Visual Communication terminology and theory.
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Projection
Process of reproducing a spatial object onto a plane. Done by projecting points
Which of the following are the elements planar projection?
3D object or scene is projected
Line of sight (LOS)
2D projection plane
Projected 2D image formed on projection plane
Line of sight (LOS)
An imaginary ray of light between the observers eye and the object
2D projection plane
An imaginary flat plane where the images lines of sight are projected
Perspective Projection
Mimics what the human eye sees.
Works by converging to a single viewpoint.
Distance changes size of projection
Not very useful in engineering application because it doesn’t show the true size.
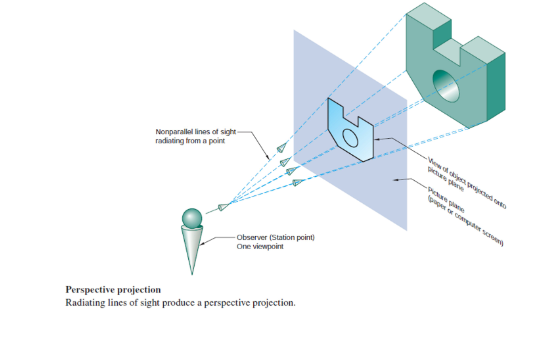
Center of projection (CP)
Represents position of the observer in perspective projection. It’s a finite distance from the object
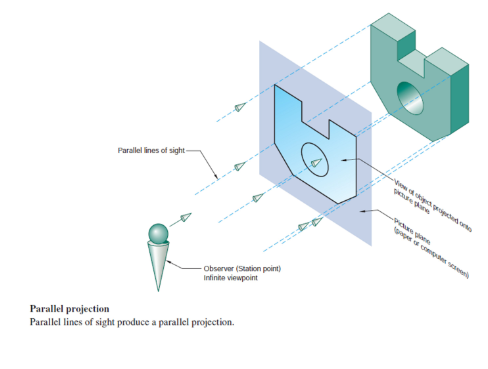
Parallel Projection
Plane of projection is always parallel to the object
It’s useful for ability to do realistic depiction of an object and show the true size
Pictorial projection
A type of projection which includes all three dimensions, hence creating an illusion of depth.
Multiview projection
Presents an object in a series of projections which only show two of an object’s dimensions
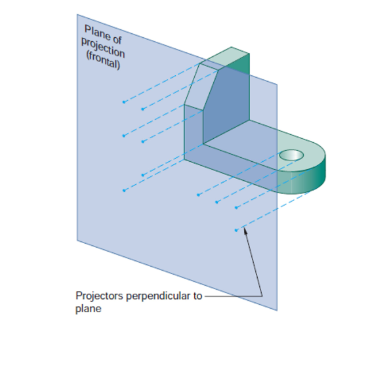
Orthographic projection
A parallel projection technique where the plane of projection is between the observer and the object.
The object is perpendicular to the lines of site
lines of site are parallel
Oblique Projection
Parallel projectors intersect a projection plane at an oblique angle. One principle face of the object will be parallel to the projection plane
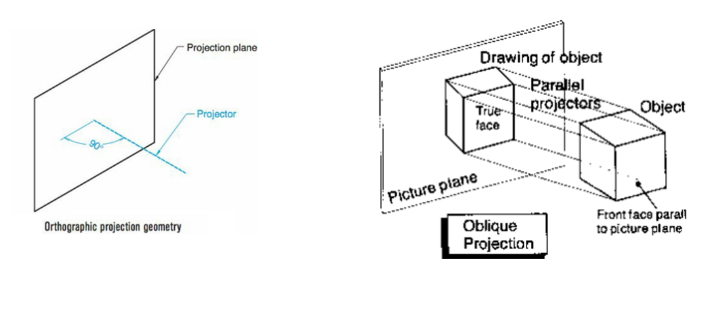
Features of Oblique projection
More focus on the front side of an object or face
Combines the ease of sketching in two dimension with a need to represent the third
Useful when majority of features are on the front face of an object
Engineering design
Process of devising a system, component, or process to meet desired needs and specifications within constraints.
