AP Psych Chap 8 & 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/280
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:45 PM on 11/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
1
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
Contribution: developed the theory of "classical conditioning" while working with dogs
Significance: Father of Classical Conditioning
Significance: Father of Classical Conditioning
2
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Learning that takes place when two or more stimuli are paired together
UCS = UCR; NS + UCS = UCR; & CS = CR
UCS = UCR; NS + UCS = UCR; & CS = CR
3
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulus
Part of Classical Conditioning
It is the stimulus that triggers a natural reflexive response.
Pavlov's Dogs: "Meat"
Little Albert: "Loud noise"
It is the stimulus that triggers a natural reflexive response.
Pavlov's Dogs: "Meat"
Little Albert: "Loud noise"
4
New cards
Conditioned Stimulus
Part of Classical Conditioning
It initially has no effect but after conditioning, it triggers a natural reflexive response.
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Bell"
Little Albert: "White Mouse"
It initially has no effect but after conditioning, it triggers a natural reflexive response.
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Bell"
Little Albert: "White Mouse"
5
New cards
Extinction
Classical Conditioning: The disappearance of a behavior because CS no longer paired with the UCS
Operant Conditioning: The disappearance of a behavior because it is no longer reinforced or punished
Operant Conditioning: The disappearance of a behavior because it is no longer reinforced or punished
6
New cards
Spontaneous Recovery
Classical Conditioning: When a previous CR returns after it has been extinguished
Operant Conditioning: Occurs when a response begins again after extinction
Operant Conditioning: Occurs when a response begins again after extinction
7
New cards
Stimulus Generalization
Classical Conditioning: When the NS and the CS are different. (Example: Little Albert being afraid of any thing that is white and furry)
Operant Conditioning: When a reinforced/punished behavior occurs in a setting/situation where it was NOT learned (Example: Not cursing at home or at school)
Operant Conditioning: When a reinforced/punished behavior occurs in a setting/situation where it was NOT learned (Example: Not cursing at home or at school)
8
New cards
Stimulus Discrimination
Classical Conditioning: When the NS and the CS are the same (Example: Little Albert being afraid of a white mouse)
Operant Conditioning: When a reinforced/punished behavior occurs in a setting/situation where it was learned (Example: Cursing only at home because it is acceptable but not at school)
Operant Conditioning: When a reinforced/punished behavior occurs in a setting/situation where it was learned (Example: Cursing only at home because it is acceptable but not at school)

9
New cards
Higher Order Conditioning
When the first CS is paired with a second CS
The second CS is presented briefly before the first CS
The second CS is presented briefly before the first CS
10
New cards
Taste Aversions
Psychologist: Garcia
Defined: If you ingest an unusual food or drink and then become nauseous, you will probably develop an aversion to the food or drink.
Significance: Violates the acquisition principles of classical conditioning
Defined: If you ingest an unusual food or drink and then become nauseous, you will probably develop an aversion to the food or drink.
Significance: Violates the acquisition principles of classical conditioning
11
New cards
Operant conditioning
Defined: Learning is based on the association of one's behavior and its consequences. Consequences are reinforced or punished
Example: You choose to break curfew based on the consequences
Example: You choose to break curfew based on the consequences

12
New cards
Law of Effect
Psychologist: Edward Thorndike
Defined: if a behavior results in a satisfying consequence, it will likely be repeated whereas; if a behavior results in a unsatisfying consequence, it will NOT likely be repeated
Example: If you complement your mother and she lets you stay out past curfew, you will complement her again
Defined: if a behavior results in a satisfying consequence, it will likely be repeated whereas; if a behavior results in a unsatisfying consequence, it will NOT likely be repeated
Example: If you complement your mother and she lets you stay out past curfew, you will complement her again
13
New cards
B.F. Skinner
Contributions: Invented the Operant chamber, aka his ________ box, to use in his research of animal learning.
