Invert. Zoology II
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Midterm 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Phylum Annelida
Lamarck 1802- “little rings”
spiralia (Lophotrochozoa)
20,000 species- 3 classes (polychaeta, oligochaeta, Hirudinea)

Class polycheata
-marine worms
-w/ parapodia
-13,000 species
Parapheletic (ancestral species→most descendants)
Class Clitellata (oligochates and leeches)
-w/ clitellum (thick reproduction band)
-7,400 species
Annelid Bauplan
-bilaternal symmetry
anterior-posterior axis → undirectional
-defined head region → cephalization
-triploblastic
-true coelomate- schizocoelous development
-spacious colem
-vermiform
-segmented→metamerism (linear serious of segments)
→ homonomous segmentation (same amount of space between)
→Heteronomous segmentation (different, odd)
-have appendages, parapodia- lobe like
-chaetae (chitin coating)
- 4 body regions (prostomium- head, peristomium-head, body segments-trunk, pygidium- tail)
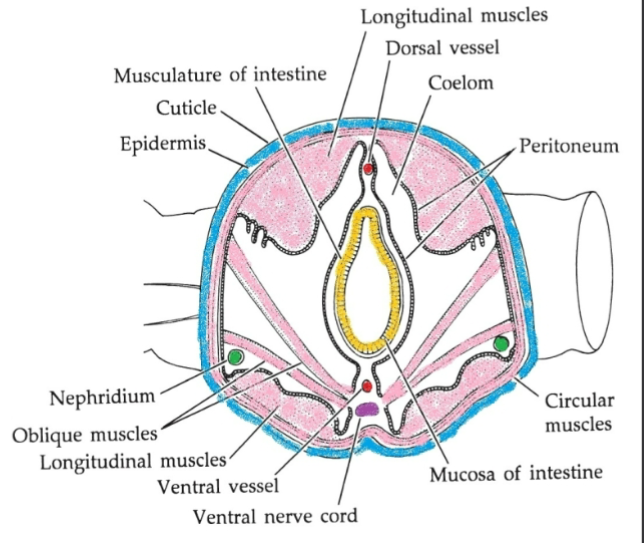
Annelid Body Wall
-thin cuticle (non-living)
-epidermis→ often ciliated
-connective tissues (basement layers)
-circular muscles, longitudinal muscles
-peritoneum (membrane that lines coelom, body cavity, surrounds organs)
-coelom divided by septa
Annelid Coelom
Annelid Skeleton
hydrostatic→body wall muscles, coelomic fluid
-evert and retract proboscis, gills
-move parapodia
-rigid chaetae (aciculae- needle shaped structure, ,muscles, cats claws
Annelid Locomotion
polychaetes:
errant :(longitudinal muscles, undulations, parapodia power-wavelength movement, burrowing- proboscis as shovel and anchor)
OR sedentary: (weak body wall muscles, reduced parapodia, strong retractor muscles)
Clitellates:
mostly errant
oligochates- strong circular+ longitudinal muscles, peristaltic motion
leeches- suckers, inch worming
Annelid Feeding
Diverse!
