[APK2100C] Chapter 15
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Autonomic Nervous System
- System of motor neurons that innervates smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and body glands
- Involuntary control
- Autonomic activation or inhibition of viscera
Describe the PNS structure of the Somatic Nervous System.
- Single neuron from the CNS to effector organs
- Consists of a heavily myelinated axon
How many CNS cell bodies do the Parasympathetic Nervous System have?
1
Cranial and Sacral Outflow of the Parasympathetic Ganglia
- Formation of cell bodies for the preganglionic neurons
- 4 cranial nerves make up the cranial outflow
- Sacral spinal nerves make up the sacral outflow
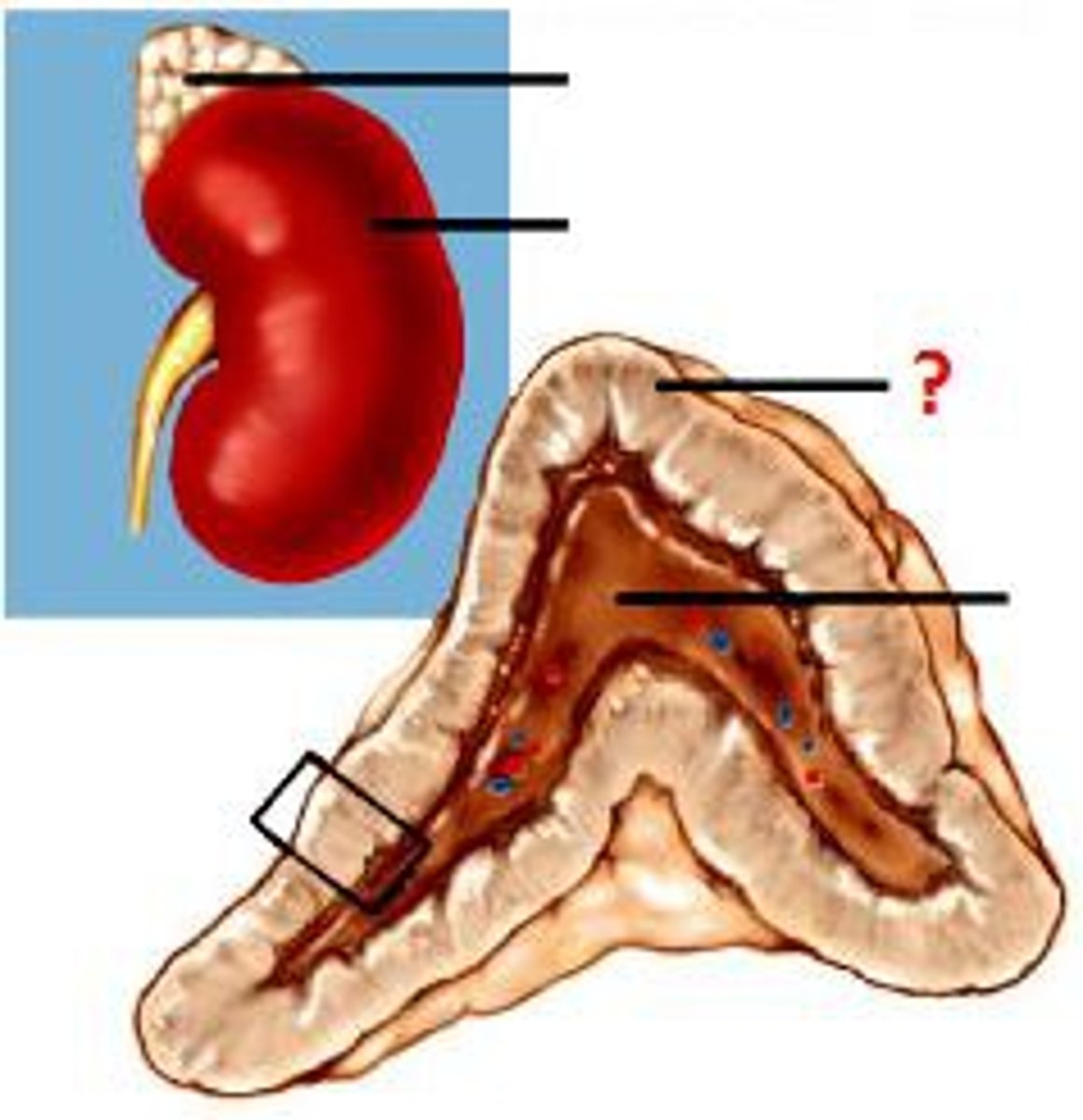
Adrenal Medulla
