Digital Data 💾
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Digital Technology Unit 1: Digital Technology (Core)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
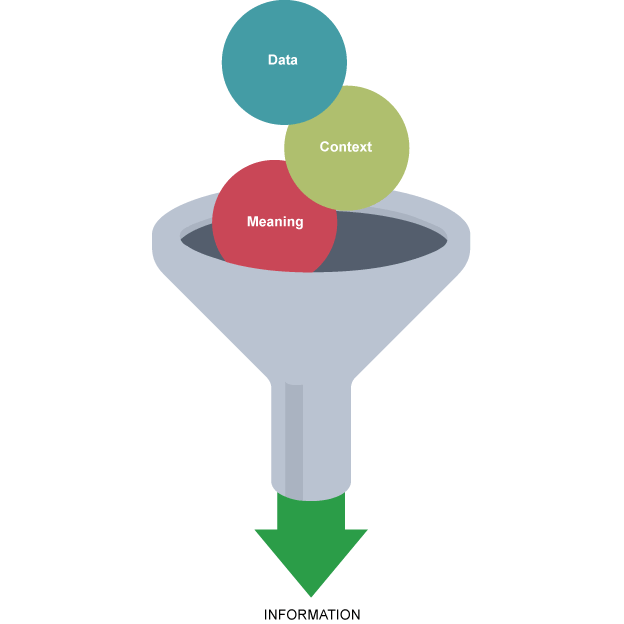
Data
raw facts and figures with no context or meaning
Information
data entered into a computer and processed, giving it meaning
Binary
number system in bits used by computers
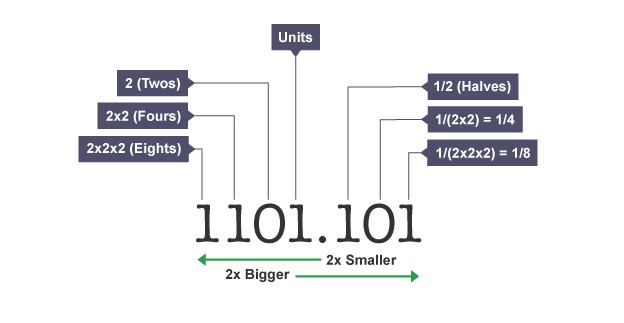
Bit
smallest unit of digital data represented by a 1 or 0
Nibble
4 bits
Byte (B)
8 bits
Kilobyte (Kb)
1024 bytes
Megabyte (Mb)
1024 kilobytes
Gigabyte (Gb)
1024 megabytes
Terabyte (Tb)
1024 gigabytes
What are units of data used for?
to describe memory capacity
Numeric (integer)
positive or negative whole numbers
Numeric (real)
positive or negative numbers with decimal/ fractional parts
Date/time
represents date and time in multiple formats

Character
single letter, number or symbol which takes up 1 byte of storage
ASCII
character set with each character represented uniquely by a single byte
String (text)
textual data in the form of a sequence of characters
Pixel
smallest unit of an image that can be changed, displayed with its own colour
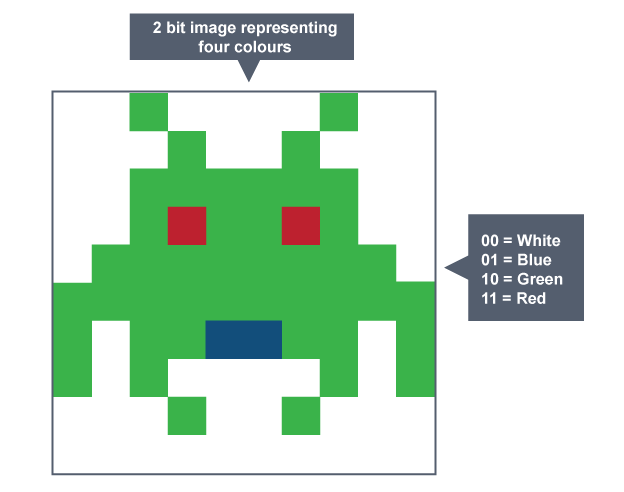
Resolution
number of pixels per unit measurement which determines the quality/ clarity of the image

Effect of high resolution on file size
contains large number of pixels so increases file size as every colour code has to be stored
Storing images
needs to have colour codes and metadata stored e.g dimensions to reconstruct/ display on screen
Colour depth
N bits per pixel can have 2N different colours
Typical bits per pixel (JPEG)
24 bits or 224 (16.7million colours)
Bitmap graphics
Stored as a grid of pixels, each with a specific colour and can be compressed
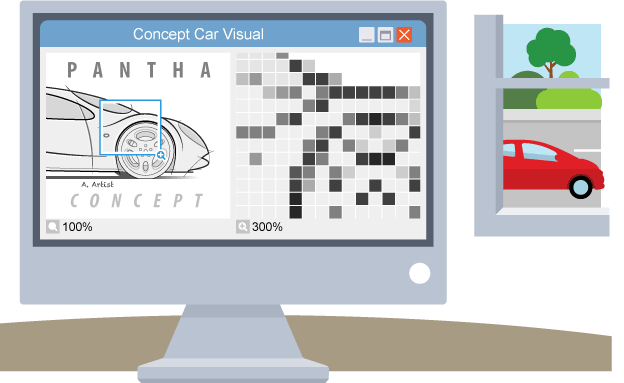
Vector based graphics
mathematical instructions about individual components which create shapes and lines
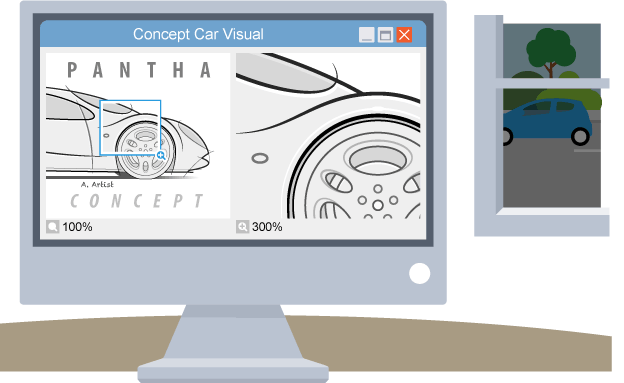
Bitmap vs vector based graphics
Bitmap loses quality when resized while vector scales to retain detail
Vectors more efficient, they don’t store each individual pixel so smaller file size
Bitmaps can be compressed to reduce their file size
Bitmaps take long to load due to processing
Formats for bitmap graphics
.bmp
.dib
.jpeg
.gif
.tiff
.png
Formats for vector based graphics
.svg
.cgm
.odg
.eps
.xml
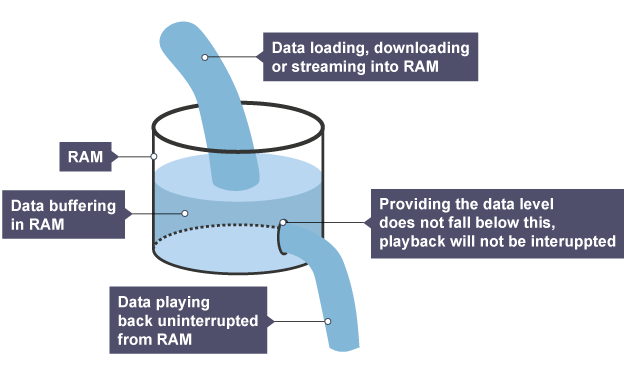
Streaming
allows videos to be viewed on a website without downloading or a time delay
How does streaming work?
downloading successive segments in ‘real time’ to prevent waiting, then discarding after use
Advantages of streaming
video is unlikely to be replicated as user doesn’t save full copy
allows video to be watched while it downloads
computer doesn’t need to be capable of storing entire file
Buffer
intermediate storage area used to hold downloaded segments of video not played yet
Why use buffering?
prevents possible interruptions if there are time delays in streaming
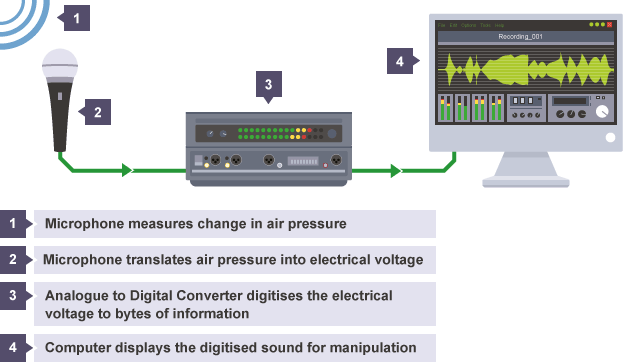
Analogue signal
continuous varying signal to represent physical quantity e.g sound waves
Analogue to digital converter (ADC)
converts analogue signal (detected by microphone) into voltage variations so computer can store it digitally
Sound sampling
taking regular measurements of sound waves to process digitally
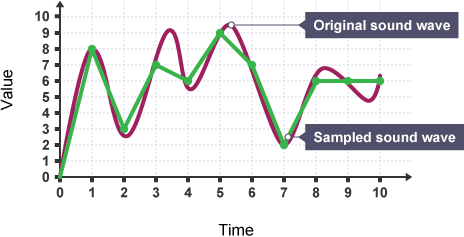
Need for sound sampling
infinitely minor variations in sound waves require too much storage and some we are incapable of hearing
Sample rate
quantity of audio samples captured per second, measured in hertz/ kilohertz
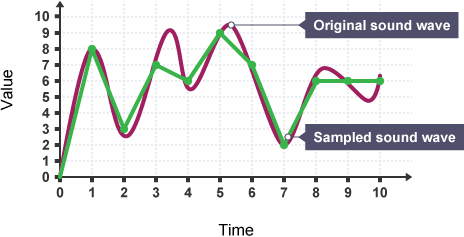
How does sample rate affect file sizes?
higher gives larger file sizes as more measurements are stored
Bit depth
number of bits available for each sample, higher depth is greater quality
Bit rate
data (bits) required to store 1 second of sound, measured in kbps
Calculating bit rate
bit depth × sample rate
Units for frequency
Hertz (Hz)