predators: homologous and fat, carnivores and omnivores, strong chemo/mechanoreceptors- use pharynx with jaws and teeth)
deposit: selective
suspension: tube worms, tentacles/gills→use currents, chaetopterus
blood: jaws, powerful pharynx, anticoagulant, anesthetic
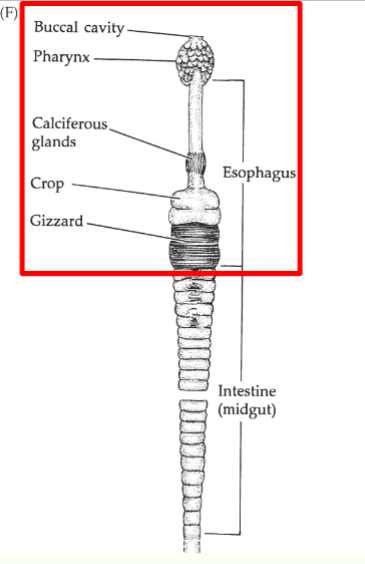
Annelid Digestion
-complete gut→straight, specialized regions
foregut: mouth, buccal cavity, glands, pharynx, esophogus-, crop, gizzard-? mechanical pocessing
midgut: intestine (extracellular), cecae
hindgut: mucous glands, anus (terminal)
Annelid Circulation
Closed circulatory system (vessels, hearts(s) lacking
Blood= hemolymph (hemoglobin)
Annelid Gas Exchange
Specialized structures
often co-opted (parapodia, gills, tentacles)
highly vascular
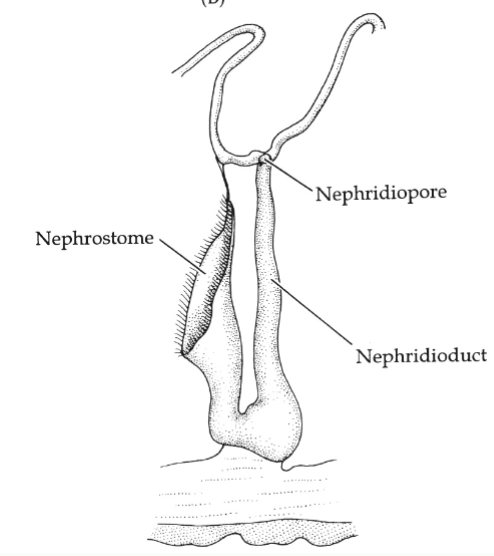
Annelid Excretion/ osmoregulation
Metanephirdia→ nephrostome (intake)
Niphridioduct → selective resportion
nephridiopore→ waste removal
segmental arrangement
*marine polychaetes: osmoconfomer
*Estuarine, freshwater, and terrestrial: osmoregulator
Annelid Nervous System
Cerebral ganglion
circumenteric
longitudinal ventral nerve cord
ganglion in each segment, parapodia too
+tube worms have giant nerve fibers that bypass ganglia
Mechano/ Chemoreceptors: antennae, palps, tentacles, cirri
photoreceptors- oceili to eyes with lenses!
Annelid Asexual Reproduction
fragmentation
budding
regernation present but limited→ neoblasts (pluripotent- stem cells)
Annelid Sexual Reproduction
Polycheates: gonochorisitc, no gonads, gametes spawned out of metanephirdia- or body wall (epitoky)
Clitellates: Hermaphriditic, true gonads, cross-fertilization internal, clittelum (thick band)
Annelid Development and Life Cycle
Protosomes
spiral, holoblastic cleavage
gastrulation by invagination or epiboly
schizocoelous
Clitellates: direct development→juveniles crawl out of cocoon
Polychaetes: indirect or mixed→trochophore larve, gradual metamorphosis, teloblastic growth
Larval regions correlate to regions of adult worm (preprototroch=prostomium, prototroch=peristomium, pygidium-=pygidium-)
Phylum Mollusca
-Jonston 1650
-“soft nut with hard shell”
-80,000 species → 8 classes
polyplacophora (chitons)-850 species
gastropoda (slugs/snails)-70,000 species
bivalvia (clams/kin)- 9,200
Scaphopoda (tusk shells)- 500 species
cephalopoda (nautilus, squid, octopus, cuttlefish)- 700 species
Molluscan Bauplan
Diverse
bilateral
anterior-posterior→undirectional
defined head region - cephalization (not bivalves!)
