SOC 101 Final Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Williams “Glass Escalator”
An article, written by Christine Williams, introducing the concepts of "glass escalator" and "glass ceiling". She showed research that supported both concepts, however, it lacked analysis of intersectionality (the effects of race, class, etc).
The glass escalator refers to the advantages given to men in predominantly feminine jobs.
The glass escalator refers to the advantages given to men in predominantly feminine jobs.
2
New cards
Transgender
a person whose gender identity is different from the sex assigned at birth.
3
New cards
Cisgender
a person whose gender identity is the same as the sex assigned at birth.
4
New cards
Non-binary
a person whose gender identity is neither male or female
5
New cards
Sex
the biological and physiological distinctions between male and female; the dividing roles of male and female based on their reproductive functions.
6
New cards
Gender
socially constructed cultural, phycological, and behavioral characteristics that associate with one's sex.
7
New cards
Social construction of gender
refers to the creation of gender meanings through social interactions and norms.
ex. blue (masculine) and pink (feminine) as gendered colors, speech patterns ("uptalk" and "vocal fry" for women, deep voices for men).
ex. blue (masculine) and pink (feminine) as gendered colors, speech patterns ("uptalk" and "vocal fry" for women, deep voices for men).
8
New cards
“Doing” gender
reveals socially guided theoretical assumptions of what gender is; the belief that there are specific ways to express gender.
- Candace West and Don Zimmerman developed the idea that we do gender. They suggested that we perform actions that produce gender; we do gender in interactions with others, and we take into consideration what is believed to be appropriate for our gender.
- Candace West and Don Zimmerman developed the idea that we do gender. They suggested that we perform actions that produce gender; we do gender in interactions with others, and we take into consideration what is believed to be appropriate for our gender.
9
New cards
Gender binary
also known as binarism, is the cultural or societal idea that there are only to classifications of gender: male and female.
10
New cards
Intersectionality
refers to the overlap of multiple social identities (race, gender, class, etc) that contributes to specific systematic discrimination or oppression experienced by an individual; the ways in which different types of social relations are linked together in complex ways, creating very different experiences for different groups of people.
11
New cards
Feminism
advocacy for equal human rights (socially, politically, and economically) for both sexes: male and female.
12
New cards
Institutional inequality
how institutions increase inequality in their workspace by reproducing social patterns that emerged in that time frame.
ex. motherhood penalty, glass ceiling
ex. motherhood penalty, glass ceiling
13
New cards
Motherhood penalty
The drecese of women's salaries once they become mothers, followin the idea that women will work less for the institutions. Influenced by the belief that women's role is at home.
14
New cards
Fatherhood bonus
the advances received (compared to working mothers and childless men) by fathers within their workspaces in terms od pay and perceived competence.
15
New cards
Glass ceiling
refers to the invisible barriers or impediments that women experience in predominately male workspaces.
16
New cards
Jezebel caricature
a caricature which discriminated black women reinforcing the stereotype of them being sexually lascivious and promiscuous, even predatory.
17
New cards
Positivist theories of deviance
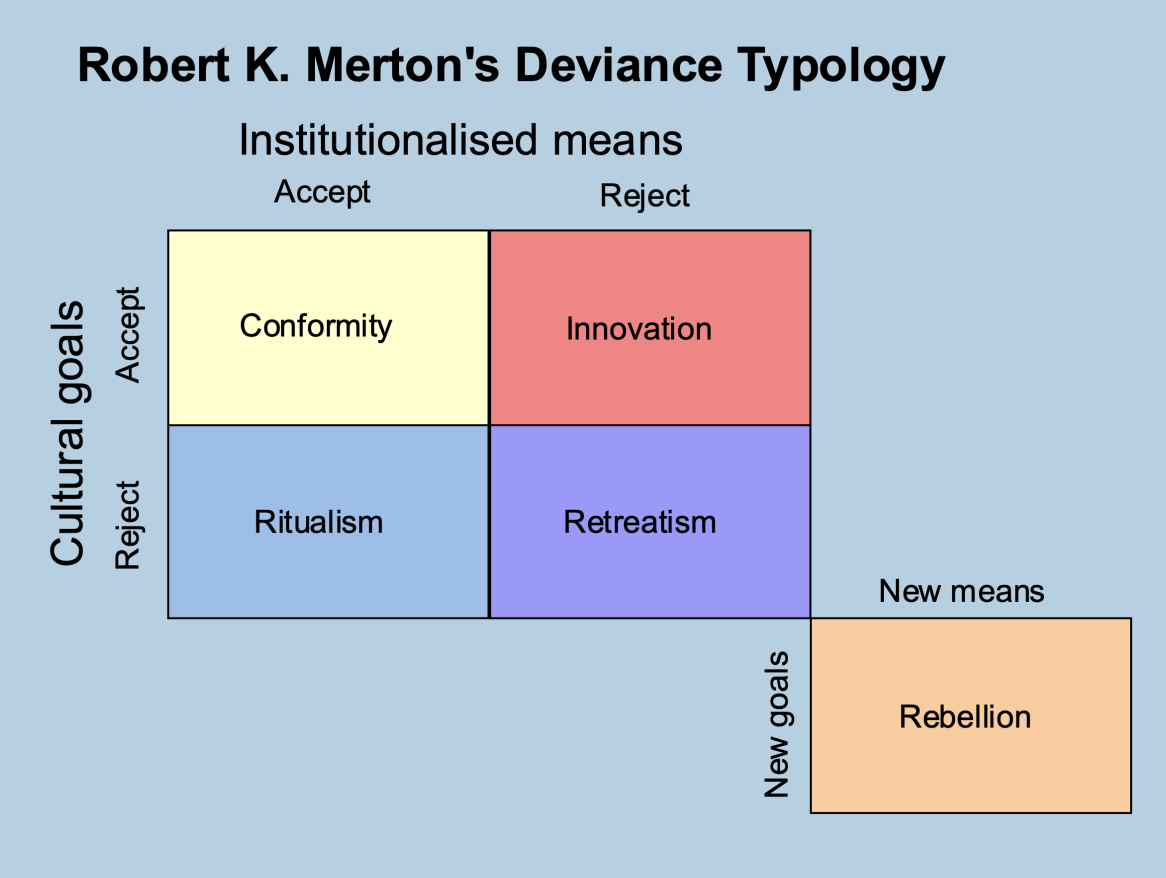
