bis 2b mt 02
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/206
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
1
New cards
what factors influences population growth?
# of births, # of deaths, # of immigrants, # of emigrants
2
New cards
for population size, what does it mean when r > 0?
population is increasing over time
3
New cards
for population size, what does it mean when r = 0?
population remains the same
4
New cards
for population size, what does it mean when r < 0?
population is decreasing
5
New cards
what is one method for estimating population size?
mark/recapture
6
New cards
what happens in mark/recapture?
mark: capture some individuals and visually tag or mark them
recapture: release the ind. into the wild, wait long enough for them to evenly spread through the population, and then, recapture a second set of ind. to see how many are marked.
recapture: release the ind. into the wild, wait long enough for them to evenly spread through the population, and then, recapture a second set of ind. to see how many are marked.
7
New cards
R/C = M/N, where:
* N = total pop. size
* M = the # of caught, marked, and released (1st sampling)
* C = # caught in second sampling
* R = the # of marked ind. recaptured in 2nd sampling
* N = total pop. size
* M = the # of caught, marked, and released (1st sampling)
* C = # caught in second sampling
* R = the # of marked ind. recaptured in 2nd sampling
the ratio of tagged ind. in our second sampling should equal # of tagged ind. in FULL population
8
New cards
can population size increase exponentially forever? why or why not?
no because at some point, some kind of factor will limit size of popuation
9
New cards
density independent controls
factors (usually abiotic) affecting pop. size that DO NOT depend on the # of organisms in the population
* factors affect pop. in the same way, regardless of how many ind. there are
* factors affect pop. in the same way, regardless of how many ind. there are
10
New cards
density dependent controls
factors (usually biotic) affecting pop. size that DO depend on the number of organisms in the population
* has a stronger impact on pop., when there are more individuals in pop.
* has a stronger impact on pop., when there are more individuals in pop.
11
New cards
alcohol is produced as a byproduct of fermentation of sugar by yeast. the maximum ABV% that a solution can achieve is \~15% because yeast cannot survive in higher concentrations of waste products. this is an example of…
a. density dependent control
b. density independent control
a. density dependent control
b. density independent control
a. density dependent control
* this is because more individuals → more waste
* this is because more individuals → more waste
12
New cards
wildfire is an example of…
a. density independent control
b. density dependent control
a. density independent control
b. density dependent control
b. density dependent control
* this is because we are talking about the species that are the fuel. the answer would be ‘a’ if we are referencing the species that are not the fuel.
* this is because we are talking about the species that are the fuel. the answer would be ‘a’ if we are referencing the species that are not the fuel.
13
New cards
when N_0 is large, (K - N_0) = 0 (approx.), (K - N_0)/K = 0 (approx) and…
growth is slow
14
New cards
when N_0 is small, (K - N_0) = K (approx.), (K - N_0)/K = 1 (approx) and…
growth is *mostly* exponential
15
New cards
survivorship
the proportion of individuals surviving from birth to age class *x*, represented by *l_x*
16
New cards
fecundity
the avg. # of offspring an individual will produce during age class *x*, represented by *m_x*
* tells us how much reproduction is occurring __per__ individual
* not how many babies were produced per individual
* tells us how much reproduction is occurring __per__ individual
* not how many babies were produced per individual
17
New cards
R_0
the net reproductive rate; the mean # of offspring produced per individual across their lifetime
* represented by Σ*lxmx* (a.k.a. survivorship x fecundity)
* represented by Σ*lxmx* (a.k.a. survivorship x fecundity)
18
New cards
G
generation time; average age of parents across all offspring produced
* average age of production
* G = *xl_xm_x* (for ind.)
* average age of production
* G = *xl_xm_x* (for ind.)
19
New cards
what is r in terms of R_0 and G?
r is approx. \[ln(R_0)\]/G
20
New cards
R_0 and r are (positively/negatively/not) related
positively
21
New cards
if R_0 = 1
the population is not changing
* each ind. only has ONE offspring, replacing itself in next gen.