triploblastic
true coelomate- → schizocoelous development
coelom reduced→replaced with hemocoel
not vermiform, not appendages
Body divided into: head, foot, visceral mass
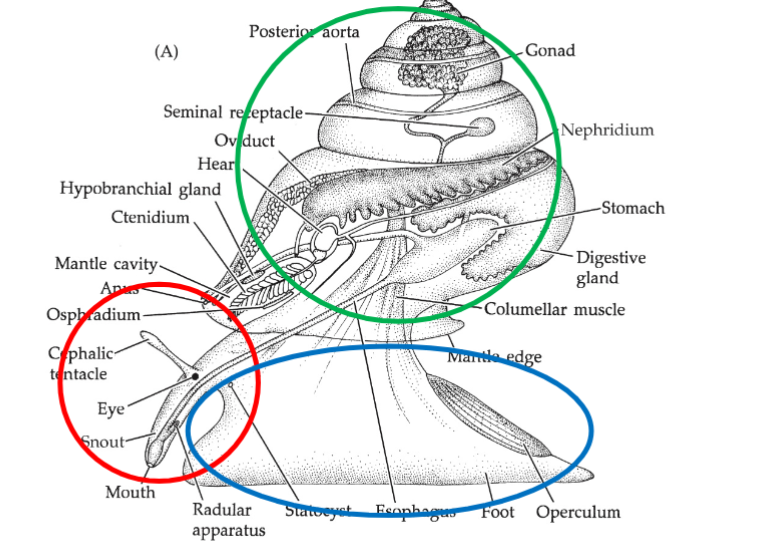
Molluscan Bauplan II
Mantle: surrounds, visceral mass, secretes shell
Mantle cavity: ctenidia (respiratory/gill), cloacoa-like
torsion: viscal mass rotates 180 (switching head-foot areas)
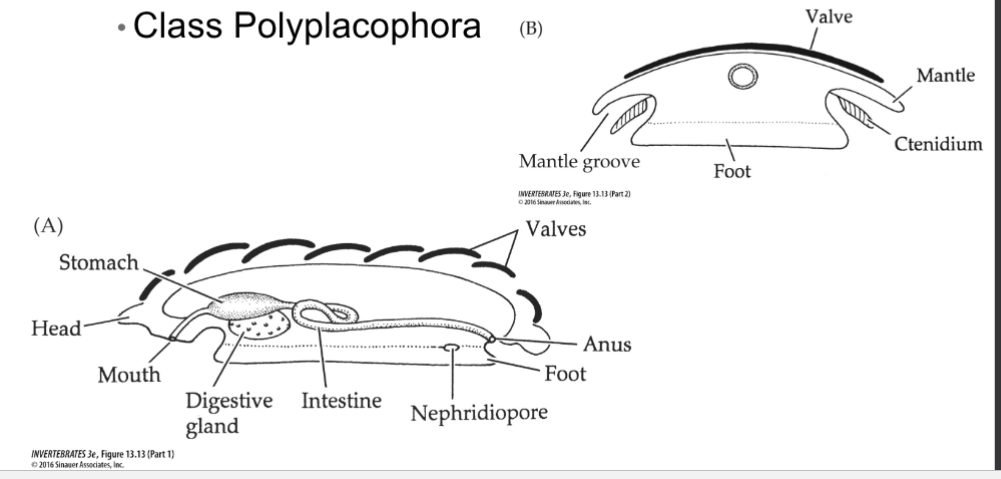
Polyplacophora bauplan
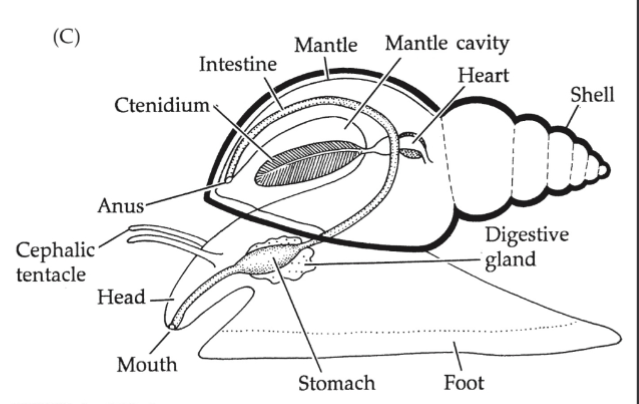
Gastropoda Bauplan
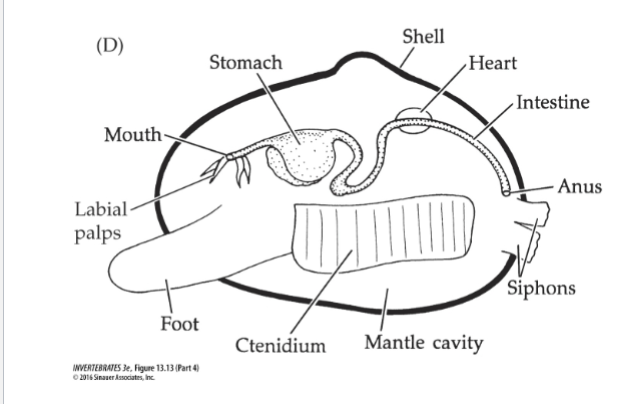
Bivavlia Bauplan
Scaphopoda Bauplan
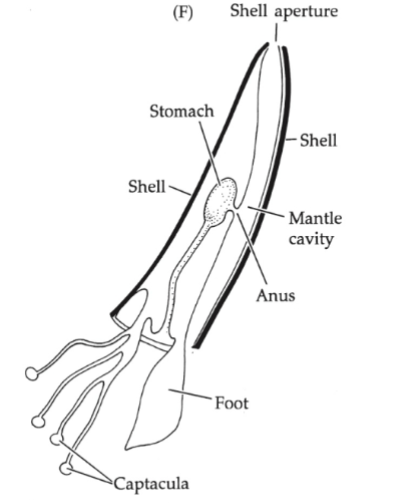
Cephalopoda Buaplan
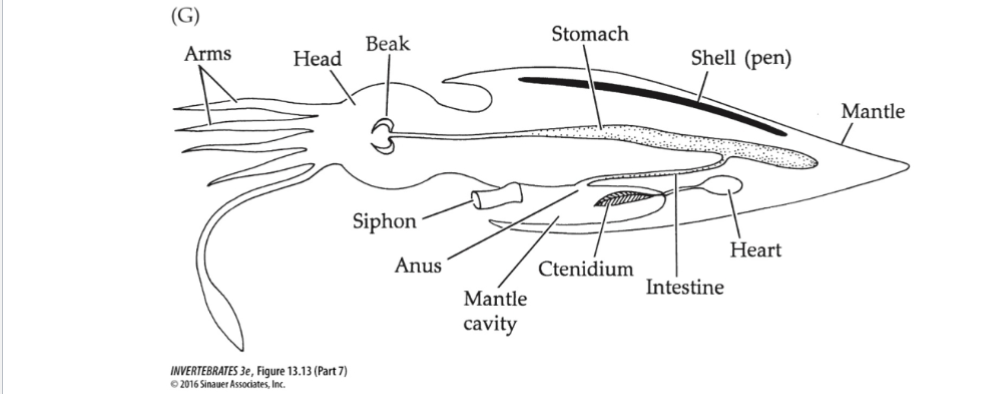
Mollusca Body Plan
Cuticle (co-opted into shell)→conchin, not chitin
Epidermis- (ciliated, secretion)
Basement membrane
muscles (outside in): micrular, diagonal, longitudinal
Mollusca Skeleton
hydrostatic skeleton→ body wall muscles + epidermis
Shell: Calcium carbonate on protein matrix (outside in:epidermis, nacreous layer(s), prismatic layer, periostracum)
shell diversity
Mollusca Locomotion
Crawling; muscle aided gliding, muscle waves
