IMED1004 - Drug Related Issues 1 - Addiction (L20)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
DSM-V
- taking the substance in larger amounts and for longer than intended
- wanting to cut down or quit but not being able to do it
- spending a lot of time obtaining the substance
- craving or a strong desire to use the substance
- repeatedly unable to carry out major obligations at work, school, or home due to substance use
- continued use despite persistent or recurring social or interpersonal problems caused or made worse by substance use
- stopping or reducing important social, occupational, or recreational activities due to substance use
- recurrent use of the substance in physically hazardous situations
- consistent use of the substance despite acknowledgement of persistent or recurrent physical or physiological difficulties from using
Tolerance
a need for markedly increased amounts to achieve intoxication/desired effect or markedly diminished effect with continued use of the same amount
Withdrawal
as either characteristic syndrome or the substance is used to avoid withdrawal
THE 5 Cs
- Chronic
- Compulsive use
- control impaired
- craving
- continued use despite harm
Substance dependence is a chronic relapsing brain disesae
- Chronic
- Relapsing
- Brain
- disease
Who becomes dependent
- in a national US survey of persons over 12, found that 13.4% of heroin, 9.2% of crack, 5.8% of marijuana, 3.7% of cocaine and 3.2% of alcohol users were dependent 12 months after initial use
- why do they become dependent:
Genetics and Dependence
- Heritability: a statistic that estimates the degree of variation in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population
- Heritability ranges from 0 to 1
- Heritability estimates close to 0 = trait is mostly due to environmental factors
- Heritability estimate close to 1 = trait is mostly due to genetic factors
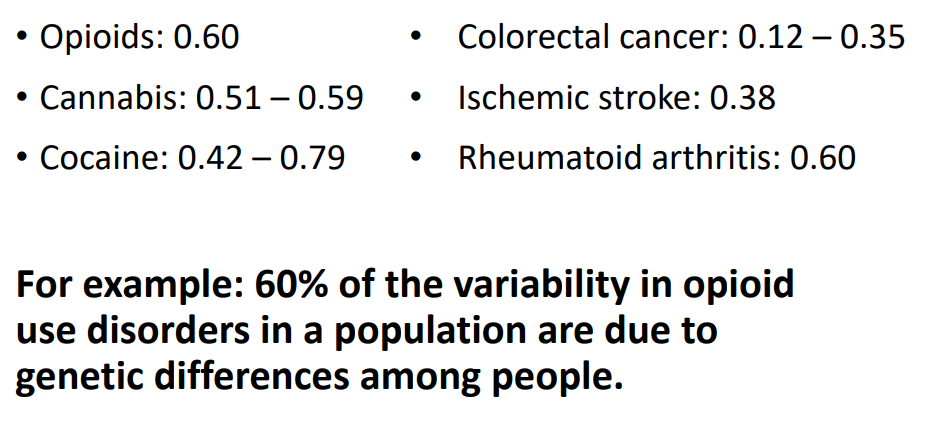
Heritability of substance use disorders
- For example: 60% of the variability in opioid use disorders in a population are due to genetic differences among people

The right environment - risk factors
INITIAL USE:
- gender
- family
- peer and community substance use
- poor academic achievement and low academic aspirations
- mental health disorders
- antisocial behaviour
.
DEPENDENCE:
- child and adult trauma
- emotional, physical and sexual abuse
- homelessness
- socio-economic status
- mental health disorders
The health problems associated with drugs
THE DRUGS:
- overdose
- withdrawal
- endocrine effects
- organ damage e.g kidneys and liver
- neurological disease
- fetal damage
.
THE DRUG LIFESTYLE:
- suicide
- blood borne viruses
- infection
- mental health
- accidents and injury
- homicide
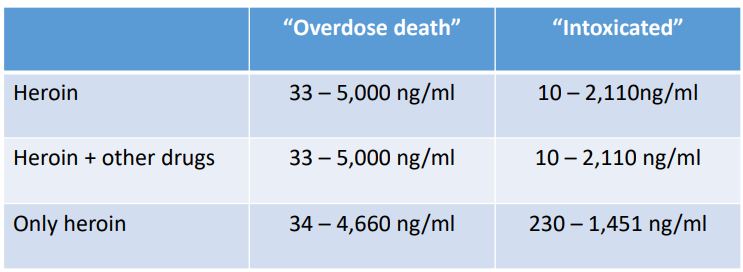
Overdose and Overdose Myths
- only a very small portion of overdose involve excessive quantities of a single drug
- in Australia there is no strong evidence to suggest changes in drug purity or contaminants contribute significantly to overdose
- Although there are high rates of suicide by drug users, drugs are not usually used to commit suicide (<5% overdoses are deemed suicides)
- an interview of 256 heroin overdose survivors found only 9 (3.5%) had intentionally overdoses
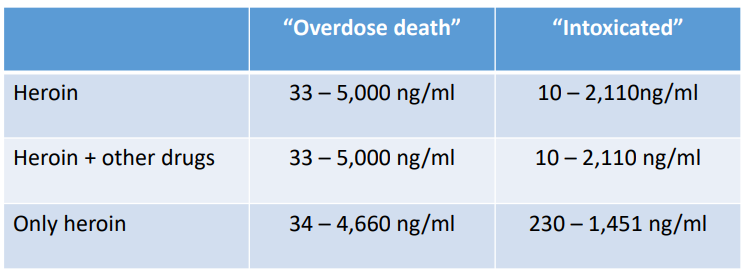
Overdose Other info
- one of the biggest factors associated with overdose are changes in tolerance
- the other biggest factor is the use of multiple drugs, especially depressants (opioids, alcohol, benzodiazepines)
- Deaths deemed overdoses are often complicated/associated with other problems, for example: aspiration of vomit, heart attack, accidents e.g drowing, pulmonary embolism
Fatal vs Non-Fatal Overdoses
- for every fatal overdose, there is around 25 non-fatal overdoses
- in australia, 2.5x as many people die of a prescription opioids overdoses compared with a heroin overdoses

Withdrawal (no learning outcome)
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 27


Pregnancy (no learning outcome)
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 32

Prevention - Targeting risk factors
- strong families - breaking the cycle of drug use
- positive role models
- support for mental illness
- support at school (academic, behavioural)
- participation in activities (sport, clubs etc.)
- social support - housing, healthcare, welfare
Treatment for substance dependence
- treatments include medication for withdrawal and abstinence, residential treatment ('rehab'), counselling, 12 step programs
- approved medications for opioids and alcohol dependence (The right patient, the right medication, the right time, the right dose, and the right route)
- patients often require other services - medical, financial, legal, child, housing, transport, vocational
Medications for opioid dependence
- methadone - mu opioid agonist
- Buprenorphine - mu partial agonist, kappa antaognist
- Naltrexone - mu, kappa and delta antagonist