W8: Communication and Change/stress management in Organizations
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Communication
The process of transferring meaning and understanding from one person to another.
Sender
The person who initiates the communication.
Message
The information or content being communicated.
Channel
The medium through which the message is transmitted.
Receiver
The person who receives and interprets the message.
Feedback
The response from the receiver back to the sender.
Noise
Barriers that can disrupt the communication process.
Control (Function of Communication)
Regulates behavior within organizations, such as company policies and procedures.
Motivation (Function of Communication)
Encourages employees to achieve goals through performance feedback and incentives.
Emotional Expression (Function of Communication)
Allows employees to express feelings through workplace discussions and employee recognition.
Information (Function of Communication)
Facilitates decision-making by sharing knowledge through reports and data sharing.
Upward Communication
Flows from employees to higher management, such as employee feedback, reports and grievances.
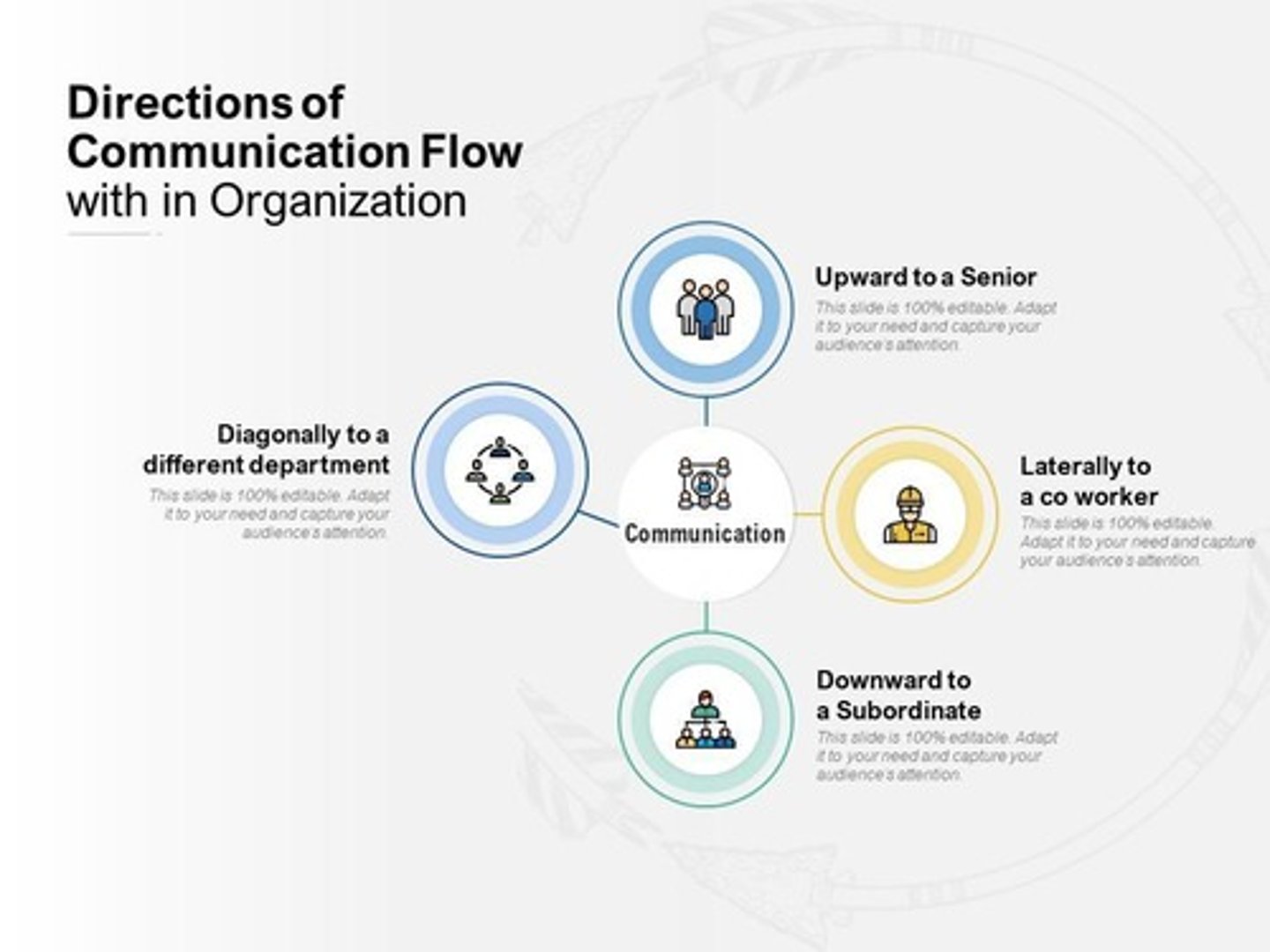
Downward Communication
Flows from management to employees, including company announcements and instructions.