burrowing: foot as shovel, plow, and anchor
Swimming: flapping foot, pteropods, heteropods, jet propulsion (scallops, Cephalopod), fins for hovering
Walking: octopi
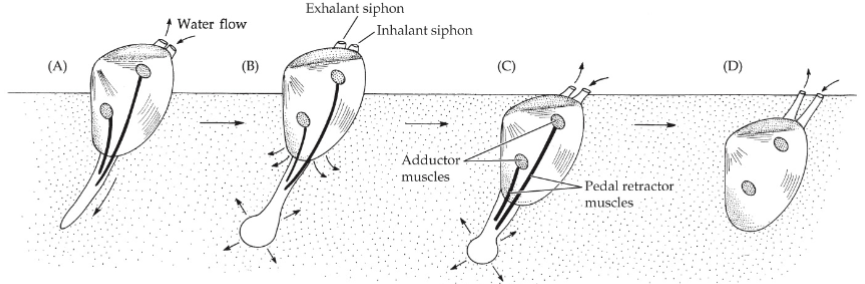
Mollusca Feeding
radula; all but bivalves (gastropods and chitins)→toothed tongue (rasping, boring, cutting and piercing)
herbivores, predators, scavengers,
suspension (bivalves +gastropods→siphons, ctenidia)
deposit feeders (scaphopds +bivalves→captcula and siphons)
-Cephalopods: tentacles (extend to capture),arms (grab and manipulate), break (tearing→venom
Mollusca Digestion
Complete gut- straight/twisted, specialized regions
Foregut: mouth, buccal region w/ redula, esophagus, glands (extracellular)
Midgut: stomach (muscular), Digestive glands (cecae, extracellular), crystalline style
Hindgut: intensine (intracellular), Ink sac (Cephalopods), anus (mantle cavity)
Mollusca Circulation + Gas Exhange
Open circulatory system (vessels +sinuses, hemocoel)
chambered hearts
Blood: hemolymph (hemocyanin, sometimes hemoglobin)
Ctenidia (mantle cavity, cilated)
Cephalopods: closed circulation, branchial hearts
terrestrial molluscs: pneumostome (opening in slugs to breath) +lung