It’s and interactive, creative, decision-making process which uses basic sciences, mathematics, and engineering sciences to apply when in converting resources into solutions
Wicked problems
ill-formulated problems with confusing information.
Can be many clients and decision makers with conflicting values so ramifications in the whole system is confusing
D
Axonometric projection
When orthographic projections are subdivided based on orientations of the object with respect to the projection plane.
All principal axes are inclined.
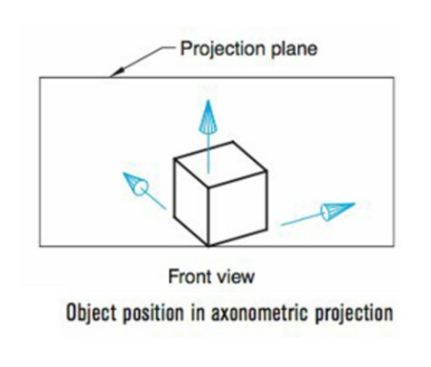
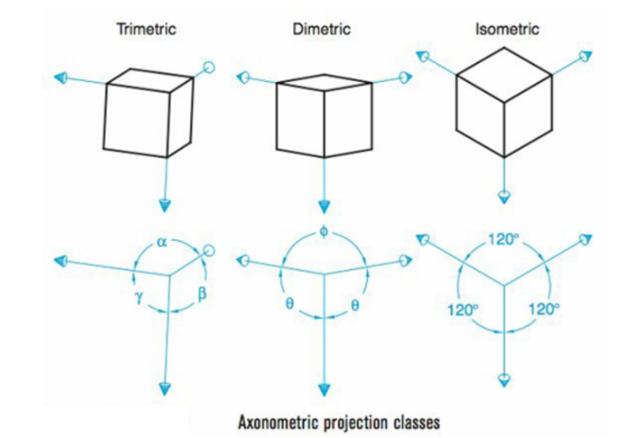
Classifications of Axonometric Projection
Trimetric: No angles between principle axes are equal
Dimetric: 2 angles between principle axes are equal
Isometric: All angles between principle axes are equal
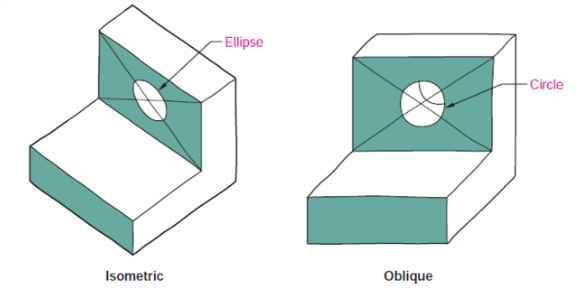
What is the difference between Isometric and Oblique Projections?
Oblique sketching: The front face of the object is squared with the paper and the depth is drawn at an angle to the horizontal.
Isometric: No faces are squared with the paper
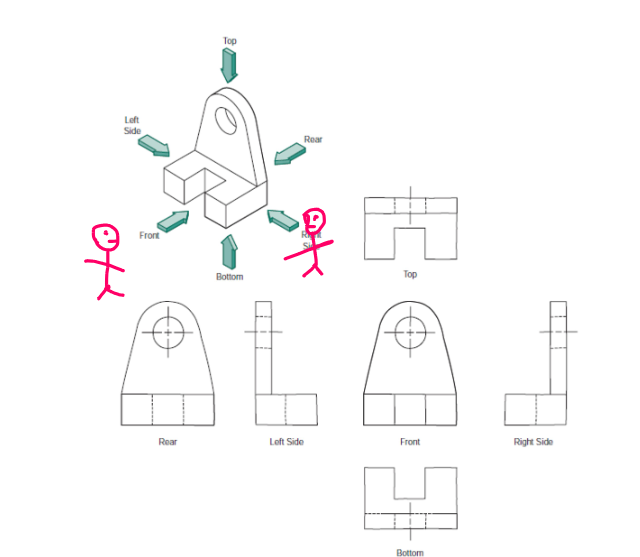
Multiview Drawing
Based on parallel projections. It’s application is to represent features more accurately than a pictorial view can represent.