Lateral (Horizontal) Communication
Occurs between peers or departments,
ex, collaboration between teams.
Modes of Communication: Verbal Communication
Involves spoken words and tone of voice, such as in meetings and phone calls.
Modes of Communication: Non-Verbal Communication
Includes body language, gestures, and facial expressions, like eye contact and posture.
Modes of Communication: Visual & Written Communication
Consists of documents, reports, and emails, such as company memos and contracts.
High-Richness Communication Channel
Includes face-to-face and video calls, best for sensitive topics and complex messages.
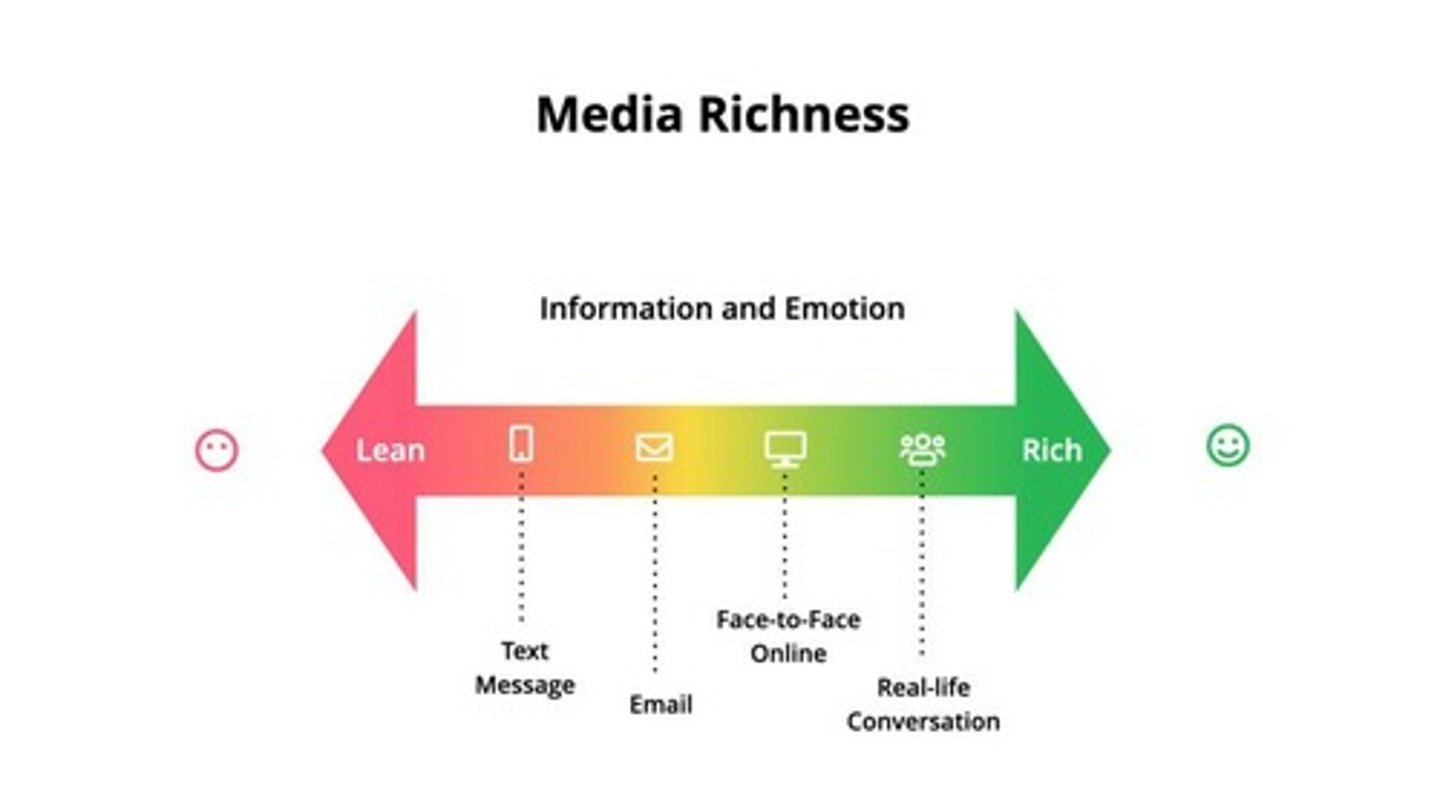
Medium-Richness Communication Channel
Includes emails and texts, good for general communication.