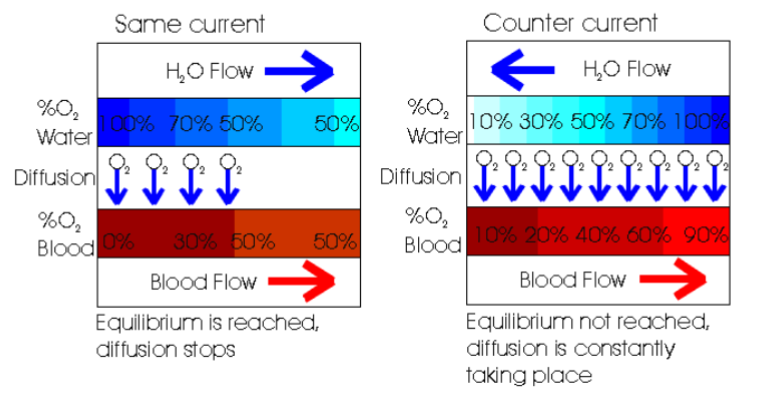
Gas Exchange- countercurrent exchange
fluids flow in opposite directions to enhance the transfer of a substance (like oxygen), is found in the gills of molluscs (with ctenidia). This mechanism is crucial for efficient gas exchange, maximizing the uptake of oxygen from the water into the molluscs blood.
Mollusca Excretion
Metaephridia- Mephrostome → intake
Nephridioduct →selective resorption
Nephridiopore→waste removal (opens in mantle cavity)
nephrostome in percardial coelom
*marine:osmoconformers
*fresh/terrestrial: osmoregulators
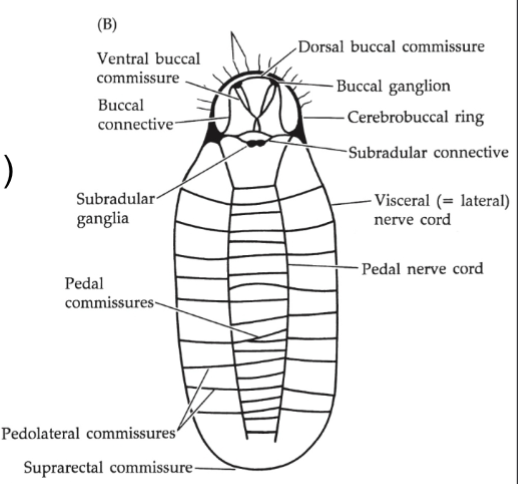
Mollusca Nervous System
Ladder like variation
cerebral ganglion circumenteric
ventral cord and ganglia
pedal cords (ventral)→ foot muscles
visceral cords (lateral)→visceral mass, mantle
cephalopods→ cranium, arms+tentacles, giant neurons
Mollusca Sensory Structures
Mechanoreceptors: lots of surface area
chemoreceptors: siphons, osphradia (sensory organ mantle cavity near gills), suckers, slime trails (“home scars”)
Photoreceptors-: shell eyes, pigment cup ocelli, eye with lenses, cephalopod eyes (no blind spot!)