* each ind. only has ONE offspring, replacing itself in next gen.
22
New cards
higher survivorship at large juvenile stages leads to
higher reprodctive power later on
23
New cards
r is correlated with the number of individuals at the
reproductive age
24
New cards
if there is a large proportion of ind. at reproductive ages,
large r
25
New cards
how could the fossil record provide evidence for gradualism?
gradual difference in the fossils over time
26
New cards
descent with modification produces
homologous traits
27
New cards
homologous traits
traits that are similar in different organisms because they were inherited from common ancestor
28
New cards
convergent evolution produces
analogous traits
29
New cards
analogous traits
traits similar in different organisms because of similar selective pressure
30
New cards
arew wings analogous or homologous?
analagous
* common ancestor of all mammals did not have wings as not every mammal has wings
* common ancestor of all mammals did not have wings as not every mammal has wings
31
New cards
which of the following evolves (in scienctific terms)?
a. some populations
b. all populations
a. some populations
b. all populations
b. all populations - evolving at all times
32
New cards
evolution
genetic change over time
33
New cards
adaptation
a type of evolution that occurs through natural selection
34
New cards
microevolution (within ____)
species; changes in genetic variants over generations
35
New cards
macroevolution
speciation; btwn. species; accumulation of many microevolutionary changes, such that new groups arise
36
New cards
4 conditions for natural selection
reproduction, variation, inheritance, success
\
\
37
New cards
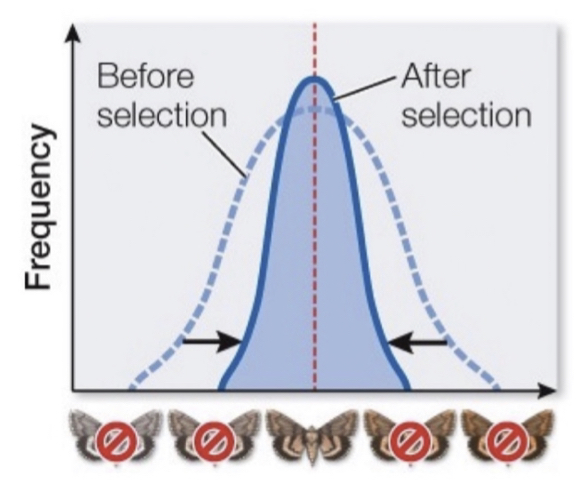
what kind of selection is this?
stabilizing selection
38
New cards
Stabilizing selection
Phenotypes nearest the mean have the highest fitness. The mean stays the same and variation is reduced.
39
New cards
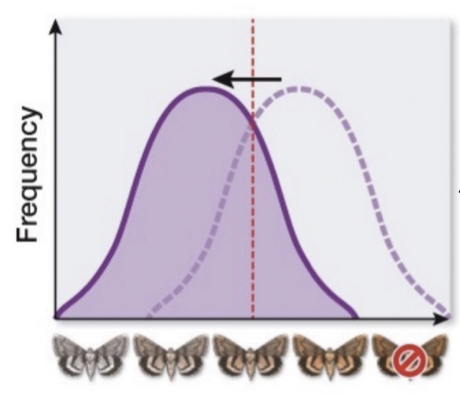
what kind of selection is shown below?
Directional selection
40
New cards
Directional selection
Phenotypes at one extreme have the highest fitness, and the mean trends toward that extreme.
41
New cards
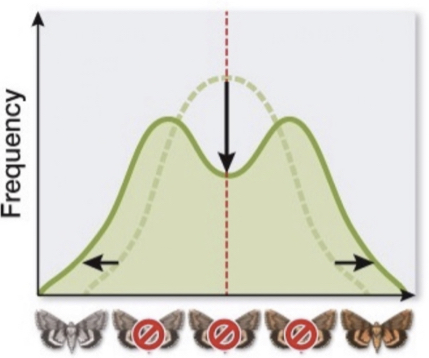
What kind of selection is shown below?