These theories support that deviance is determined or caused by forces or influences outside the individual's control. The theories seek to answer the “Why do some people engage in ‘X’?”. They were developed by Robert Merton.
ex. Strain theory, learning theory, and control theory.
ex. Strain theory, learning theory, and control theory.
18
New cards
Constructionist theories of deviance
Seeks to answer the question “Through what process did X come to be understood as deviance in the first place?”
ex. Symbolic Interactionism, Labeling theory
ex. Symbolic Interactionism, Labeling theory
19
New cards
Social control
the way we enforce normative behaviors through social interaction, values and worldviews, and laws.
20
New cards
Moral panic
widespread sense of fear, usually based on misconceptions, that something or someone is threating or damaging the values, norms, interests or well-being of the community.
21
New cards
Moral entrepreneurs
individual, groups or organizations that try to make a claim or take the resposability of bringing awareness to a "problem".
22
New cards
Anomie
(introduced by Emile Durkheim) the condition of inestability and desintegration of values and standards that from a lack of purpose or ideas
23
New cards
Strain theory
due to societal disadvantages, the individual will most likely seek alternative pathways to the American Dream.
24
New cards
Conflict theories
- they argue that people who have the power
to define and police deviance will do so
with the specific intent of maintaining
their class status.
- dominant groups
in society define as deviant any behavior
or activity that threatens their power or
conflicts with their class interests.
to define and police deviance will do so
with the specific intent of maintaining
their class status.
- dominant groups
in society define as deviant any behavior
or activity that threatens their power or
conflicts with their class interests.
25
New cards
Labeling theory
(introduced by Howard Becker) assumes that public labeling, or branding, as deviant, has adverse consequences for further social participation and self-image. The most important drastic change is in public identity, which is a crucial step towards building a long-term “deviant career”.
ex. When someone is labeled as an “outsider,” they are treated differently. Smoking marijuana may not change someone much, but being labeled a pothead may shift how a person is treated and how she sees herself.
ex. When someone is labeled as an “outsider,” they are treated differently. Smoking marijuana may not change someone much, but being labeled a pothead may shift how a person is treated and how she sees herself.
26
New cards
Stigma
the phenomenon in which an individual is labeled as socially "disqualified"; when an individual is rejected for being different from their society.
27
New cards
Differential association / learning theory
A person becomes delinquent because of an excess of definitions favorable to violations of law over definitions unfavorable to violations of law.
28
New cards
Control theory
- Seeks to answer “What is it that makes people NOT commit crimes?”
-focuses on how ties to mainstream social groups and societal institutions make us less likely to become deviant.
- People violate social norms because they lack social bonds to conventional others (family, school, work).
- developed by Eric Hirsch.
-focuses on how ties to mainstream social groups and societal institutions make us less likely to become deviant.
- People violate social norms because they lack social bonds to conventional others (family, school, work).
- developed by Eric Hirsch.
29
New cards
Symbolic Interactionism
is a micro-level theory based on the idea that people act in accordance with shared meanings, orientations, and assumptions.