Significance: Father & Developer of Operant Conditioing
Significance: Father & Developer of Operant Conditioing

14
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Part of Operant Conditioning
Adding something to increase the likelihood of a behavior occuring again
Example: Receiving $5 for every "A" in high school
Adding something to increase the likelihood of a behavior occuring again
Example: Receiving $5 for every "A" in high school
15
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
Part of Operant Conditioning
Increasing the likelihood of a behavior occurring again by removing a negative stimuli
Example: Taking aspirin to relieve a headache
Increasing the likelihood of a behavior occurring again by removing a negative stimuli
Example: Taking aspirin to relieve a headache
16
New cards
Positive Punishment
Part of Operant Conditioning
Adding something to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring again
Example: Spanking and yelling
Adding something to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring again
Example: Spanking and yelling
17
New cards
Negative Punishment
Part of Operant Conditioning
Removing something to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring again
Example: Grounding
Removing something to decrease the likelihood of a behavior occurring again
Example: Grounding

18
New cards
Shaping
Part of Operant Conditioning
Positively reinforcing closer and closer approximations of a desird behavior to teach a new behavior
Positively reinforcing closer and closer approximations of a desird behavior to teach a new behavior
19
New cards
Primary Reinforcers
Reinforcers that are rewarding such as food, water, rest, whose natural properties are reinforcing.
20
New cards
Secondary Reinforcers
Defined: Reinforcers that are rewarding because we learned that are reinforcing.
Example: praise, money, the chance to play video games.
Example: praise, money, the chance to play video games.
21
New cards
Fixed-Ratio Schedule
Defined: schedule of reinforcement after a set number of responses.
Example: Being paid for every 10 pizzas made
Example: Being paid for every 10 pizzas made
22
New cards
Variable-Ratio Schedule
Defined: schedule of reinforcement after a varying number of responses.
Example: playing a slot machine
Example: playing a slot machine
23
New cards
Fixed-Interval Schedule
Defined: schedule of reinforcement after a fixed amount of time has passed
Example: cramming for an exam
Example: cramming for an exam
24
New cards
Variable-Interval Schedule
Defined: schedule of reinforcement after varying amounts of time
Example: pop (surprise) quizzes in class
Example: pop (surprise) quizzes in class
25
New cards
Instinctive Drift
Defined: when animals revert to instinctive behaviors rather than the operantly conditioned behaviors
Examples: Rats will not walk backward, chickens won't hit a ball and run to first base, and pigs won't put wooden dollars into a piggy bank
Examples: Rats will not walk backward, chickens won't hit a ball and run to first base, and pigs won't put wooden dollars into a piggy bank
26
New cards
Observational Learning
Defined: learn by watching others
Example: BoBo Doll Study
Example: BoBo Doll Study
27
New cards
Latent Learning
Defined: Learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
Example: Tolman's rats would only complete the maze if there was cheese for them at the end of the maze
Example: Tolman's rats would only complete the maze if there was cheese for them at the end of the maze
28
New cards
Insight Learning
Defined: suddenly knowing the solution to the problem
Example: When taking a test and the previous answer comes to you without effort
Example: When taking a test and the previous answer comes to you without effort
29
New cards
Acquisition of Classical Conditioning
Frequency: the more often the CS and the US are paired together
Timing: the CS is presented a half a second before the US
Timing: the CS is presented a half a second before the US
30
New cards
Biological Preparedness
Defined: humans and animals have predisposed fears that help us survive
Examples; Phobia of heights keeps us away from danger
Examples; Phobia of heights keeps us away from danger
31
New cards
Unconditioned Response
Part of Classical Conditioning
It is the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the stimulus
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Salivating to the Meat"
Little Albert: "Screaming at the Loud Noise"
It is the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the stimulus
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Salivating to the Meat"
Little Albert: "Screaming at the Loud Noise"
32
New cards
Associative Learning
Defined: learn by putting together two events
Example: Expect to hear thunder after viewing lightening
Example: Expect to hear thunder after viewing lightening
33
New cards
Habituation
Defined: An organisms decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
Example: Your parents yell at you a lot and eventually you tune out their yelling
