Dermatology Exam 1 Lecture 5 (Sandy)
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Buboe
Swollen or inflamed lymphnode in groin or axilla
Gumma
Solitary granulomatous lesion with central necrosis.
Psoriasiform
resembling psoriasis
cutaneous rash caused by fever or disease
Exanthema
This is a bacterial illness transmitted via tick bite. It is caused the Rickettsia rickettsii (gram negative bacteria).
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
How is RMSF transmitted?
Ticks
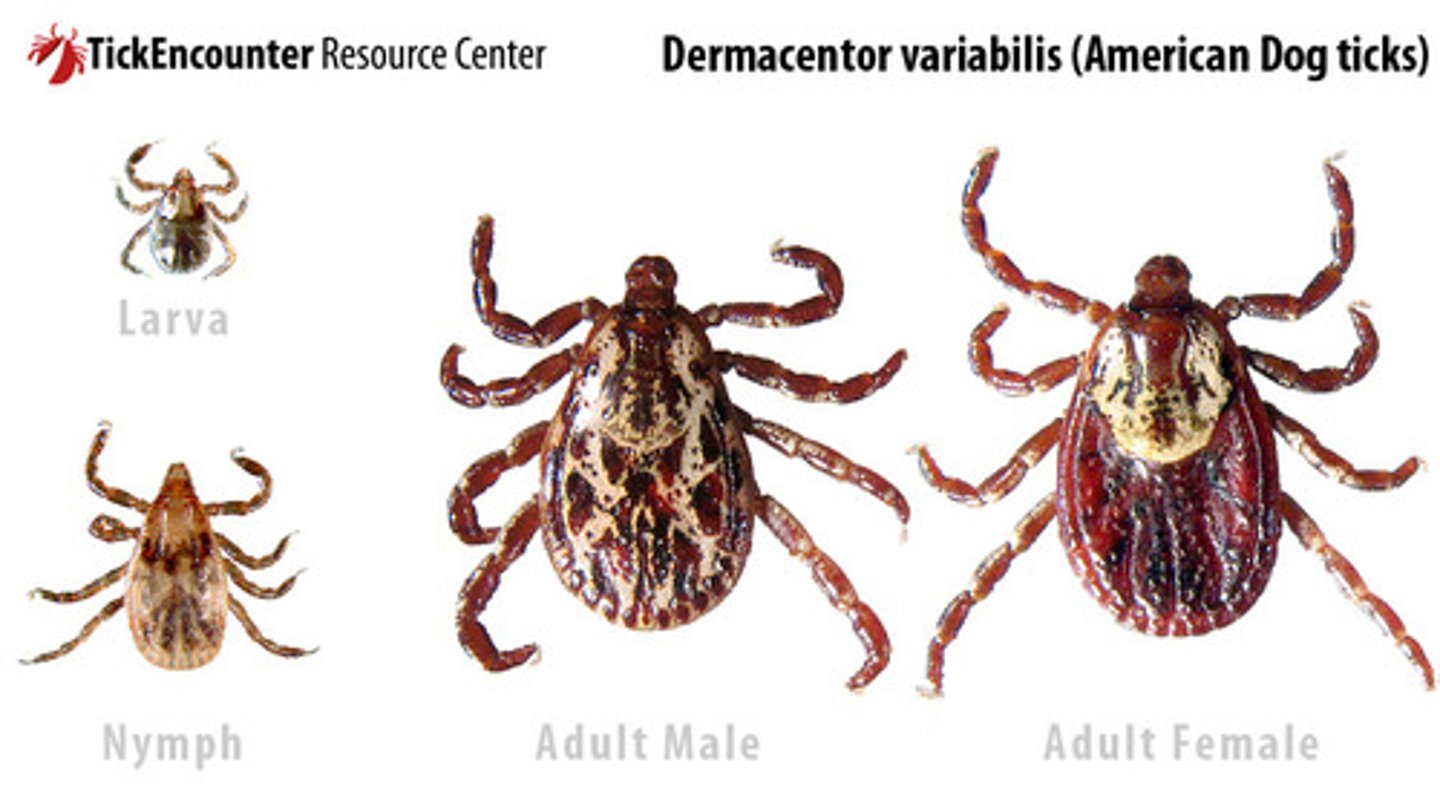
Dermacentor variabilis (Dog Tick) is found in the ?