- Inner pores of the adrenal gland that can secrete both epinephrine (85%) and norepinephrine (15%)
- Innervated by the sympathetic motor neuron
- Stimulated by the preganglionic sympathetic neuron
- One of the paired adrenal (suprarenal) glands located on the superior poles of the kidney
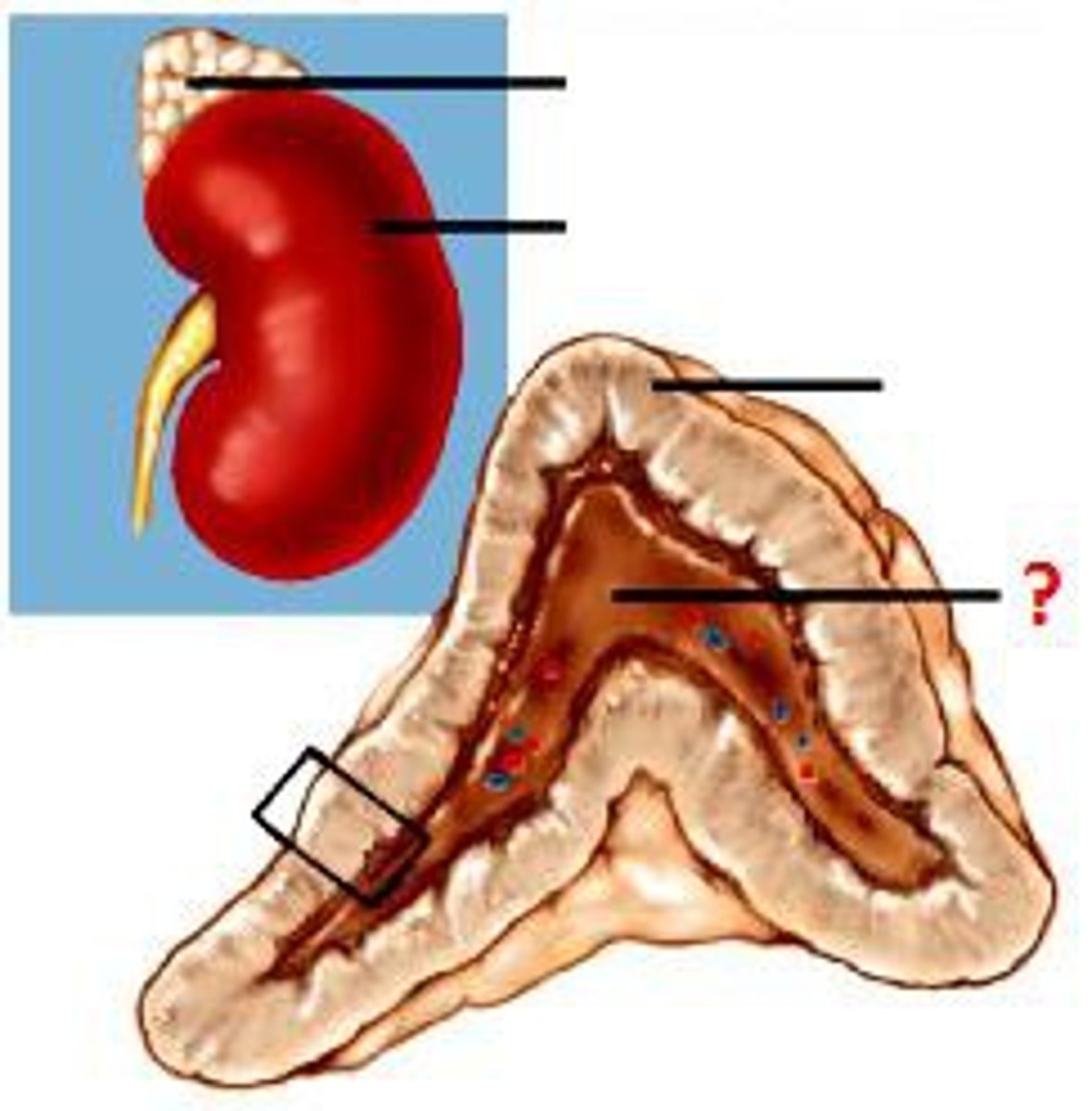
Adrenal Cortex
- Outer section of the adrenal gland
- Secretes steroid hormones
Autonomic Tone
- "How much sympathetic and parasympathetic activity can be going on in any given organ"
- Normal background rate of activity that represents a BALANCE of the 2 systems according to the body's changing needs
- Balance between stimulatory and inhibitory effects
Ex: Parasympathetic system decreases heart rate, while sympathetic system increases heart rate.
