4-Crystallisation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is crystallisation?
Process of transforming a molten silicate magma to a solidified igneous rock
What is the difference between extrusive and intrusive environments?
Extrusive environment e.g. lava at earth’s surface
Intrusive environment e.g. sills within crust
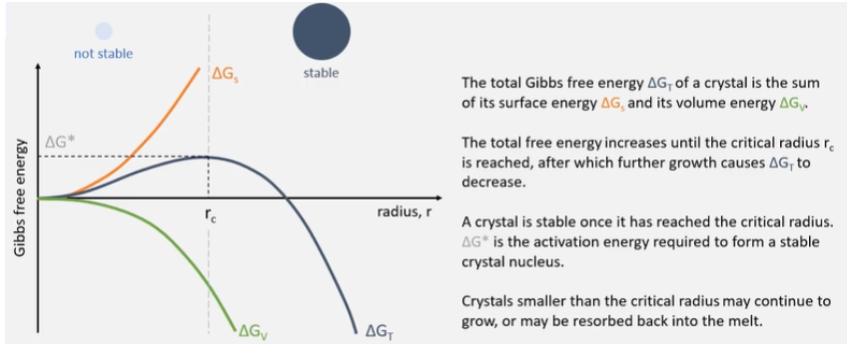
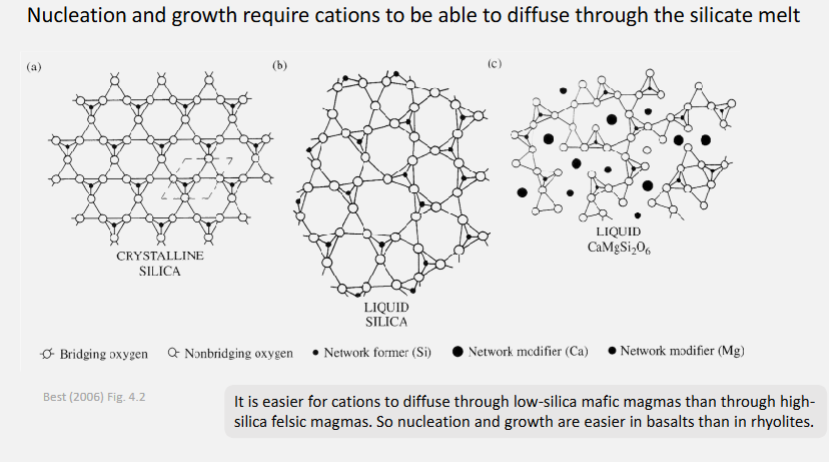
What is meant by nucleation?
Formation of a stable new crystal.
After reach rc, to minimise free energy it continues to grow, nucleation event occurred. Needs to reach a size whereby its continued growth will lower its Gibbs free energy.
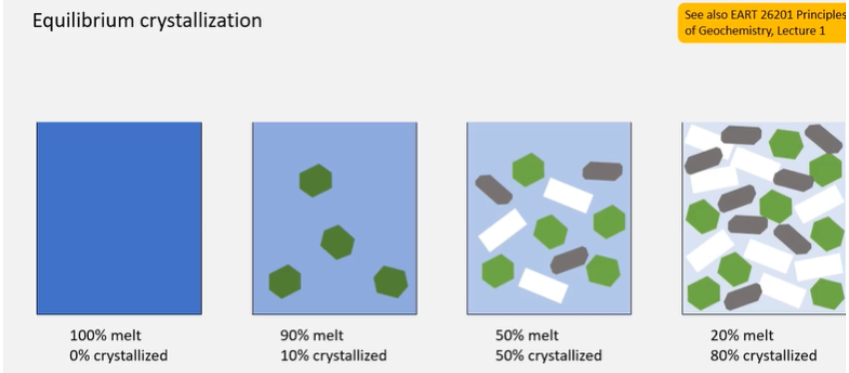
What is equilibrium crystallisation?
