Adult Safeguarding - the Pharmacist role + perspective
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
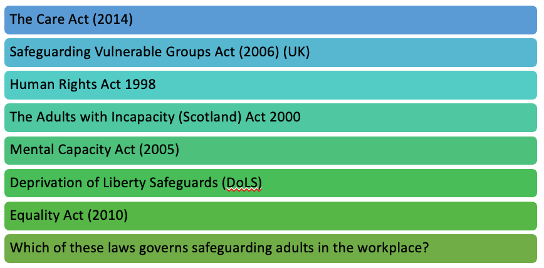
Legislation + Process
MCA - assessing and making decisions on behalf of individuals who lack the mental capacity to make decisions for themselves. The MCA applies to all individuals aged 16 and above.
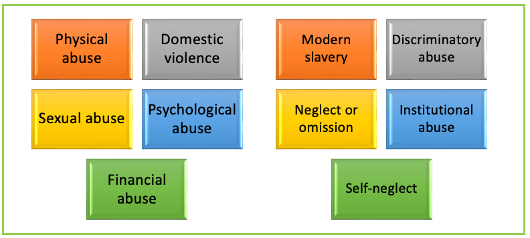
Safeguarding: Types of abuse
Neglect indicators – Poor hygiene, untreated medical issues, malnutrition
Self-neglect – an individual is unable or unwilling to take care of their on basic needs, leading to harm or danger to their health or well-being. The individual neglecting themselves may not seek help or fail to recognise the need for it ie do not know what the basic needs are, or the usual/expected care is
Physical indicators – A client suddenly starts showing visible bruising in areas that are difficult to explain
Behavioural indicators – An adult with learning disabilities becomes withdrawn when their caregiver enters the room
Domestic violence (DV) – broader term that encompasses not just physical abuse, but also emotional, psychological, sexual, + financial abuse within an intimate or domestic relationship ie between partners, spouses, or family members. Pattern of power + control
Modern slavery – Human trafficking, forced labour, child labour, sexual exploitation, debt bondage, domestic servitude
Discriminatory abuse – targets protected characteristics, such as race, gender or gender identity, age, sexual orientation, religion, disability + can take lots of forms such as verbal abuse, physical abuse, social exclusion
Levels of safeguarding for professionals
Level 1-2 Safeguarding
Level 1: All staff working in health and care settings
Level 2: All practitioners that have regular contact with patients, their families or carers, or the public
Level 3 Safeguarding
Registered health and care staff who engage in assessing, planning, intervening and evaluating the needs of adults where there are safeguarding concerns (as appropriate to their role)
Level 4 Safeguarding
Specialist roles, named professionals, lead doctors, heads of adult safeguarding, name GPs/doctors in primary care
Level 4 (gap analysis, self-neglect, fabricated illness, induced illness, homeless health etc)
Adults at risk of harm
Adults at risk of harm vs. vulnerable adults
Aged 18 or over
Have care or support needs
Experience or are at risk of abuse/neglect
Unable to protect themselves
May lack understanding and/or capacity for decision-making
Steven Hoskin
Actions to take if concerned
Consent? Informed consent?
Report ALL concerns
Immediate action
→ Are they safe? Options for engaging with that adult around risk, safety and wellbeing
→ Who is best to report to?
Documentation
→ What happened, individuals involved, actions taken
Protocols and policy to support
→ Organisational policy and protocol
Person centred support mechanisms
→ Access to emotional and practical support
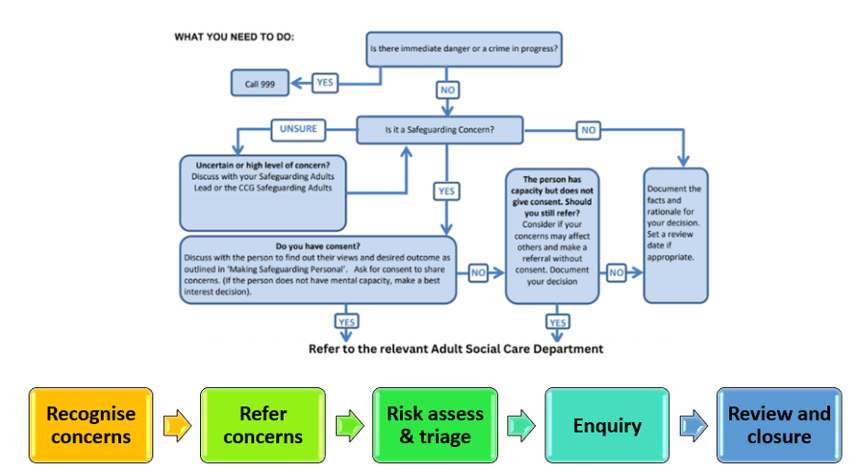
Managing safeguarding concerns
Do not press the person for more details
Do not stop someone who is freely recalling significant events
Do not dismiss what you have been told
Do not promise to keep secrets; but do explain that the information will only be passed to those who "need to know", and try to be specific about who these might be
Do not be judgmental e.g. "why didn't you run away? “
Do not make promises that you cannot keep
Do not contact the alleged abuser or anyone who might be in touch with him / her
Do not ask leading questions
Do not tell anybody who doesn't need to know – remember the rules of confidentiality
What do safeguarding adult boards do?
Authorise the policy, process, strategy and guidance required to support Board priorities and effective safeguarding
Publish a strategic plan that sets out how it will meet its main objectives
Scrutinise, challenge and maintain an overview of adult safeguarding
Ensure that Safeguarding Adult Reviews (SARs) are undertaken in accordance (S44 )the Care Act 2014
Assess whether partner agencies are fulfilling statutory obligations in relation to safeguarding adults at risk
Quality assure practice through joint audits of case files and identifying lessons to be learned
Monitor and evaluate effectiveness of training, including multi-agency training