Eastern US
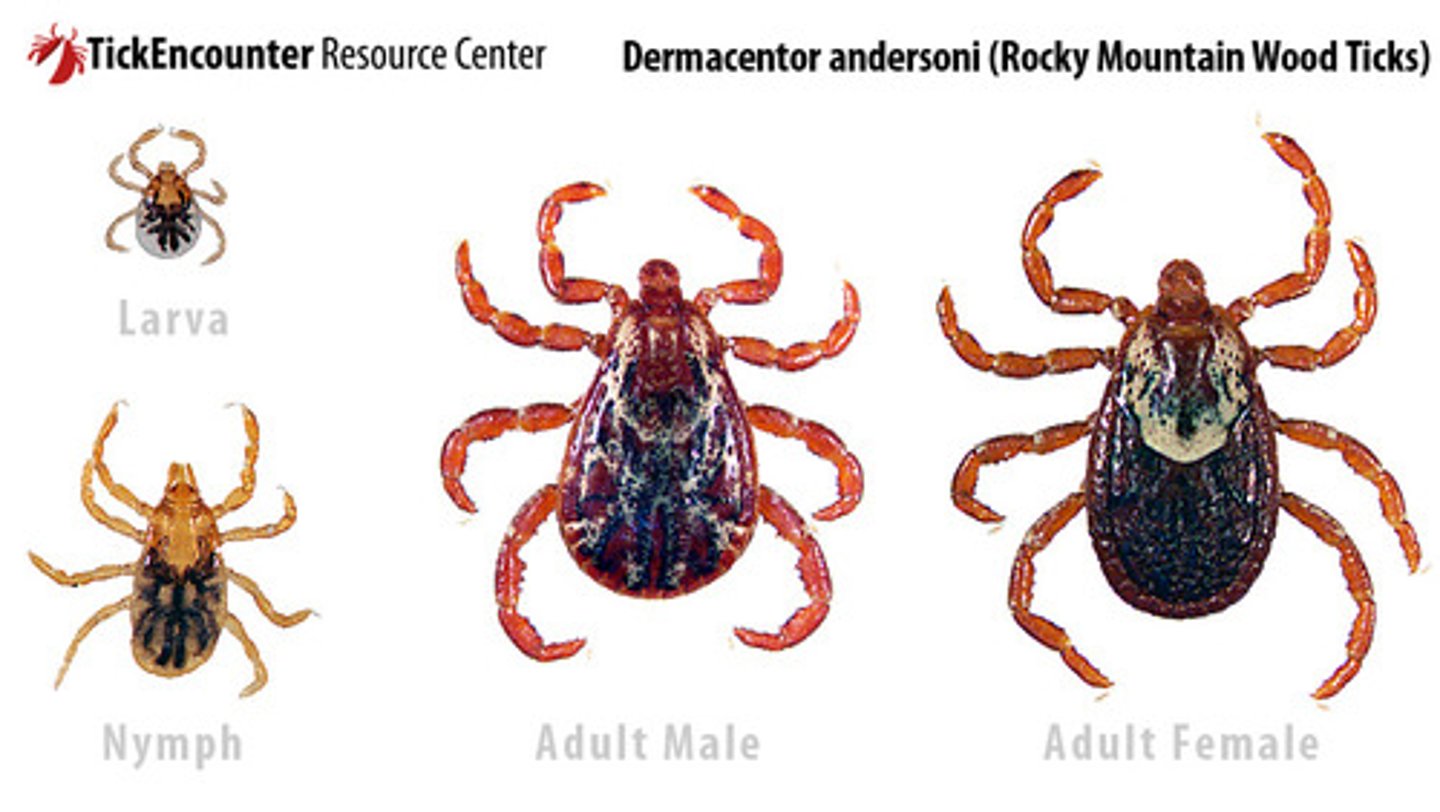
D. andersoni (Wood Tick) that is found in the ?
Southwestern/south central US
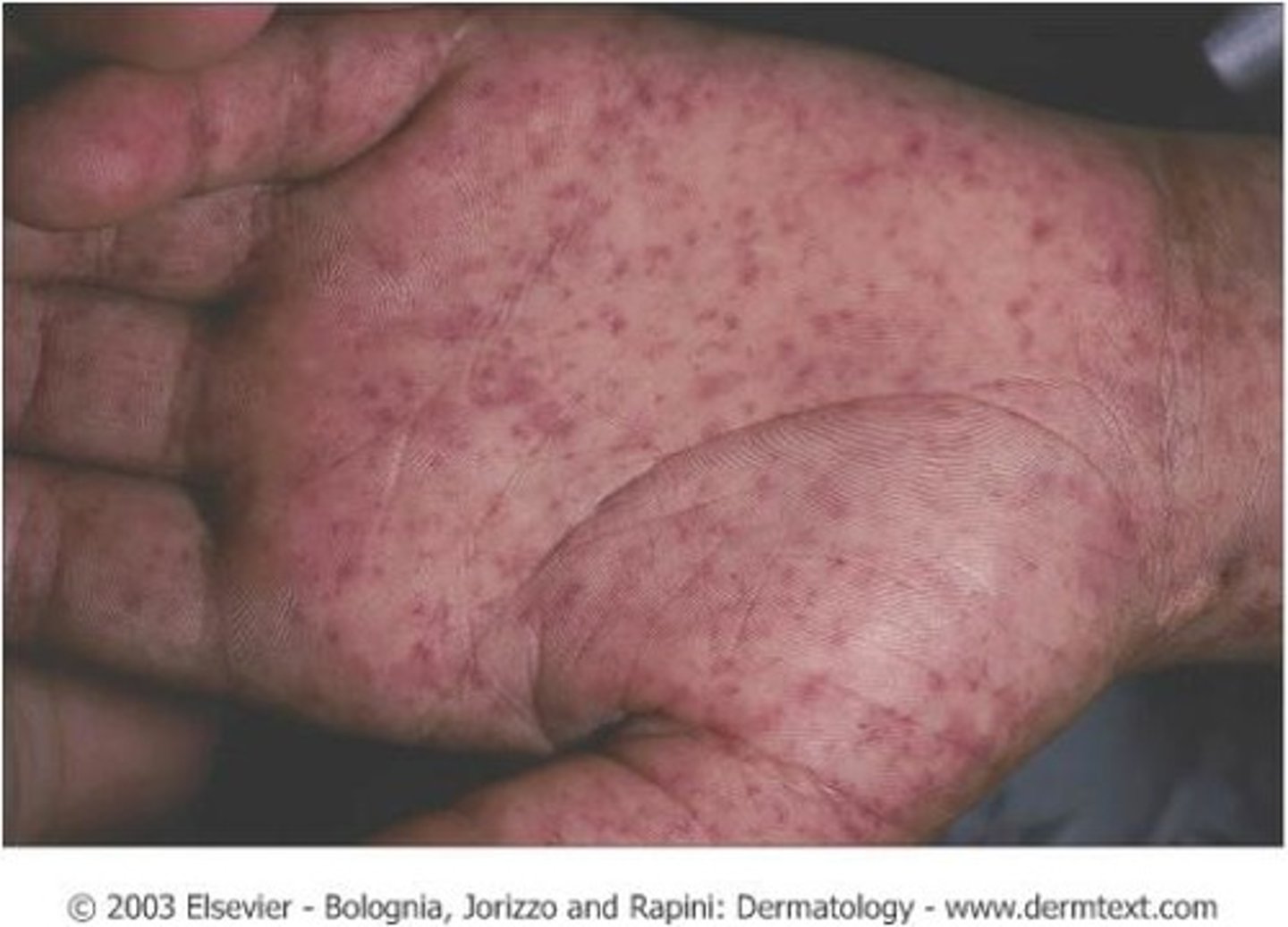
Pink macular rash, initially blanching, beginning at the distal extremities (palms/soles). Rash then spreads proximally in 24 hours and becomes hemorrhagic in 4-5 days. What condition is this the characteristic rash of?
RMSF
Is this a description of the Early or Late exanthema that is present in RSMF?
"Hemorrhagic petechiae on palms and soles then rest of body forming purpura, does not blanching, and local edemas present. Next, necrosis in acral extremities occurs."
Later exanthem: 5 to 7 days
Is this a description of the Early or Late exanthema that is present in RSMF?
"2-6mm, pink, blanchable macules on wrists & ankles. Palms and soles may be involved. In 6-18hrs it spreads centrally to arms, thighs, trunk, and face that evolves to deep red papules. "
Early exanthem (2-4 days)
Explain the characteristic rash of RMSF
Pink macular rash, initially blanching, beginning at the distal extremities (palms/soles). Rash then spreads proximally in 24 hours and becomes hemorrhagic in 4-5 days.
Which age group is MC affected by RMSF?
1. Febrile Children
2. Adolescent
3. Men > 60
What symptoms can you see in a pt with RMSF?
1. Fever
2. severe headache,
3. myalgia
3. chills, shaking rigors. Anorexia, N/V, malaise, irritability
Thrombocytopenia and hyponatremia should increase your suspicion for which vector-borne viral condition?
RMSF
What abnormalities can you expect to see on the labs of a patient with RMSF?
Thrombocytopenia
Hyponatremia
The diagnosis is made clinical but needs to be confirmed later by ?
Biopsy of petechial papule or eschar followed by PCR
What is the tx of choice for RMSF?
Doxycycline
Tick borne illness due to spirochete infection where transmission is 24 to 72 hours.
Lyme Disease
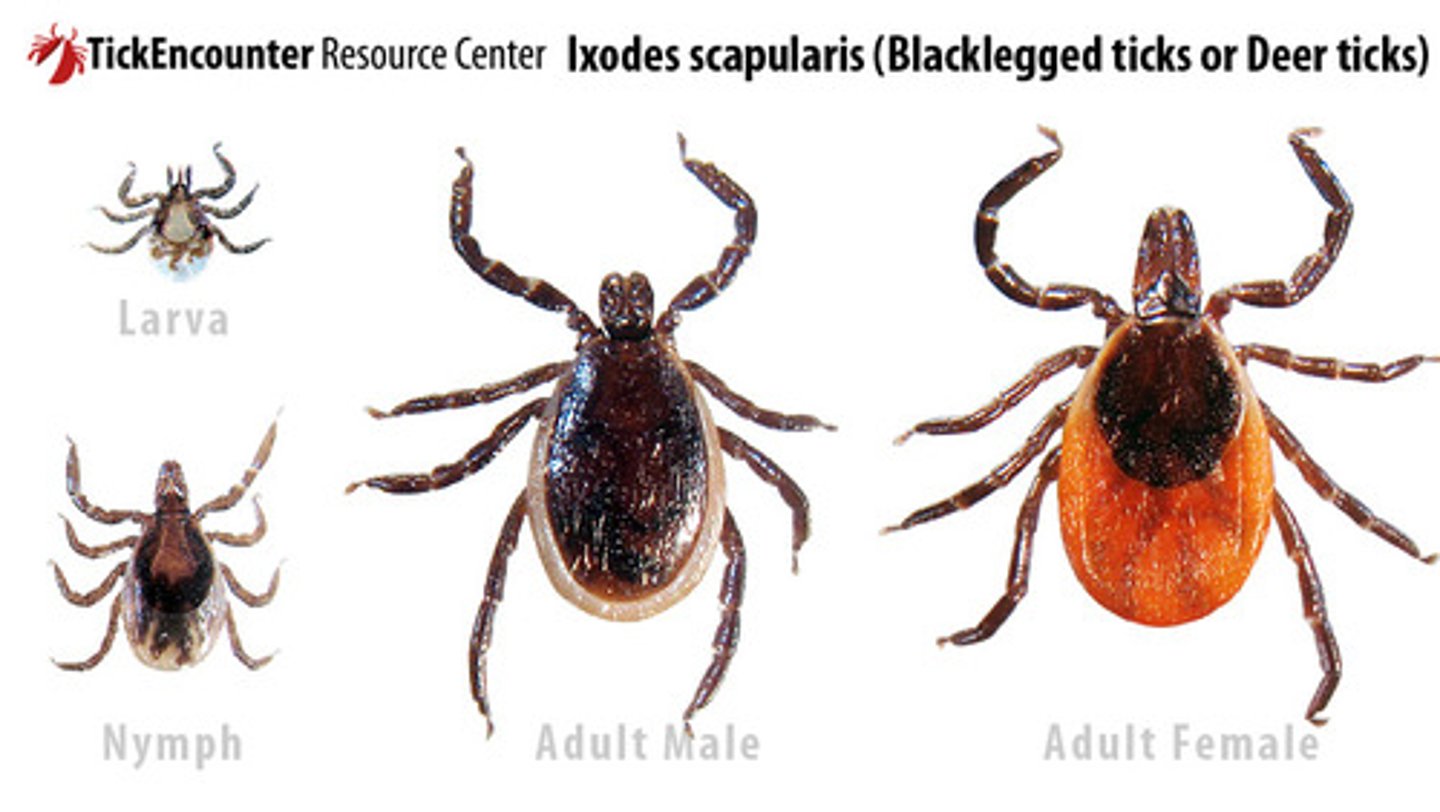
Patients generally are not at risk for contracting Lyme disease until the tick has been feeding for ____ hours or more
72 hours
What type of bacteria causes Lyme disease and type of tick transmits it ?
Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted via Ixodes tick
What are the 3 stages of Lyme disease?
Stage 1: early localized
Stage 2 :early disseminted
Stage 3 :late disease
What is the name of the classic rash of Lyme disease?
Erythema migrans
What's stage will you see an initially erythematous macule or papule that
expands centrifugally to form a target shaped lesion. Warm to touch and can be up to 15cm. Can appear up to 30 days after tick bite (avg 7-14 days). Pt can experience burn, pruritic, pain along with F, chills, myalgia, HA, weakness and photophobia.
