Water origin (1)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
What is heavy water made from
Deuterium
2
New cards
What is deuterium
Isotope of hydrogen used in nuclear plants
3
New cards
How is the hydrogen bond formed
dipole-dipole
4
New cards
Why does ice have a higher volume
Crystal structure, hexagonal ice
5
New cards
By how much does ice volume increase
9%
6
New cards
What and how many forms of ice are there?
19 forms in total, 16 crystalline and 3 amorphous
7
New cards
How is the density of ice compared to liquid water
ice has lower density
8
New cards
What temperature is maximum density at
4 degrees
9
New cards
Why are circulation periods important
Circulation of compounds and biotic part of ecosystem
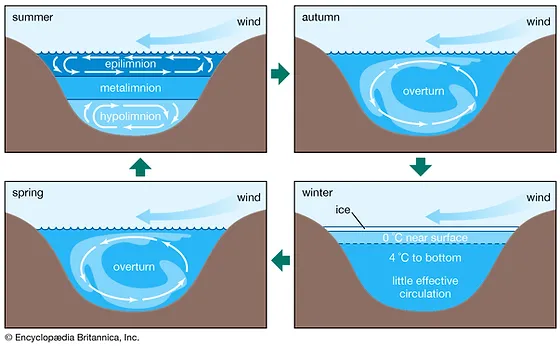
10
New cards
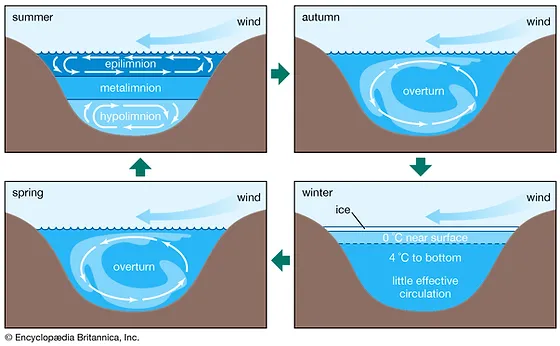
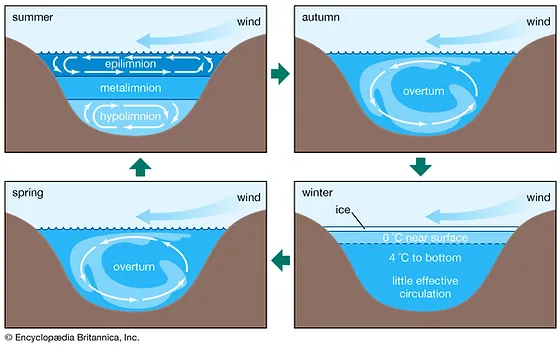
Epilimnion
Top layer of water in the summer, holding circulation. Photosynthesis
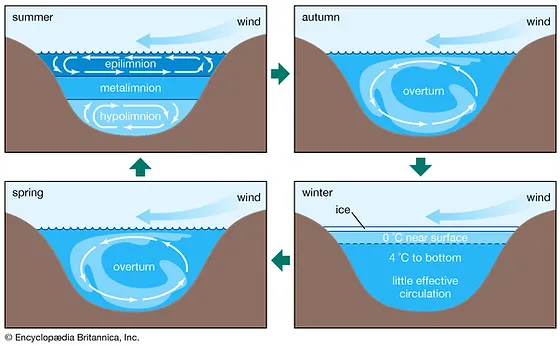
11
New cards
Metalimnion or thermocline
stagnation layer, water does not move here in the summer, most O2 concentration here
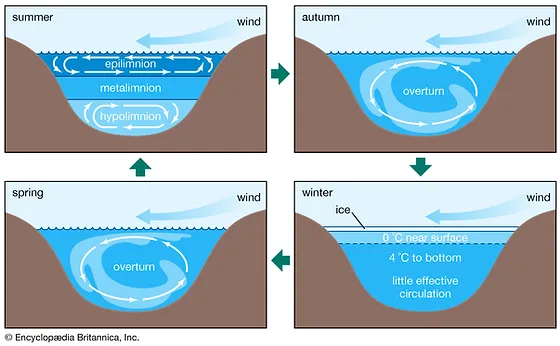
12
New cards
Hypolimnion
Bottom layer of water in the summer, holds circulation in opposite direction than the epilimnion. Respiration and decomposition
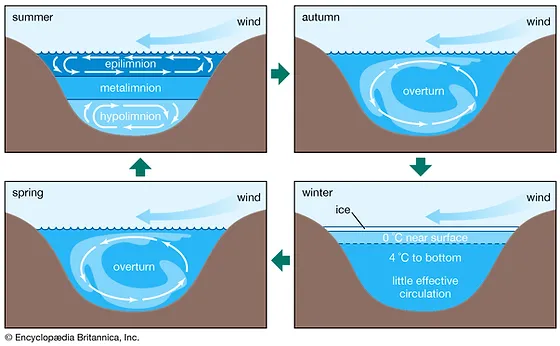
13
New cards
What happens in the autumn and spring with the water in a lake?
Overturn - happens when the top layer cools down to the temperature of the layers below
14
New cards
What happens in winter with the layers in a lake?
The top layer is ice, right below the water is around 0 degrees and 4 degrees tp the bottom. At the very bottom there is very little effective circulation.
15
New cards
Amicitic lake
Ice covered year-round
16
New cards
Cold monomictic
Water temperature never exceed 4 degrees, one circulation period in summer
17
New cards
Dimictic
Circulation in spring and autumn, stagnation in summer and stratification in winter
18
New cards
Warm monomictic
Not ice covered, one free circulation in winter at 4 degrees and stratified for the rest of the year
19
New cards
Oligomictic
Stratified much of the year but cool sometimes to circulate - irregularly, no ice
20
New cards
Polymictic
Frequent periods of circulation, no ice
21
New cards
Name the types of lakes
Amicitic, Cold monomictic, Dimictic, Warm monomictic, Oligomictic, Polymictic
22
New cards
What type of molecules does water dissolve?
Polar molecules
23
New cards
What is water solubility dependent on
Mineralisation of inorganic and organic substances
24
New cards
Mpemba effect
Hot water can freeze sooner than cold water