MIC 206: Lab 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 - Winogradsky column, Membrane filter method, Biofilms, Fungi, Protozoans
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the winogradsky column
A self-sustaining ecosystem for environmental microbes
What elements comes from each of component of the construction of the winogradsky column
Source of microbes: pond water and mud
Carbon source: egg shells and newspaper
Carbon, sulfur, and calcium source: egg shells
What are coliforms
Indicator organisms associated with water polluted with biological waste
Why do you test for coliforms
To test water for specific harmful microbe: viruses, protozoa, and bacteria is very time-consuming and expensive
*Coliform testing does not indicate presence of specific chemical contaminants
What are characteristics of coliforms
Facultative, rod-shaped, gram negative, non-sporulating, lactose fermenting, gas producers
What type of plate is the m-ENDO agar LES:
Selective: inhibits the growth of gram-positive organism (contains bile salts to inhibit gram positive)
Differential: displays a color difference between lactose fermenting and nonfermenting organisms (contains fuchsin sulfite as an indicator to identify lactose fermenters)
What are biofilms
Microbial community that attaches to surface and form a matrix structure
What does biofilm structure provide
Provides a physical barrier to antimicrobial agents, antibodies, and antibiotics
What are the steps to a biofilm formation
1. Individual cells populate the surface
2. An extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) is produced and attachment becomes irreversible
3 & 4. Biofilm architecture develops and matures
5. Single cells are released from biofilm
What are fungi
- All eukaryotic cells (with membrane bound nucleus)
- Some are single cell/branching filaments organisms
- Common agents of human disease (athlete’s foot, ringworm, valley fever)
- Obtain food from other organisms by decomposers
- Major divisions (phyla) of fungi are mainly classified based on sexual reproductive structures
What are molds
- Average size: 10 × 40 um
- Filamentous: each filament is referred to as hypha → mass of hyphae is called mycelium
- Sporangia: enclosure where spores are formed
What are yeast
- Average size: 5um
- Single-cell organisms of spherical, elliptical, or cylindrical shape
- Replicate by budding: pseudohyphae
What are classification of microorganisms (prokaryotes vs eukaryotes)
Prokaryotes: bacteria
Eukaryotes: algae, fungi, protozoa
Viruses: neither
What is a protozoa
Single-celled eukaryotes that can be found in 2 forms: cysts and trophozoite
What is a cyst (1of 2 forms of protozoa)
Cysts: usually passed in feces and provided with highly condensed cytoplasm and resistant cell wall (usually more roundish compared to trophozoite)
What is a trophozoite (1of 2 forms of protozoa)
Trophozoite: active, feeding, multiplying stage → contains many organelles and some unique structures to aid in identification (nucleus, vacuoles)
What is protozoa classification based on
- Amoeboid: pseudopodia → false feet, extensions of internal guts of a cell
- Ciliated: cilia → hair-like projections used for movement
- Flagellated: flagella → long, filament-like tails used for swimming
- Sporozoan: non-motile
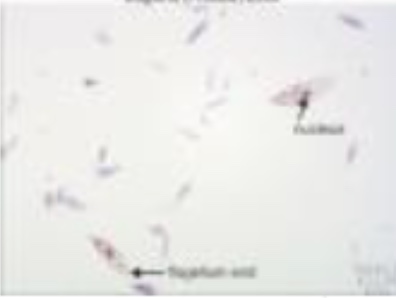
What is this (classification of protozoa based on locomotion structure)
Flagellated
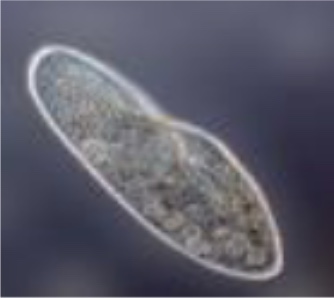
What is this (classification of protozoa based on locomotion structure)
Ciliated
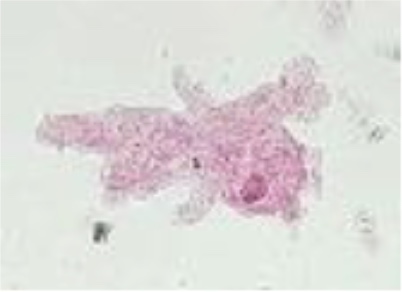
What is this (classification of protozoa based on locomotion structure)
Amoeboid
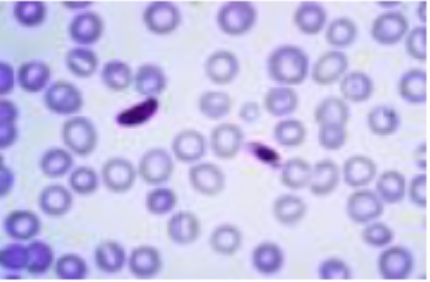
What is this (classification of protozoa based on locomotion structure)
Sporozoan
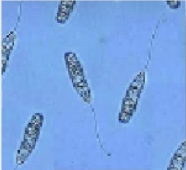
What is this (1/4 classification of protozoans)
Subphylum mastigophora (flagellates)
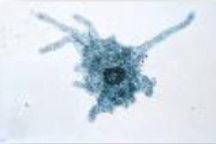
What is this (1/4 classification of protozoans)
Subphylum sarcodina (amoebas)
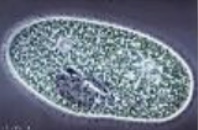
What is this (1/4 classification of protozoans)
Phylum Ciliophora (ciliates)
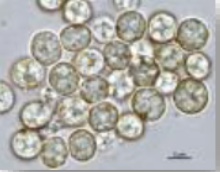
What is this (1/4 classification of protozoans)
Phylum apicomplexa (sporozoans)
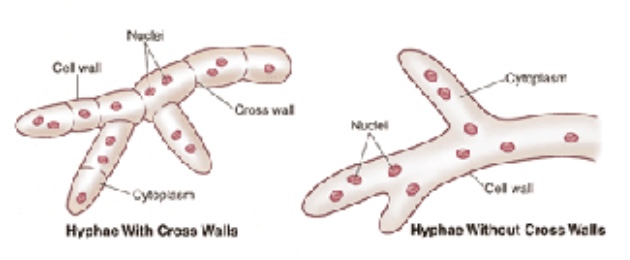
What is septate and and aseptate in mold
Septate: crosswalls
Aseptate: lack crosswalls
What is the order of bacteria, mold and yeast from smallest to biggest and how can you differentiate them if shown
(Smallest) bacteria → yeast → mold (Largest)
*Bacteria has the highest magnification so if shown a microscope, if its on 100x, its probably bacteria whereas if its on 10x, it might be mold. Mold will have have the little filaments sticking out
What does a more intense crystal violet indicate in a test tube regarding biofilms
More intense crystal violet means more mass you have on biofilm
Describe the oxygen and sulfur gradient in the winogradsky column
Oxygen is the highest at the top and sulfur is the lowest at the top. As you move down the gradient, oxygen levels decrease and sulfur levels increase
What is an example of an associated organisms in the GI tract relating to coliforms
E. coli → if E. coli is found in water source, there may be a recent fecal contamination of the water source, meaning a disease-causing agent count be present