In general they should minimize views needed to describe object and avoid repetition
Freehand sketching
Sketching without a tool
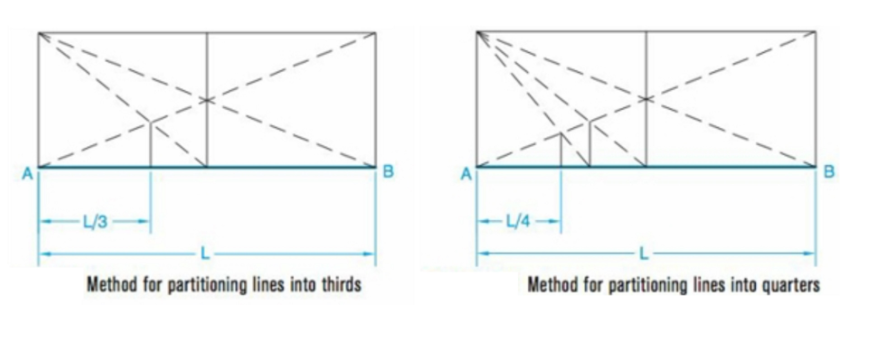
Partitioning Lines
A technique
Contour Sketch
Created by observing the outline of a object. The technique can improve sketching ability
What is Transfer of Depth
Something done by using a 45 degree miter line to do feature alignment with the two depth sides in a Multiview drawing
What are the line conventions?
Visible line
Hidden line
Center line
Dimension & Extension lines
Section lines
Applications of visible lines:
Edge view of a surface
Edge between two intersecting surfaces
Extent of a contoured surface
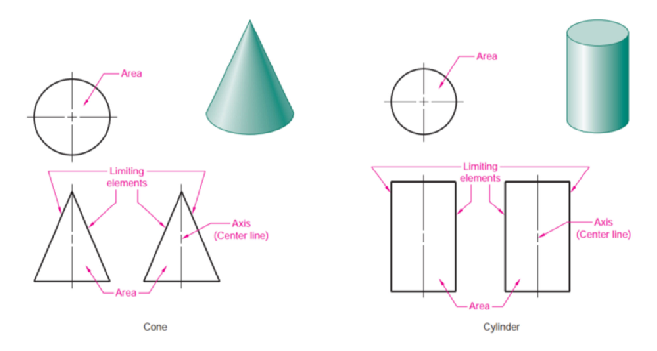
Limiting element
A line that represents the furthest outside of a feature in a curved surface. It is not the boundary between faces. This line is tangent to the curved edge at each end of a cylinder
What are hidden lines used for?
They represent:
a hidden edge of a surface
a hidden change of planes
the hidden extents or limiting extents of a hole
What are center lines used for
To represent the axis of a cylinder or hole.
Note that a circular view would use crossing centerlines
What is the line precedence?
Visible line takes priority over hidden line. Hidden line takes priority over center line
What decisions much be made to determine the best views?
Best position of the object
Front show should show object in its natural, assembled state and be most descriptive
A minimum number of views should be chosen to completely describe the object
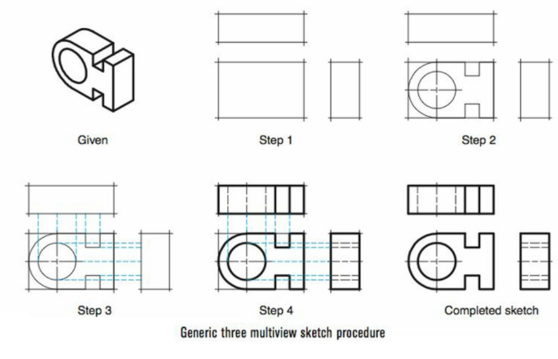
How do you create a Three-View Sketch?
Use light construction line to create properly proportions bounding box views
add front view details
project further details from front views to adjacent views
then go bold starting with curved features
What is foreshortening?