Stage 1: Early localized
(Erythema migrans 80%)
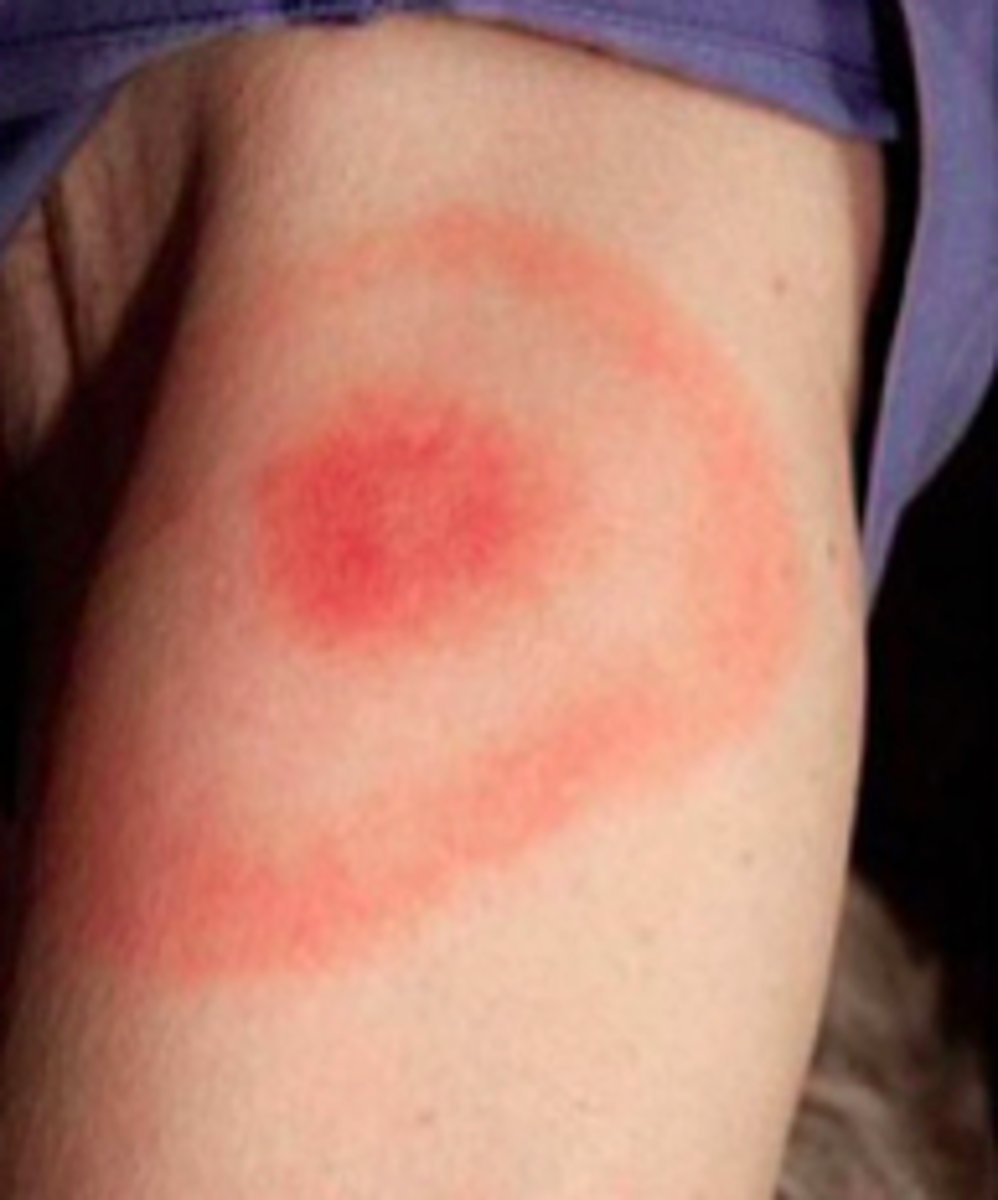
Initially Red macular-papular rash, expanding over days-weeks with central clearing and blanching. This describes the rash of which viral condition?
Lyme disease
This stage happens 1-12 weeks later after multiple EM's may be present and the patient can experience neurological symptoms like cranial nerve palsies (Bells Palsy), HA, aseptic meningitis, weakness, cardiac issues (AV block).
Stage 2: Early Disseminated Lyme Disease
This stage occurs months to years after Lyme infection. The patient can experience intermittent or persistent arthritis in the large joints. Additionally, persistent neurologic symptoms such as confusion, disorientation and lack of concentration
Stage 3 Late Lyme Disease
How much time must pass between tick exposure and blood testing for Lyme disease?
4 weeks
What is the initial test for diagnosis of Lyme disease?
ELISA
What does the ELISA test for Lyme disease (LD) look for?
Antibodies to B. burgdorferi
If the ELISA test is positive, what is the next step to confirm dx?
Western blot
You perform a Western blot on a patient whose ELISA was positive for B. burgdorferi antibodies. The results of the western blot are + for IgM and - for IgG. What is the next appropriate step?
Repeat the test in a month
If only IgM is positive still after 1 month, ELISA was a false positive
What is the prophylactic treatment of LD?
Single dose of doxycycline within 72 hours of tick removal
What is the treatment for active LD?
Doxycycline for 14-21 days
_alternatives to Doxy in the treatment of LD
Amoxicillin or cefuroxime
What are the circumstances in which Amoxicillin would be chosen over Doxycycline for the treatment of LD?
Patient < 8 y/o
Patient allergic to doxy
Patient is pregnant
If LD is severe, we can give?
IV Ceftriaxone
Chronic granulomatous disease affects superficial tissues (skin & peripheral nerves). The incubation few months to 20-50 years.
Leprosy (Hansen's Disease)
Leprosy is more common in cooler areas of skin, such as ___ and ___
Peripheral nerves and testes
What are the two types of leprosy?
1. Paucibacillary leprosy (tuberculoid)
2. Multibacillary leprosy (lepromatous)
More mild leprosy characterized by localized 5 or few skin skin lesion. Sharply demarcated hypopigmented macular lesions/plaques with well-defined erythematous purple borders. There is a loss of sensation (advanced lesion) with atrophic center.
Paucibacillary leprosy (tuberculoid)
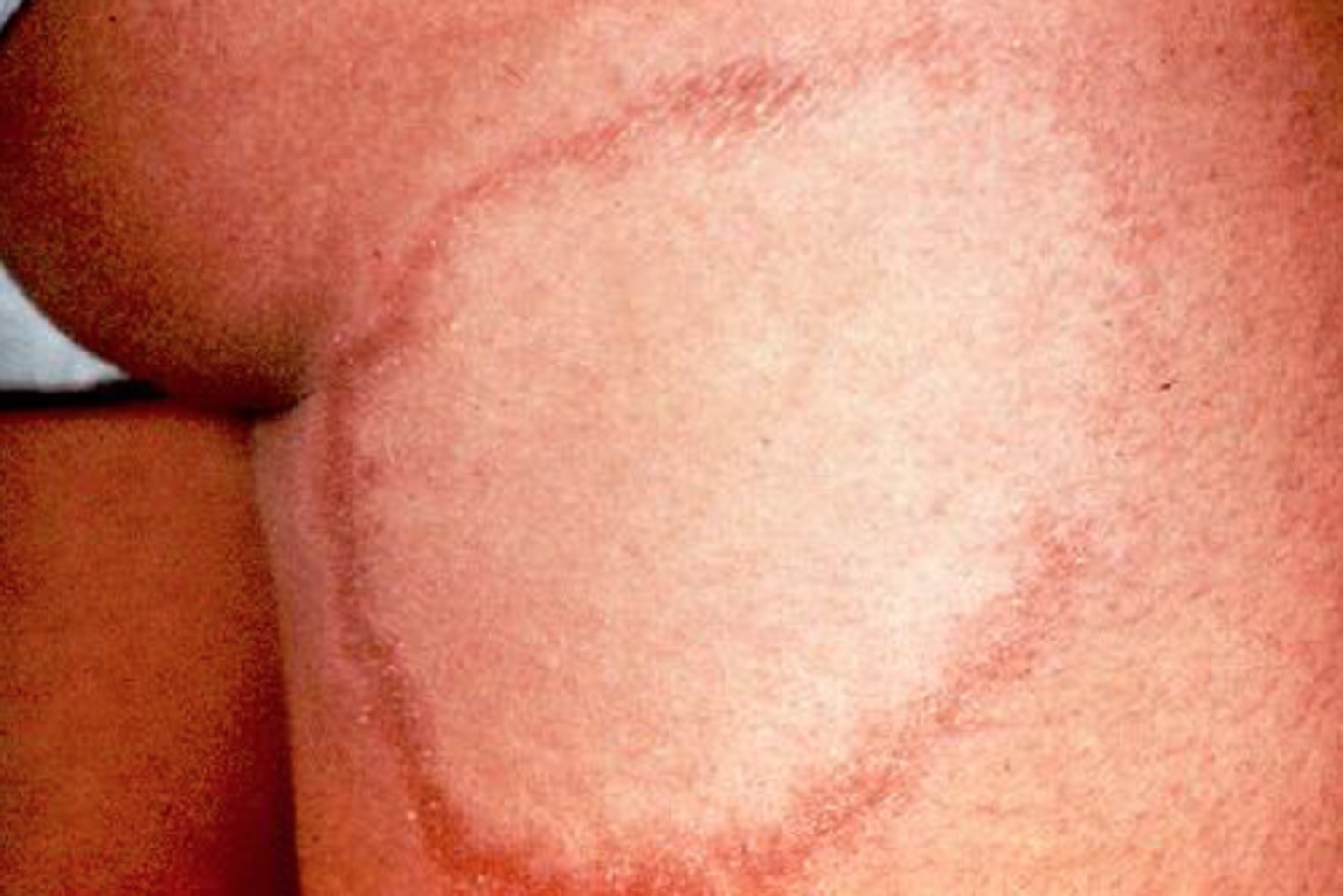
Paucibacillary leprosy causes a sudden onset of _______. Usually the numbness will first start will temperature sensation loss followed by light touch, pain, and the deep pressure
asymmetric nerve involvement
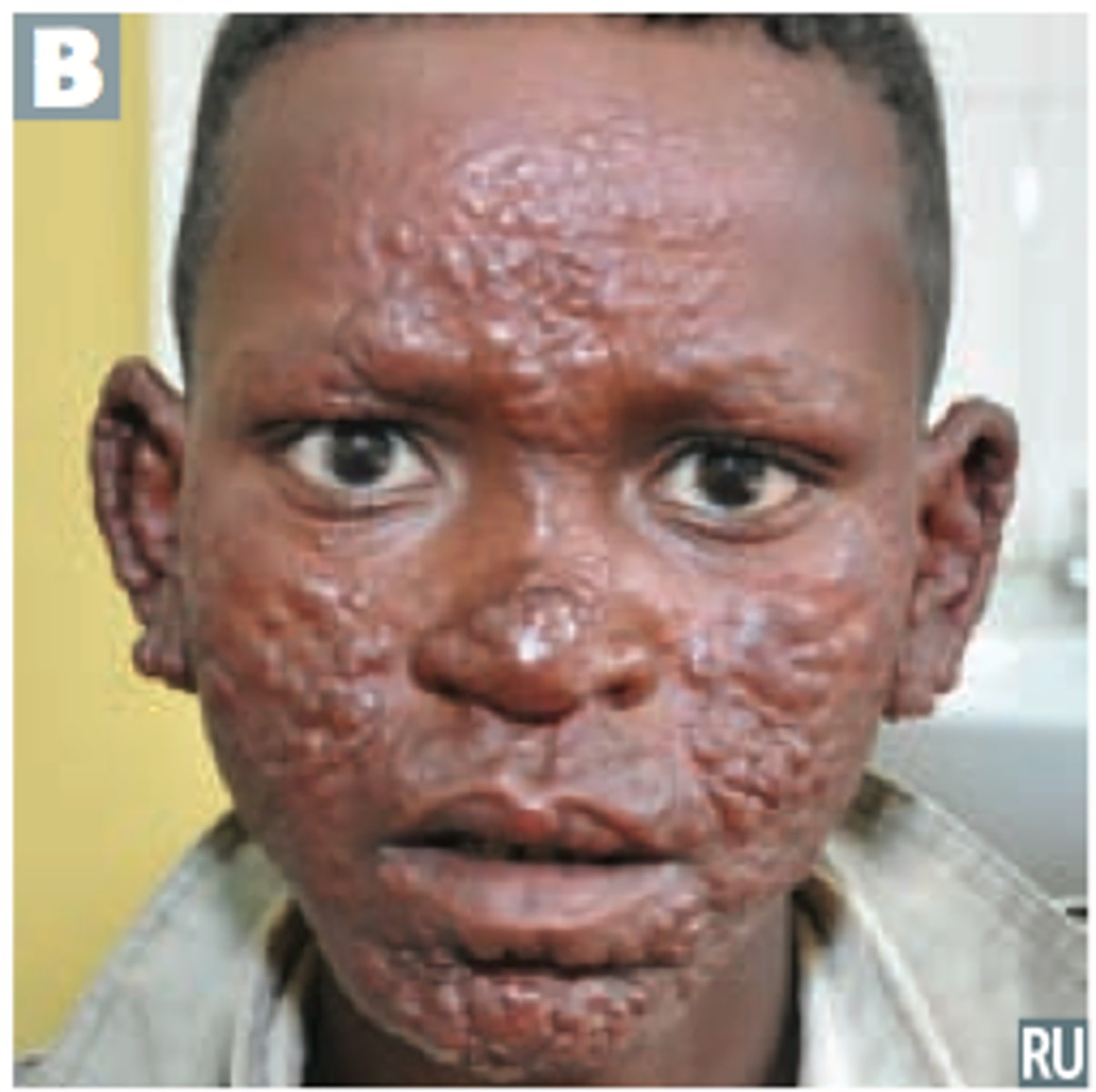
Leprosy characterized by generalized involvement including the skin, upper respiratory mucous membrane, reticuloendothelial system, adrenal glands, testes.