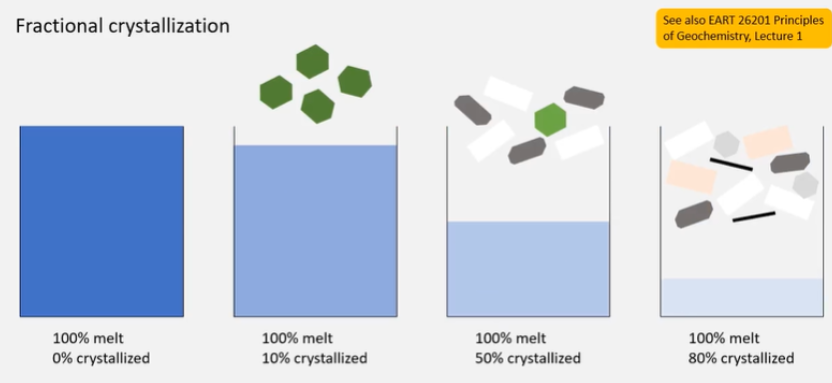
What is fractional crystallisation?
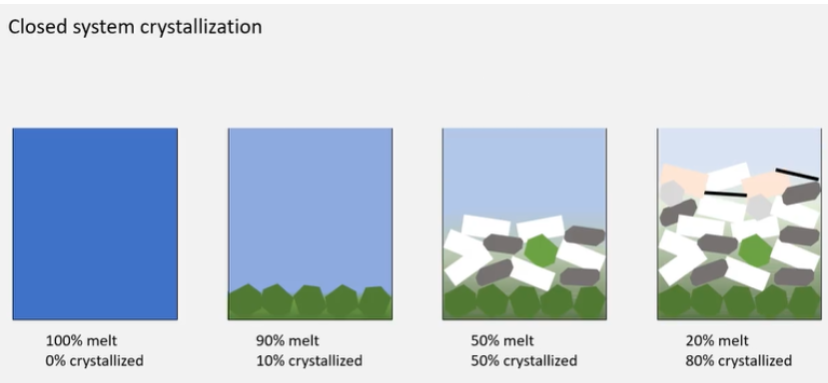
What is closed system crystallisation?
e.g. in large mafic intrusions - large melt injected, system is closed, crystals sink to form cumulate piles, limited crystal exchange. Bulk composition is same.
What is Bowen’s reaction series?
Olivine crystallises first.
Tells us which minerals are likely to form together. e.g. never get olivine with quartz, biotite or amphibole
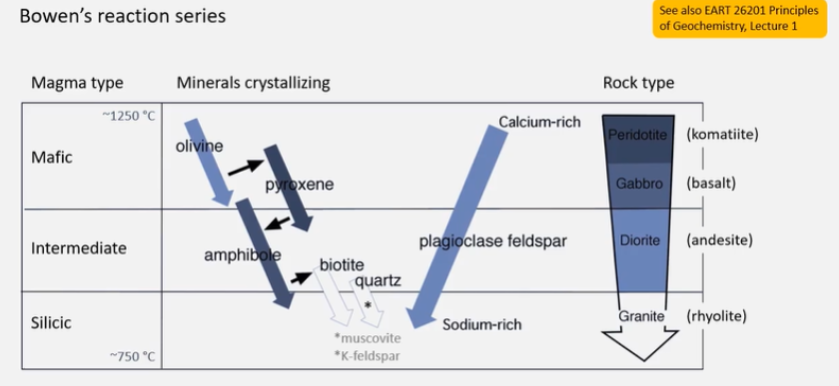
Fractional crystallisation, remove the solid, get specific compositions.
How do we describe the grain size and colour index of igneous rocks?
Groundmass crystals, smallest crystals, tell us about the final stage of cooling.