When features get foreshortened due to lines of sight not being perpendicular to a feature
Fundamental Views
True size is shown. This happens when parallel to the plane of projection, hence making it perpendicular to the line of sight. Also is true length when perpendicular to the plane of projection
Normal line
Also known are true-length line. Is parallel to the plane of projection
Normal Face
Also known as principal plane. Happens when parallel to the plane of projection, causing it to be perpendicular to the line of sight. Therefore, it is true size
Inclined Face
It will be a normal surface when rotated about a line parallel to a principal axis. It will be perpendicular to one principal plane the inclined to other views. They will appear foreshortened
Oblique Face
A planar surface that has been rotated about two principle axes. It will be inclined in all principal projections planes. Therefore, none will show the true size.
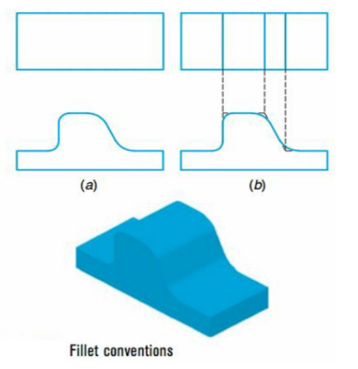
What are fillets/rounds? What do they do?
They connect two object with a tangent arc in 2D and create a round transition between adjacent faces of a 3D solid
Fillets: Inside corner
Round: outside corner
What can happen when drawing fillets or rounds
They can be ignored and still drawn as edges despite being theoretically not being drawing since there’s no change in plane
Intersections and Tangency
When plane surfaces intersects with a curved surface, a line can be drawn with respect to intersecting surfaces
When tangent, no edge is shown
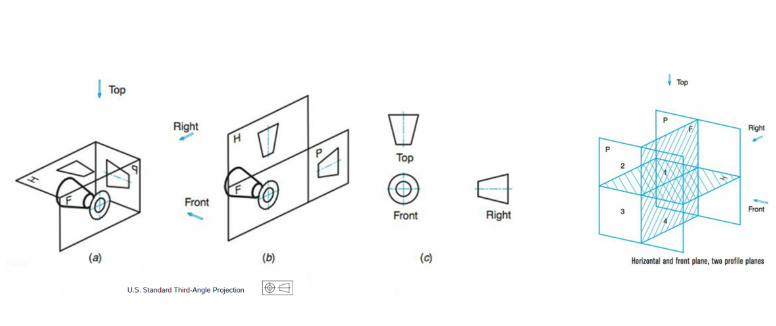
Third angle projection
Standard in use and Canada when box is drawn from third quadrant.
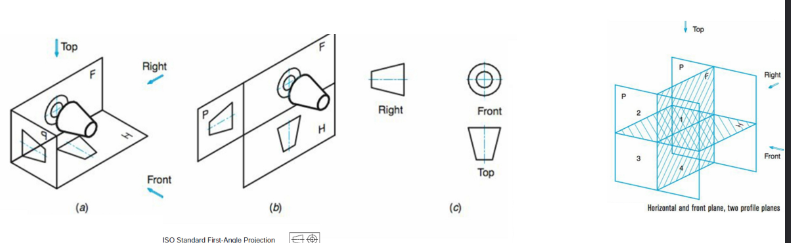
First angle projection
Standard in Europe and other countries. Object is drawn from the first quadrant
What is visualization?
The process by which a shape information on a drawing is translated so that the viewer can understand the objects’ representation.
It should be possible to create a 3D drawing from a Multiview drawing
What are visualization techniques?