Lepromatous (multibacillary) leprosy
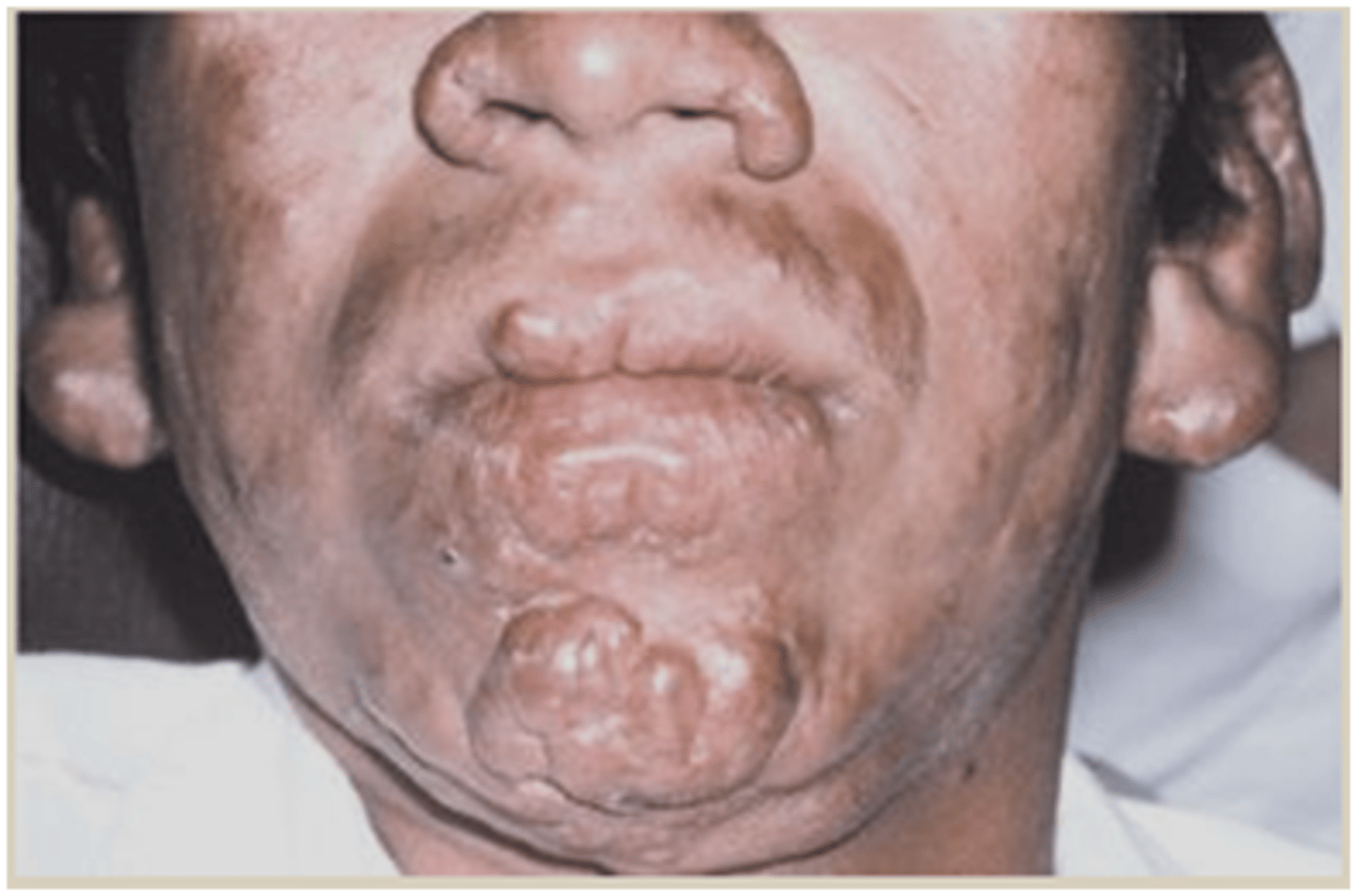
Leprosy that initially starts with hypopigmented or erythematous macules with poorly defined borders and normal sensation. It progresses to widespread infiltration with nodules and plaques. Symmetric nerve involvement with paresthesias in peripheral nerves
Lepromatous (multibacillary) leprosy
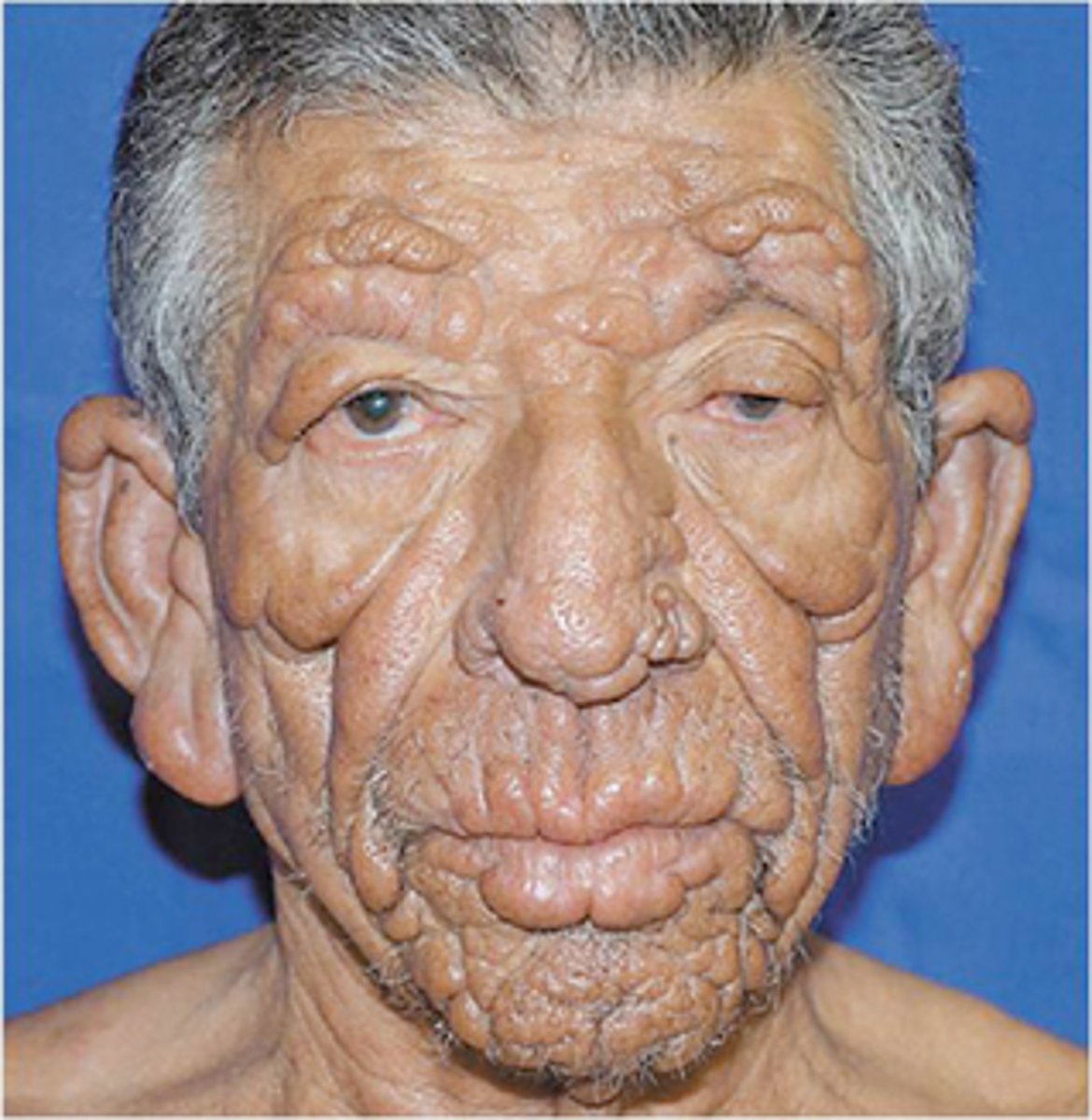
Thickening of forehead, loss of eyebrows and eyelashes, distortion of the nose, thickened earlobes. What type of facies is this and is seen in what disease?
