Hand, UE, Wounds & PAMs 💪🏻
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Active words for OT practice
-Pick answers that have words or verbs that are active and not passive
-For example, explain or guide are passive, whereas "develop strategies" is more active
Refusal of service
-best answer: respect decision, and ask for a re-eval in a month
-other answers: respect and discharge from therapy
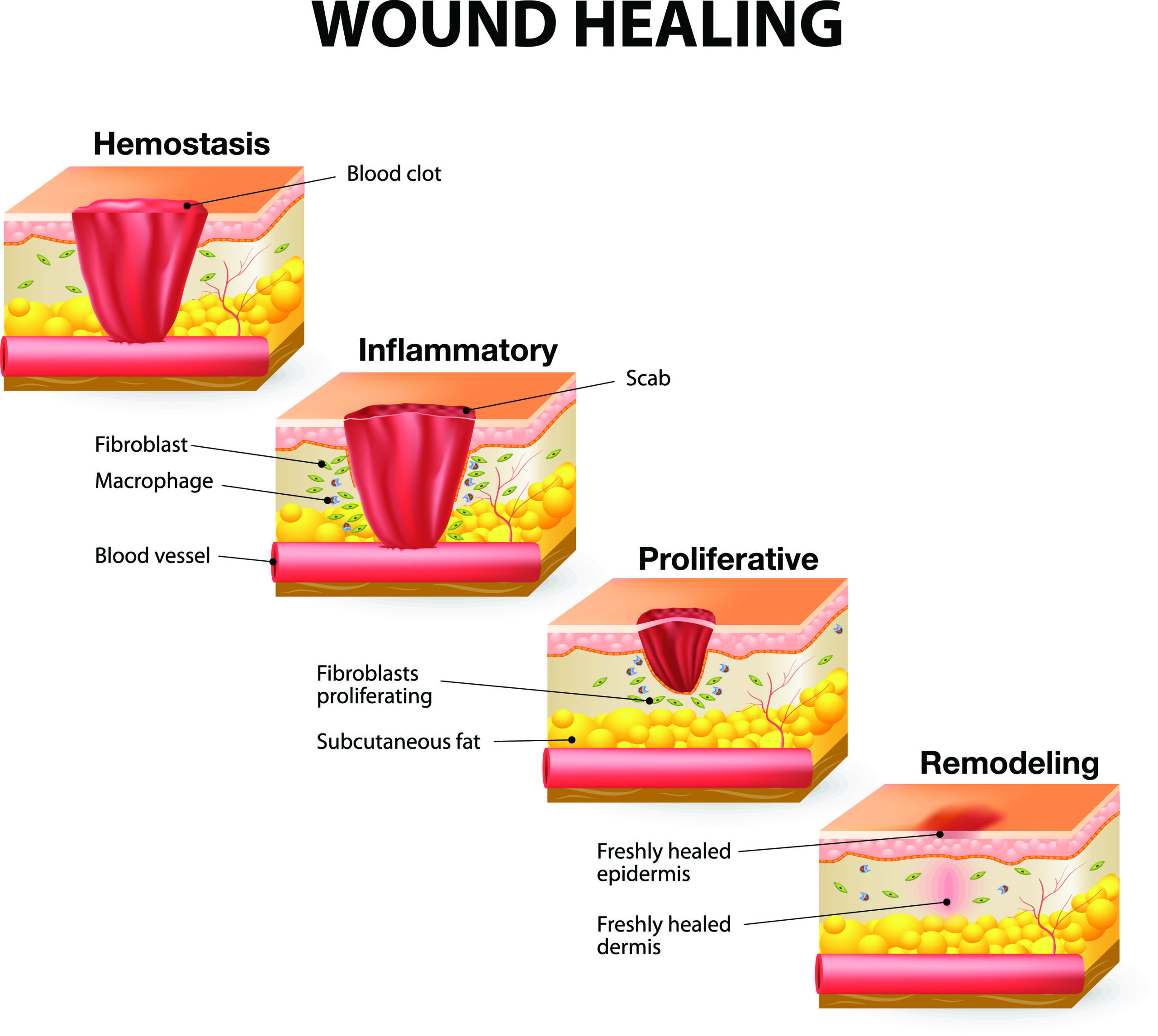
Wound Healing
Stages
1- Inflammatory Phase
Acute phase: 24/48 hours- 7 days
Subacute phase: 7- 14 days
Typical Signs: redness, swelling, heat, pain
Signs of Infection that Require Attention:
Pus, pain, purulent drainage, odor
Need antibiotics, proper debridement, cleaning, and dressing
Systemic signs: fever, leukocytosis
Things occurring during this phase
clotting
vasoconstriction
WBC migration
release of histamines/prostaglandins that cause vasodilation & increased tissue permeability
2- Proliferative Phase
aka fibroplastic/granulation/epitheliazation process
Things occurring during this phase:
lactic/ascorbic acid stimulate fibroblasts to synthesize collagen
cross linkage of collagen increases the tensile strength of repaired skin to 80%
Epithelialization resurfaces the wound
Tissue granulation forms new collagen and blood vessels
Myofibroblasts connect to the wound margins
Wound contraction takes 5 days up to 3 weeks
Linear wounds heal quickly
Rectangular wounds heal moderately quickly
Circular wounds heal the most slowly
3- Maturation/Remodeling Phase
Lasts from 2 weeks to 1-2 years
Things occurring during this phase:
Scar tissue first consists of randomly arranged collagen fibers, but as the scare matures, the collagen is broken down and remodeled
The scar becomes more elastic, smoother, and stronger
If collagen synthesis exceeds collagen lysis, hypertrophic & keloid scars can form
Pressure garments help collagen fibers realign in linear/lateral orientation
Dynamic splinting, serial casting, continuous passive motions, positional stretching, NMES, and silastic gel pads can help decrease hypertrophic scarring
Types
Primary healing: the use of sutures, plates, screws
Delayed Primary healing: wound is cleaned/debrided and observed ~5 days before suturing it closed
Secondary healing: when the wound cannot easily be closed (jagged edges), it is left to heal more naturally
Tertiary healing: need for the wound to be left open (fluid secretions)
Joint protection strategies
-commonly used for arthritis
-only do an activity if it can be easily stopped if your capacities are exceeded
-stand in front of containers
-pain as an indicator to stop/change
-ROM/strength should be maintained
Superficial thermal modalities: Cryotherapy- general uses, forms, and contraindications
Pain relief
Decreases edema, muscle spasms, inflammation, and metabolic activity of tissues
Reduces nerve conduction velocity
Ice massage (after 20 minutes of ice, the analgesic effect should last 5-10 minutes or when the redness goes away)
Cold packs
Cold water immersion baths
Cool whirlpools
Cold compression units
Vapocoolant sprays
Contraindications
impaired circulation (Raynaud’s)
Peripheral vascular disease
Hypersensitivity to cold
Impaired sensation
Open wounds
Infections
Superficial thermal modalities: heat- general uses, forms, and contraindications
-Increases blood flow, rate of cell metabolism, inflammation, muscle contraction velocity, capillary permeability, oxygen consumption
-Decreases pain, muscle, spasms fluid viscosity
-hot packs (good for increasing blood flow and healing)
-Paraffin (good for decreasing stiffness and pain *arthritis)
-Warm Whirlpool (good for wound care to debride and heal)
-Fluidotherapy (good for decreasing pain/sensitivity and increasing mobility for some small body parts)
-Infrared (good for decreasing pain and tightness)
-Contrast baths
Common Contraindications:
-Impaired cognition/ sensation
-Vascular supply issue/blood hemorrhage/blood clot
-Open wounds
-Acute inflammatory conditions
-Cancer
-Edema
-Infection
-Cardiac problems
Deep thermal modalities- general uses and forms
-good for acute injuries, contractures, scarring, pain, muscle spasms
-gives more oxygen to area than superficial thermal modalities
-Ultrasound- high frequency waves that helps to heal tissues (goes as deep as 5 cm)
increase tissue extensibility/blood flow/protein synthesis/bone healing; decrease pain/joint stiffness/muscle spasm/chronic inflammation
-Phonophoresis- ultrasound with topical med
Decreases inflammation and speeds up tissue repair
⚡️talk to your baby on the phone using ultrasound
-Diathermy- high frequency electromagnetic energy that decreases swelling and increases ROM
Take Caution With
inflammation
Fractures
Breast implants
Clients with cognitive/language/sensory impairments
Contraindications
cancer
Pregnancy
Pacemaker
Bleeding
Infection
Do NOT use over eyes, blood clots, or kid’s bone growth plates
Electrotherapeutic modalities- general uses, forms, and contraindications
-increases muscles strength/ re-education
-decreases pain/swelling
-TENS (good for decreasing pain and easy to use at home)
-NMES (good to lengthen and strengthen muscles)
also promotes wound healing and decreases edema/spasm/spasticity
May be used as an orthotic substitute
-HVGS- High Voltage Galvanic Stimulation (good to decrease pain and edema)
-Iontophoresis (decreases inflammation and controls pain)
uses ionized meds to transfer to tissues within electric field
Contraindications:
-Pacemaker/cardiac conditions/epilepsy/cancer/infection
-Metal implants/stimulators
-Do not use over carotid sinus, pregnant uterus, or eyes
-Sensory deficits
Iontophoresis
-typically used for inflammatory conditions (i.e. carpal tunnel)
-used to deliver anti-inflammatory meds (dexamethasone)
-after doing it, make sure to lotion the area, NOT alcohol wipes
Low-Level Laser & Light Therapy- general uses, forms, and contraindications
—Decrease pain, edema, inflammation, scar tissue
— Increase wound healing
light-emitting diodes
Super luminescent diodes
Low-level laser diodes
*Wear protective eyewear when using laser
*Do NOT use over vagus nerve, carotid sinus, pregnant uterus, eyes, or endocrine glands
Contraindications:
Client with cancer or infection
Orthosis purpose
-prevent/correct deformity
-control spasticity by aligning joints
-correct biomechanical malalignment
-position hand in functional posture
-compensate for weakness
-immobilize joint for healing
-immobilize the joints
-remodeled by OT over time
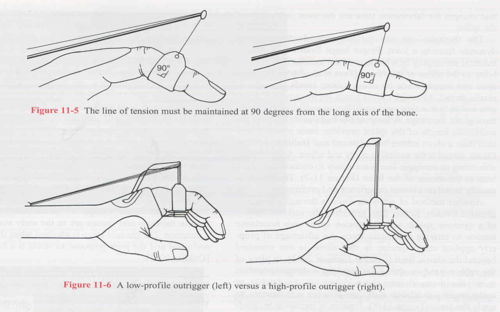
Dynamic splints
-Good for long term attempts to fix contractures, increase ROM
-90 degree line of pull for even distribution of pressure
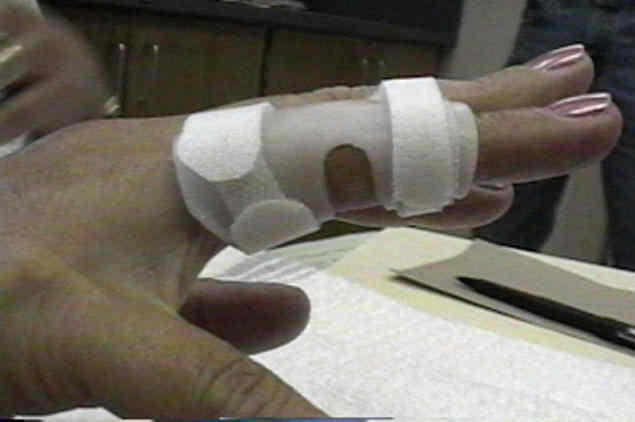
Circumferential PIP joint orthosis
-used to keep the finger in extension, typically for boutonniere deformity
-should be worn continuously for 6 weeks for healing
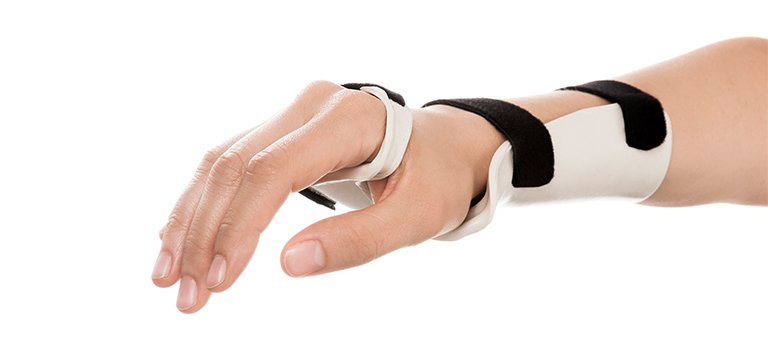
Cock up splint
-provided stability and extension of the wrist
radial nerve palsy, wrist extensor tendonitis, colles' fracture
DIP joint orthosis
-used to keep finger in extension, typical for mallet finger (slight hyperextension)
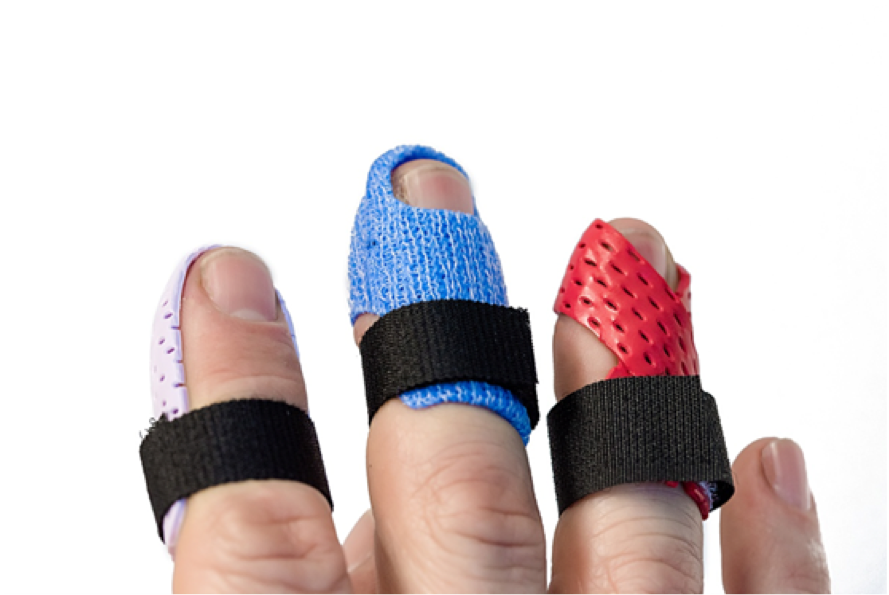
Dorsal blocking splint
-used for flexor tendon repairs (duran protocols)
-allows for movement in flexion
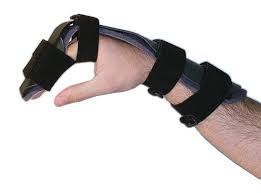
Flail arm orthosis
-Typically for brachial plexus injuries with total arm involvement, keeps the arm from flailing around
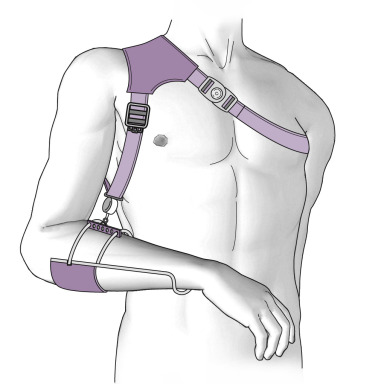
Milwaukee brace/orthosis
-Worn for scoliosis, stabilizes the spine from the neck to the pelvis. The brace will often be worn at night several years after growth is complete to maintain the spinal correction.