Disruptive (diversifying) selection
42
New cards
Disruptive (diversifying) selection
Phenotypes at both extremes have higher fitness than the mean. variation is increased, and bimodal pattern emerges
* intermediate have lowest fitness
* intermediate have lowest fitness
43
New cards
Balancing selection is also known as
Frequency dependent selection
44
New cards
Balancing selection maintains
variation in a population
45
New cards
Frequency-dependent selection
Rarer phenotypes have the highest fitness. frequency of a given phenotype oscillates.
* will always see oscillation over time
* variation is maintained
* will always see oscillation over time
* variation is maintained
46
New cards
Sexual selection is selection driven by
* Competition for mates
* mate choice
* mate choice
47
New cards
Altruism
A behaviour that reduces individual fitness and increases the fitness of other individuals
48
New cards
Kin selection
Favors behaviors that increase the reproductive success of relatives
49
New cards
Inclusive fitness
The sum of an individual's own fitness, and its contribution to the duchess success/survival of relatives
50
New cards
hamilton’s rule
rB = C, where:
* r = coefficient of relatedness: the fraction of genes shared between relatives
* B = benefit to relative: the increase in offspring for the relative
* C = cost to the altruist: the loss in offspring for the altruist
* r = coefficient of relatedness: the fraction of genes shared between relatives
* B = benefit to relative: the increase in offspring for the relative
* C = cost to the altruist: the loss in offspring for the altruist
51
New cards
reciprocal altruism
when the altruist has a reasonable expectation that the sacrifice will be reciprocated in the future
* need to have repeated interactions with the same individual
* need to have repeated interactions with the same individual
52
New cards
What are constraints of natural selection?
laws of physics, evolutionary history, trade offs, lack of variation
53
New cards
At what scale do human differ in their genetic make up?
A. Alleles
B. Genes
C. Chromosomes
D. Genomes
A. Alleles
B. Genes
C. Chromosomes
D. Genomes
A. Alleles
54
New cards
Alleles
Different versions of a gene
55
New cards
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a particular trait
56
New cards
Chromosomes
A long strand of DNA containing hundreds to thousands of genes
57
New cards
How many pairs of chromosomes does a person have?
23
58
New cards
Genome
All the genetic material an individual carries
59
New cards
Nucleotides
Organic molecules that make up DNA and RNA
60
New cards
what are the possible nucleotides in DNA?
adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
61
New cards
What are the possible nucleotides in RNA?
adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine
62
New cards
what are the nucleotide pairings in DNA?
thymine pairs with adenine, and cytosine pairs with guanine
63
New cards
What are the nucleotide pairings in RNA?
Uracil pairs with adenine, and cytosine pairs with guanine
64
New cards
The Central dogma
The flow in of genetic information through the two-step process of transcription (DNA → RNA) and translation (RNA → proteins)
65
New cards
DNA is (__) stranded
Double
66
New cards
The sense strand and the antisense strand should look the (__) except the (__)
same; Us and Ts
67
New cards
what happens to the antisense strand?
It gets transcribed into RNA
68
New cards
What happens during translation, and where does it occur?
RNA → protein, occurs in the cytoplasm with the help of tRNA
69
New cards
In translation, the anticodon
binds in to the mRNA and adds their amino acid
70
New cards
the anticodon should be (__) to the mRNA
complementary
71
New cards
The genetic code won’t work well if:
* there is no start/stop codon
* if the stop codon is too early
* if the stop codon is too early
72
New cards
Primary protein structure
Sequence of a chain of amino acids
73
New cards
Secondary protein structure
Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes the amino acids to fold into a repeating pattern
74
New cards
tertiary protein structure
3D Folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
75
New cards
Quaternary protein structure
Protein consisting of more than one amino acid chain
76
New cards
Different alleles produce
Different phenotypes of the same trait
77
New cards
Different phenotypes can result from the
* Amount of mRNA transcribed (produce more mRNA, could produce more protein → different phenotype)
* different amino acid sequences
* different amino acid sequences
78
New cards
What are three of types mutations?