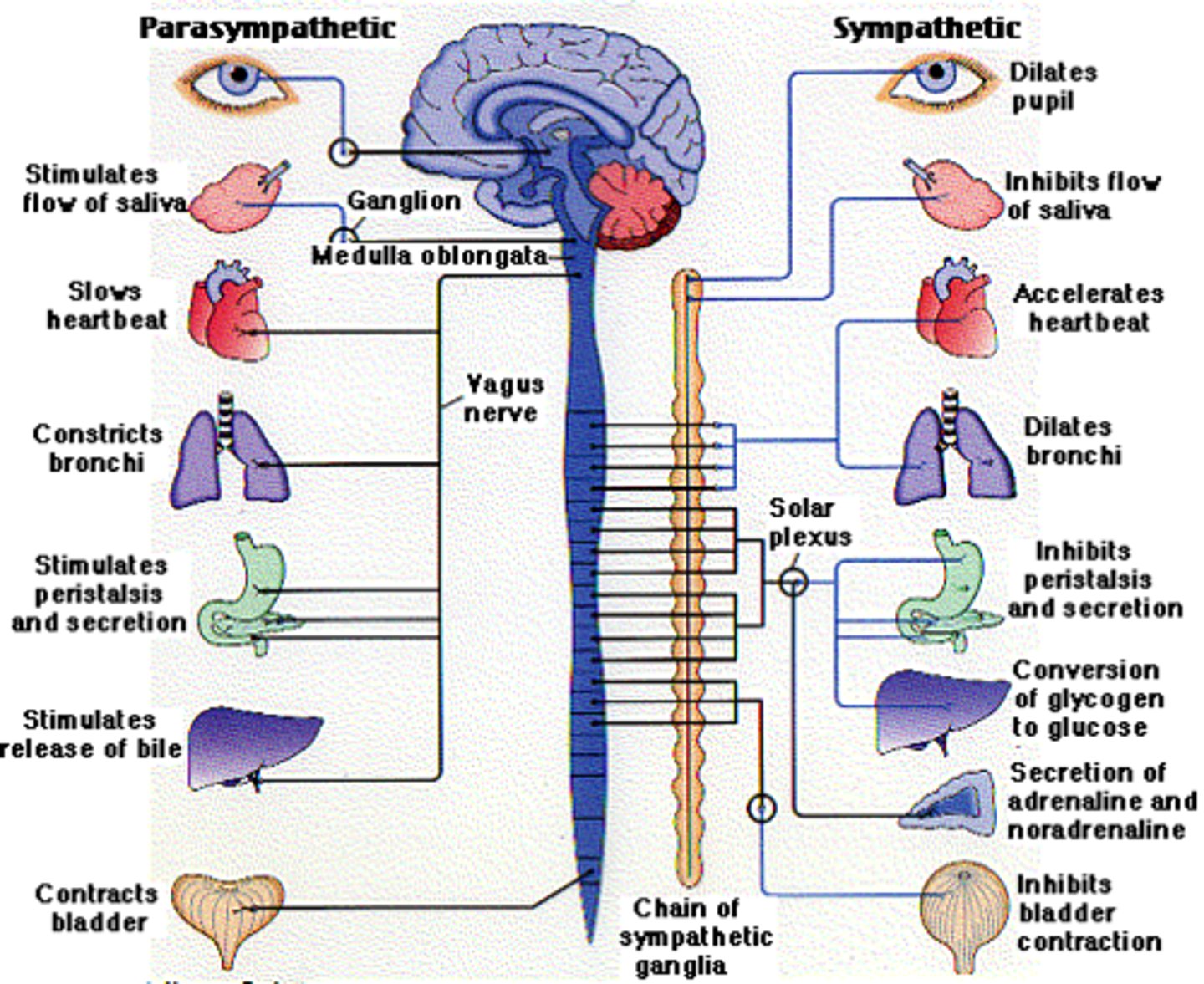
Which organs are innervated by ONLY the sympathetic nerves?
(1) Skin
(2) Liver
(3) Adrenal Gland
What types of cells self-generate electrical signals for the heart rate?
Pacemaker cells
How do vagal nerves and sympathetic chains/nerves affect heart rate when paired up with pacemaker cells?
- Vagal nerves DECREASE heart rate
- Sympathetic chains/nerves INCREASE heart rate
What action can be produced by lining the sympathetic nerves along the heart wall?