-used for kids with kyphosis as well
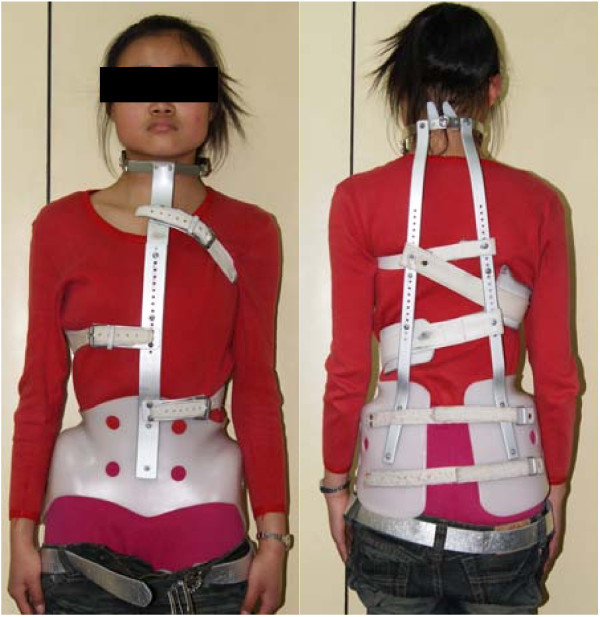
Resting hand (pan) splint
-For ppl who need to have their wrist, digits, thumb supported in a fx position for prolonged periods
-used for prevention of deformities (CVA, RA)
-can reduce morning stiffness for RA
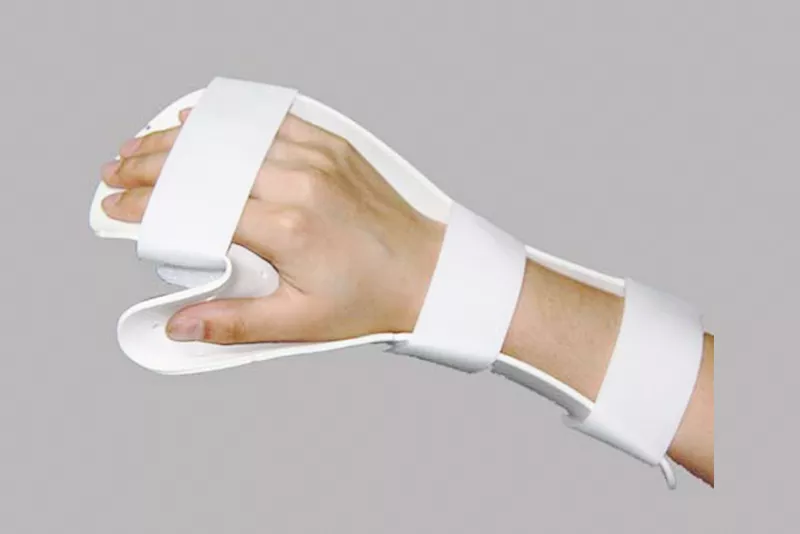
Thumb loop splint
-puts the thumb in an optimal position for opposition
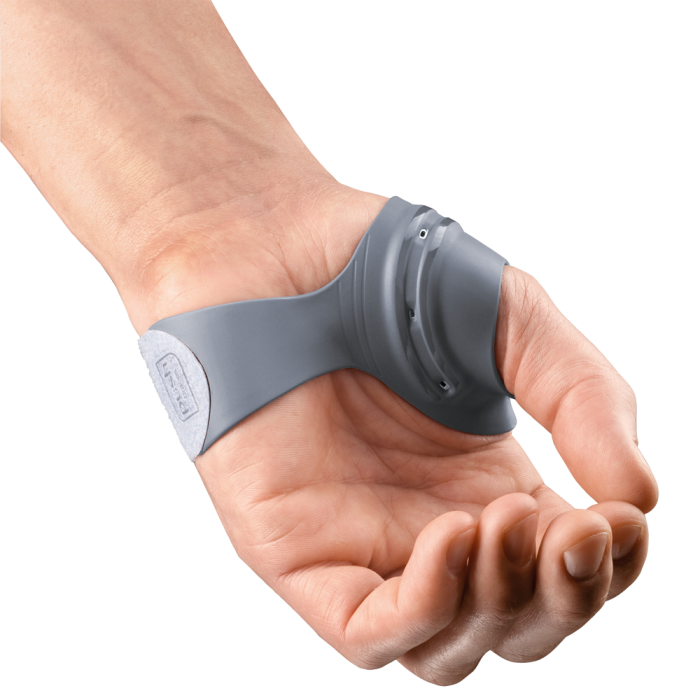

Thumb Spica Splint
-used to support the CMC joint instability
-used for de Quervains, CMC joint weakness/instability, thumb sprains
-used for the ulnar collateral ligament the thumb (Skiier’s thumb)
-length depends on what is injured, longer if the muscles extend to the forearm
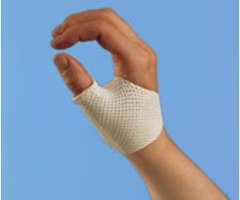
Ulnar deviation splint
-keeps the MCPs from doing an ulnar drift
-common for RA

Intrinsic hand muscles innervated by median nerve
-abductor pollis brevis
-opponens pollicis
-flexor pollicis brevis
-lumbricals (radial side)
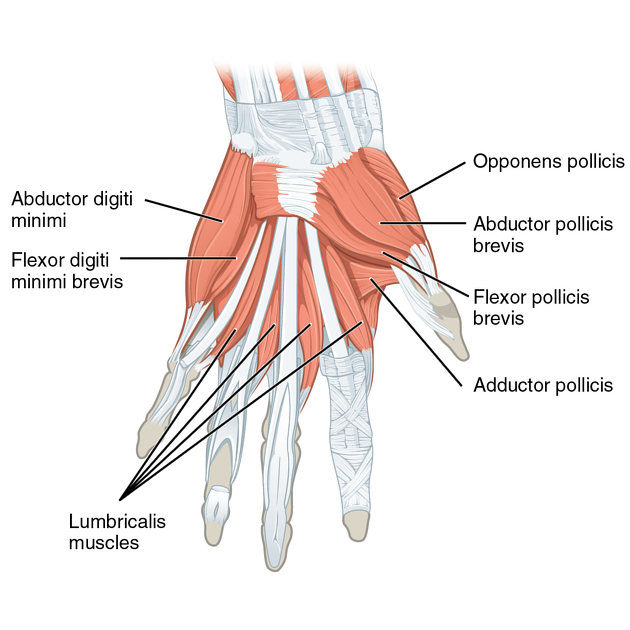
Intrinsic hand muscles innervated by ulnar nerve
-abductor digiti minimi
-opponens digiti minimi
-flexor digiti minimi
-lumbricals (ulnar side, MCP flex)
-palmar interossei (adduction)
-dorsal interossei (abduction)
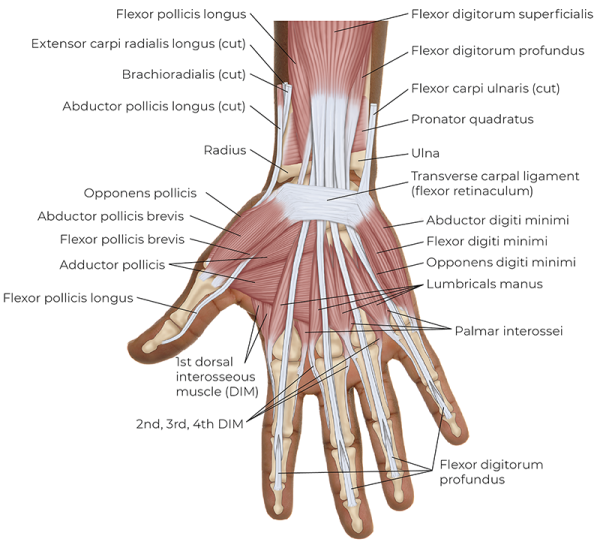
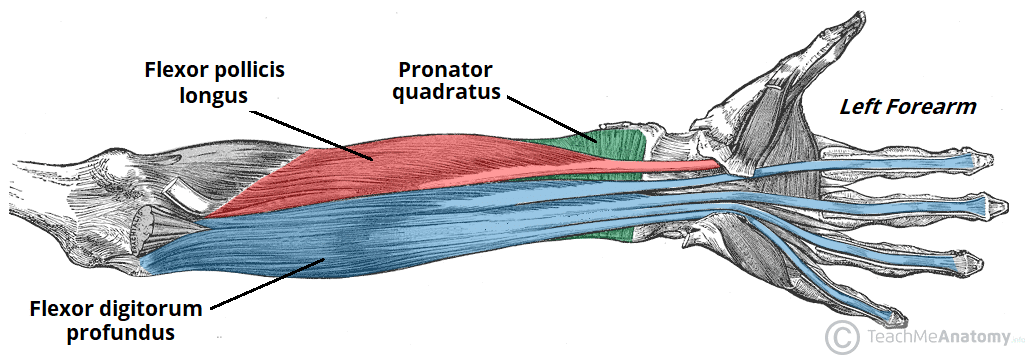
Extrinsic hand muscles innervated by median nerve
-flexor digitorum superficialis
-flexor digitorum profundus
-flexor pollicis longus
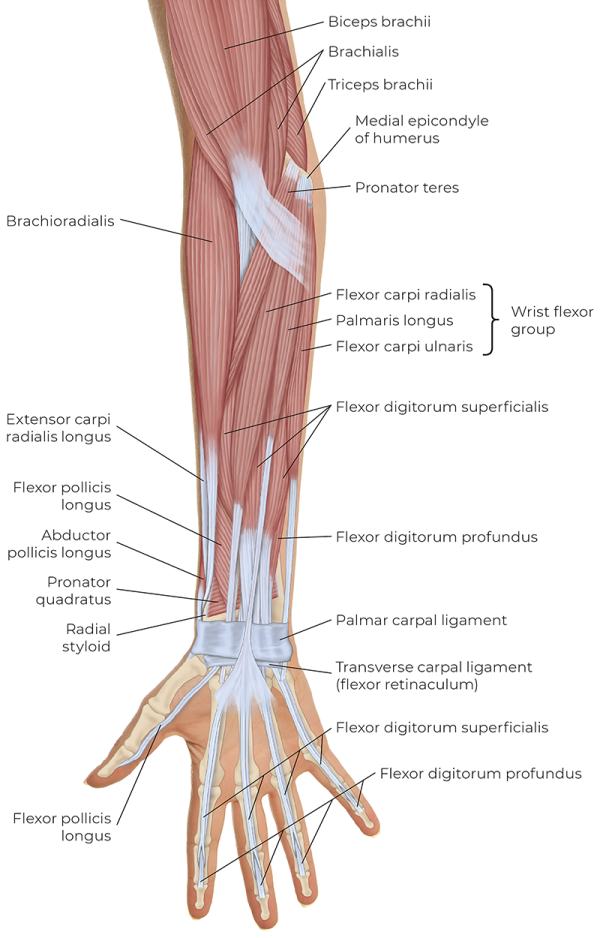
Extrinsic hand muscles innervated by ulnar nerve
-flexor digitorum profundus
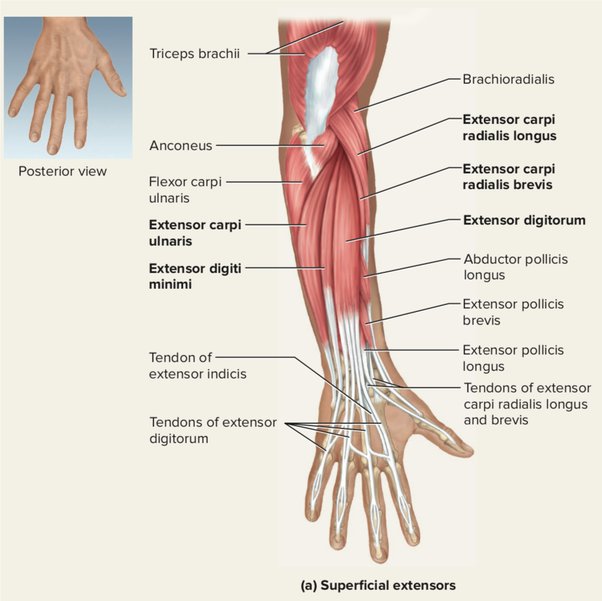
Extrinsic hand muscles innervated by radial nerve
-extensor digitorum
-extensor digiti minimi
-extensor indicis
-extensor pollicis longus
-extensor pollicis brevis
-abductor pollicus longus
Wrist muscles innervated by median nerve
-flexor carpi radialis
-palmaris longus
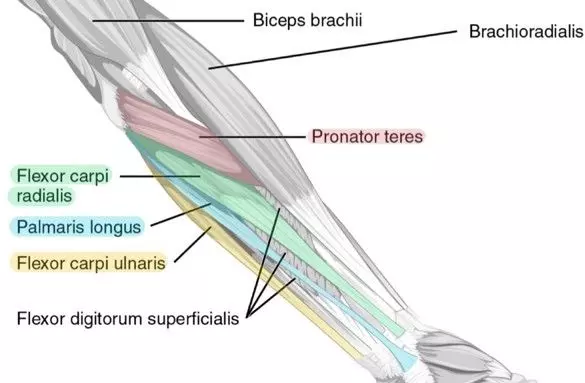
Wrist muscles innervated by ulnar nerve
-flexor carpi ulnaris
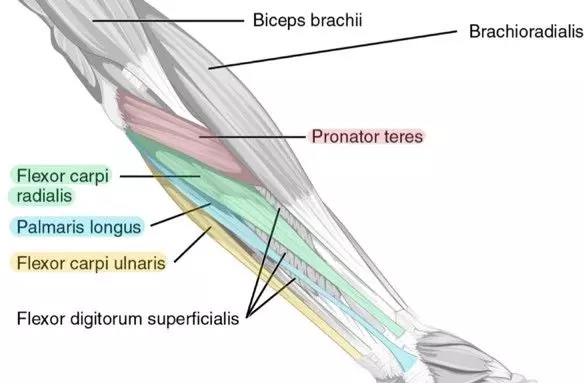
Wrist muscles innervated by radial nerve
-extensor carpi radialis brevis
-extensor carpi radialis longus
-extensor carpi ulnaris
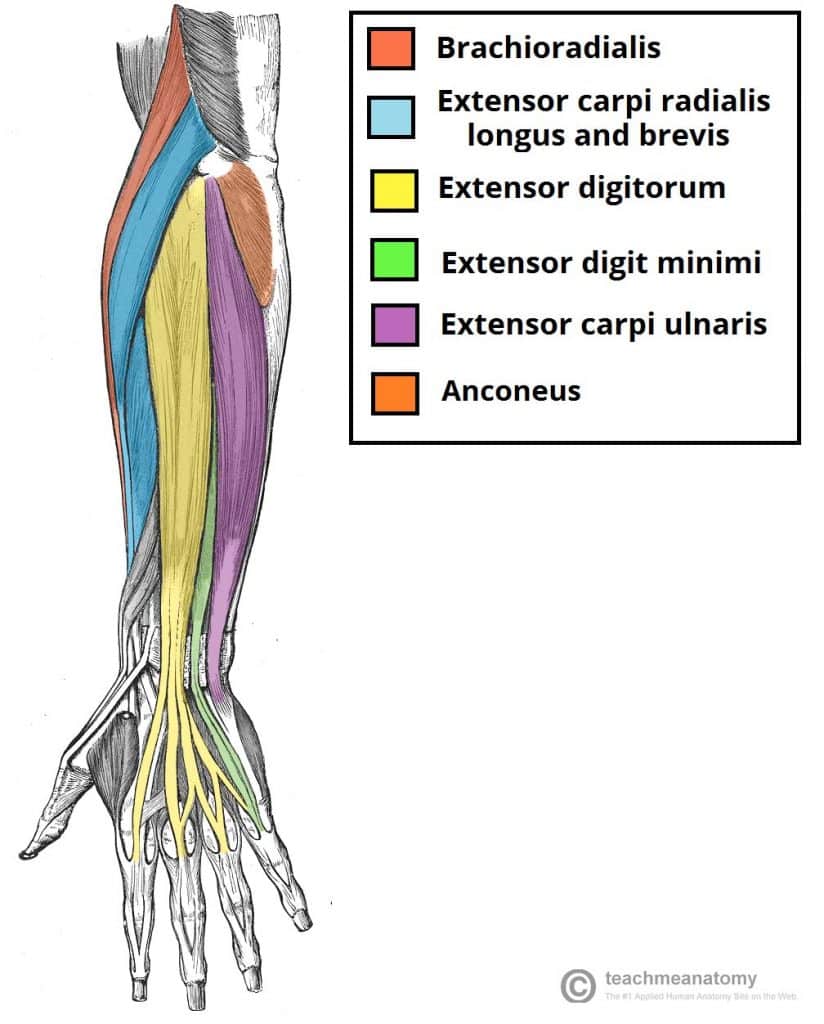
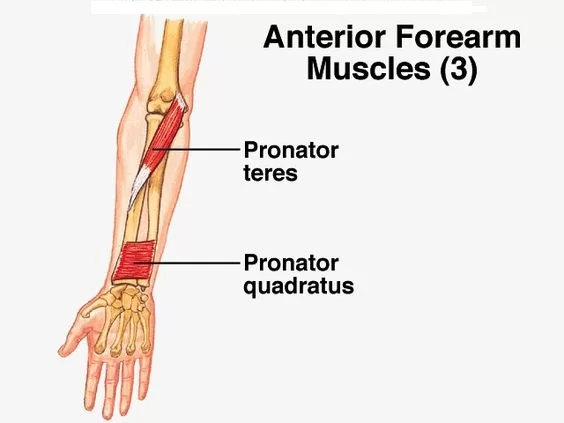
Forearm muscles innervated by median nerve
-pronator teres
-pronator quadratus
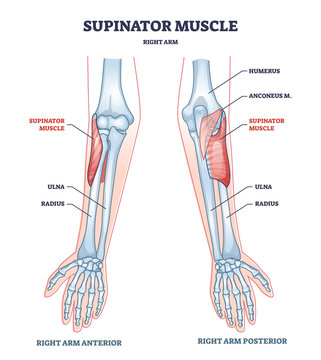
Forearm muscles innervated by radial nerve
-supinator
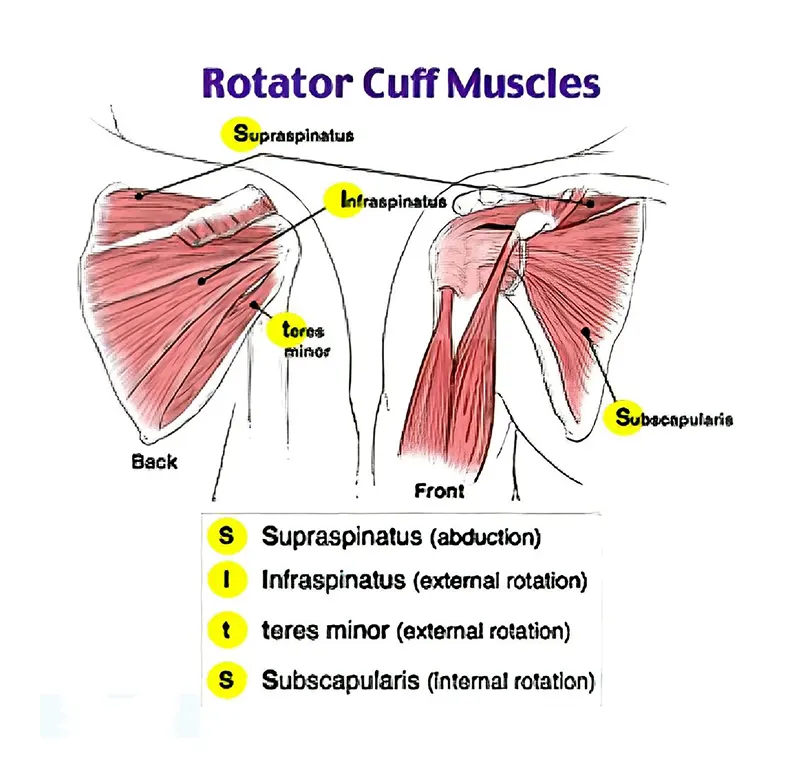
Rotator Cuff Muscles & Innervations
~SITS
-supraspinatus (suprascapular nerve)
-infraspinatus (suprascapular nerve)
-teres minor (axillary nerve)
-subscapularis (subscapular nerve)
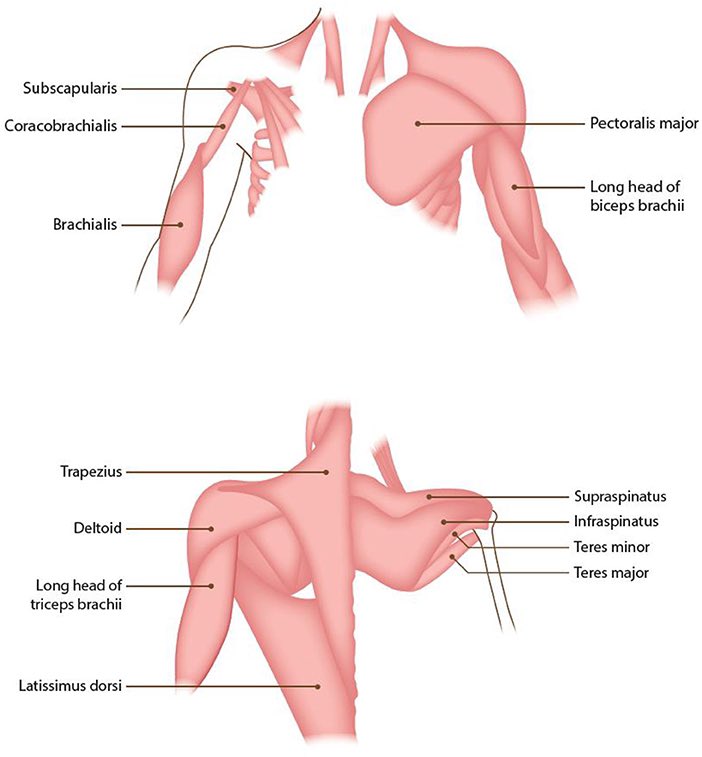
Shoulder Muscles & their Innervations
-anterior, middle, posterior delts (axillary)
-coracobrachialis (musculocutaneous)
-pectoralis major (lat pect nerve)
-latissimus dorsi (thoracodorsal)
-teres major (subscapular)
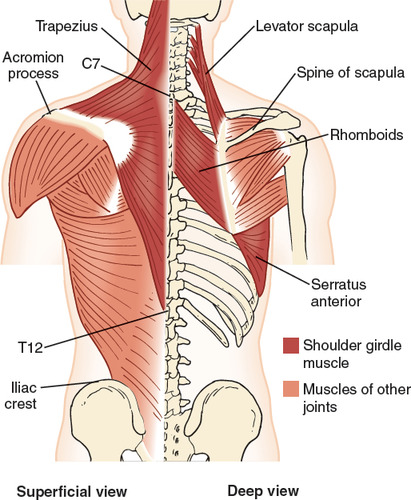
Scapular Muscles & Innervations
-trapezius (CN 11)
-serratus anterior (long thoracic nerve)
-levator scapulae (c3-4)