Low-Richness Communication Channel
Includes reports and bulletins, best for routine updates.
Persuasive Communication
Effective communication that involves credibility, emotional appeal, logical structure, and audience understanding.
Common Communication Barriers
Obstacles that hinder effective communication, such as filtering and selective perception.
How Culture Affects Communication: High-Context Cultures
Cultures that rely on indirect communication and non-verbal cues, like Japan and China.

How Culture Affects Communication: Low-Context Cultures
Cultures that rely on direct, explicit messages, such as the U.S. and Germany.
Time Orientation: Monochronic Cultures
Cultures that value punctuality, such as the U.S. and Canada.
Time Orientation: Polychronic Cultures
More flexible with time (Latin America, Middle East).
Organizational Change
The process by which organizations adapt to new conditions, strategies, structures, or technologies.
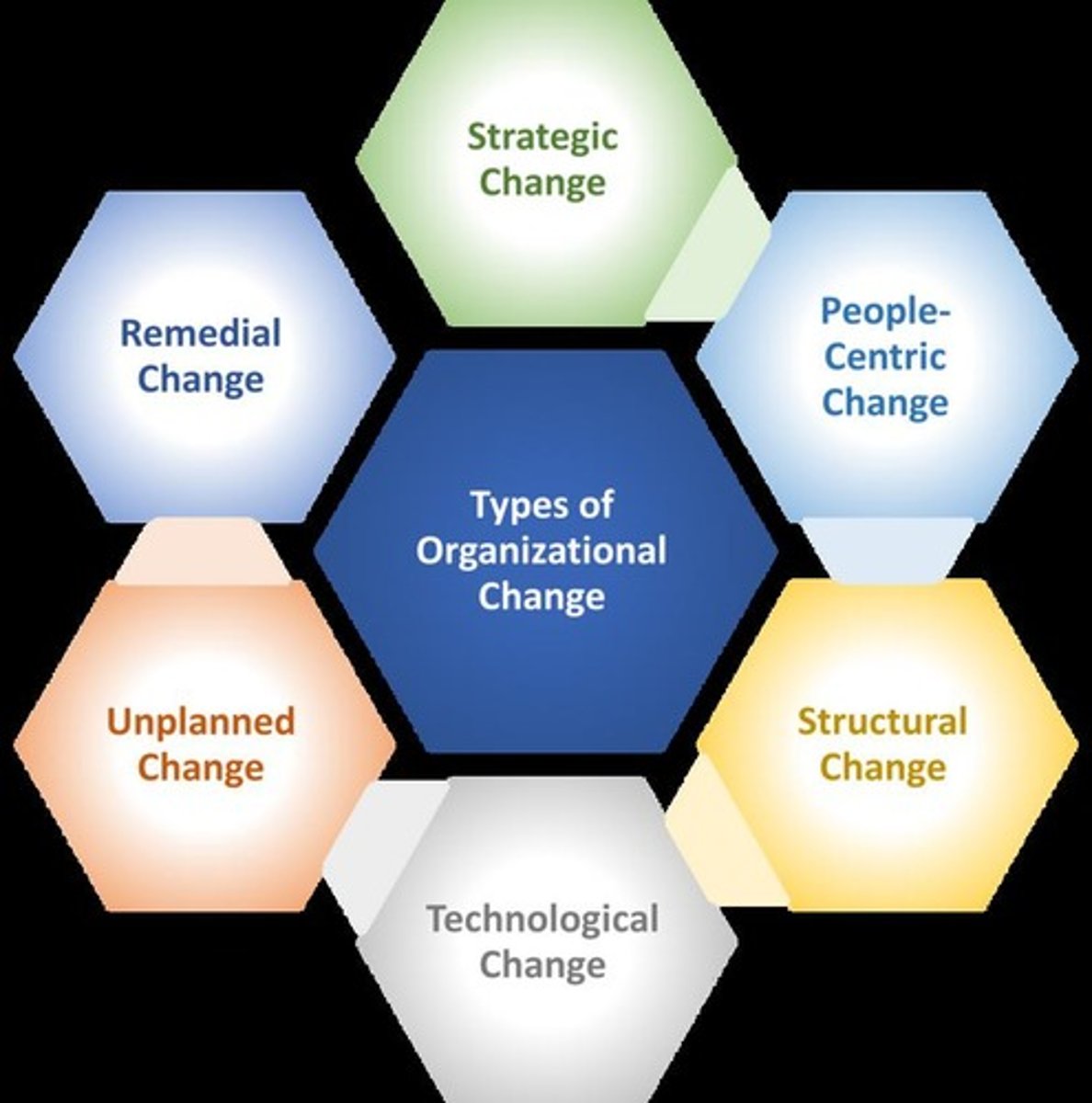
Types of Change: Planned Change
Intentional and goal-oriented (e.g., restructuring, new policies).
Types of Change: Unplanned Change
Reactionary due to external forces (e.g., economic crises, pandemics).
Forces Driving Change
Technology, globalization, workforce diversity, and regulatory shifts.
Why Do People Resist Change?Individual Resistance
Habit and comfort with routines, fear of the unknown, economic insecurity (fear of job loss), selective information processing (focusing only on favorable details).
Why Do People Resist Change?Organizational Resistance
Structural inertia (rigid processes), threats to existing power structures, limited resources and financial constraints.
Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Change
Communication & Education (best): Explain why change is necessary.
Participation & Involvement (best): Involve employees in decision-making.
Support & Facilitation: Provide training and emotional support.
Negotiation & Incentives: Offer rewards for embracing change.
Coercion (Last Resort): Enforce change through authority when necessary.
