Respiratory System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Type I Pneumocyte
A Squamous cell, allows enhanced diffusion
Type II Pneumocyte
A Cuboidal cell, it secretes pulmonary surfactant
Surfactant
Lowers cohesion, therefore lowering surface tension
Psuedostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
The cita beat to move mucous and help keep the airway clear (Toward the pharanix)
Pleura
Air tight membrane.
Visceral: Outside of the lung
Parietal: Lines cavity
Diaphragm
Main muscle for breathing
Skeletal muscle
Phrenic Nerve (C3-C5)
Larynx
Skeletal muscle and is controlled by CN X
Epiglottis Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage (all others are Hyland)
Thyroid Cartilage
The biggest
Cricoid Cartilage
The base of the Larynx
Arytenoid Cartilage
Moves and controls tension of vocal cords
Corniculate Cartilage
Tip of the Arytenoid
Cuneiform Cartilage
Bronchopulmonary Segment
There are 10 segments in both right and left lung. Each bronchoplumonary segment is an anatomical and functional subdivision of a lobe.
What happens to BR during vigorous exercise?
↑Exercise → ↑Metabolic Demand → ↑Kreb’s Cycle → ↑CO2 in blood → ↑Medullary Activity → ↑BR
How does BR change at 8,000 feet above sea level?
↓O2 in air → ↓Diffusion of O2 → ↓O2 in blood → ↑Medullary Activity → ↑ BR
La Place’s Law
↑Radius → ↓Pressure
↓Radius → ↑Pressure
↑Tension → ↑Pressure
↓Tension → ↓Pressure
Oxygen Cascade
The pressure of oxygen decreases as you breathe in because the air picks up water from the lining of the respiratory tract. The water “dilutes” the partial pressure of the oxygen.
Henry’s Law
Change the partial pressure of a gas (make it better) to improve diffusion.
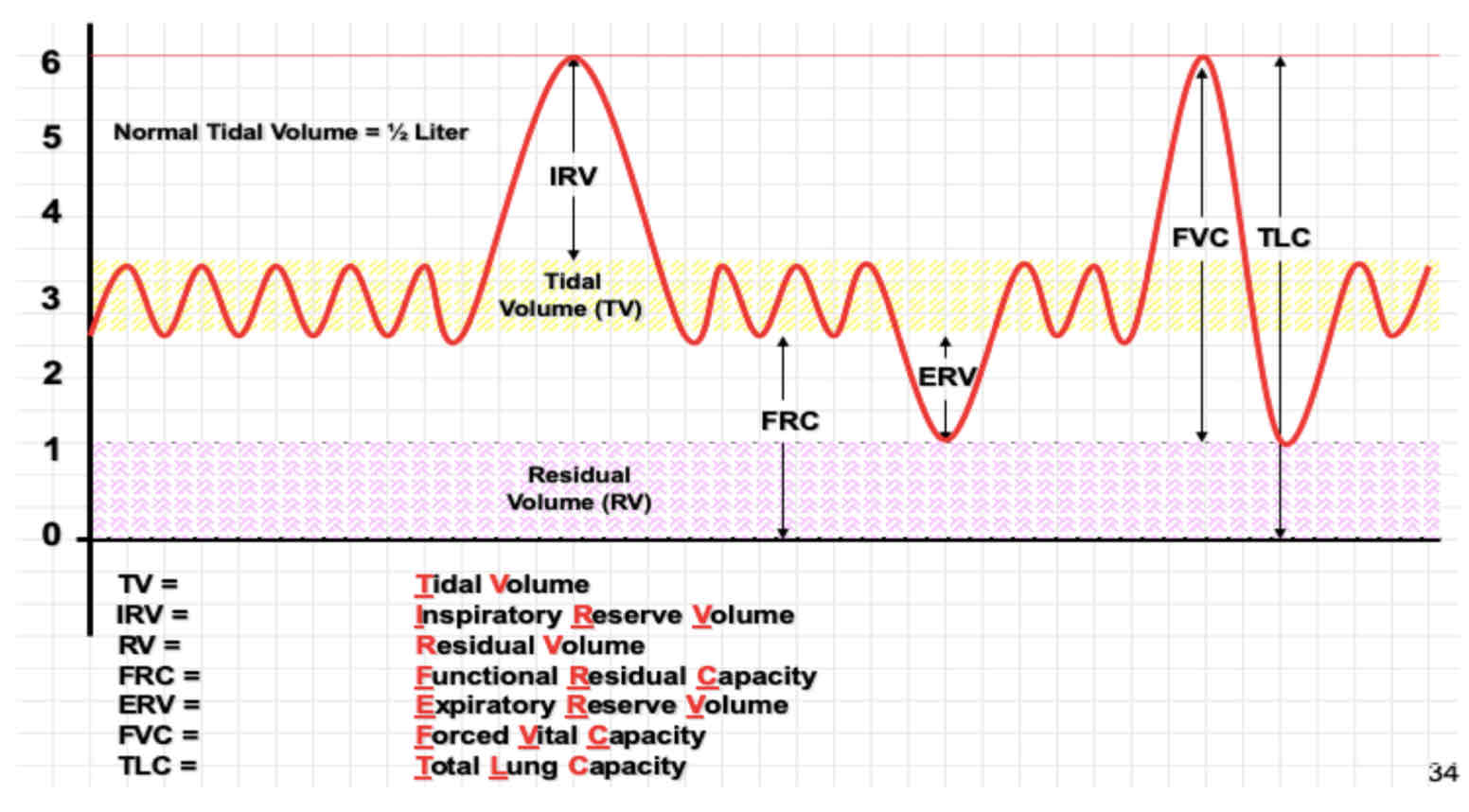
Spirogram
FEV6 and FVC are the same thing.
Boyle’s Law
As volume increases, Pressure decreases
As volume decreases, Pressure increases
Medulla Activity
Hypercapnea (↑CO2) → ↑Medullary Activity → ↑BR
Academia (↓pH) → ↑Medullary Activity → ↑BR
Hypoxemia (↓O2) → ↑Medullary Activity → ↑BR
Where is Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium found?
Posterior Nasal Cavity, Nasopharynx, and Trachea. It move across its surface.
What cranial nerve controls the vocal cords?
CN X
What nerve controls the diaphragm?
Phrenic Nerve
Conducting Airway
Trachea, Bronchi, and Large/Small/Terminal Bronchioles
Respiratory Airway
Respiratory Bronchioles, Alveolar Ducts, and Alveoli
Hearing-Breuer Reflex
Stretch Receptors in the lungs and chest wall monitor the amount of stretch as you breathe in. As the lungs inflate they also stretch, the stretch receptors signal the respiratory centers of the Pons to trigger exhalation and inhibit inspiration.
Different kinds of respiration
External Respiration:
Pulmonary Capillaries
Blood - Air Gas (Exchange)
Internal Respiration:
Systemic Capillaries
Blood - Tissue Gas (Exchange)
Chemical Respiration