Example: Your parents yell at you a lot and eventually you tune out their yelling
34
New cards
Watson
Contribution: applies Classical Conditioning to Humans through the "Little Albert" Experiment
Significance: Creates "Behaviorism" Theory
Significance: Creates "Behaviorism" Theory

35
New cards
Thorndike
Contribution: studied cats in puzzle boxes and recorded their behaviors
Significance: Creates "Law of Effect" theory
Significance: Creates "Law of Effect" theory

36
New cards
Bandura
Contribution: Studied how children mimic others behaviors and repeat that same behavior
Significance: Creates "Observational Learning" Theory
Significance: Creates "Observational Learning" Theory

37
New cards
Seligman
Contribution: Used dogs to demonstrates the significance of cognitive processes in classical conditioning
Significance: Creates "Learned Helplessness" theory
Significance: Creates "Learned Helplessness" theory
38
New cards
Tolman
Contribution: demonstrated the significance of cognitive processes in operant conditioning by studying rats in mazes
Significance: Creates the "Latent Learning" theory
Significance: Creates the "Latent Learning" theory
39
New cards
Pavlov's Dogs
First experiment that created and demonstrate the theory of classical conditioning
40
New cards
Little Albert
First experiment to demonstrate how emotions can be classically conditioned in humans
Provides a foundation for the "Behaviorism Theory"
Provides a foundation for the "Behaviorism Theory"
41
New cards
Conditioned Response
Part of Classical Conditioning
Occurs after conditioning when the conditioned stimulus (CS) triggers an innate response
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Salivating to the Bell"
Little Albert: "Screaming/Crying"
Occurs after conditioning when the conditioned stimulus (CS) triggers an innate response
Pavlov's Dogs: It was the "Salivating to the Bell"
Little Albert: "Screaming/Crying"
42
New cards
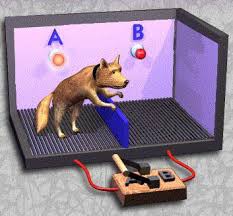
Learned Helplessness
Defined: Exposure to inescapable and uncontrollable aversive (bad) events produces passive behavior
Study: Seligman delivering shocks to dogs
Example: If a student consistently fails math, they may start to give up or a sports team that consistently loses may start to belive they can't win
Study: Seligman delivering shocks to dogs
Example: If a student consistently fails math, they may start to give up or a sports team that consistently loses may start to belive they can't win
43
New cards
Reliable Signals
Defined: A cognitive process in classical conditioning where the organism must decide if the NS accurately predicts the UCS
Example: Pavlov's Dogs-the dogs had to think that the NS (bell) predicted the UCS (meat)
Example: Pavlov's Dogs-the dogs had to think that the NS (bell) predicted the UCS (meat)
44
New cards
Concerns regarding Punishment
It does not teach the learner appropriate behavior and can also increase violent behavior in the learner
45
New cards
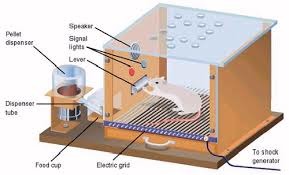
Skinner Box
Also known as: Operant Chamber
Description: A chamber containing a bar or key that an animal (rat or pigeon) can manipulate in order to obtain a reward
Description: A chamber containing a bar or key that an animal (rat or pigeon) can manipulate in order to obtain a reward
46
New cards
Immediate Reinforcer
Defined: when you are immediately rewarded for a behavior (it's all about the short run)
Example: skipping school and enjoying time with friends
Example: skipping school and enjoying time with friends
47
New cards
Continuous Reinforcement Schedule
Defined: When every behavior is reinforced
Example: a multiple choice test
Significance: best for "establishing" a behavior
Example: a multiple choice test
Significance: best for "establishing" a behavior
48
New cards
BoBo Doll Study
Psychologist: Bandura
Description: Children watched (through a one way glass)a confederate play with the BoBo doll and then played with the BoBo doll in the same way as the confederate
Significance: used to develop "observational learning"
Description: Children watched (through a one way glass)a confederate play with the BoBo doll and then played with the BoBo doll in the same way as the confederate
Significance: used to develop "observational learning"
49
New cards
Densensitization
Defined: after viewing a similar act/behavior, you become less emotionally responsive (indifferent or unaware) to the stimulus
Example: The first murder on TV is shocking but becomes less shocking as you watch violent television
Example: The first murder on TV is shocking but becomes less shocking as you watch violent television
50
New cards
Delayed Reinforcer
Defined: when you complete a behavior but not awarded immediately (it's all about the long run)
Example: getting good grades in school and attending class in order to get a good job in the future
Example: getting good grades in school and attending class in order to get a good job in the future
51
New cards
Partial Reinforcement Schedule
Defined: When a random behavior is reinforced