Study completed Multiviews of completed objects
Create physical model from clay, wax or Styrofoam
Decompose complex geometries into simple geometries
Study or adjacent areas
similar shaped surfaces
Surface labeling
Vortex labeling
solving missing-line problems
solving missing view problems
Sketching well proportions pictorial view of the object
What do adjacent areas represent?
surfaces are different levels
inclined or oblique surfaces
cylindrical surfaces
combination of the above
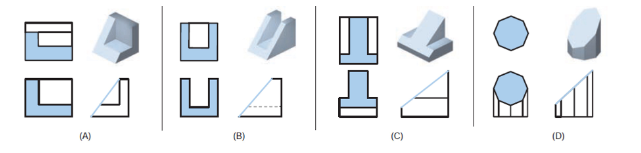
Explain the similar shaped surfaces technique
Similar shaped surfaces retain their basic configuration in all views except when viewed on the edge
Explain vortex labeling
In addition to labeling surfaces, vertices of complicated surfaces should be labeled and then projected
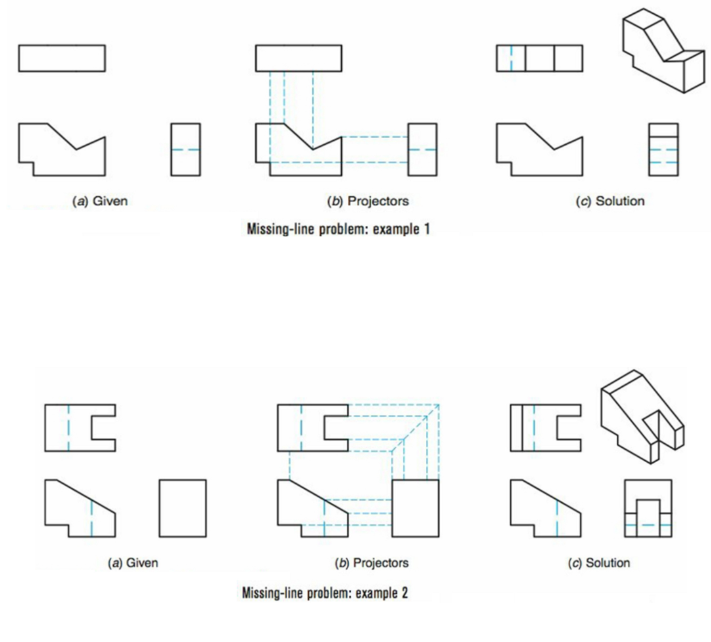
What is solving missing-line problems?
Accomplished by identifying edges in one view that don’t appear in an adjacent or related view. When projecting the location of these edges, locations of missing lines can be identified
What is solving missing-view problems?
When trying to find a missing third view, edge features that are provided can be projected to help find the missing view
How do you sketch a well-proportioned pictorial view of an object
First sketch the object’s bounding box, then use given views to identify prominent object features. These features can be added to the pictorial sketch
What is a similarity and a difference between isometric drawing and isometric projection
The same methods is used for drawing both. However isometric drawing has actual dimensions while isometric projection dimensions should be multiplied by 0.8
What is the theory of isonomic projection?
The object gets rotated 45 degrees about the vertical access, then it’s tilted forward until the body diagonal appears as a point in the front views.
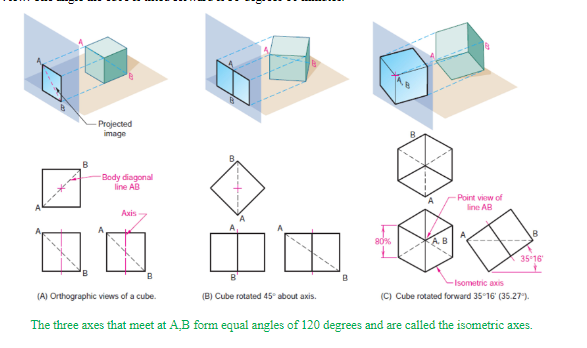
Isometric lines
A line parallel to a leg in the isometric axis. True-length distance can be measured along these lines
Isometric Planes
Anything parallel to the cube faces
What are the standards for hidden lines, center lines, and dimensions in isometric drawing.
Hidden lines are typically omitted unless absolutely necessary to describe the object. Center lines are typically not shown since isometric drawings communicate to non-technical people.
What is dimensioning?
The process of adding size information to a drawing.
What is the dimensioning criteria?