-rhomboids (dorsal scapular)
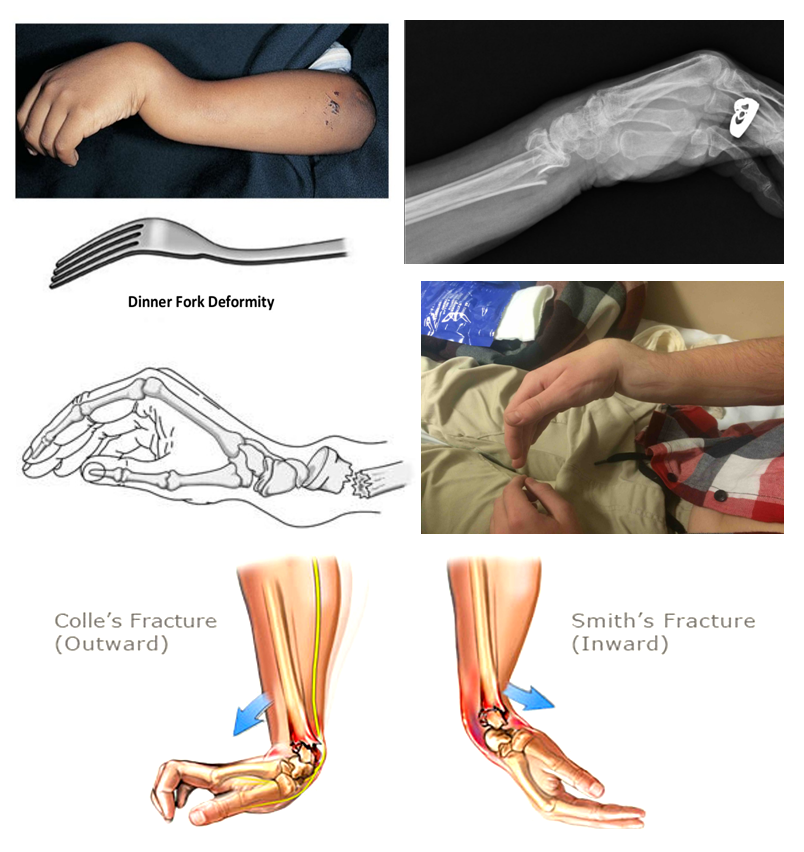
UE Fractures Medical Treatment (Closed vs. Open)
-closed reduction: casting, splints
-open reduction aka primary healing: nails, screws, plates
Types of Distal Radius Fractures
-Colles fx (distal radial head dorsal displacement)
-Smiths fx (distal radial head volar displacement)
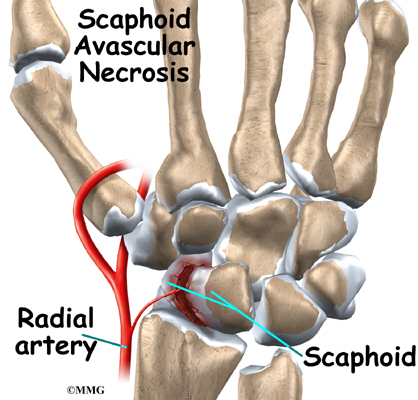
Scaphoid fx
-Broken scaphoid carpal bone
-may become necrotic
Phalanx fx
-commonly lose PIP ROM
Proximal Radial Head Fx
-aka elbow fx
-most common complication is elbow stiffness/limited ROM
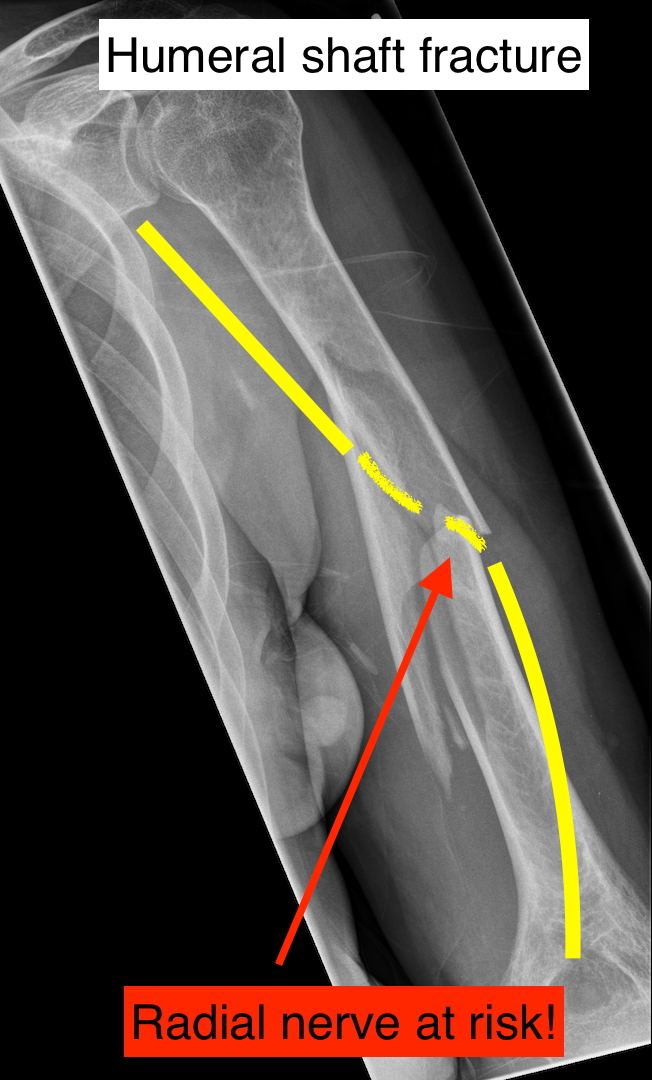
Humerus fx
-may cause injury to radial nerve
-weird exception- humerus fractures often begin with PROM/AAROM while this should be avoided initially with other fractures
Fractures OT Intervention
-Edema management
-Pain management
-assess PROM/MMT with physician order
Immobilization phase (AROM above and below stabilized area, retrograde massage for edema, one handed techniques if it breaks immob)
Mobilization phase (edema manage, splint for protection in some cases, AROM, PROM/strengthening when ordered)
Children & Fractures
-Children younger than 12 usually are given immobilization protocols as they cannot follow the rules readily
-for fingers, taping the injured finger to an adjacent finger is useful
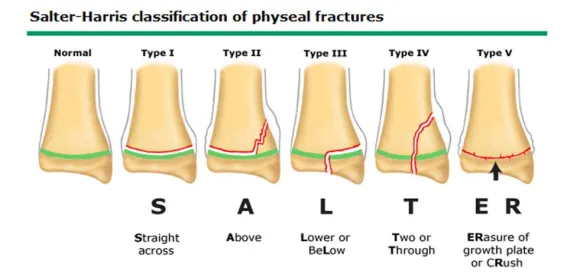
Salter-Harris Fracture
Occur in children at growth plate of long bones
Type 1: fx at growth plate
Type 2: above growth plate
Type 3: at growth plate and it goes down (ORIF typical, and splint after with ROM)
Type 4: above, at, and below growth plate
Type 5: compression of growth plate
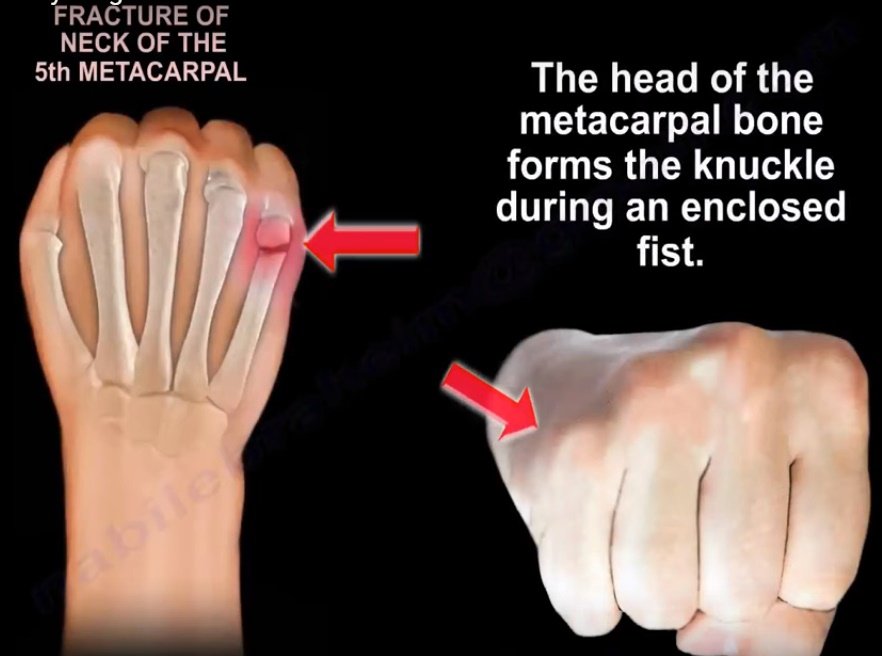
Boxer‘s Fracture
-4/5th digit fx, typically to metacarpophalangeal neck
-ulnar gutter orthosis
Bennett Fracture
-intra articular fx of 1st metacarpal
⚡️Ben been feeling bad because his thumb metacarpal bone is broken 👎
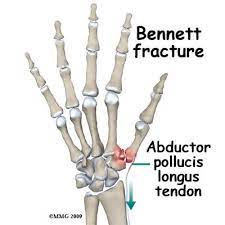
General tx for CMC Thumb Injuries
-In the acute phase of healing or after surgery (arthroplasty), immobilization with active ROM of IP joint
-thumb spica
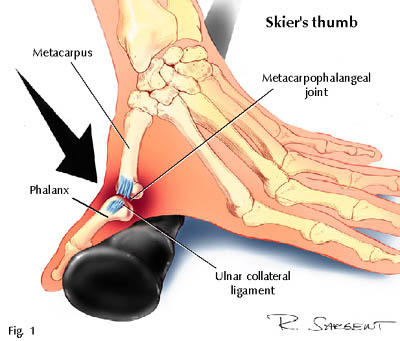
Skier's Thumb (gamekeeper's thumb)
-rupture of ulnar collateral ligament of MCP of thumb
⚡️Go skiing in Utah (skier’s=UCL tear)
-OT int: thumb splint (4-6wk), start with gentle AROM at 2-4 wks, then AAROM/lateral pinch strengthening with doc approval (6-12 wks post-op)
Cumulative Trauma Disorder (CTD)
AKA overuse syndrome AKA repetitive strain injury
-Diagnosable forms: tendinitis (lateral epicondylitis, de Quervain’s tenosynovitis) and nerve compression syndromes (carpal tunnel, cubital tunnel)
-Five grades from low to high severity
-Risk factors at work are high force, direct pressure, vibration, cold, prolonged static positions
-OT Intervention: first reduce inflammation (static splinting, ice, contrast baths, ionto/phonophoresis), then add slow stretching/myofascial release, progressive resistance exercises, body mechanics, IDing/reducing triggers at work, static splint during pain causing activities
