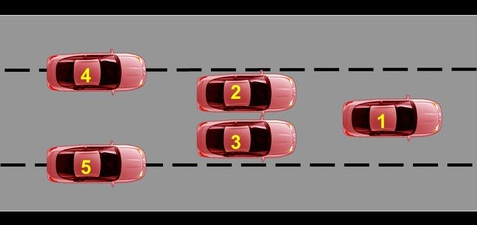
29
New cards
Where is lane position 3
The right of the lane, not passing lane line
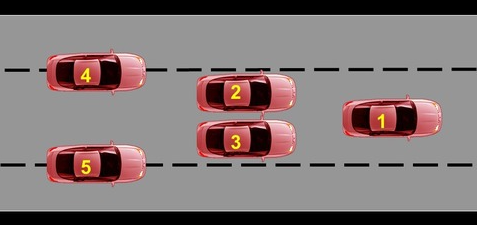
30
New cards
Where is lane position 4
The far left on the lane, partially passing lane line
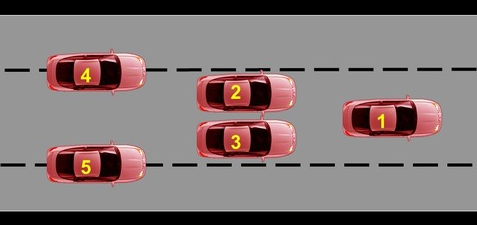
31
New cards
Where is lane position 5
The far right on the lane, partially passing lane line
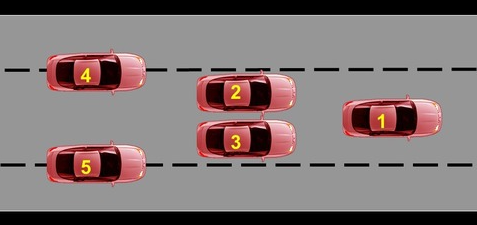
32
New cards
What vision is needed for reference points and lane lines?
Fringe vision
33
New cards
Zone control searching
Searching zones for changing conditions and LOS/POT problems
34
New cards
Reference points help you:
Maneuver tight spaces accurately, determine LP and front/rear position
35
New cards
Can you start your turn after the legal stop?
Yes, if no safety stop is needed and after yielding/waiting (if required)
36
New cards
Emergency vehicles
Vehicles going in both directions on a non-divided highway or street (no median) must pull over/stop for emergency vehicles passing with lights/sirens on
37
New cards
Bicycles can share the road when:
They are going in the same direction as traffic
38
New cards
Approaching intersection look:
Rearview, 45 left, front, 45 right
39
New cards
At intersection look:
Rearview, 90 left, front, 90 right
40
New cards
Crossbuck=
Yield
41
New cards
Proper intersection search pattern (without degrees)
Rear, left, front, right
42
New cards
When checking mirror(s) look for:
Speed, size, and distance away of the vehicles behind
43
New cards
Point of no return
When you do not have 2 seconds to stop
44
New cards
Fixed zones
Stationary
45
New cards
Moving zones
Moving
46
New cards
When you back and turn, your pivot point is:
Over the rear wheels
47
New cards
ARSMOG
Alert, Rearview Mirror, Signal, Mirrors, Over the shoulder, Go when safe
48
New cards
Required insurance coverage
Liability, PIP, Uninsured motorist bodily injury
49
New cards
WORST way to communicate with other drivers
Flashing high-beam headlights
50
New cards
Roads are slickest from rainfall:
First 15 minutes of rain after a long dry spell
51
New cards
Don’t use high beams in:
Fog, snow, or when oncoming traffic is within 500 ft and following within 350 ft
52
New cards
If a vehicle drifts into your lane
Look to crash softly, steer to right (LP 3/5)
53
New cards
On freeways left lane is used for
Passing left and turning left
54
New cards
Tailgated
Consider increasing follow distance
55
New cards
Check the rear when driving once every
15 seconds
56
New cards
Regaining control from skid
Don’t brake/accelerate, aim towards target
57
New cards
Fog line
A bright white line painted on the right side of a roadway separating the roadway from what is known as an improved shoulder
58
New cards
Rumble strips
A series of raised elements intended to alert inattentive drivers at or near the center line of a roadway
59
New cards
Why is it good practice to have headlights on during the day?