Lewin's Three-Step Model
1. Unfreezing - Creating awareness and preparing people for change.
2. Changing - Implementing new behaviors, policies, or systems.
3. Refreezing - Reinforcing and institutionalizing the change.

Workplace Stress
A psychological and physical response to job demands that exceed an employee's coping ability.
Common Workplace Stressors
Heavy workloads & unrealistic deadlines, job insecurity & organizational change, poor leadership & unclear expectations, work-life imbalance.

Effects of Workplace Stress
Physical: Headaches, fatigue, high blood pressure.
Psychological: Anxiety, depression, burnout.
Behavioral: Absenteeism, low productivity, increased conflicts.
Strategies for Managing Workplace Stress (Individuals)
Develop time management skills, set boundaries and prioritize self-care, seek social support and stress relief activities.

Strategies for Managing Workplace Stress (Organizations)
Encourage a healthy work-life balance, offer employee wellness programs, provide clear communication and role expectations.
Common Communication Barriers- Filtering
Withholding or distorting information to suit the receiver.
Common Communication Barriers- Selective perception
People interpret messages based on their biases.
Common Communication Barriers-
Information Overload
Too much information at once leads to confusion
Common Communication Barriers- Language and jargon
Misunderstanding due to technical terms.
Common Communication Barriers- Emotional barriers
Feelings like stress can distort message interpretation
How Culture Affects Communication: Formality & Hierarchy
Some cultures emphasize status and titles more than others
How Leaders Drive Change:
-Encourage open communication.
-Build trust and credibility.
-Address employee concerns proactively.
-Lead by example.
-Reward and recognize adoption of new behaviors.
Lewin's model emphasizes
Lewin's model emphasizes that change doesn't happen overnight. The unfreezing stage is critical, without it, people resist moving forward