De Quervain's
-Stenosing tenosynovitis of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis
-Positive finkelstein test
⚡️Moms feel like Frankenstein’s monster from changing so many diapers in the middle of the night and getting De Quervain’s
-Conservative tx
thumb spica
ice massage
AROM
-Postop tx
forearm thumb spica
0-2 weeks: AROM
2-6 weeks: strengthening

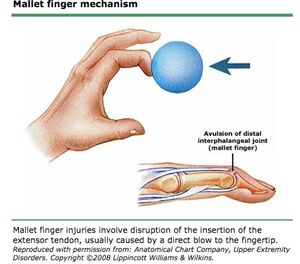
Mallet Finger
-inability to extend DIP into full extension d/t tendon injury
-requires splinting of DIP into slight hyperextension for tendon repair
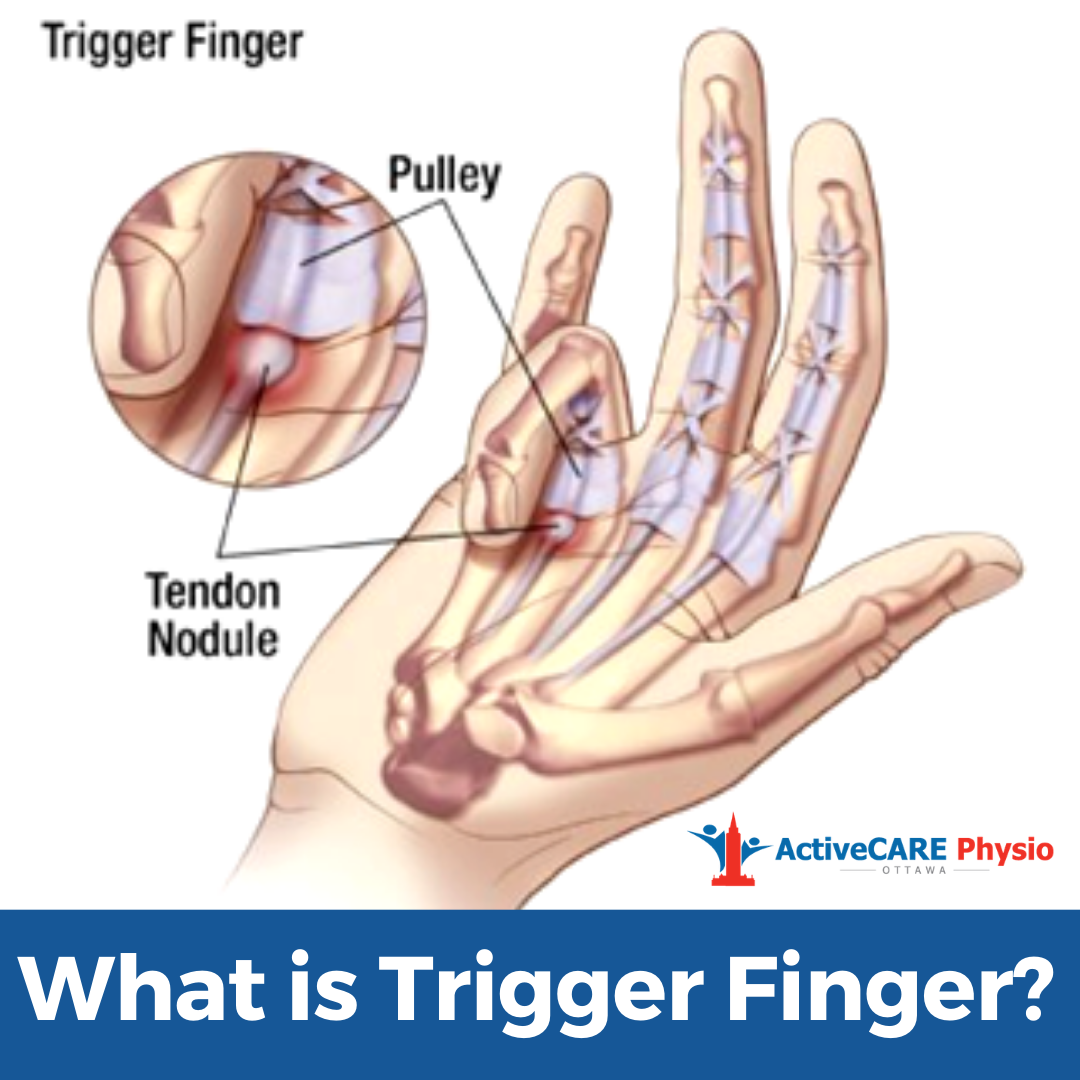
Trigger Finger
-Tenosynovitis of the finger flexors (A1 pulley)
Conservative tx
trigger finger MCP ext splint, IP joints free
To rest the tendon/prevent snapping put on splint then gently bend & straighten PIP joints 20x every 2 hours
scar management
tendon glides
Edema control
-tendon glide consists of locked (fist), hooked fist, then extended added fingers
Boutonnière deformity
-DIP is hyperextended, PIP is flexed
-circumferential PIP joint orthosis should be worn continuously for 6 weeks, prevents flexion deformity

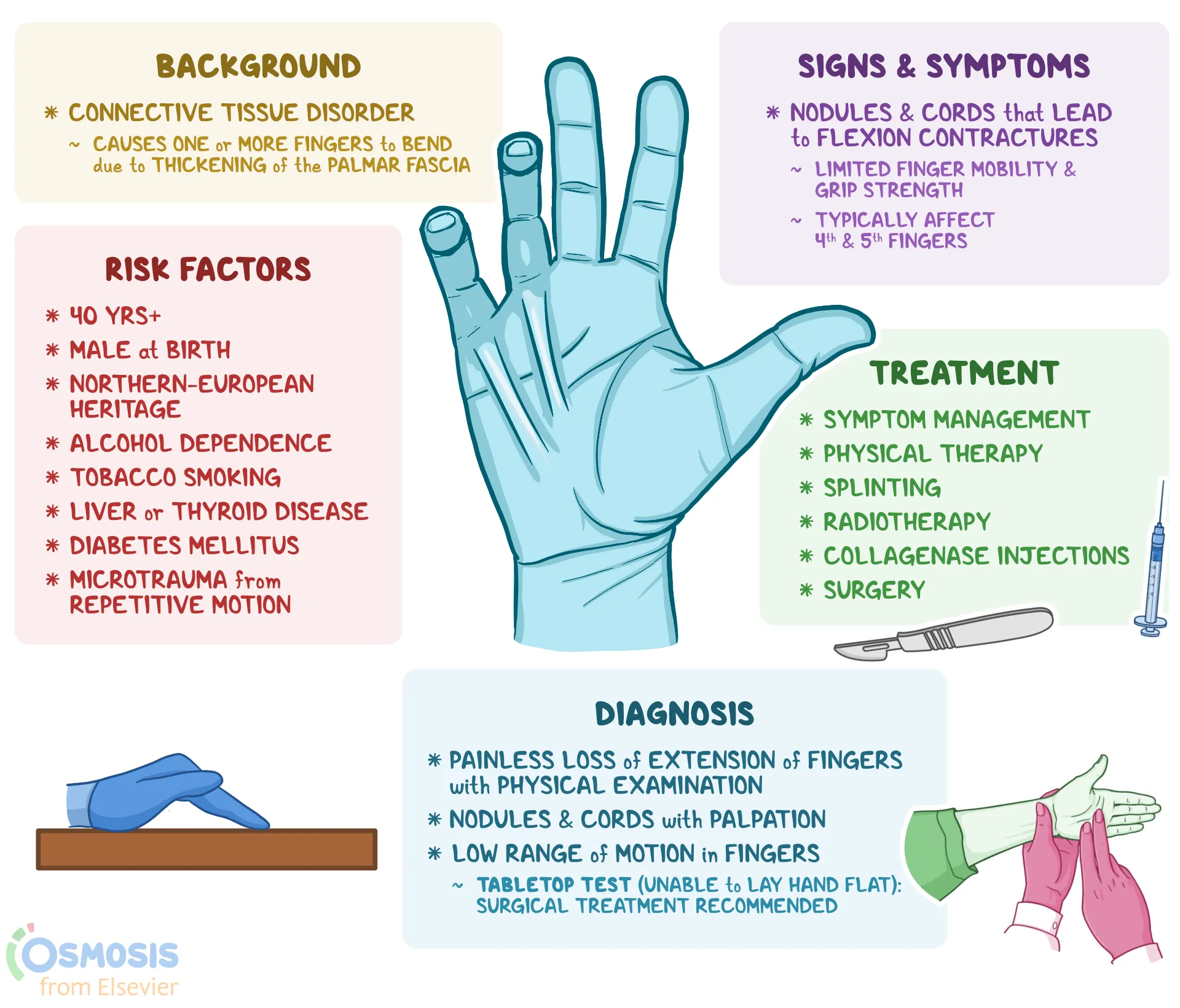
Dupuytren's Disease
-Disease of the fascia of palm/digits
-flexion deformity involving the digits
-conservative OT tx is NOT successful
-OT post surgery int:
hand-based extension splint is ideal (not always possible if contracture/damage is too extensive so collab with surgeon in that case)
AROM/PROM (remove splint for ROM and bathing)
progress to strengthening when wound heals ~4 weeks
scar massage
Occupations that require gripping and release
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
-Vasomotor dysfunction resulting in abnormal reflex (severe pain, edema, discoloration, abnormal sweating)
-FKA reflex sympathetic dystrophy
-Type I- spontaneous/unknown; Type II- develops after known nerve injury
-OT int:
modalities to dec pain (TENs, hot packs, static then dynamic splinting)
edema management (contrast baths, compression garments)
gentle AROM
stress loading (scrubbing floor, carrying weighted bag)
weight bearing
fluidotherapy for desensitization
joint protection
tendon gliding
mirror therapy (cortical audio-tactile interaction)
-caution: PROM, passive stretching, joint mob
Lateral and medial epicondylitis
-Overuse of wrist extensors (lat) 🎾
-Overuse of wrist flexors (med) 🏌♂️
Conservative tx (elbow strap, wrist splint, ice, stretching, work mod, iso/eccentric strengthening with pain dec, progress to resistance exercises for prevention)
-splints should be worn during activities that cause pain
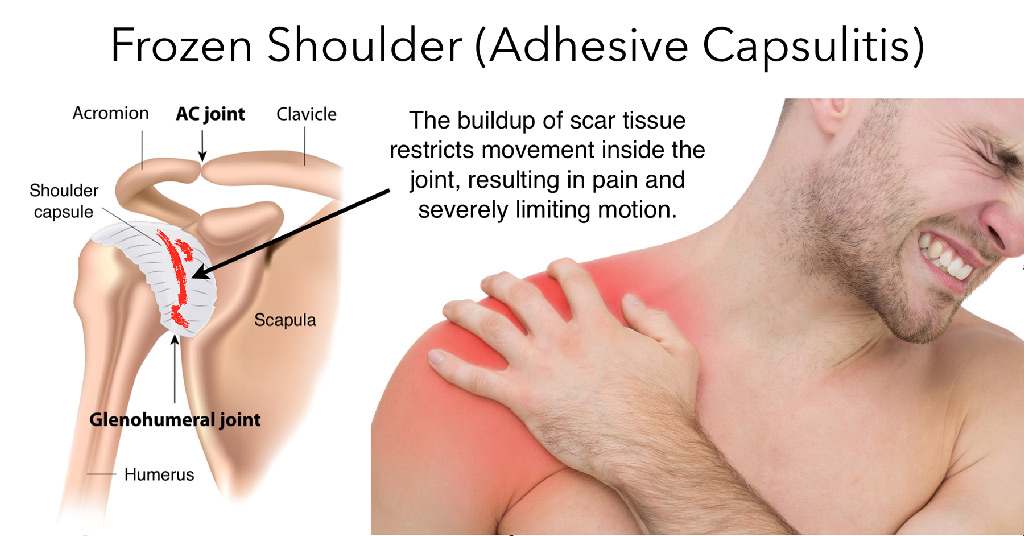
Adhesive Capsulitis
AKA Frozen Shoulder
- Inflammation and immobility of the glenohumeral ligaments and joint capsule
- Causes restrictions in passive range of Motion
Freezing shoulder pain at end ranges
Address pain with ice packs/e-stim, positioning
Gentle pain free ROM i.e. reaching to small of back/ behind head
HEP with gentle exercises i.e. table glides, functional movements