Leonine facies in Lepromatous Leprosy
How do you dx Leprosy ?
One or more of the following:
1. From endemic area
2. Skin lesions characteristic of disease
3. Enlarged peripheral nerve
4. Loss of sensation or diminishment of
5. Biopsy with acid fast bacillus smear or PCR
MC sexual transmitted infection
HPV
How do you tx Tuberculoid Leprosy ?
Dapsone plus rifampin x 6 m
How do you tx Lepromatous Leprosy ?
Dapsone + rifampin + clofazimine x 1 year
Uncommon form of extrapulmonary TB. Cutaneous infection through exogenous or
endogenous innoculation. Presents with a wide array of presentations that depends on route of inoculation and immune status.
cutaneous TB
What is in the classification of Exogenous CTB ?
1. Primary inoculation tuberculosis
(PIT)
2. Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis
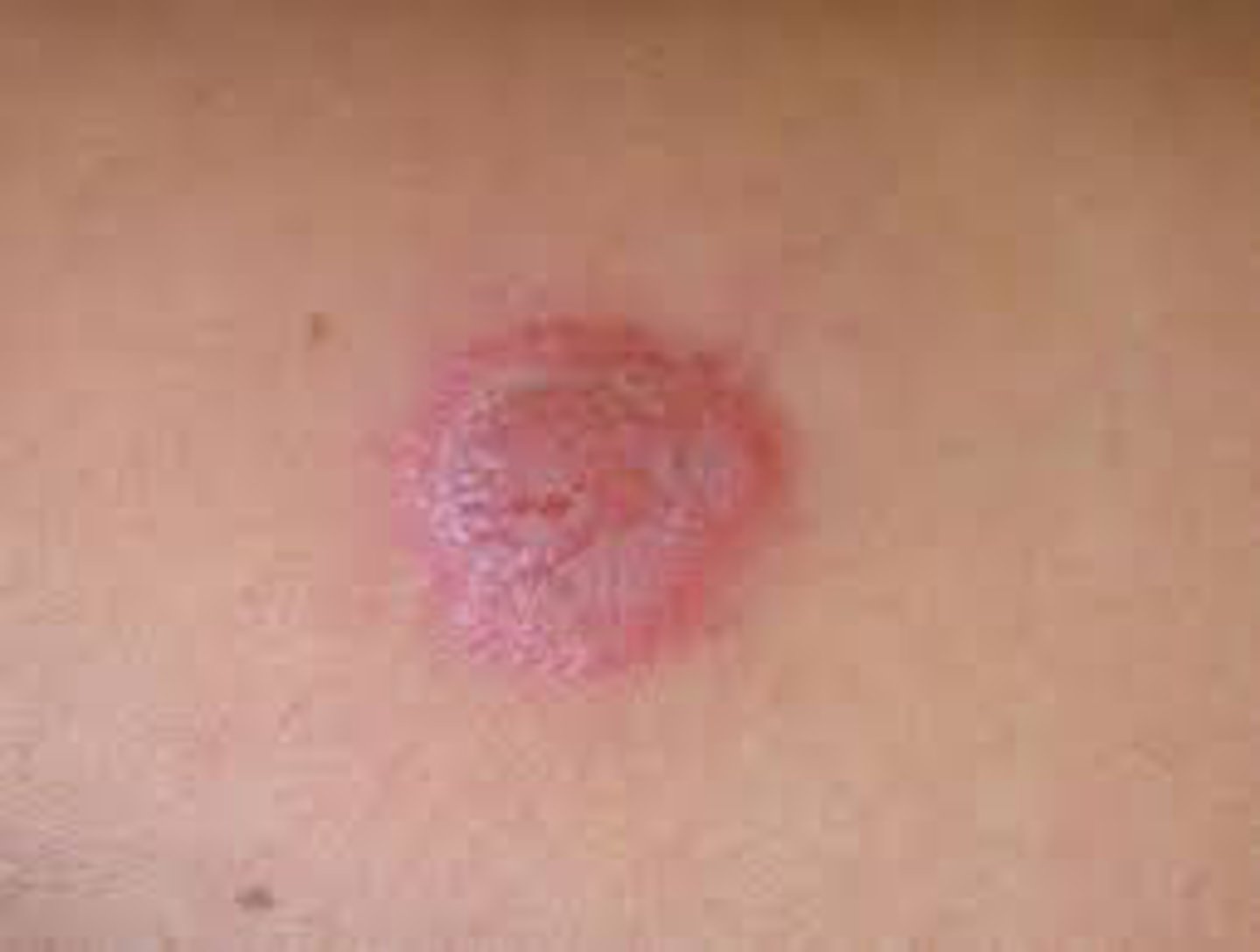
Occurs at inoculated site of in nonimmune host usually through minor trauma. Can occur in mouth resulting in ulcers from bovine bacilli in unpasteurized milk.
Primary Inoculation TB
Initially 2-4 wks after inoculation a Papule forms into a painless ulcer/tuberculosis chancre with shallow granular base. Can have crust and abscess may also occur. Can resolve spontaneously or within a year and its M/C located on the upper/ lower extremities and. buttocks
Primary Inoculation TB
This CTB occurs at site of inoculation in a patient with a prior Tb infection. It Initially starts off as papule with a violaceous halo. The lesion than becomes firm, dense and takes on appearance of a verrucous plaque with irregular borders. It is painless. Its MC on the dorsolateral hands and fingers. On children its MC on the lower extremities/knees
Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis
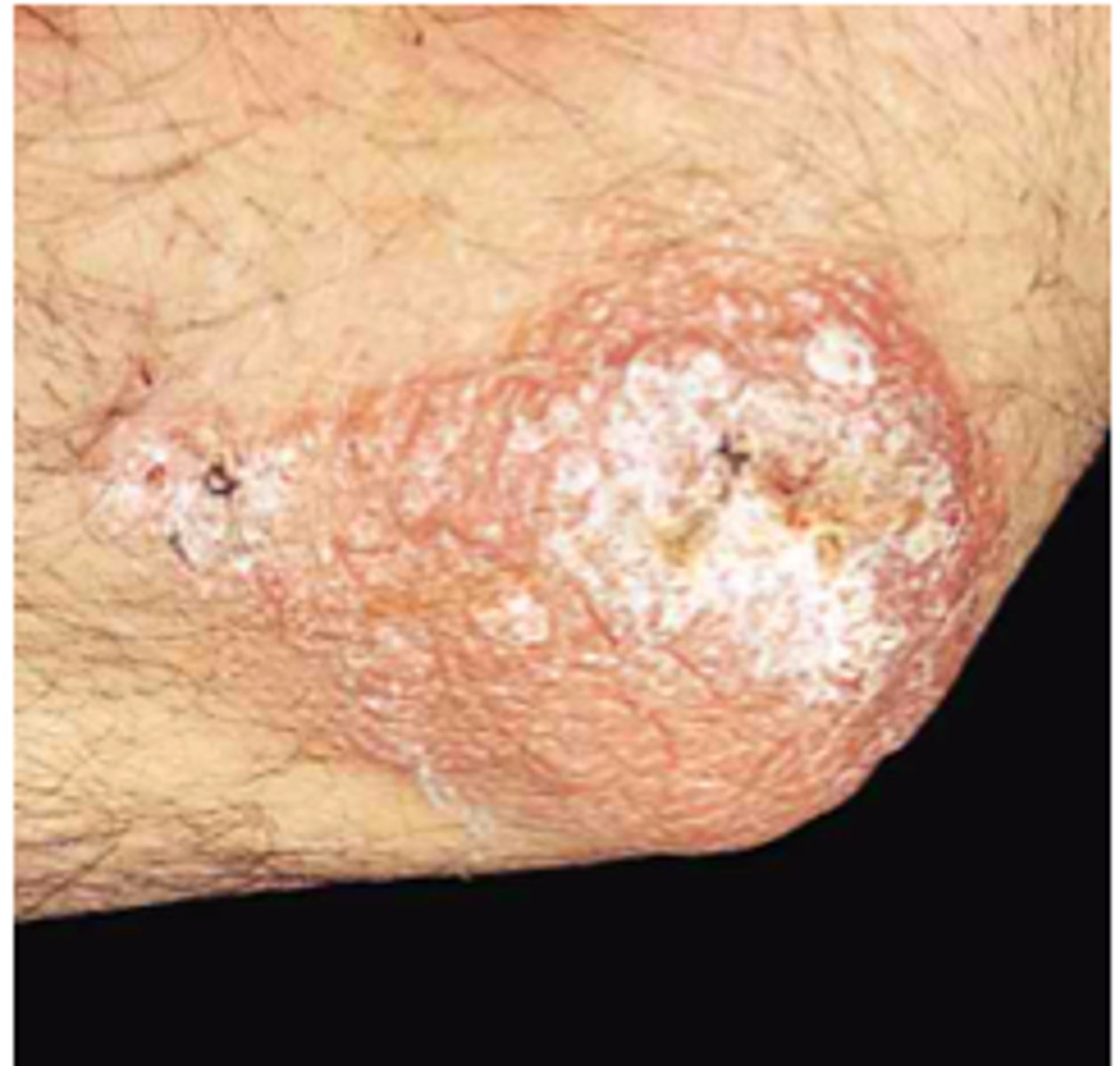
What is the tx for CTB?
RIPES
1. Rifampin
2. Isoniazid
3. Pyrazinamide
4. Ethambutol
5. Streptomycin
(need to tx with two of these)
Infects epithelial tissues of skin and mucous membranes causing slow growing hyperplastic keratinzation
HPV
What is the MC STI in the US?
HPV
What is the most common presentation of HPV
Warts
Common wart is known as ____
Verruca vulgaris
Firm, hyperketatotic papules with "bleeding points" (thromboses capillaries) and disruption of normal skin lines. Most commonly found on hands and feet that can be transmitted via Skin to Skin contact or Fomites.