So other drivers can see you from all angles
60
New cards
Reference points help overcome blind spots by
Maneuvering tight spaces, determine LP, front/rear, comprehending distance
61
New cards
Cars going straight typically:
Go first, while cars backing yield to EVERYONE
62
New cards
How should you approach your vehicle?
You should approach your vehicle with your key in hand facing out and searching for dangerous circumstances. Do not unlock your car before you have approached.
63
New cards
Shape of regulatory signs
Triangle, octagon, or vertical rectangle
64
New cards
Shape of warning signs
Triangular, diamond
65
New cards
Shape of guide signs
Circle, rectangle (trapezoid?)
66
New cards
How should you yield to pedestrians crossing at intersections or crosswalks?
Stop and remain stopped at any crosswalk (marked or unmarked) until people walking have cleared your lane, plus the lane next to you.
67
New cards
How should you yield to blind pedestrians?
Stop if the person is about to cross or is crossing the road. Remain stopped until the person has crossed the entire road, even if you have a green light.
68
New cards
What is required when turning right on a red light?
Bring the vehicle to a complete stop, yield to oncoming traffic and pedestrians (LP 1/3)
69
New cards
What is required when turning left on a round green light?
Yield to pedestrians and oncoming traffic (LP 1/2)
70
New cards
How do you yield at a two way stop
Drivers turning left yield right of way to cars approaching or going straight-usually the driver that gets there first has right of way (when in doubt yield to driver on right)
71
New cards
How do you yield at an uncontrolled intersection?
Yield to vehicles in the intersection or approaching from the right
72
New cards
How do you yield at a T-intersection?
If you are driving on the dead end road, you must yield to traffic that is going past from the left and right
73
New cards
How do you yield in a roundabout?
Entering traffic must yield to both lanes of the circulating roadway
74
New cards
What are the two biggest factors in work zone related crashes?
Driver inattention and speeding
75
New cards
How should you safely handle railroad crossing?
Treat it as a yield/stop sign
76
New cards
Define yield
Let other road users go first
77
New cards
Oregon’s Basic Speed Law
A motorist must drive at a speed that is reasonable, not surpassing the speed limit, and safe for conditions
78
New cards
Solid Yellow Line
Passing is prohibited, two way
79
New cards
Dashed Yellow Line
Passing is allowed, two way
80
New cards
Solid White Line
Passing is prohibited, one way
81
New cards
Dashed White Line
Passing is allowed, one way
82
New cards
Double Solid Yellow Line
Passing is prohibited, two way
83
New cards
One solid line, one dotted line
Passing is prohibited on one side, for the other it is allowed
84
New cards
Use of central vision
Central Vision to see our target, provide a visual lead, and read signs and signals
85
New cards
Use of fringe vision
Fringe Vision to see reference points for precision vehicle placement
86
New cards
Line of sight blockage
Your line of sight is the visible path of travel from your vehicle to the target area. A blockage is something stopping you from seeing something in your line of sight
87
New cards
Path of travel blockage
Path of travel is the series of continuous positions your vehicle takes in the process of moving to your target. A blockage is something that prevents you from continuing on your path safely.
88
New cards
How do you drive safely through curves
Reduce speed before entering the curve, and slowly lighten the pressure on the brake until reaching the apex point. At the apex or exit point, apply light acceleration to pull the car out of the curve.
89
New cards
What type of zone is a curve
Closed
90
New cards
Zone Control
An organized method for managing six zones of space surrounding your vehicle. Allows you to see and respond to changes in the traffic environment.
91
New cards
Searching in zone control
Search for LOS/POT blockages
92
New cards
Types of insurance converage
Propety damage liability, bodily injury liability, medical payments insurance, collision coverage, comprehensive coverage, no fault coverage, uninsured motorist coverage
93
New cards
How do you enter a freeway
On the on ramp
94
New cards
Freeway speed
Match speed of others
95
New cards
Who yields on freeways
People on the on ramp to people already on the freeway
96
New cards
3 Stop positions
before the line, before the crosswalk, before the two roads meet
97
New cards
3 Braking actions
Controlled braking, Threshold braking, Cover braking
98
New cards
Controlled braking
Press the brakes smoothly while applying steady pressure
99
New cards
Threshold braking
Brake with maximum pressure until car almost fully stops, then lightly roll forward until desired stop position
100
New cards
Cover braking
Removing your right foot from the accelerator and hovering it over the brake pedal, without initially applying any pressure