Mollusca Reproduction
Asexual:
-parthenogenesis (virgin birth-rare)
-regeneration possible but limited
Sexual:
mostly gonochorisitc
(gastropods: herm. + protandrous)
true gonads
gonopores (mantle cavity, urogenital pores (gastropods))
spawning (indirect development)
shift to internal fertilization
Cephalopod mating: complex, Hectocotylus (mating arm- holds onto spermatophore- sperm packer)
egg sac or string
mixed-/ direct development
Mollusc Development + Life Cycle
Protostomes
spiral cleavage (64 cell stage)
Indirect development (chitons- broadcast spawning)
→trocchophore larva (annelids too)
→veliger larva w/ velum (secondary larval stage- calms +snails)
Mixed development (early dev. tp veliger stage)
→trophopore in egg, veliger free living (ciliated)
Direct Development
→cephalopods (no larval stage)
→mercoblastic cleavage (have large yolk)
→discoblastula (looks like disc on yolk-feed on yolk)
Phylum Bryozoan
Hatschek 1891
“moss animal”
Lophotrochozoa→ Lophaphorata
with phyla Phoronida + Brachuopoda
→Lophophore
→Epistome
→sessile
→U-shaped gut
~6,000 species- 2 classes
Bryozoan- class Hymnolaemata
marine
lack epistome
hard crystids
with heterozoids (cannot feed itself- bird beak)
Bryozoan- class Phylactolaemata
freshwater
with epistome
gelatinous cystids “dino snot”
lack heterozoids
Bryozoan Bauplan
bilateral symmetry
anterior-posterior axis- difficult to see
weak cephalization
triploblastic
true colemate- divided into 3 parts
colonial (flat, branching, gelatinous
Zooids (cystids, polypide-retractable)
Zooid types: autozoids (feeding), Heterozoids (vibracula, avicularia-bird beak)
colonial network; funiculus (connects stomach tract to body wall-shares food) , stolon (tube extensions), pore plates (connect zooids to colony)
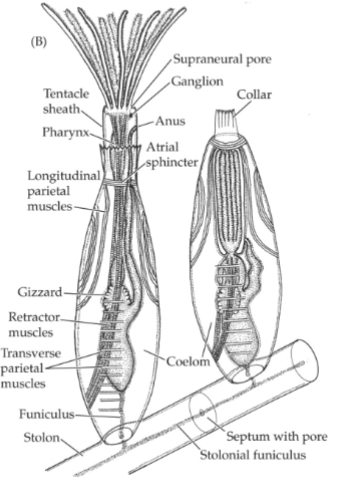
Bryozaon Body Wall
Cystid- gelatinous, hardened/ calcified (Zoecia-protective)
Epidermis→secretes cystids covering
Muscle layers→longitudinal + circular
Muscle groups→specialized; retractors
peritoneum →lines abdominal cavity
Bryozoan Skeleton
Rigid zoecium
hydrostatic skeleton; coelomic fluid, muscles, membrane
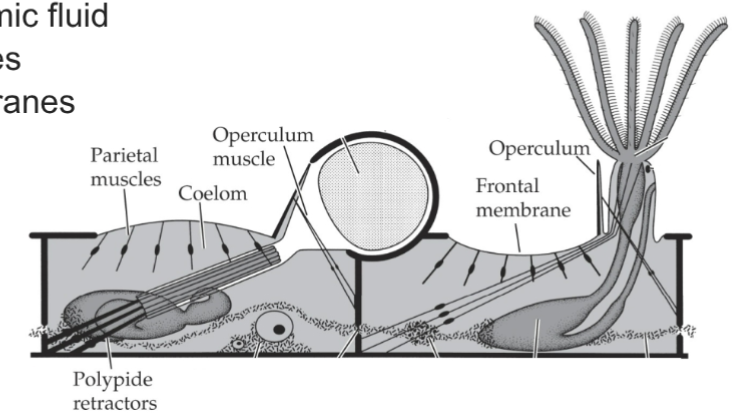
Bryozoan Locomotion
Adults- sessile (retractions + extension)
some colonies crawl
Bryozaon Feeding
suspension feeders
ciliated phophore (circular or horseshoe shaped, mouth in middle)
lophore current
particle capture→ flicking!