Example: Fixed Ratio, Variable Ratio, Fixed Interval, Variable Interval
Significance: best for "maintaining" a behavior
Example: Fixed Ratio, Variable Ratio, Fixed Interval, Variable Interval
Significance: best for "maintaining" a behavior
52
New cards
Garcia Effect
conditioned taste aversions, a single bad experience can stay with us
53
New cards
William James
an American philosopher who viewed consciousness as a continuous flow or "stream of consciousness" // saw consciousness as an evolutionary adaptation to environment that made it possible for humans to thrive and to continue to adapt
54
New cards
consciousness
our state of awareness of our existence, sensations, thoughts, and environment // we are conscious to the degree that we are aware of what is going on both inside and outside our bodies
55
New cards
dualism
belief that mind and brain are distinct entities // the mind (nonphysical) and the brain/body (physical) are completely different things and neither one can be inferred form the existence of the other
56
New cards
materialism
all phenomena are matter, energy, or the interaction between the two // the mind exists as a function of the brain
57
New cards
conscious awareness
includes all the sensations, perceptions, memories, and feelings you are aware of at any given moment // "all the ideas in your immediate awareness, such as your thoughts, feelings, senses"
58
New cards
walking consciousness
your normal, alert awareness that includes your working memory
59
New cards
nonconscious level
includes all the various biological processes that are taking place internally and constantly without your noticing // "biological functions occurring without your awareness, such as respiration and digestion"
60
New cards
preconscious level
includes stored information about yourself or your environment that you are not currently aware or thinking of but can easily recall to mind when asked // "items we can access from long-term memory"
61
New cards
subconscious level
includes information you have been exposed to but cannot recall // but, this hidden information or experience can influence your behavior // ex: "mere exposure effect" or familiarity principle // "hidden memories that influence behavior despite no clear memory of them"
62
New cards
unconscious level
Sigmund Freud // an invisible force deep within our minds, a series of unconscious conflicts between competing parts of our personalities that influence our attitudes and actions // parts include id, superego, and ego // "from the psychoanalytic perspective, hidden memories that influence behavior but can never be known to the conscious mind"
63
New cards
id
life and death instincts, immediate gratification, pleasure-seeking
64
New cards
superego
societal or parental standards that we try to live up to
65
New cards
ego
self-image and reality-based part of the mind that tries to balance the id and the superego
66
New cards
biological rhythms
periodic fluctuations in physiological functioning
67
New cards
circadian rhythm
A biological rhythm that defines the sleep/wake cycle of about 24 hours without external cues // 16 hours of wake and 8 hours of sleep
68
New cards
ultradian rhythm
A biological rhythm that follows a cycle of less than 24 hours but longer than an hour // ex: such as eye-blinks, heartbeats and sleep patterns
69
New cards
infradian rhythms
biological rhythms that occur more than a day // ex: menstruation, breeding, seasonal migration cycles
70
New cards
diurnal
active during the day
71
New cards
nocturnal
active at night
72
New cards
chronobiology
the study of these various temporal biological rhythms
73
New cards
electroencephalography (EEG)
measures electrical currents in the brain, recording them as a visual tracing (encephalogram) // electrodes are attached to the scalp to measure the brain's electrical currents during sleep and compare the results to those recorded during the waking hours // EEG measures electrical currents produces as the brain cells communicate with one another // EEG measures wave patterns in hertz (Hz)
74
New cards
delta waves
up to 4 Hz; slow waves // show deep sleep; stage 3 of NREM
75
New cards
theta waves
between 4 and 7 Hz // show stages 1 and 2 of NREM sleep
76
New cards
alpha waves
between 7 and 12 Hz // show relaxed, ready for sleep
77
New cards
beta waves
between 15 and 30 Hz; quick and rapid waves // show awake, alert, anxious
78
New cards
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
"master clock" // in hypothalamus // interprets information taken from the eye and signals the pineal gland to secrete melatonin
79
New cards
melatonin
the sleep hormone // increases naturally at night as darkness falls and then decreases during the day when the light returns
80
New cards
wake/sleep cycle
as daylight lessens, the eyes (rods/cones in the cornea) detect lower light levels, and cells in the retina (ganglion cells) communicate directly w/ the SCN // SCN interprets information taken from the eye and signals the pineal gland to secrete melatonin into the bloodstream
81
New cards
Stage 1 of sleep
