L4-covalent and non-covalent bonding
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
why do bonds form
as atoms want a full outer shell of electrons they will either try to lose the electrons ( ionisations ) or share and gain electrons /form bonds
what is a bond ?
a bond is a force that holds atoms together in a molecules/compound and they form due to the transfer or sharing of electrons
what is ionisation
ionisation is when ions are formed when atoms lose or gain electrons in an ionic bond to become charged particles
explain how ionic bonding works
it occurs between a metal and a non-metal the metal becomes a positive ion and loses an electron whilst the non-metal gains electrons to become negative ions the salts formed are held together by strong electrostatic forces
what is a covalent bond and why does it occur
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms
it happens as when the two atoms are brought closer together the orbitals now overlap and merge into a single bond orbital that contains both electrons
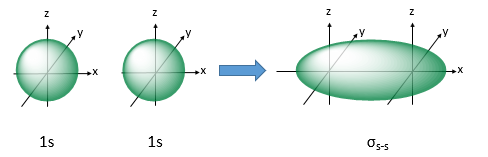
explain sigma bonds
they are the strongest type of covalent bond and they form when orbitals overlap in a head-on-head arrangement
they can form when 2 s-orbitals merge
also can be formed when an s and a p orbital overlap
also when a sp and an s orbital overlap
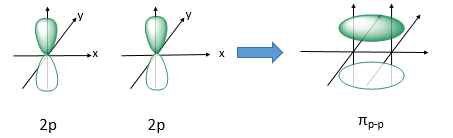
Explain pi bonds
pi bonds are covalent bonds formed from the overlap of two orbital lobes on one atom with two orbital lobes on another side to side ( two p orbitals over lapping )
area of high electron density
what is a hydrogen bonding
its a partially electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen ( which is delta positive ) and the electronegative N,O,F
its an electrostatic dipole-dipole interaction
What are Van der Waals forces?
weak forces that attract neutral molecules to one another found in gases and in almost all organic liquids and solids
they can occur in three different ways
1.neutral molecules can have permanent dipoles e.g. water
2.induced dipoles - molecules with a permanent dipole may temporarily distort the electric charge in a nearby molecule
3. dispersion forces-molecules with no permanent dipoles can form temporary dipoles can form randomly as electrons are always moving sometimes on one side more than the other
what is pi stacking
attractive non covalent bonds between aromatic rings ( which contain pi bonds )
the three arrangements are sandwich, t-shaped and parallel displaced

explain hydrophobic interactions
theses interactions are the segregation between water and non-polar substances e.g. water and oil not mixing
water contains a strong network of hydrogen bonds but non-polar molecules like hydrocarbon chains for example cant form h- bonds
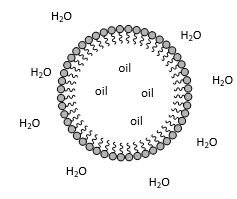
explain how amphiphilic molecules ( mainly proteins ) react in water
they will form micelles in water, the hydrophilic head unit is found on the outside and the hydrophobic tails on the inside
when the protein folds into a three dimensional shape, its common to have a hydrophobic core composed with hydrophobic elements
explain protein structure ( primary, secondary, tertiary )
primary- sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide held together by peptide bonds
secondary-the additional folding into either beta-pleated sheets or alpha helix's through hydrogen bonding interactions
tertiary-the three dimensional shape of a protein molecule, the secondary structure is folded into a compact globular structure driven by hydrophobic interactions, salt bridges and hydrogen bonds and van der Waals
quaternary-assemblies of two or more polypeptide chains into one functional unit