Frozen- less pain but loss of motion with capsular patterns (difficulty with external rotation, then abduction, then internal rotation, and then flexion)
Start with hot packs, end with ice
AROM + gentle pain free stretching
Continue HEP i.e. table glides, functional tasks, cane exercises, wall walking
Thawing- pain subsides and ROM gradually returns
More stretching
Focus on restoring ROM and function
Post-op OT intervention: PROM immediately after surgery, PAMs for pain
Rotator cuff tendonitis
-from overuse
-impingement can occur at acromion, coracoacrominal ligament, coracoid process
-caused by repetitive use, weak rotator cuff, weak scapular muscles, ligament/capsule tightness
Conservative tx (avoid above shoulder until pain goes away, avoid sleeping with arm overhead or adducted with internal rotation, pain free ROM, strengthen below shoulder level)
Post op txPROM (this is different than most post surgical recs) 0-6wk, AAROM/AROM 6-8wk based on MD, sling/abduction orthosis that can be removed for exercises, ice then heat modalities, isometric then isotonic strengthening 8-10wk)
Flexor Tendon Zones
Flexor Tendon Repairs - (mobilization, goals, splint, major timeframe healing concern)
-Early mob: prevent adhesions, inc wound/tendon healing
-Goals: improve tendon excursion, inc strength/ROM
-Splint: dorsal blocking splints
-repairs are weakest 10-12 days post op d/t fibroplasia phase
Kleinert protocol:
For flexor tendon repair
0-4wk (dorsal block, wrist is 20-30flex, MCP 50-60flex, IP extended. passive flex, active ext) achieved with dynamic splint with elastic bands
4-7wk: adjust wrist to neutral, flexor tendon glide exercises
6-8wk: AROM, tendon gliding, d/c splint
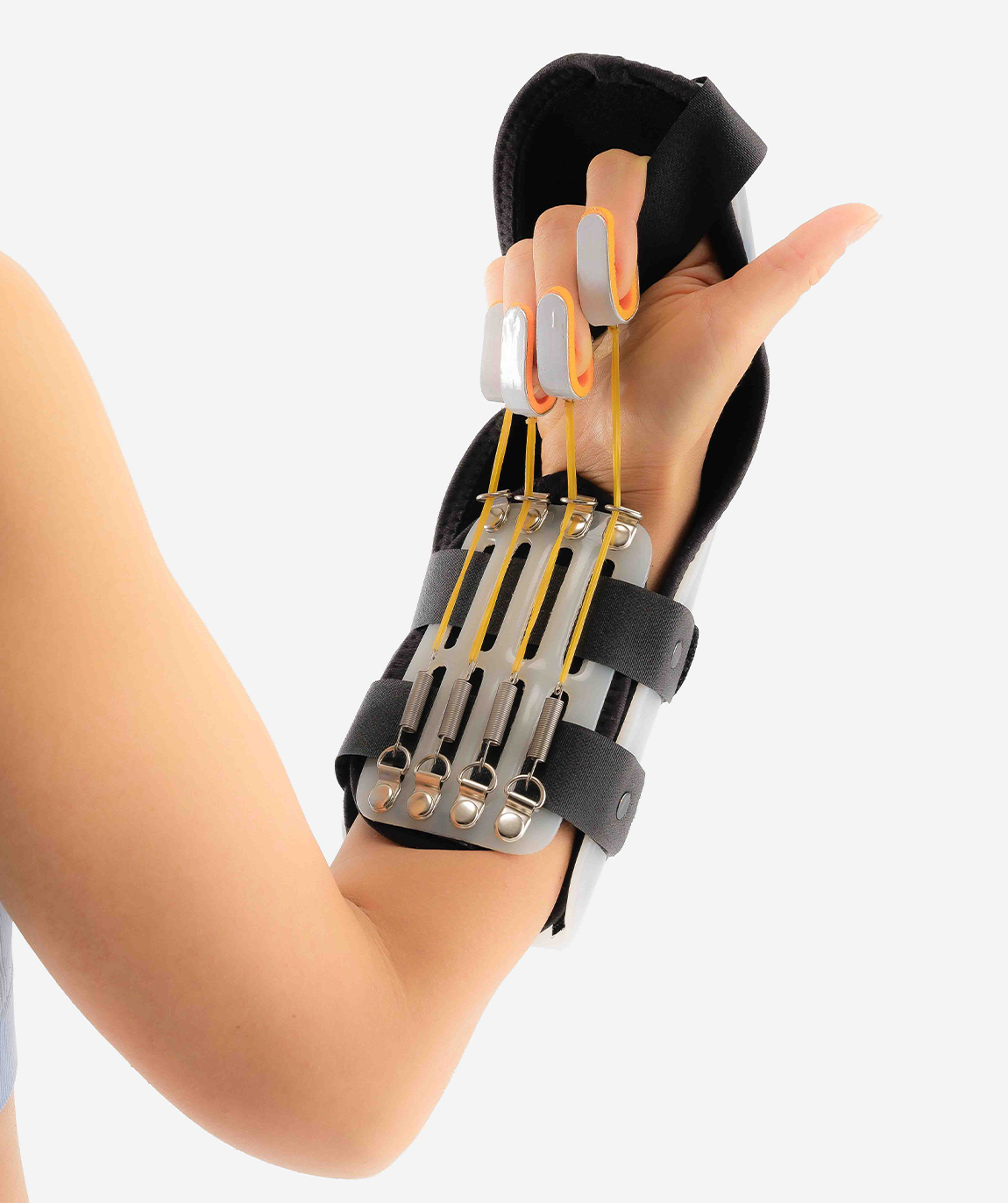

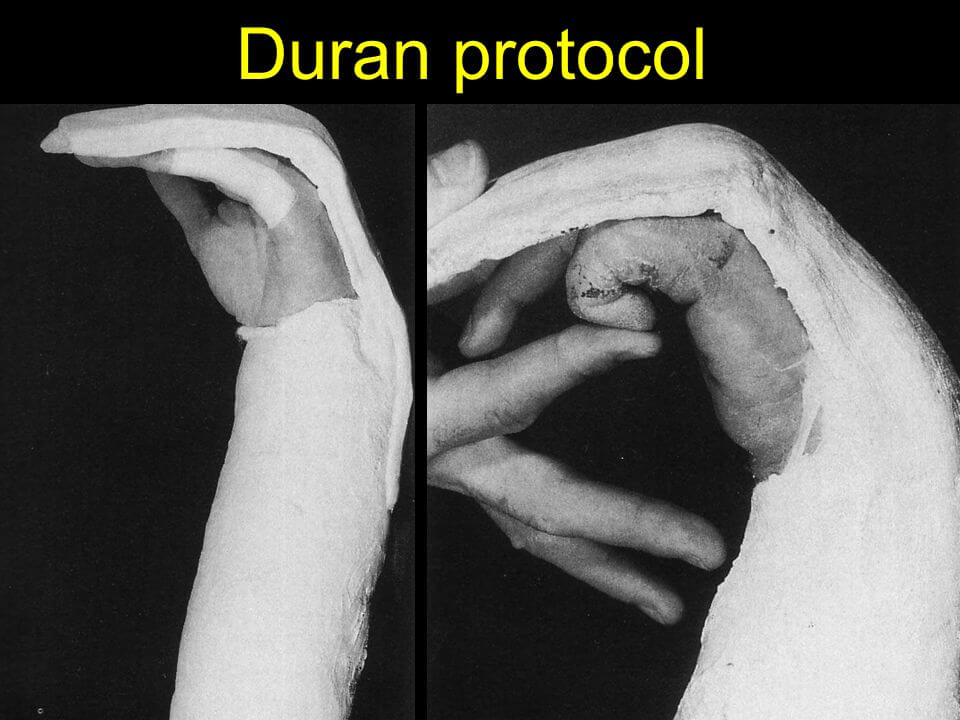
Duran protocol:
For flexor tendon repair
~”Do it yourself” protocol- where client uses static splint and provides own passive flexion (self-range of motion for flexion)
0-4wk (dorsal block splint, passive flex of PIP/DIP. ten reps per hour
4-6wk: active flex/ext
6-8wk:tendon gliding, scar management
Extensor Tendon Zones
⚡️extensors are more extensive
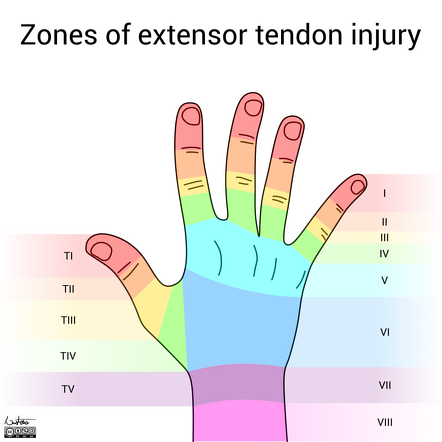
Tendon repairs- extensors
Zone 1 and 2: mallet finger deformity (0-6wk DIP ext splint)
Zone 3 and 4: boutonniere deformity (0-4wk PIP ext splint, DIP free. AROM of DIP in split. 4-6wk AROM of DIP, flexion of digits)
Zone 5,6,7: (0-2wk volar wrist splint, wrist 20ext, MCP 0 flex, IP full ext. 2-3wk shorten splint to allow flex/ext of IP. 4wk remove splint MCP active flex/ext. 5wk AROM wrist, wear splint between sessions)
*zone 6 is proximal to juncturae tendinum which connects extensors of digits 2-4- if you repair one of these tendons, you should immobilize all fingers to avoid putting extra stress on the healing tendon
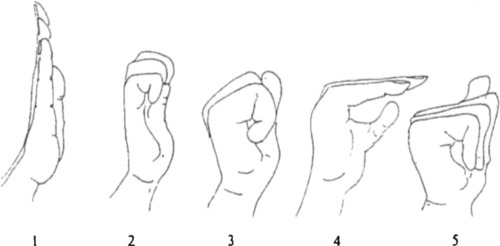
Tendon Gliding Exercises
-straight
-hook
-fist
-tabletop
-straight fist
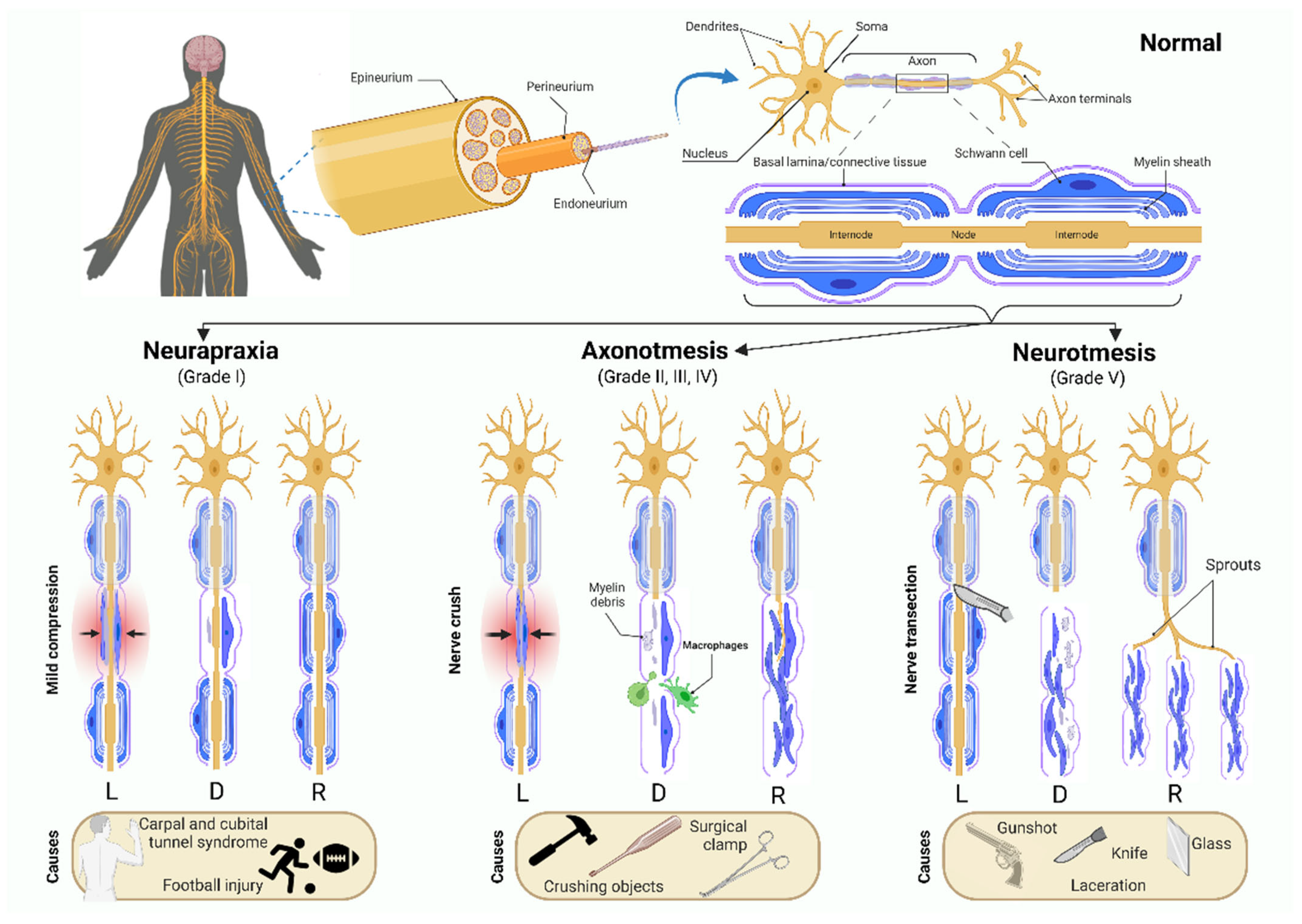
Axonotmesis
-a more severe grade of injury to a peripheral nerve. is reversible injury to damaged fibers.