* substitution: a nucleotide is exchanged
* insertion: a nucleotide is added
* deletion: a nucleotide is removed
* insertion: a nucleotide is added
* deletion: a nucleotide is removed
79
New cards
Mutations are more likely to have an effect if they happen in
Protein coding regions
80
New cards
The E. coli genome is 87.8% protein coding (compared to 1.5% in humans). Which of the following would you expect to be true?
A. Mutations are mortar likely to be beneficial (increase fitness) in humans.
B. Mutations are more likely to be deleterious (causes lower fitness) in E. coli.
C. There are probably more mutations in humans
D. there are probably more mutations in E. coli
\
A. Mutations are mortar likely to be beneficial (increase fitness) in humans.
B. Mutations are more likely to be deleterious (causes lower fitness) in E. coli.
C. There are probably more mutations in humans
D. there are probably more mutations in E. coli
\
B. Mutations are more likely to be deleterious (causes lower fitness) in E. coli.
81
New cards
Particulate model of inheritance
Traits passed down as discrete units rather than being blended together
82
New cards
Law of segregation
When any individual produces gametes, the 2 copies of the genes separate so that each gamete receives only one copy
83
New cards
Law of independent assortment
Alleles of different genes assort independently of one another during gamete formation
* what happens to one gene doesn’t affect what happens to another gene
* what happens to one gene doesn’t affect what happens to another gene
84
New cards
Diploid
Having 2 copies of each chromosome (2n)
85
New cards
Meiosis is used for
Making gametes
86
New cards
What is the result of meiosis 1?
2 cells containing duplicates of 1 chromosome
87
New cards
What is the result of meiosis 2?
4 cello containing 1 chromosome each
88
New cards
What are the 3 types of dominance?
* complete dominance
* incomplete dominance
* codominance
* incomplete dominance
* codominance
89
New cards
Complete dominance
A single dominant allele produces the dominant phenotype. the homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes have the same phenotype
90
New cards
Incomplete dominance
The heterozygote phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes
91
New cards
Codominance
The heterozygote shows both the homozygous phenotypes
92
New cards
Do dominant traits skip generations?
No.
93
New cards
Recombination
The rearrangement of genetic material, especially by crossing over in chromosomes or by artificial joining of segments of DNA from different organisms
* occurs when you have two genes on the same chromosome
* occurs when you have two genes on the same chromosome
94
New cards
Is recombination more likely to occur between 2 genes that are closer together or farther apart?
Farther apart
95
New cards
The likelihood of recombination between two genes is proportional to
The distance between the 2 genes (on the chromosomes)
96
New cards
If you have two linked genes, the parental types (same chromosomes as parents) will always
Have more offspring
offspring than those that require recombination
offspring than those that require recombination
97
New cards
Phenotype of offspring is entirely determined by
What kind of gameto they get from parent
98
New cards
Linkage mapping
Determining the recombination frequency for numerous genes allows us to map each gene's on the chromosome
99
New cards
One gene affects () characteristic(s)
Multiple
100
New cards
The ‘frizzle’ phenotype in chickens is determined by a a single gene (the F gene). Chickens with the frizzle gene also there's to have increased metabolism. What are potential explanations for this phenomenon?
A. The F gene and the metabolism gene(s) must be on different chromosomes.
B. The F gene and the metabolism gene(s) are very close together on the same chromosome
C. Pleiotropy
A. The F gene and the metabolism gene(s) must be on different chromosomes.
B. The F gene and the metabolism gene(s) are very close together on the same chromosome
C. Pleiotropy
B. The F gene and the metabolism gene(s) are very close together on the same chromosome