Increasing the force of cardiac contractions
Intrinsic Rate
Rate at which a pacemaker of the heart normally generates impulses (~100-110 bpm) WITHOUT additional input from parasympathetic + sympathetic nerves
Bronchodilation
Smooth muscles lining the bronchiole RELAX, which allows MORE air in -> Sympathetic
Bronchoconstriction
Smooth muscles lining the bronchiole CONTRACT, which allows LESS air in -> Parasympathetic
Why is the ANS operate like a "stereo" to activate or inhibit viscera?
The ANS never acts as an activator or deactivator for a system. It only adjusts the level of motor output.
2 Divisions of the ANS
(1) Sympathetic
(2) Parasympathetic
Sympathetic Division
- "Fight or Flight"
- Responds to stresses (physical + emotional)
- INCREASES body functions for supporting physical activity
- DECREASES digestive/urinary functions
Parasympathetic Nervous System
- "Rest and Digest"
- Conserves + Restores body energy
- DECREASES body functions for supporting physical activity
- INCREASES digestive/urinary functions
What is a common pattern between the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
Both mainly have opposing functions
How many CNS cell bodies do the Somatic Nervous System have?
1
What neurotransmitter is released at the effector under the Somatic Nervous System?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What effector organs do the Somatic Nervous System affect?
Skeletal muscles
What effect does the Somatic Nervous System induce?
Stimulatory effects (+)
How many CNS cell bodies do the Sympathetic Nervous System have?
2
Describe the PNS structure of the Sympathetic Nervous System.
- 2 neuron chains from the CNS to effector organs
- Both chains consist of short, lightly myelinated preganglionic axons that release ACh into a ganglion or adrenal medulla -> Followed through with a long unmyelinated postganglionic axon or blood vessel that eventually releases its neurotransmitter
What neurotransmitter is released at the effector under the Sympathetic Nervous System?
Norepinephrine (NE) -> Primarily
What effector organs do the Sympathetic Nervous System affect?
Smooth muscle, glands, cardiac muscle
What effect does the Sympathetic Nervous System induce?
Stimulatory (+) or Inhibitory (-)
*Depends on type of neurotransmitter released and receptors on the effector organs
Describe the PNS structure of the Parasympathetic Nervous System.
- 2 neuron chains from the CNS to effector organs
- Long, lightly myelinated preganglionic axon releases ACh at a ganglion and is followed through by a short unmyelinated postganglionic axon to release its neurotransmitter
What neurotransmitter is released at the effector under the Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
What effector organs do the Parasympathetic Nervous System affect?
Smooth muscle, glands, cardiac muscle
What effect does the Parasympathetic Nervous System induce?
Stimulatory (+) or Inhibitory (-)
*Depends on type of neurotransmitter released and receptors on the effector organs
Differences between lengths of preganglionic/postganglionic axons for the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions.
[Sympathetic] SHORT preganglionic axon + LONG postganglionic axon
[Parasympathetic] LONG preganglionic axon + SHORT postganglionic axon
ANS Neurons
- Cell bodies and axons that are found on the VENTRAL side of grey matter
- Contain both preganglionic and postganglionic neurons
Preganglionic Neuron
- Soma located in the CNS
[Sympathetic] Located on the lateral horn of the thoracolumbar spinal cord
[Parasympathetic] Located in the brainstem of sacral spinal cord
Postganglionic Neuron
Soma located in the PNS
Parasympathetic Ganglia
- Also called the "Craniosacral Division of the ANS"
- Contains terminal ganglia that are located close to or within the walls of organs
- Located CLOSE to the effector organs
[CNS to Ganglia] LONG preganglionic axons
[Ganglia to Effector] SHORT preganglionic axons
What are the 4 cranial nerves that make up the cranial outflow of the parasympathetic ganglia?
(1) CN III - Oculomotor
(2) CN VII - Facial
(3) CN IX - Glossopharyngeal
(4) CN X - Vagus
[Parasympathetic Effector] CN III - Oculomotor Nerve
Pupils for pupillary constriction
[Parasympathetic Effector] CN VII - Facial Nerve
Lacrimal gland for tears + Sublingual/Submandibular salivary glands
[Parasympathetic Effector] CN IX - Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Parotid gland
[Parasympathetic Effector] CN X - Vagus Nerve
Visceral organs of the thorax + upper 2/3 of abdomen
*90% of the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers are from here
Sympathetic Ganglia
- Also called the "Thoracolumbar Division of the ANS"
- Contains a paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia
- Located CLOSE to the spinal cord
[Spinal Cord to Ganglia] SHORT preganglionic axons
[Ganglia to Effector] LONG preganglionic axons
Paravertebral Ganglia of the Sympathetic Division
Located on the vertical row to either side of the vertebral column
Prevertebral Ganglia of the Sympathetic Division
Located anterior to the vertebral column on the abdominal aorta