Only use dimensions needed to completely define a part
Dimensioned part should not be subject to different interpretations
Don’t specify manufacturing methods that will be used in building a part
Arrange dimensions for optimum readability
Dimensions should appear in true profile views and refer to visible object edges
List dimensioning terminology
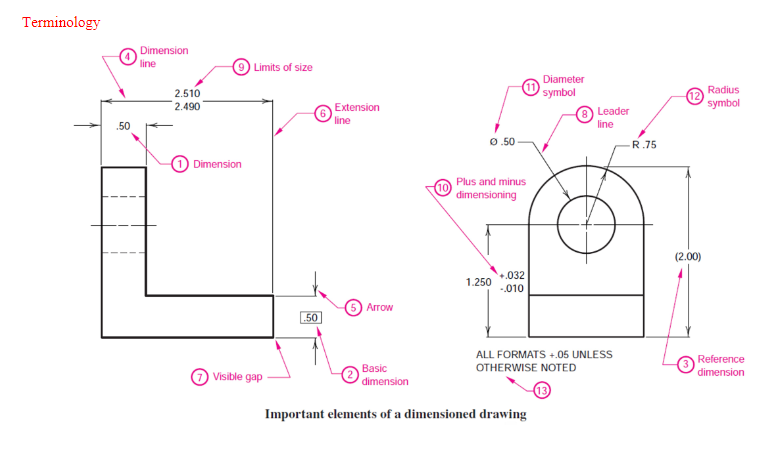
Group dimensions
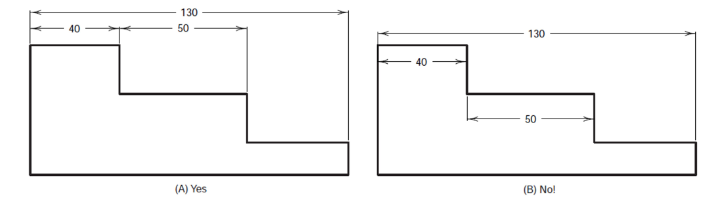
Dimensions are grouped in a drawing. Object lines should not be used as extension lines
What is the purpose of section view?
When there’s complex parts containing several internal features. Often that’s apparent when those details show up as hidden lines with Multiview projection.
What are types of section views?
Full section: completely through and object
half section: halfway through an object
offset section: ben to go through features which aren’t aligned
broken-out section: Go through part of the object
What is an application of auxiliary views
Represent inclined features and show true size for something not normal to observer
Auxiliary view conventions
hidden lines are typically ommited
Letters “TS” are added to state it’s undistorted
What is the purpose of displaying results
communication
exploration
storage
calculation
decoration
What are two ways of displaying informatoin
Tables: For numerical data and small data sets
Figures: illustrations that aren’t table. They’re for large datasets
Time series
Used to display data sets with real variability
Graphical integrity
When the visual representation of data is consistent with the numerical representation
Misleading figures
Sometimes a graph is presented in a way that is confusing because it’s not in a standard, expected format. An example is making the graph upside-down
Lie factor
A way to describe the amount of distortion in a graph. This is associated with graphical integrity
Design and Data variation. What is appropriate
There should never be more design variation than data variation. The reason is because it can lead to ambiguity and deception
What is the role of context in graphical integrity?
Enables it to be truthful and revealing
Data density
Note that eye can do a lot of distinctions in a small area
Data density = number of entries/area of graph
Data-ink
A ratio of how much data there is to ink.
Ideally the ratio should be maximized to not use redundant ink
Chart Junk
When the interior decoration of graphics doesn’t tell the reader anything new. Often related to low data-ink ratio
Moiré Vibration
Is a form of chart junk which is an optical effect creating a shake-illusion
The Grid
When there’s one or more sedate graphical elements. It should be suppressed so that its presence doesn’t compete with data
Duck
When the decoration dominates data
Self-Promoting graphics
When there’s an additional fake perspective. It’s a form of chart junk
Ideal graphic presentation
use sans serif typeface
Have sufficiently large font
Don’t do all capital letters
Do light against dark background or vise-versa
Keep text blocks to only be 2 or less lines
Lists should only have 2-4 items and listed items should be parallel
Have a lot of white space
Limit numbers on a slide