Verruca vulgaris
What are the "bleeding points" of the common wart?
Thrombosed capillaries
Flat topped, flesh-pink warts commonly found on the face and extremities
Verruca plana
Method of treatment for warts in which liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the wart
Cryotherapy
What is used for cryotherapy in the treatment of warts?
Liquid nitrogen
What is ILC in the treatment of warts?
Intra-lesional candida. Candida is injected into the wart to kick start the immune system to fight the candida, and thus allowing it to fight the HPV
Acantholytic agent used in the treatment of warts. Creates a water blister between the epidermis and dermis, separating the layers of skin, breaking the wart off
Cantharone
Where does Cantharone come from?
Beetle juice extract
What patient population is Cantharone good for in the treatment of warts and why?
Children, because it is much less painful than cryotherapy
When treating a child for warts, what is the least painful treatment option?
Cantharone
How does Cantharone work?
Creates a water blister between the epidermis and dermis, separating the layers of skin, breaking the wart off
HPV infection to anogenital areas and/or oropharynx
Condyloma Acuminatum
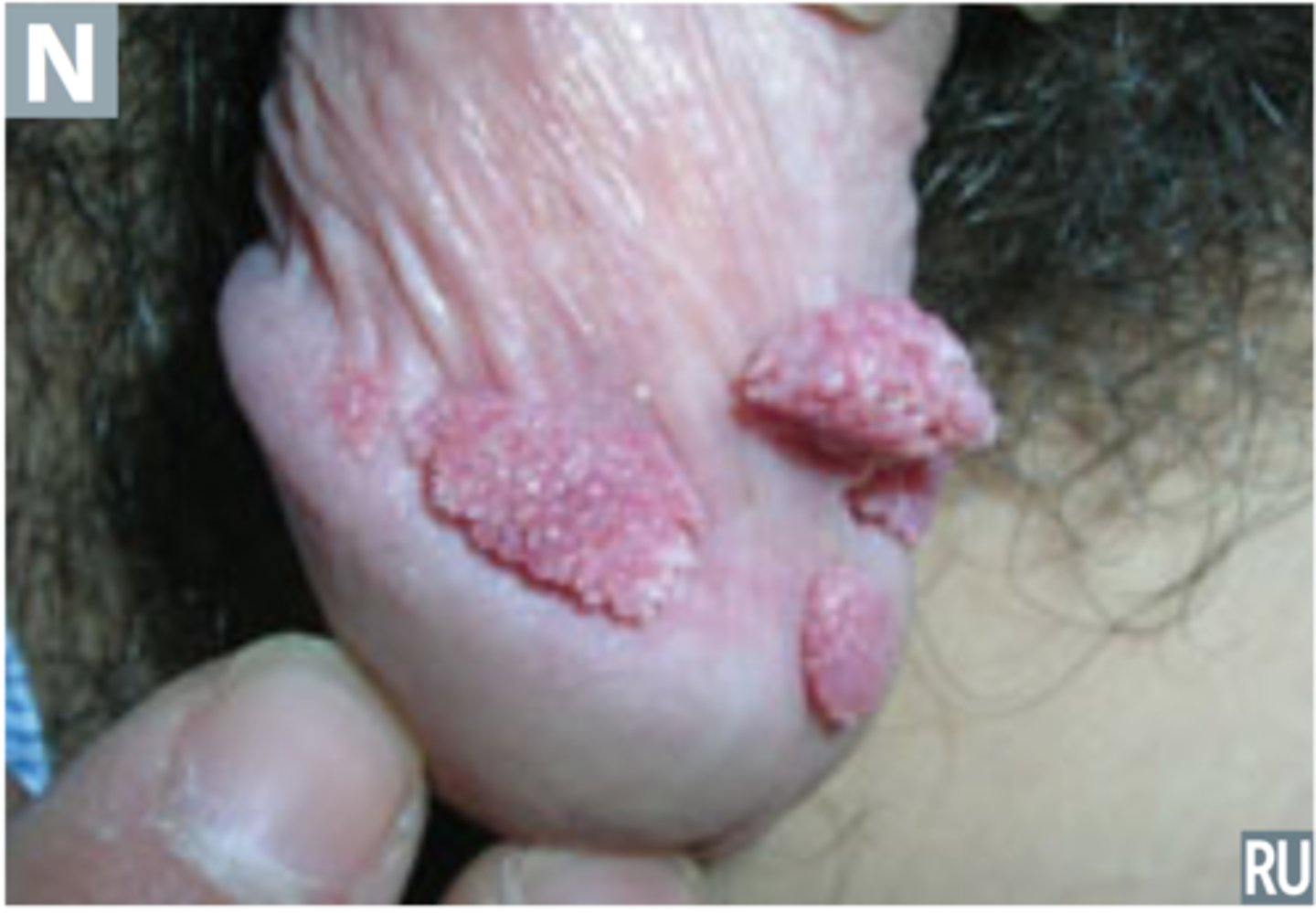
Painless papules that evolve into soft, fleshy cauliflower-like cluster lesions on the genitals, personal area or oropharynx
Condyloma
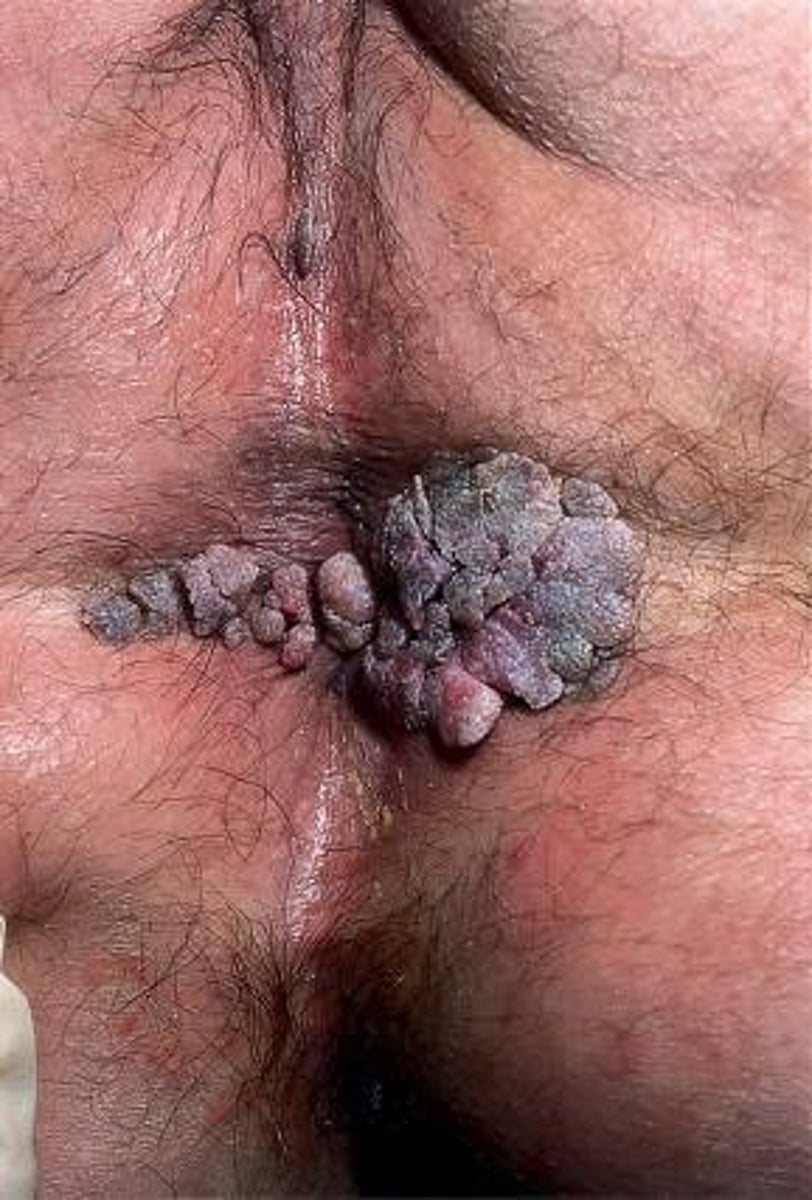
What is the causative agent of condyloma?
HPV
Left untreated, condyloma can lead to ___
Cervical dysplasi/carcinoma
What are the HPV strain responsible for causing cervical cancer?
16, 18, 31, 33, 35
Who gets Condyloma acuminatum?
M/C AA
Unprotected sex
Ages 18-59
What can you use to apply to the HPV lesion and if it is HPV it will turn the lesion white.
3-5% Acetic acid
How do you dx Condyloma Acuminatum ?
Clinical BUT biopsy for HPV DNA
What is the tx for Condyloma Acuminatum ?