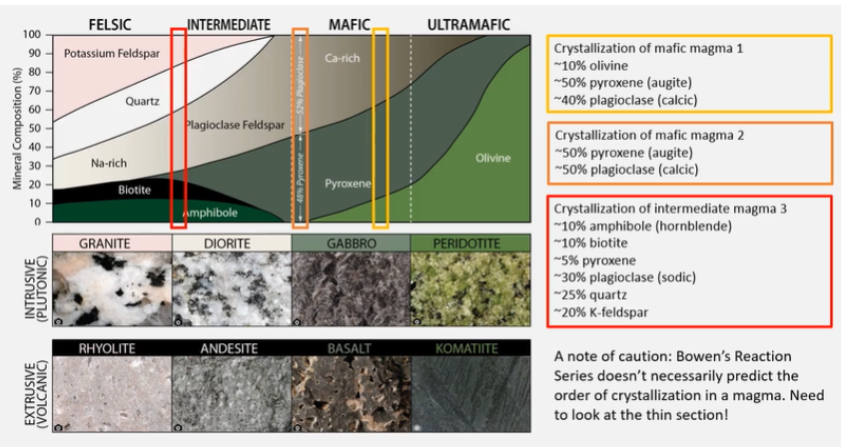
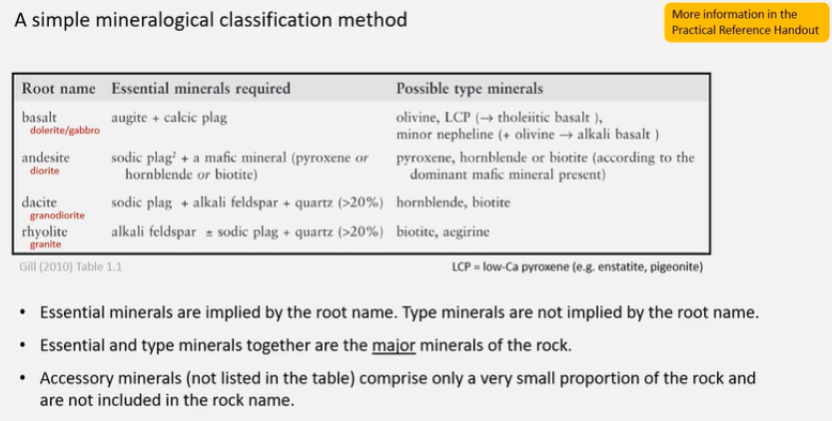
State the essential minerals found in common igneous rock types: basalt/gabbro, andesite/diorite, rhyolite/granite.
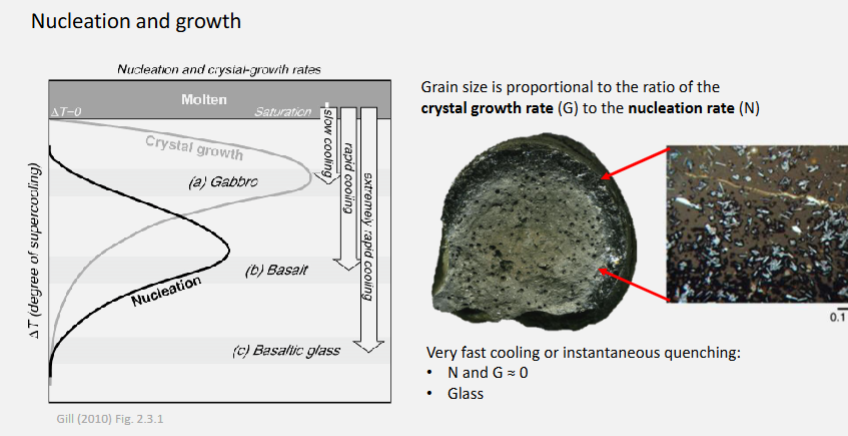
How does temperature affect the size of crystals formed?
Slow cooling forms large crystals.
Fast cooling forms small crystals.
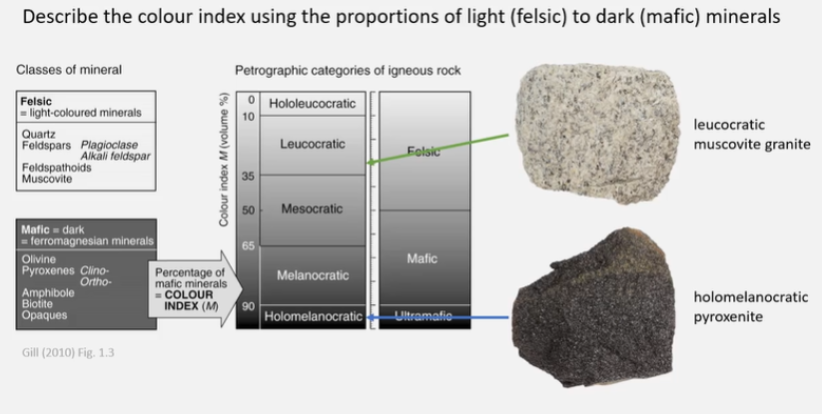
Describe the colour index using the proportions of light (felsic) to dark (mafic) minerals.