-nerve can regenerate distal to the site of lesion by one millimeter per day.
-loss of sensation means the pt will likely not be aware of injury, so important to address with visual compensation
Nerve regeneration steps for sensation acquirement
one point moving
one point discrimination
two point moving
two point discrimination
Graded tactile kinesthetic program
-rubbing various textures over area
-movement and sensation training
-movement of objects with eyes open and closed
-location of objects in container with particles
Brachial Plexus Injuries Shoulder Movement OT Consideration
-movement past 90 of shoulder abduction may put stress on the plexus
Carpal tunnel syndrome
-median nerve compression d/t repetition, posture, vibration, pregnancy
-can be exacerbated with both wrist flexion (common, typing) and wrist extension (reverse phalen test)
-numbness of thumb, index, middle
-positive tinel's sign, pos phalen's sign
Conservative tx (splint with wrist neutral at night, median nerve glides, avoid extremes of wrist flexion)
Postop tx (edema control, AROM, nerve glides, strengthening of thenar muscles 6wk)
-complications include pillar pain, pain on both sides of operation
Median Nerve Laceration
-See sensory loss for median distribution
-Motor loss
Lose thumb opposition, flexion, abduction
Lose lumbrical movement for index and middle fingers
High lesions (at/above elbow) can also lose flexion of tip of index/middle fingers/thumb, ability to flex radial aspect of wrist
-Dorsal protection splint with wrist at 30 flexion (+ extend to elbow at 90 flexion for high lesions) to help median nerve heal after repair
begin ROM with wrist flexed while wearing orthosis at 5-7 days s/p sx
-AROM out of orthosis once cleared (~4wks)
-Later orthoses may need c bar to prevent thumb adduction contracture; opponens orthosis can improve function
-Sensory reeducation
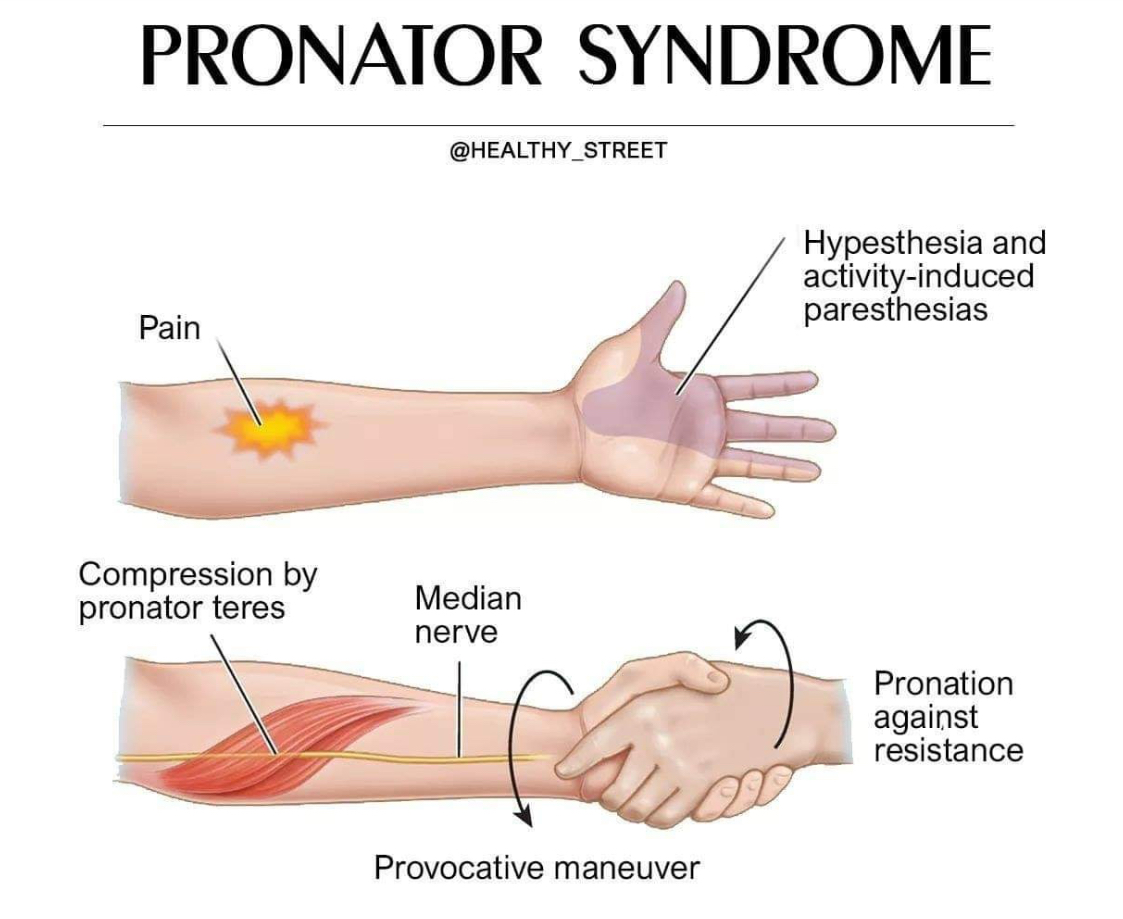
Pronator Teres Syndrome
-Median nerve compression between two heads of pronator teres
-from repetitive pron/supination
-positive tinel's sign at forearm
Conservative tx (elbow splint at 90 with forearm neutral)
Post op tx (AROM, nerve gliding, strengthening 2wk)
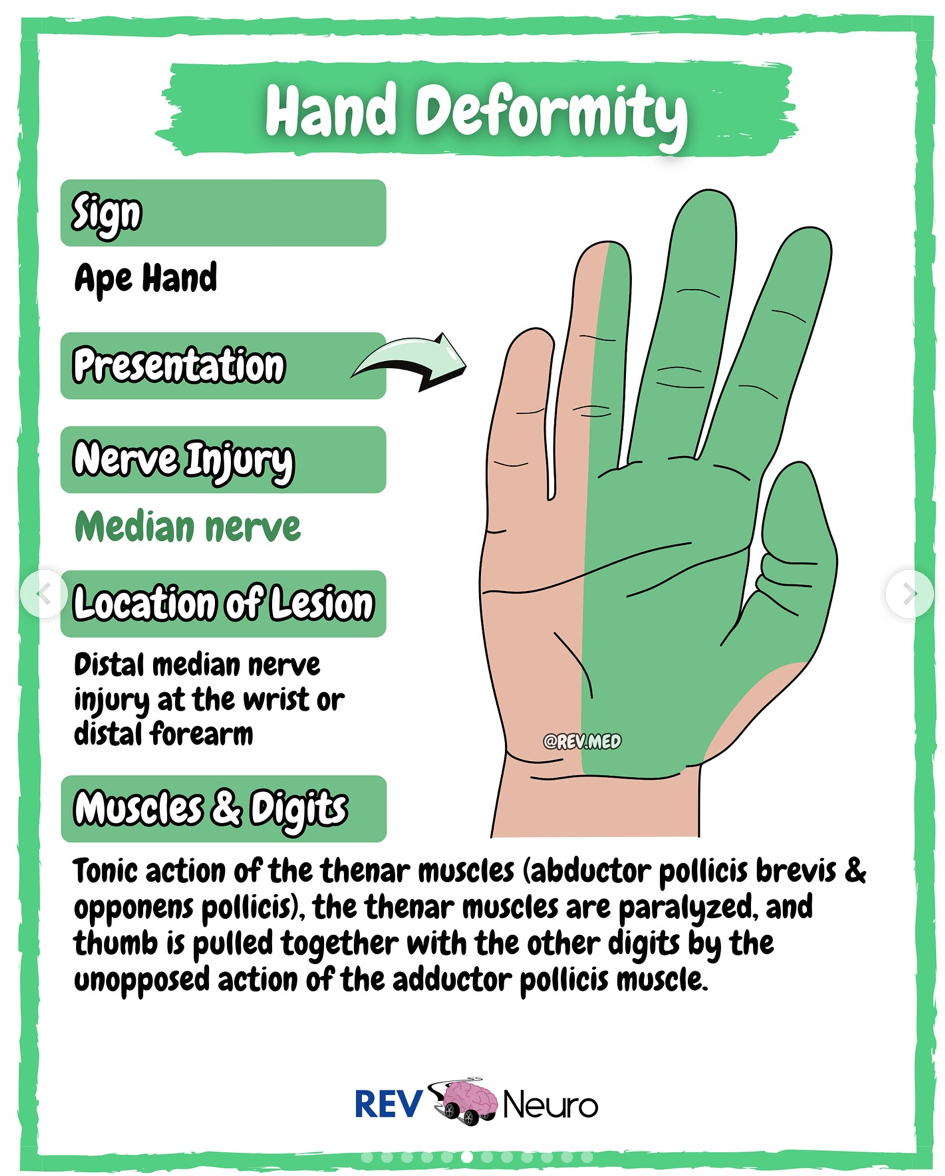
Ape Hand
(distal median nerve)
-Motor loss of lumbricals I and II (MCP flexion digit II and III), opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis
-flattening of the thenar eminence
-loss of thumb opposition
OT int: C-bar splint with thumb in opposition
Post surgery- splinting, ROM/tendon gliding when cleared
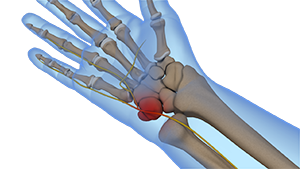
Guyon canal syndrome
-Ulnar nerve compression at wrist
-repetitive motion, pressure, fascial thickening
-positive tinel's
Conservative tx (wrist splint in neutral)
Post op tx (edema, AROM, nerve glides, strengthening 2-4wk)
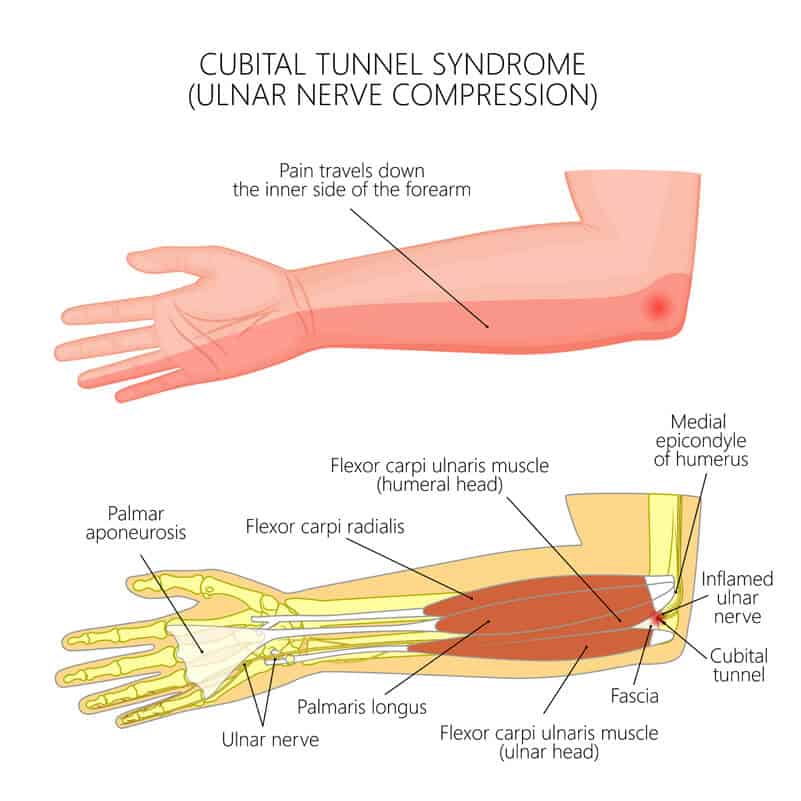
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
-ulnar nerve compression at elbow
numb at ulnar aspect of forearm
pain at elbow with consistent/extreme elbow flex
Positive Froment’s sign
⚡️easily pull the paper from someone’s pinch who has Cubital Tunnel