1. Imiquimod TIW x 16 weeks max
2. Podofilox
3. Cryotherapy
4. Gradle/cautery
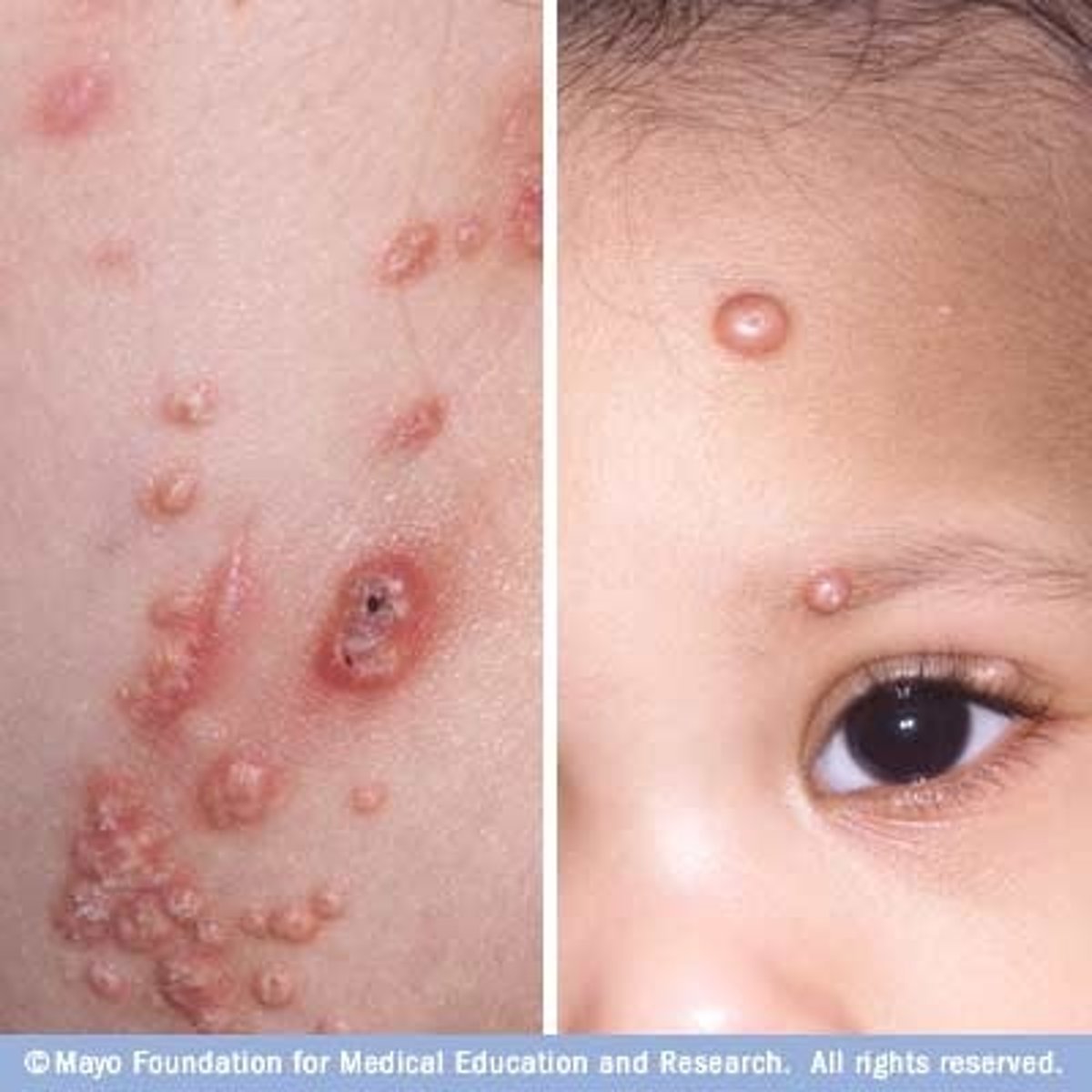
Benign viral infection that can occur anywhere on the body but spares palms and soles. Commonly seen on trunk, a.c & popliteal fossae, crural folds, and axilla.
Molluscum contagiosum
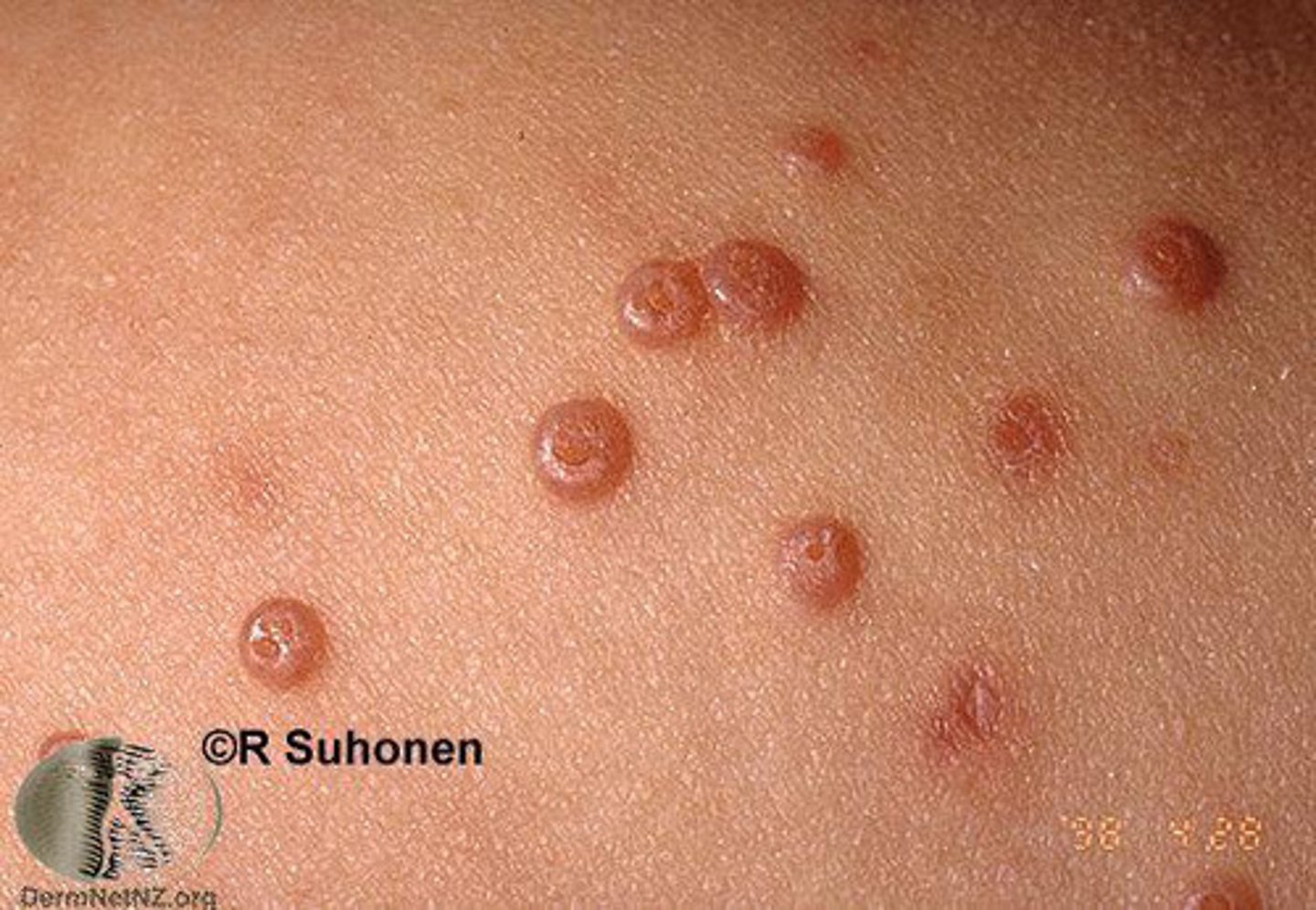
What is the causative agent of molluscum contagiosum?
Poxvirus
Children swimming together may precipitate the spread of which common pediatric viral condition?
Molluscum contagiosum
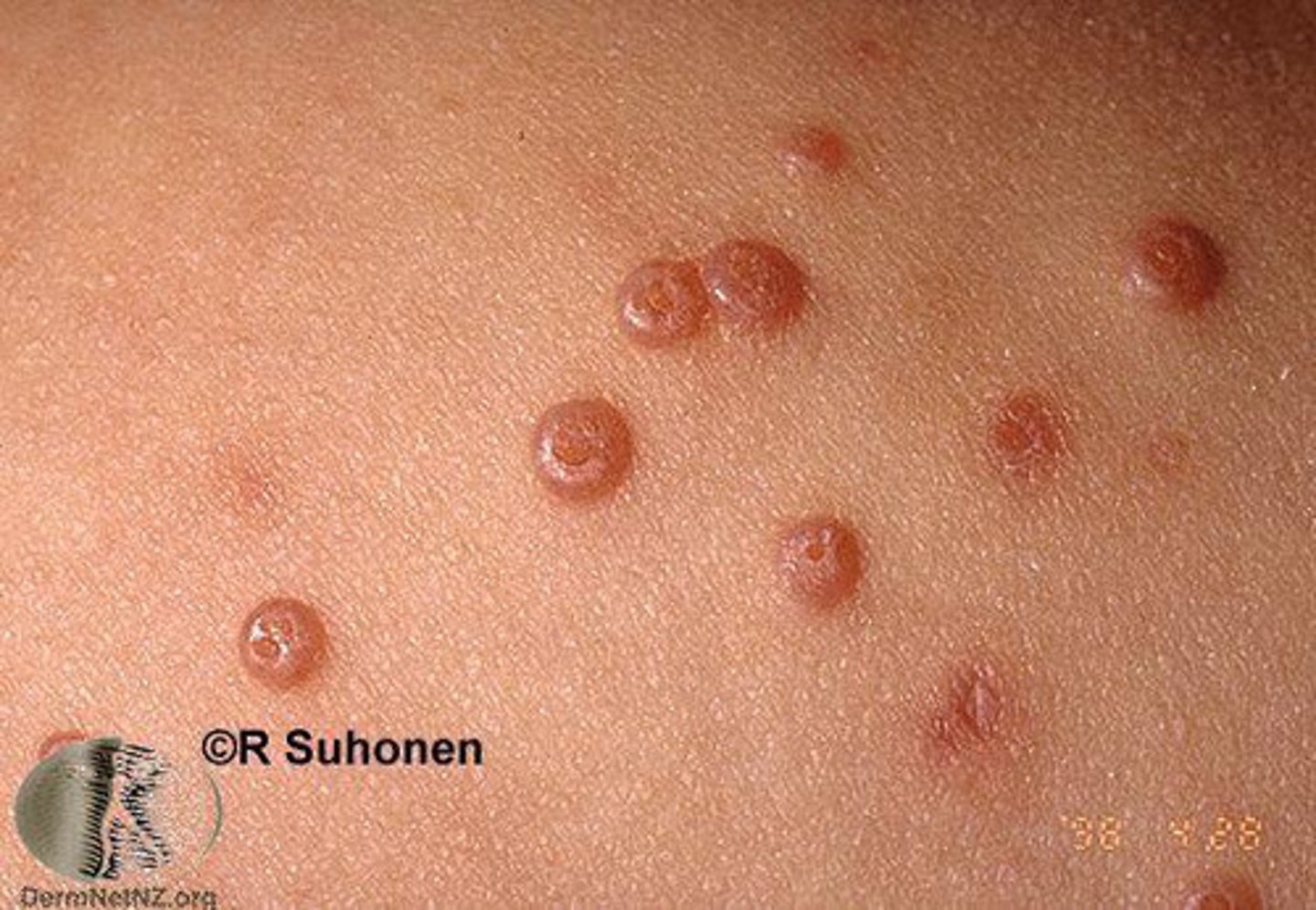
Flesh colored firm dome shaped waxy papules with central
umbilication is characteristic of ____
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum Contagiosum MC seen in?