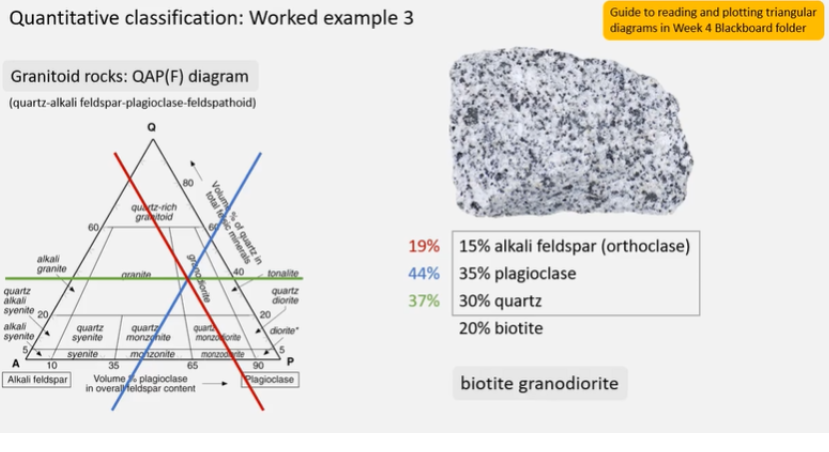
How do we plot rocks of QAP Quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase on the triangle diagram?
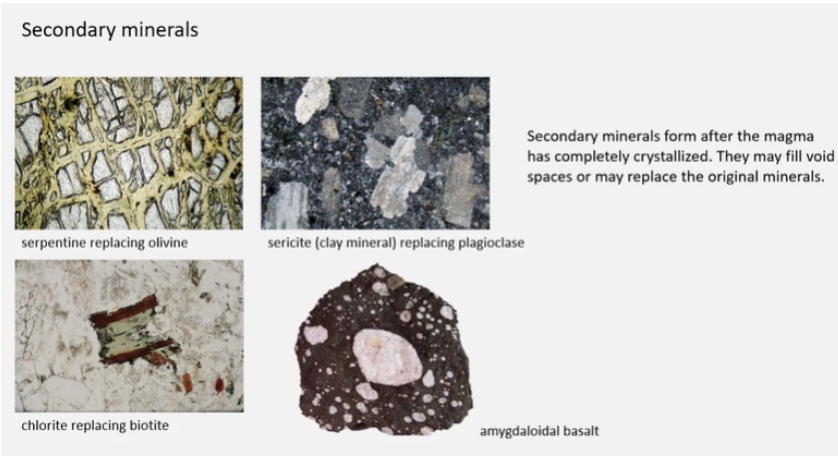
What is difference between primary and secondary minerals?
Primary - crystals formed directly from magma/lava
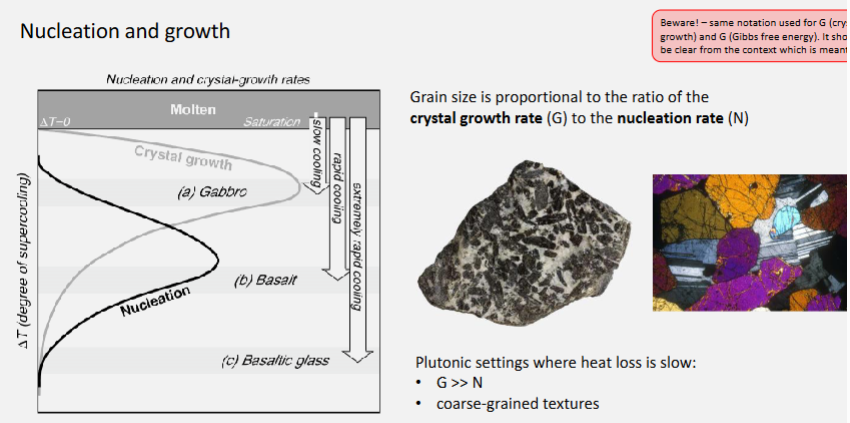
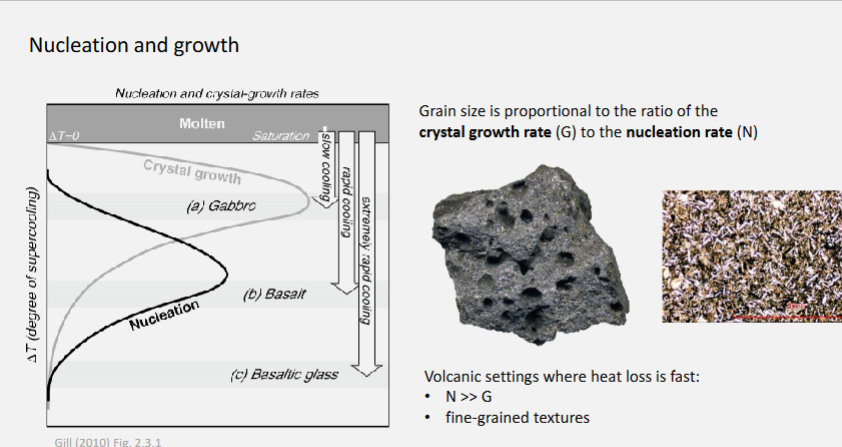
Explain the relationship between cooling rate, nucleation rate, and growth rate.