Positive Tinel’s sign at elbow
-Conservative tx
elbow splint at 30-60 flex
elbow pad
Suggest activity mods to extend elbow
Post op tx
edema & scar management
2 weeks: AROM/nerve glides
4 weeks: strengthening
MCP flexion anticlaw splint if clawing is observed
Radial Nerve Lesion
-sensory loss dorsal forearm, dorsal palm, thumb, index, middle
-low lesion motor loss of wrist extension, MCP ext, thumb ext
high lesion motor loss of ECRB, ECLR, brachioradialis, loss of tricep if at armpit
OT int: dynamic extension splint, ROM, sensory re-education, activity mods, NMES
Radial Tunnel Syndrome
-dull ache to the proximal lateral forearm (effects the posterior interosseous nerve [deep radial nerve that controls wrist and finger extension]
-OT recs
long arm splint with wrist extension/elbow in flexion/wrist in neutral
TENs
Pt advised to avoid forceful wrist/finger extension and forearm supination
![<p>-dull ache to the proximal lateral forearm (effects the posterior interosseous nerve [deep radial nerve that controls wrist and finger extension]</p><p>-OT recs</p><ul><li><p>long arm splint with wrist extension/elbow in flexion/wrist in neutral</p></li><li><p>TENs</p></li><li><p>Pt advised to avoid forceful wrist/finger extension and forearm supination</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b71b8fe6-e9b9-40d0-b6ba-816e0016c79e.jpg)
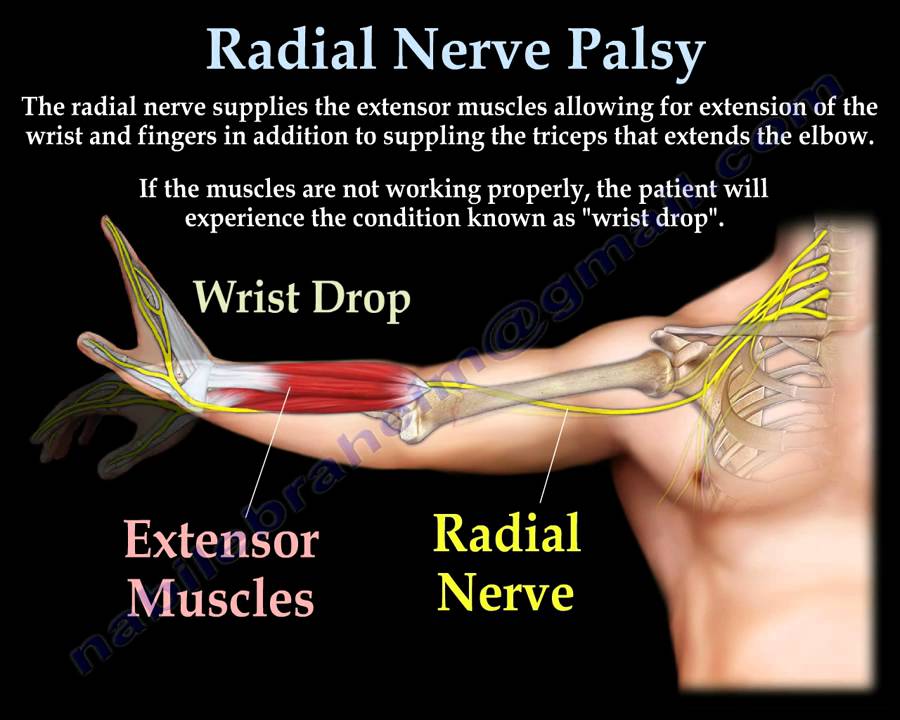
Radial nerve palsy
-compression on the radial nerve on the upper arm
-can also be caused by humerus fx
-weakness/paralysis of extensors wrist,MCP, thumb
Conservative tx (dynamic wrist/MCP ext splint, strengthening of wrist/finger extensors)
Post op tx (AROM, strength 6-8wk, avoid pronation/ elbow extension/ wrist flexion together)
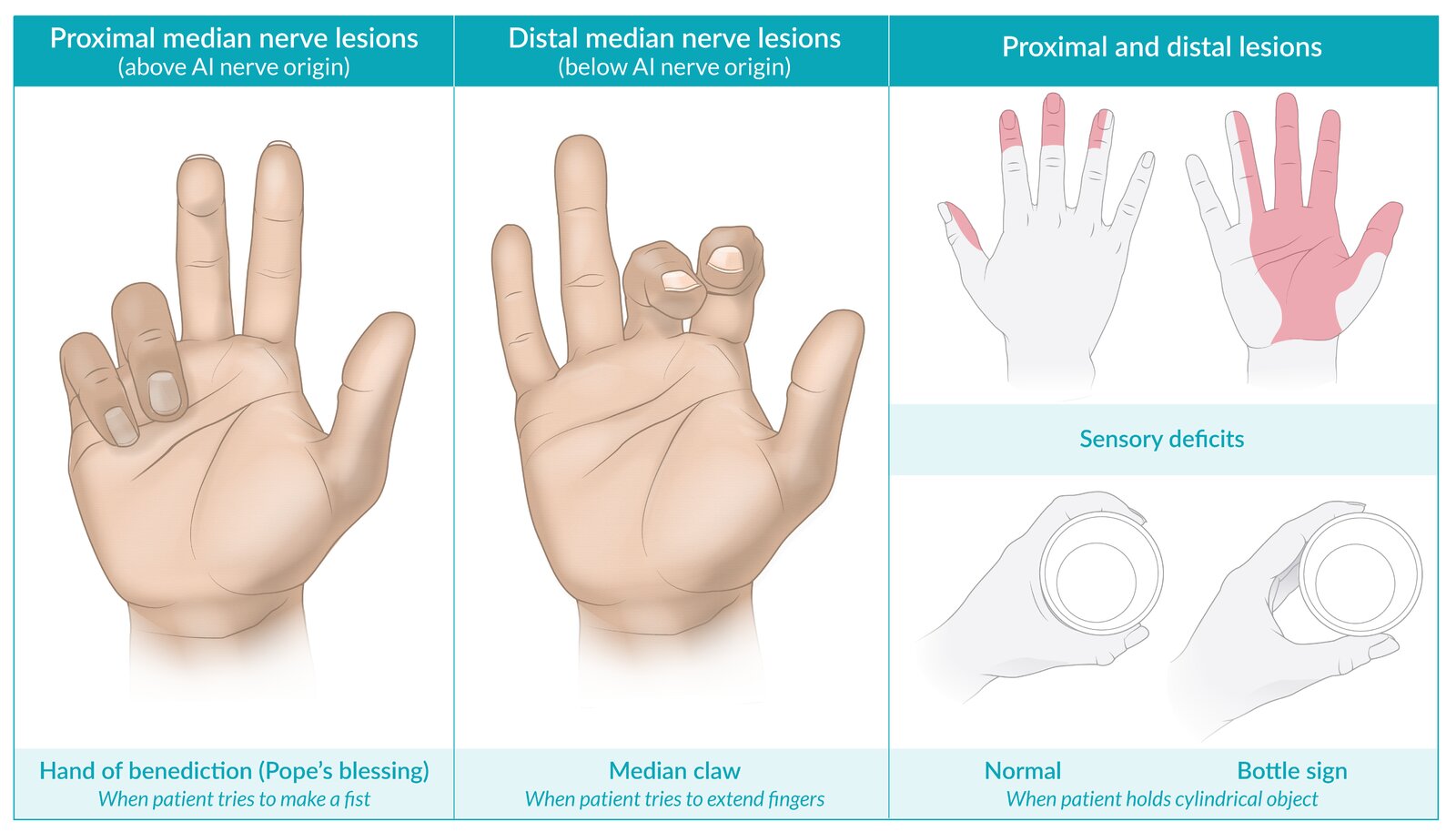
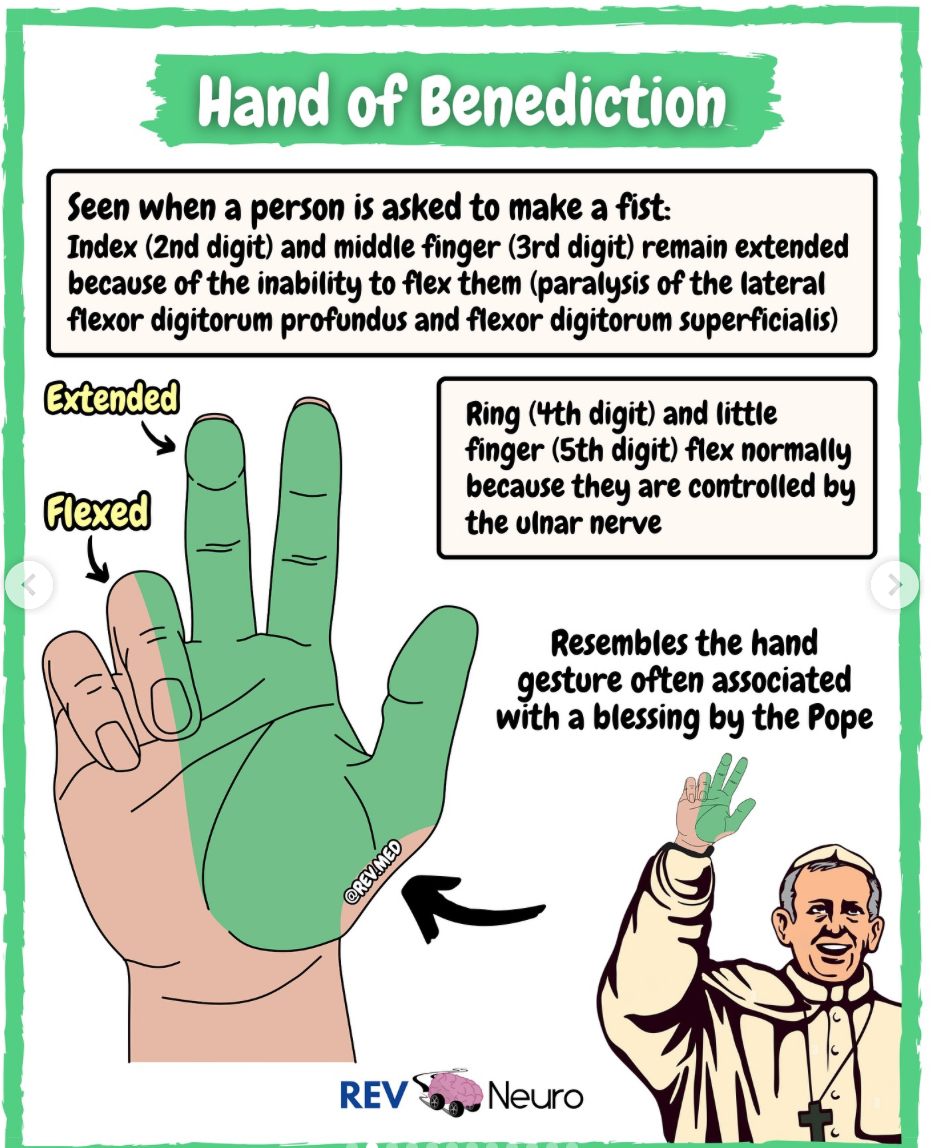
Sign of Benediction
(proximal median nerve)
~remember it is higher median nerve injury sign because pope’s hand is for higher God
-Ape hand at rest
-When client tries to make a fist only ring and pinky flex since there is a loss of MCP flexion of thumb, index, middle. First three digits can become hyperextended
OT int: dorsal protection splint, wrist at 30flex, elbow 90fex
Claw Hand
Distal ulnar nerve lesion
-sensory loss ulnar side of palm/dorsal surface
-4th & 5th digit hyperextension at MCP joints and flexion/inability to extend PIPs/DIPs
-Use MCP blocking splint AKA anti-claw splint to put MCPs in flexion
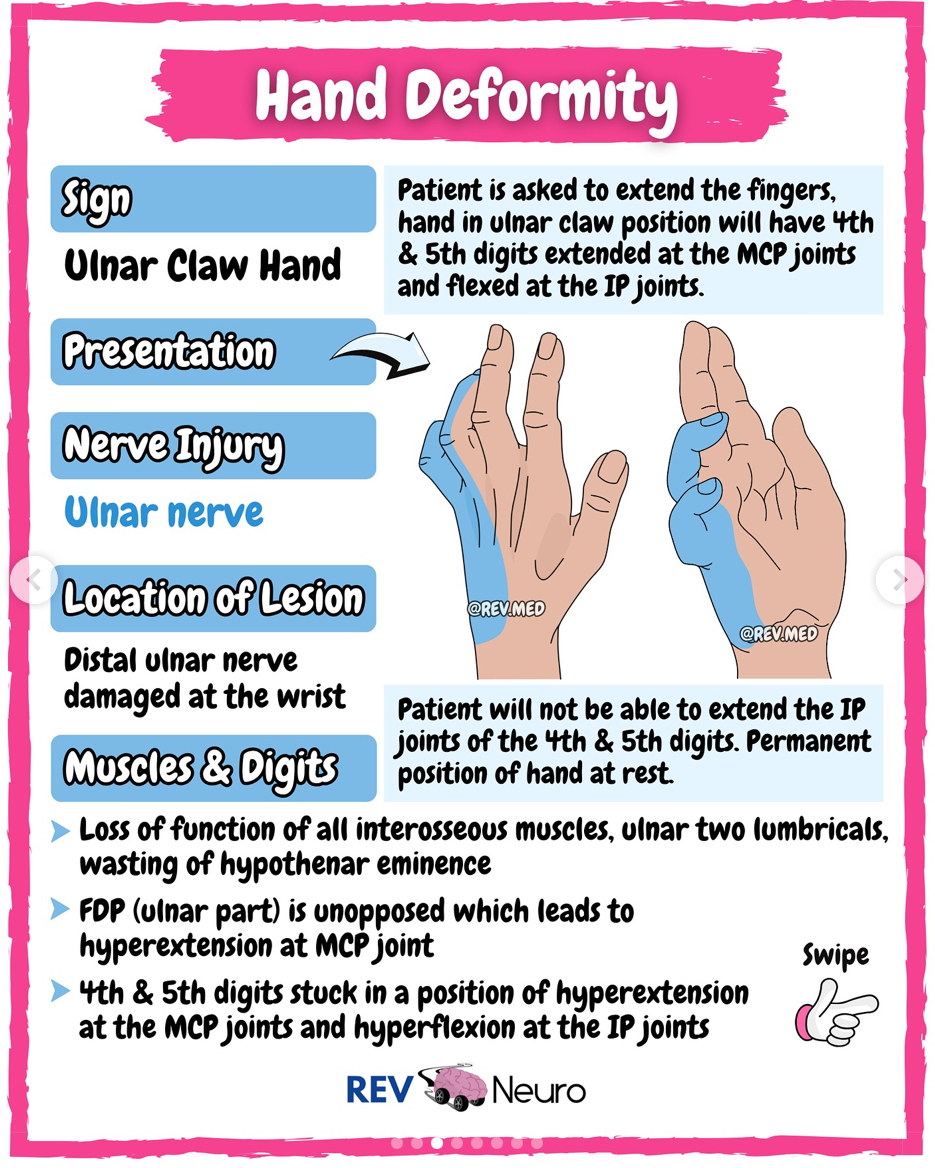
Proximal Ulnar Nerve Lesion
-motor loss includes distal ulnar lesion, and flex carp ulnaris, flex digi prof IV and V (ring, little finger)
-functional loss of power grip
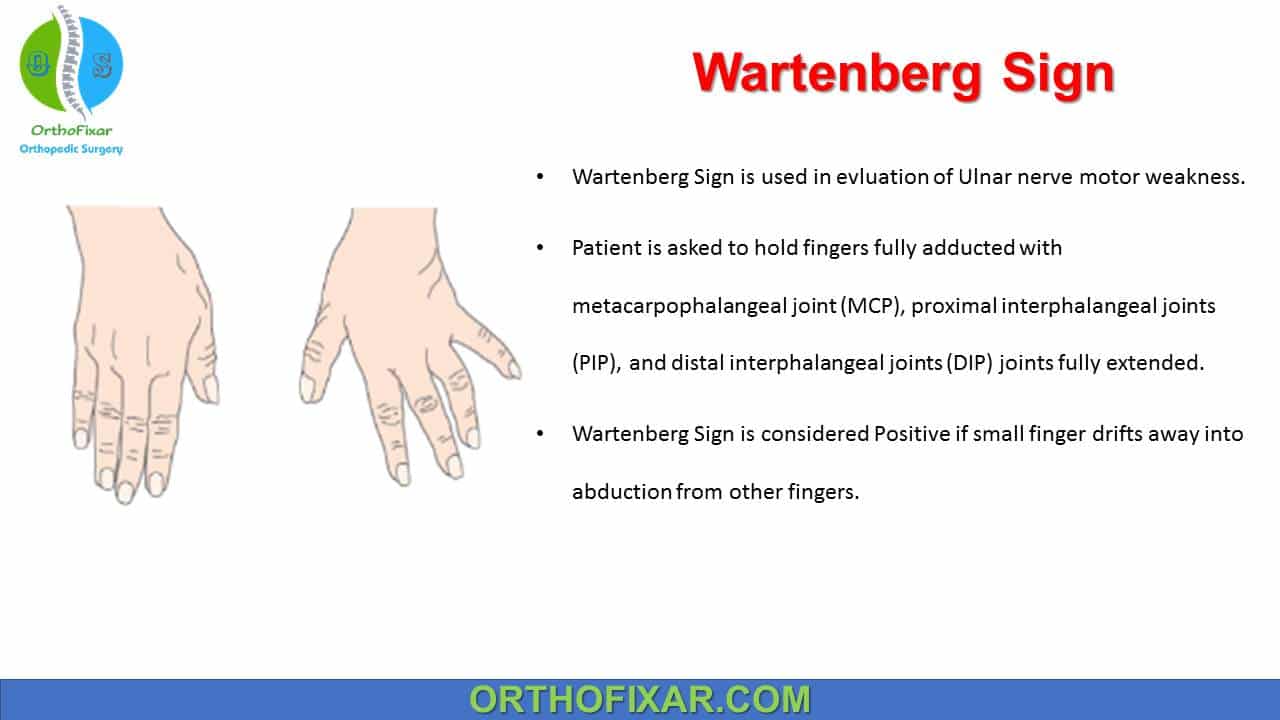
-positive Wartenberg’s Sign associated with ulnar nerve injury
OT int: MCP flexion block
Arthritis Basics
-Generally avoid
MMT/Resistive Exercises (too much resistance on joints)
Heat during acute RA/ inflammatory stage OA (worsen inflammation)
-Limit: PROM (unless during a flare-up)
-Encourage:
AROM
Functional activities
Light stretching with no inflammation
-Splints
Soft neoprene splints for RA (can still move)
Resting hand splint/hand based splint for acute CMC arthritis
-PAMs (when no acute inflammation)
Heat (baths, heat pad, paraffin wax)
Moist heat & ice rotation
Rheumatoid Arthritis
-Thought to be autoimmune; chronic & progressive with no cure
-Symmetric systemic and affecting many joints.
-Remits and has exacerbation
-AROM preferred, but during Stage I flareup do PROM b/c of pain ⚡️show off your flare at prom
-soft splints that support multiple joints preferred, especially during the night since they are more comfortable pt is more likely to wear it
-typically stiffer in the morning
-heat can help with pain but is contraindicated during flareup
- ulnar deviation and subluxation of wrist and mcp joint (useful to modify tools to decrease ulnar dev ex: ergonomic bent handles on utensils/tools)
- boutonniere deformity, Swan neck deformity
-later stages (3/4) strengthen and lengthen with stretching and isometric/tonic exercises
RA Stages & Interventions

Osteoarthritis
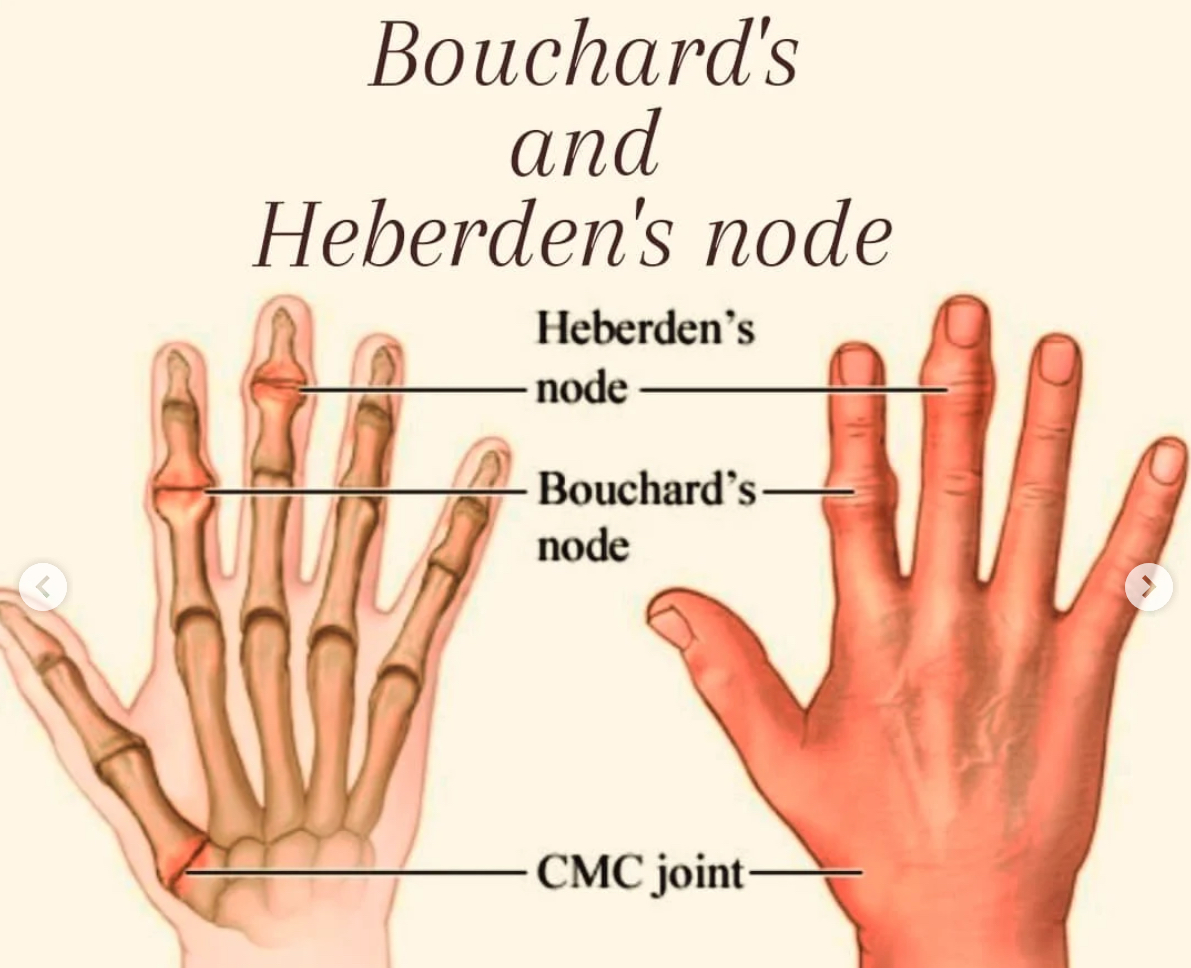
-Degenerative joint disease caused by wear and tear, typically affects large weight bearing joints and hyaline cartilage
-Non-inflammatory (although there are periodic stages of local inflammation/decreased ROM)
- Can cause bone spurs at the PIP (Bouchard’s nodes) and DIP joint (Herbedon’s nodes) ⚡️Herb dip
-PROM Should be avoided at the inflammatory stage. Avoid muscle testing.
OT int:
Resting hand splint in the acute stage, ulnar drift splint to prevent deformity, silver rings for swan neck and deformity and boutonniere deformity
Joint protection techniques, energy conservation techniques, all exercises should be pain free
Heat can help relieve stiffness/pain (paraffin), but avoid in inflammatory stage
Strengthening avoid in inflammatory stage, adaptive equipment to decrease stress on small joints
Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
-congenital joint contractures
-weakness, limited ROM, Position of rest at the upper extremity is internally rotated, elbows extended, and wrists flexed
-OT for increasing joint ROM, environmental mods,

Sensory Testing Application for SCI vs Neurological Disorders vs. Peripheral Nerve Injuries
-SCI- test proximal to distal following dermatome pattern (ASIA scale)
-Neurologic disorders- test for dermatome pattern
-Peripheral nerve injuries- test distal to proximal following peripheral nerves
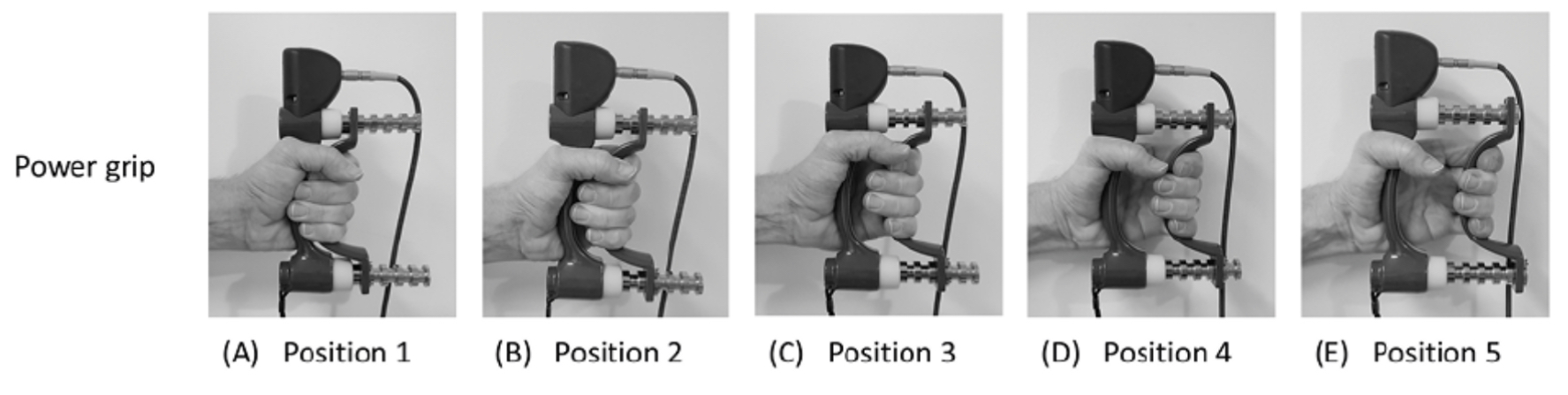
Ways to Measure Grip Strength
Dynamometer
Position #2 with 3 trials of each hand compared to norms
1 trials in all 5 positions for each hand. Check bell curve to see if pt is applying maximal effort
Sphygmomanometer cuff/vigorimeter/hand held bulb
Should be used to evaluate grip strength of pts with arthritis/older adults
Symptoms of Tendonitis vs. Partial Tendon Rupture vs. Full Tendon Rupture
-Tendonitis= Full strength with pain during movement/resistance
-Partial Tendon Rupture= Partial strength with pain during movement/resistance
-Full Tendon Rupture= Little to no strength/function with little to no pain