nondreaming stage of non-REM (NREM) sleep // our brains produce high-frequency and low-amplitude theta waves
82
New cards
Stage 2 of sleep
our brain's high-frequency and low-amplitude theta waves begin to slow down, we progress into slow-wave sleep // the sleep spindles and k-complexes begin to appear
83
New cards
Stage 3 of sleep
slow-wave deep, delta waves begin to appear more often, hormones are released into the bloodstream for growth in children, our immune system refreshes itself, and sleep is so deep that we can't be easily awakened because we're unaware of our environment // essential for good health...without deep sleep, we are at greater risk for illness and may have difficulties w/ concentration and coordination throughout the day
84
New cards
non-REM (NREM) sleep
nondreaming stage of sleep
85
New cards
slow-wave sleep
the sleep spindles and k-complexes of Stage 2 begin to appear
86
New cards
sleep spindles
slower-paced waves with spikes comparable to the low-amplitude theta waves of Stage 1
87
New cards
k-complexes
large, high-voltage waves that often appear in response to such outside stimuli as sounds
88
New cards
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
often called the "paradoxical stage" b/c the brain waves move as if we're awake // brain is active, but the brain stem blocks communication between the cerebral cortex and the motor neurons to produce REM paralysis // dream during REM sleep //plays a role in memory formation and consolidation // percentage of REM sleep reduces as we age
89
New cards
REM paralysis
when the brain stem blocks communication between the cerebral cortex and the motor neurons to keep our bodies still during dreams...but we still experience muscle twitches
90
New cards
REM rebound
if we don't experience REM sleep one night, we can make up for it the next day w/ more REM sleep to help the body recover
91
New cards
sleep process
sleep onset, Stage 1, Stage 2, Stage 3, Stage 2, REM, repeat
92
New cards
Sleep Theories
- evolutionary: sleep keeps us safely "tucked away" during the hours when our vision was limited and predators were active
- sleep helps restore health and efficiency / NREM sleep helps restore physiological functions / REM sleep helps restore mental processes
- sleeps helps us consolidate the information of the day and support long-term memory
- sleeps helps us replay and process stressors from the day through dreaming
- sleep helps restore health and efficiency / NREM sleep helps restore physiological functions / REM sleep helps restore mental processes
- sleeps helps us consolidate the information of the day and support long-term memory
- sleeps helps us replay and process stressors from the day through dreaming
93
New cards
sleep deprivation
causes memory impairment and moodiness and is associated w/ overeating and eating unhealthy foods
94
New cards
sleep debt
chronic sleep deprivation
- chronic irritability, lack of motivation, anxiety, inability to concentrate, reduced vigilance, longer reaction times, distractibility, reduced energy, restlessness, lack of coordination, poor decision-making, increased errors, forgetfulness, and physical symptoms such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and obesity
lack of REM sleep
- hallucinations
- chronic irritability, lack of motivation, anxiety, inability to concentrate, reduced vigilance, longer reaction times, distractibility, reduced energy, restlessness, lack of coordination, poor decision-making, increased errors, forgetfulness, and physical symptoms such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and obesity
lack of REM sleep
- hallucinations
95
New cards
sleep-deprivation psychosis
chronic sleep deprivation / sleep debt individuals who suffer breaks from reality
96
New cards
microsleep
when our need for sleep is so great that we're exhausted and we have a brief shift in brain activity from waking to sleeping brain waves that last up to 30 seconds // we lose consciousness and are unaware of our surroundings // symptoms: nodding of the head, drooping eyelids, constant blinking, having a blank stare, and difficulty concentrating // often unaware that microsleep occurred
97
New cards
circadian rhythm disruption
an out-of-sync sleep/wake cycle
98
New cards
jet lag
a circadian rhythm disruption that occurs when you travel across several time zones // adjustment can mentally and physically take up to a week
99
New cards
insomnia
the inability to fall asleep or to stay asleep // can be temporary or chronic // 10-20% of the population // caused by underlying medical or psychiatric conditions, stress, emotional or physical discomfort or pain, use of medications or stimulants, or disruptions to the normal sleep cycle
100
New cards
narcolepsy
a disorder in which a person suddenly falls into REM sleep during waking hours // can occur either during periods of excitement or low activity // lack of activity and staying still for long periods can make narcolepsy symptoms worse // condition occurs because the brain doesn't produce enough orexin