Global 10 Exam
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Scientific revolution
1500-1700 scholars started to question their beliefs about the world and base their conclusions on observation and reason rather than spiritual belief
The Scientific Revolution directly challenged…
Catholic Church
Scientist:Copernicus
Accomplishments: heliocentric theory – Sun center of the solar system NOT Earth
Scientist: Galileo
Accomplishments: telescope
Scientist: Newton
Accomplishments: Gravity
How did the scientific revolution change the way Europeans looked at the world today?
Find answers to the natural world throughobservation and experimentation. Started to question teachings of the Church.
How did the scientific revolution lead to the enlightenment?
New ways of thinking using reason and logic applied to other parts of society (GOVERNMENT)
Enduring issues
Ideas and Beliefs
Impact of technology
Conflict
Power
Inequality
Absolute monarch
system of government where one person (King/Queen) has absolute control over all aspect of life
Key absolute monarchs:
Akbar- India
CharlesV- Spain
Philip II- Spain
Thomas Hobbes
Philosopher, pro-absolute monarch
Absolute monarch justified their right to rule through their belief of divine right
Divine right-Belief that authority to rule came directly from God
Louis XIV, France
Palace of Versailles ,Centralized Government – all power under him
Peter the Great, Russia
Westernization and Modernization
Tried to gain warm water ports
Catherine the great, Russia
Enlightened Despot
Advantages of Absolutism
Stability in Government , Clear hereditary, lineage, one person able to make decisions quickly
Disadvantages of Absolutism
No restrictions on power- absolute control, Needs of the people neglected, Lack of rights for citizens
Where did the enlightenment happen?
Western Europe
When did the enlightenment happen?
Mid 1600s-1700s
Enlightenment
Philosopher’s applied logic and reason to understand the role of society and government
The scientific revolution influenced…
The enlightenment
Enlightenment thinker:John Locke
Life liberty property
Enlightenment thinker: Montesquieu
3 syllables=3 branches, separation of power
Enlightenment thinker: Voltaire
Voice of freedom, freedom of speech
Enlightenment thinker: Rousseau
RouSOcial contract, follow laws made by government
Enlightenment thinker: Mary Wollstonecraft
Women’s equality
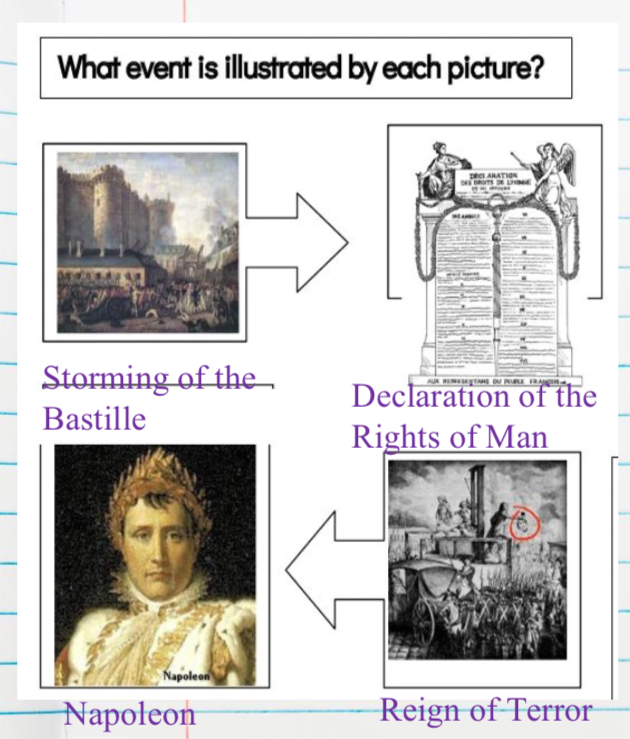
Just remember this
Just remember this
first estate
Clergy
Second estate
Nobles
Third estate
Commoners/bourgeoise