food mostly protists
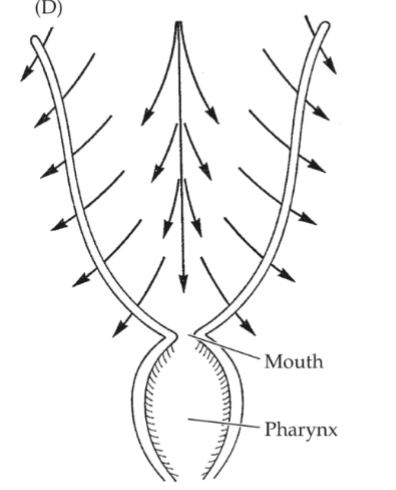
Bryozoan Digestion
Complete gut→U-shaped, specialzed regions, anus outside phophore (ectoproct)
Foregut: mouth (epistome), pharynx
Midgut: descending stomach, cardia, gizzard-like, extracellular, central stomach, cecum (extra+intracellular)
Hindgut: Pylorus, rectum, anus
sharingp funiculus (sharing nutrients with colony
Bryozoan Circulation, Gas Exchange, Excretion
no specialized structures
diffusion (surface area to volume, lophophore)
coelomic fluid, funicula, pore plates
Bryozoan Nervous System
Weak cephalization
cerebral ganlgion
circumoral nerve ring
nerves to viscera, muscles, tentacles
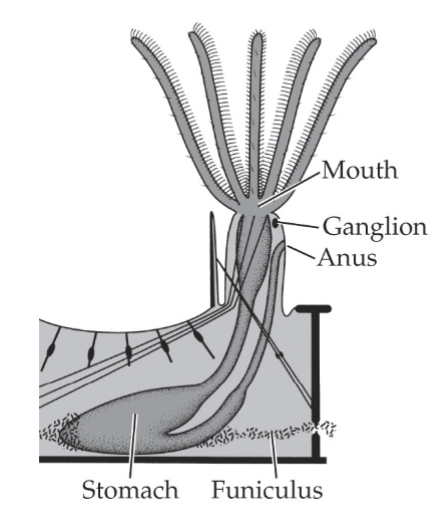
Bryozoan Sensory Structures
Mechanoreceptors: tentacles, avicularia
Bryozoan Asexual Reproduction
ancestrula
budding (distinct growth patterns, cystid→polypide)
regeneration possible
statoblast (like the gemmule- freshwater only- dormant stage)
Bryozoan Sexual Reproduction
Hermaphroditic colones
zooids male or female
no true gonads- peritoneum/funiculus
sperm spawned through tentacles
internal fertalization - capture
some fertilized eggs shed
brooding- ovicells, placental
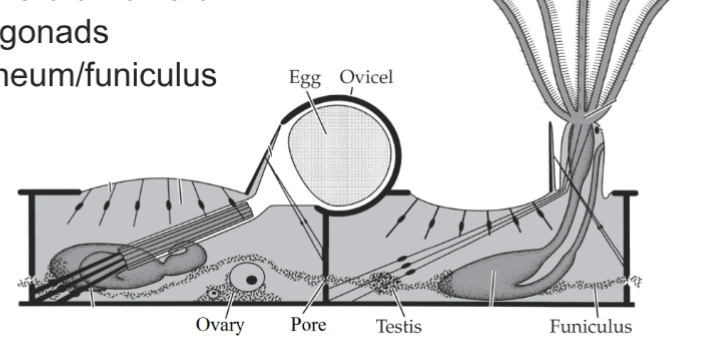
Bryozoan Development + Life Cycle
Dueterostomes-?
molecular- protostomes
radical, holoblastic cleavage
coelo-or steroblastula
gastrulation by ingression
coelom formation is mystery
Indirect development: cyphonautes larva (planktotrophic)
Mixed development: Coronate larve (Lecithrotrophic)
Dramatic metamorphosis
+polyembryony-cleaves during development, becomes many indv.
Phylum Nemotoda
Lankester 1877
“threads”
Nematoida
Ecdysozoa- includes arthropods (cuticle, molt to grow)
~25,000 species: free living + parasitic, 2 classes
Nematoda- class Enoplea
bottle shaped pharynx
pocket-like amphids
Nematoda- class Chromadorea
bulbous pharynx
slit like, pore like, or coil like amphids
Nematode Bauplan
bilateral symmetry
anterior-posterior→unidirectional
defined head region→weak cephalization
triploblastic
blastocoelomate→Pseudocoelomate
spacious coelom
vermiform
unsegmented- no appendages
round in cross section- “roundworms”
lack locomotory cilia in all life stages
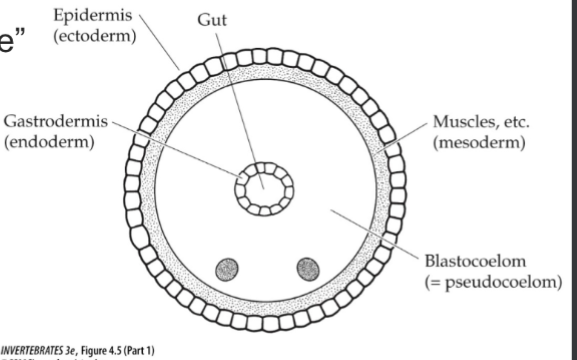
Nematode Body Wall
Cuticle- thick but flexible, multi-layered, collagen (no chitin)
textured
Epidermis: secretion, longitudinal cords (nerve cords + excretory canal)
longitudinal muscles; 4 groups, muscle cells with arms, unique
circular muscles lacking
large blastocoel (gonads)
Nematode Skeleton + locomotion
Hydrostatic skeleton (body wall muscles, coelomic fluid, elastic cuticle (high pressure!!)