Children
On a biopsy of a molluscum contagiosum lesion, you would find ____
Inclusion bodies
tx of Molluscum Contagiosum
is benign, self limiting (resolves in 12-18 months), no treatment needed
Acute reactivation of Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV) that causes pain, burning, or paresthesias usually before the rash develops by a few days. The rash is characterized by being unilateral and dermatomal that starts as papules/plaques of erythema and progresses to vesicles/ bullae that eventually are pustules that crust up and heal.
herpes zoster (shingles)
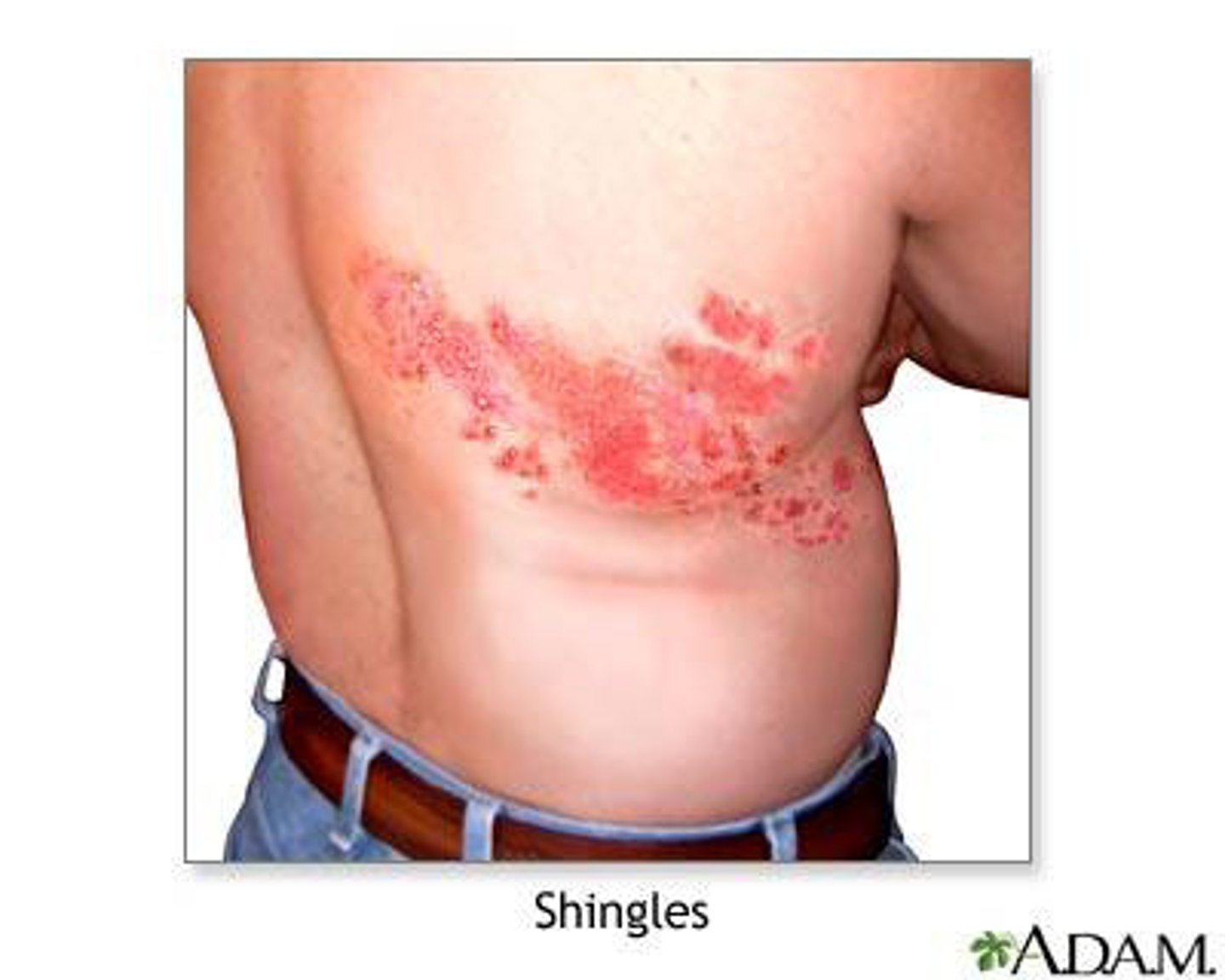
What is at risk for Herpes Zoster?
1. Advanced age (>50)
2. Immunocompromised
Can contract VZV from direct contact with _____ from _____ and from _______
fluid; vesicles; airborne transmission
Who must be avoided at all costs to prevent transmission of herpes zoster?
1. pregnant
2. immunosuppressed
3. unvaccinated
Herpes Zoster is no longer contagious once lesions crust usually within _____ days
7-10 days
Provides rapid diagnosis of HSV or VZV
Tzanck smear
What is a limitation of the Tzanck smear?
Cannot differentiate HSV-1 and HSV-2
What is the preferred when testing is needed to confirm Herpes Zoster?
PCR
Gimesa/Wright stain reveals a multinucleate giant cell with which conditions?
HSV or VZV
What would you expect to see on Gimesa/Wright stain of a HSV lesion?
Multinucleated giant cells
What is the treatment of choice for herpes zoster?
PO Valcyclovir (Valtrex)
+/- Prednisone depending on severity
What is a complication of herpes zoster?
Post herpetic neuralgia (pain > 90 days after onset)
What is a treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia?
Gabapentin (Neurontin)
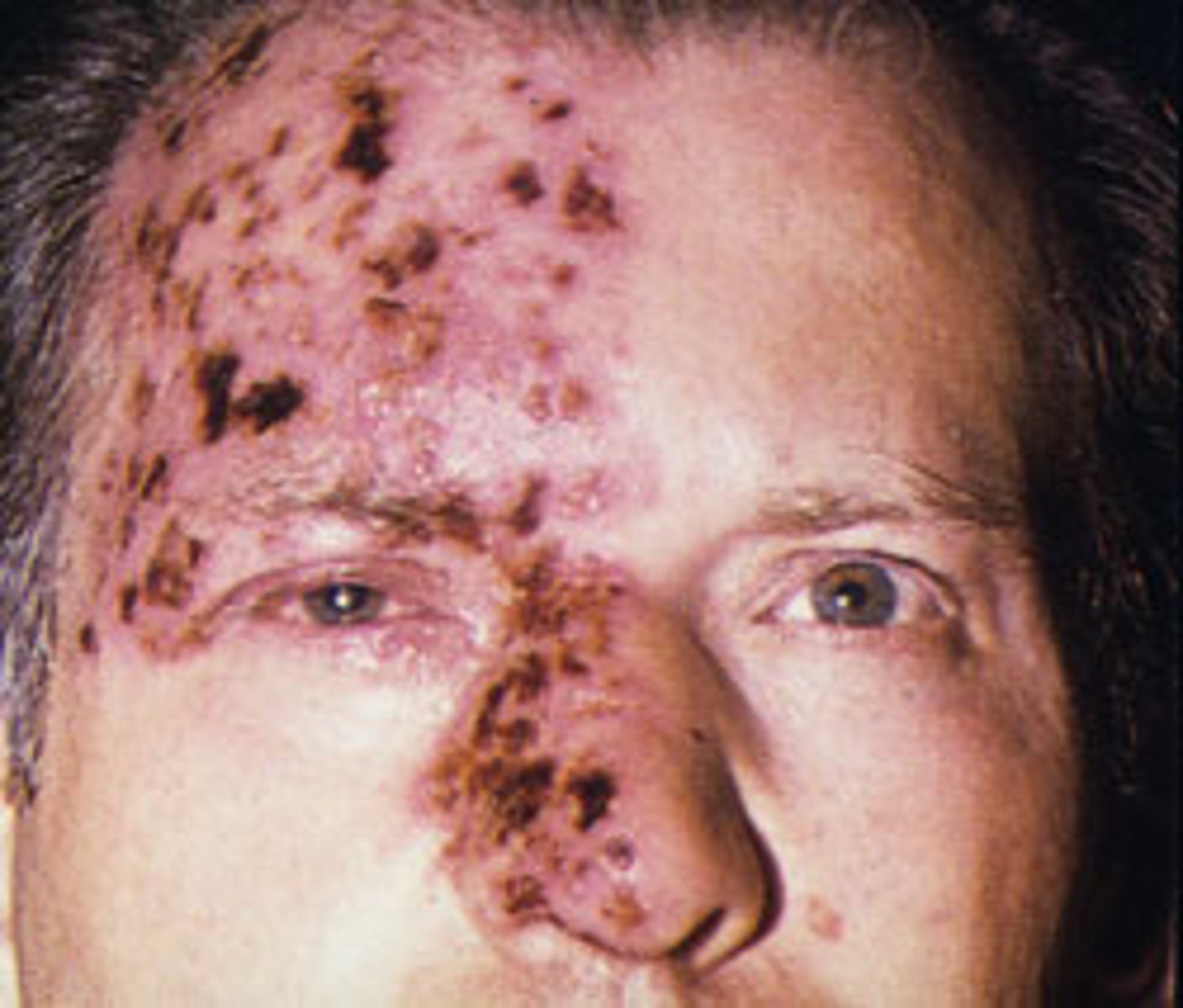
Zoster affecting V1 of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN5) that affect the ophthalmic division BUT further divided into: frontal, lacrimal, nasociliary nerve.
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmalicus