Topic 1.1 Skeletal System
1/41
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
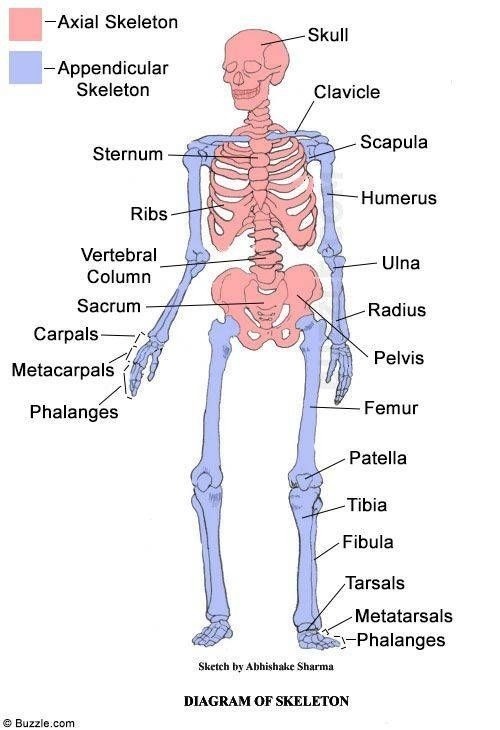
Axial skeleton
Skull, ribs, sternum, vertebral column
Vertebral column
Cervical- 7 bones
Thoracic- 12 bones
Lumbar- 5 bones
Sacrum- 5 fused as 1
Coccyx- 4 fused as 1
Appendicular skeleton
Pectoral girdle (scapula and clavicle), humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges, pelvic girdle (ilium, ischium, pubis), femur, patela, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals
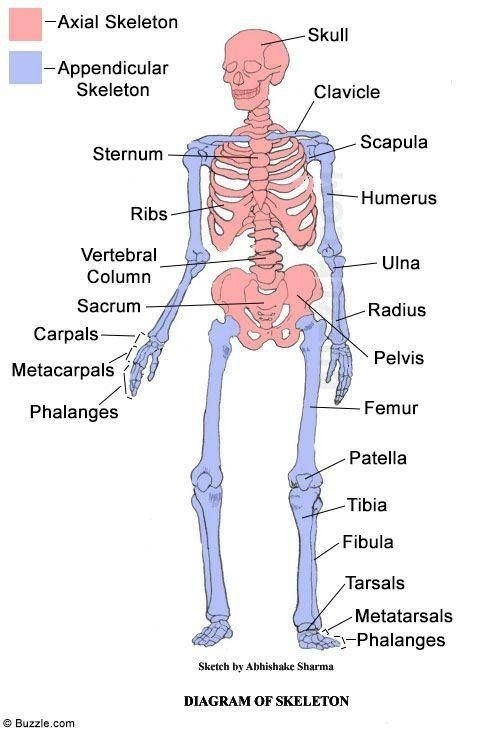
What are the functions of the axial skeleton?
Protect vital organs
Support and maintain posture
Provide attachment point for muscles
Storage and release of minerals
Blood cell production
What are the functions of the appendicular skeleton?
Provide levers to allow movement
Provide attachment for muscles to enable movement
Protect organs
Store and release minerals
Long bones
Long cylindrical shaft
Enlarged at both ends
Length is greater than width
Common for movement
Short bones
Small short cubes
Serves to transfer forces
Flat bones
Curved surfaces
Vary from thick to thin
Protection and broad surface provide large surface area for muscle attachment
Irregular bones
Specialized shapes and functions
Epiphysis
Ends of the long bone
Made of spongy and compact bone
Where blood production occurs
Diaphysis
Shaft of the bone
Made of compact bone
Envelopes marrow cavity
Spongy bone
Irregular lattice structure
Stores red bone marrow
Where blood production occurs
Articular Cartilage
Thin layer of cartilage covering the ends of the bones where joints are formed to prevent friction and absorb shock
Compact bone
External layer of the bone
Passageways for blood, nerve and lymphatic vessels
Important for protection and support
Bone marrow
Generate blood cells
Red bone marrow: produces blood cells
Marrow cavity
Space in diaphysis
Holds yellow bone marrow
Periosteum
Thin, white shiny membrane
Important for bone growth, nutrition, repair and attachment of ligaments/tendons
Blood vessel
Passes nutrient foramen in the diaphysis
Inferior
Towards the feet
Superior
Towards the head
Anterior
Towards the front
Posterior
Towards the back
Proximal
Towards the body’s mass
Distal
Away from the body’s mass
Medial
Towards the midline of the body
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Tendon
Attaches muscle to bone
Provides stability in synovial joints
Pulls on bone when muscle contracts to move
Ligament
Bone to bone
Provides stability in synovial joints
Cartilage
Bone to bone as cartilaginous joints
Allows limited movement
Joint
Where two or more bones articulate
Fibrous joints
No synovial cavity
No movement
Held by fibrous connective tissue containing collagen fibers
Cartilaginous joints
No synovial cavity
Limited movement
Held by cartilage
Synovial joint
Synovial cavity
Bones forming joint are united by surrounding articular cartilage
Free movement
Synovial fluid inside the synovial membrane
Common joint type
Articular cartilage
Smooth tissue covering the ends of the bone at a joint
Allows bones to glide smoothly over each other
Reduces friction and absorbs shock
Synovial membrane
Lines the inner surfaces of the synovial cavity
Secretes synovial fluid inside the capsule
Synovial fluid
Thick fluid inside the capsule
Lubricating articular surfaces
Provides nutrients
Absorbs debris
Bursae
Tiny sac lined with synovial membrane containing synovial fluid
Found between bone and soft tissue (tendon/ligaments)
Reduces friction between structures by preventing wear
Meniscus
Crescent shaped pad of cartilage
Helps bones fit together
Stabilizes and cushions joints
Ligament
Extension of joint capsule
Provides strength and stability in synovial joints
Strong fibrous tissue
Joint cavity
Articular cavity enclosed by the membrane and articular cartilage
Containing fluid
Articular capsule
Strong tissue enveloping the joint
Blends into periosteum
Giving joint stability and wanted particles from entering the joint area