whip like undulations
→crawling
→swimming
Nematoda Feeding
Free living species:
deposit, detritivores, microscavenger, predators, herbivores (have spines, teeth, jaws, stylets)
Parasitic:
important diseases; human parasites (Hookworm, Ascaris, Whipworm, Trichinella)
Nematoda Digestion
Complete gut→straight, specialized regions
Foregut: cuticle lining, mouth w/ lips and papillae, buccal cavity, pharynx
Midgut: intestine(not cuticle lined, extra + intracellular)
Hindgut: cuticle lined, males: cloaca + anus, females: recutum +anus (subterminal)
pressurized sphincters
Nematoda Circulation + Gas Exchange, Excretion
no specialized structures
diffusion (small and thin)
blastocoelom
lack proto- metanephridia
1-2 long renette cells (excretory canals, associated w/ epidermis)
ventral excretory pore
Nematoda Osmoregulation
marine; osmoconformers
fresh/terrestrial: osmoregulators
→water + cuticle
Nematoda Nervous System
weak cephalization
circumenteric nerve ring (nerve tissues that encircles the esophogus)
Nerve cords (dorsal and ventral, epidermal cords)
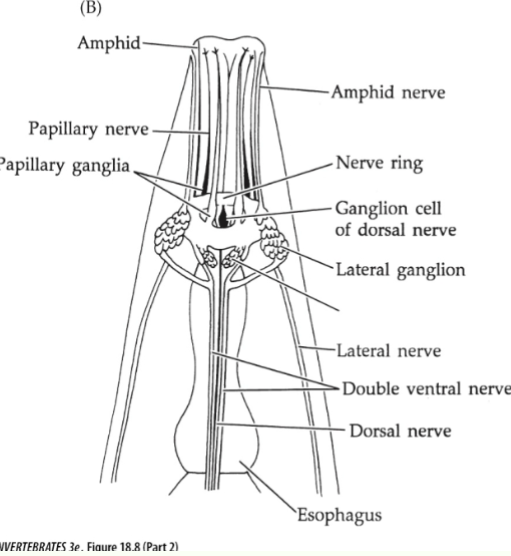
Nematoda Sensory Structures
Mechanoreceotors: papillae (head and tail- organs)
Chemoreceptors: amphids ANTERIOR (glandular- taste, smell= stimulate action potential), Phasmids POSTERIOR (send action pot., mating uses)
Photoreceptor: Ocelli (simple, no lens)
Nematoda Reproduction
Asexual: parthenogenesis (virgin birth)
Sexual: gonochoristic, true gonads, dimorphic
male system: testis, sperm duct, seminal vesticle, ejaculatory duct, cloaca, copulatory spicules + bursa
female system: 2 ovaries, oviducts, uteri, vagina + vulva
→internal fertilization, high pressure!
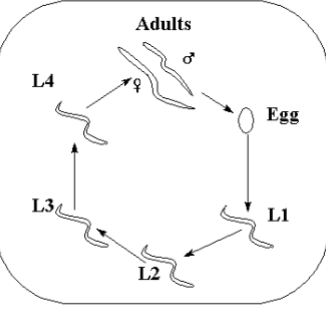
Nematoda Development + Life Cycle
zygotes coated- cysts
released as cysts
protostomes
cleavage holoblastic + unequal (neither radial or spiral, highly deterministic)
stereoblastula
gastrulation by epiboly and ingression
Eutely experiment→ C. elegans 959 cells
direct development
four juvenile stages : L1/L2- rhabditiform “larva”, L3- filaiform “larva”, L4- no name.
“duar”- rest, hiberation