Cooling rate controls how fast temperature drops.
Nucleation rate (new crystal formation) increases with faster cooling — more crystals start forming.
Growth rate (how fast crystals grow) is higher at moderate cooling but limited if cooling is too fast.
🧊 So:
Slow cooling → few, large crystals (low nucleation, high growth).
Fast cooling → many, small crystals (high nucleation, low growth).
Describe and interpret igneous textures using observations from thin sections
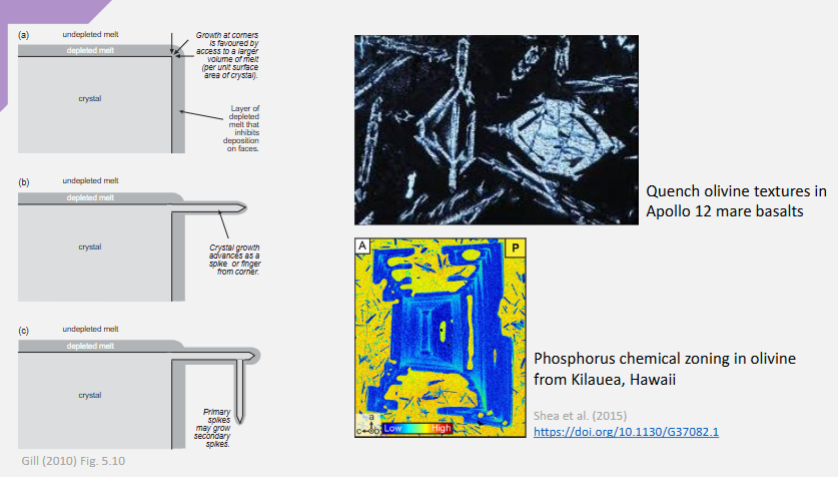
dendritic spikes when cooled
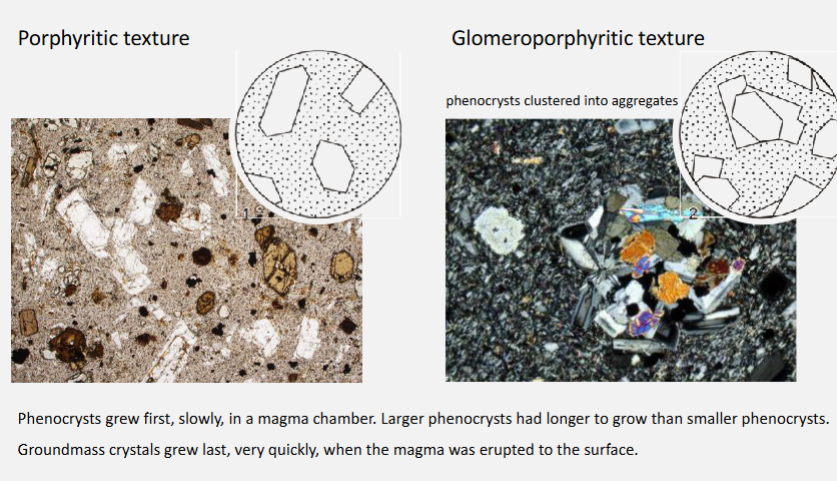
What is porphyritic texture?
Porphyritic texture - igneous rock with bimodal grain size, typical euhedral, shape and habit, grown in a slow cooling, e.g. magma chamber
Porphyritic texture = a rock texture with large crystals (phenocrysts) embedded in a finer-grained groundmass.
Classify of finer grain size, e.g. matrix. So even though big minerals that have grown, if fine-grained
What is a glomeroporphyritic texture?
Glomeroporphyritic texture = a cluster of large crystals (phenocrysts) grouped together in an igneous rock rather than being evenly distributed.
What is a poikilitic texture?
Poikilitic texture = a texture where small crystals are enclosed within larger “host” crystals.
Ophitic texture = special case of poikilitic texture involving plagioclase and clinopyroxene
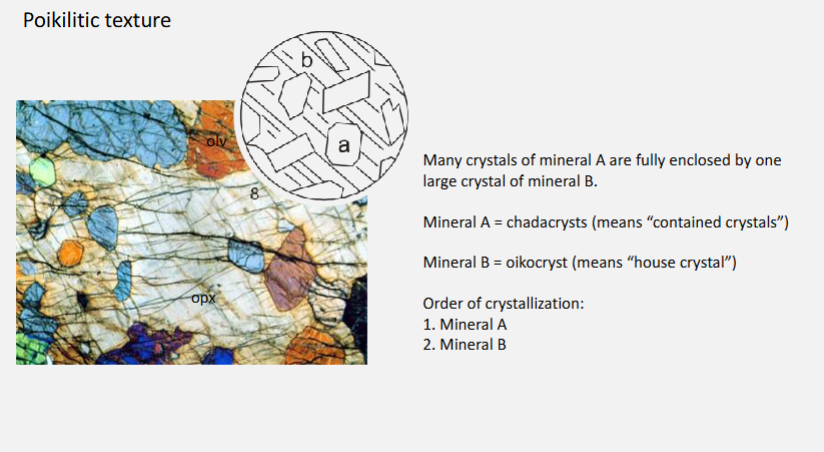
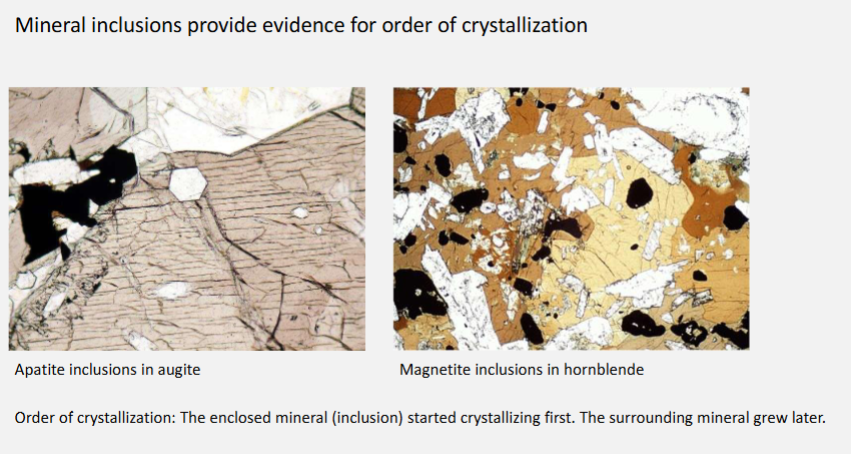
Use textural observations to deduce information about the order of crystallisation
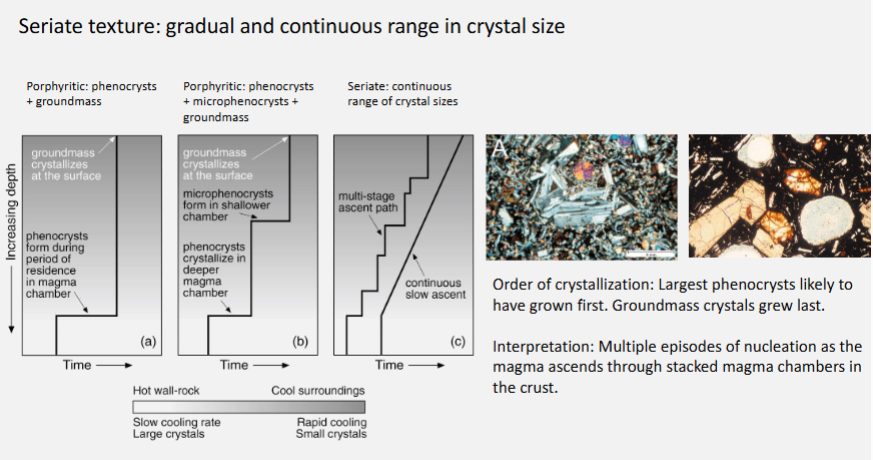
Words to describe crystal size distributions.
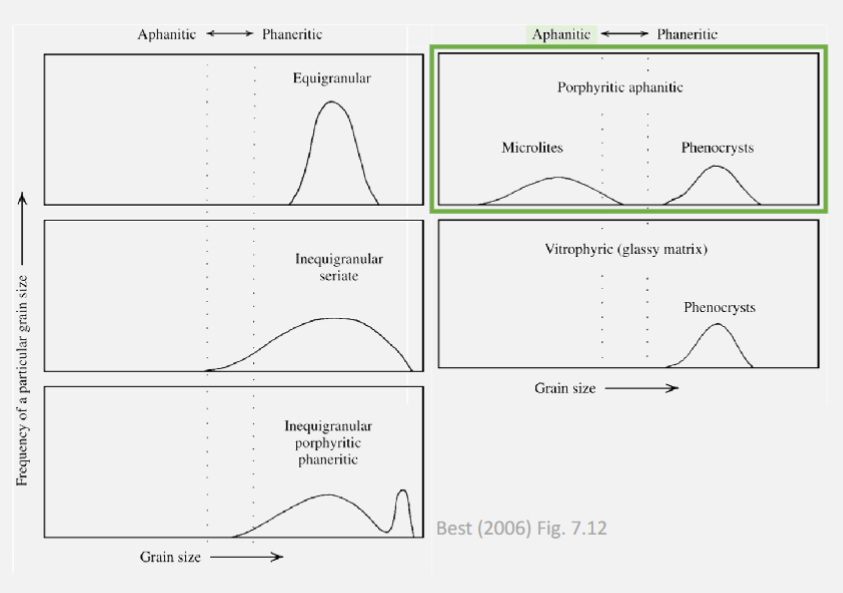
Explain the key chemical differences between mafic, intermediate, and evolved igneous rocks
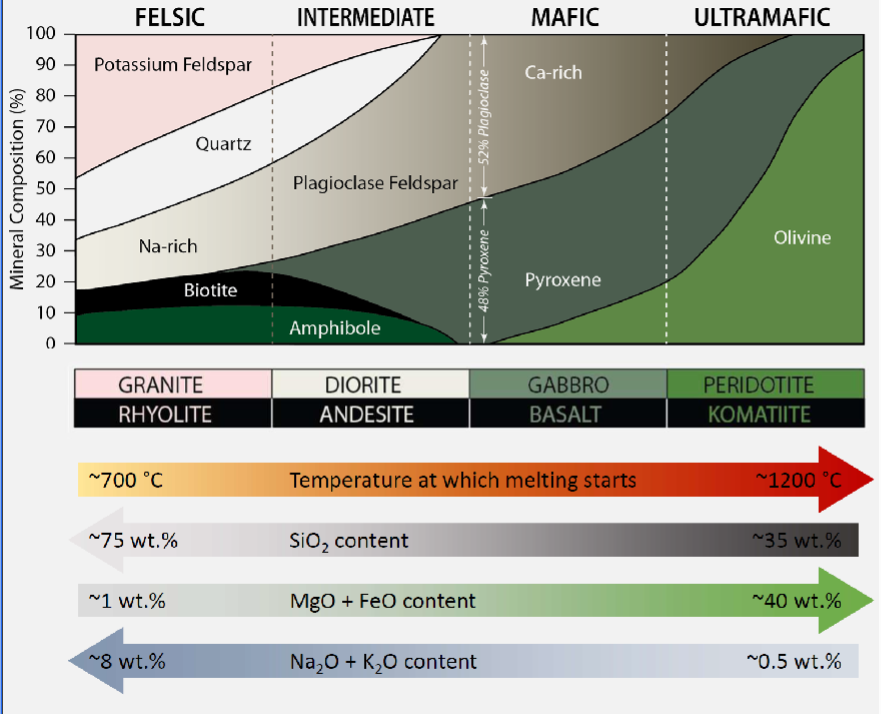
Difference between compatible and incompatible?
Compatible elements - into crystallising minerals
Incompatible - elements become concentrated in the melt.
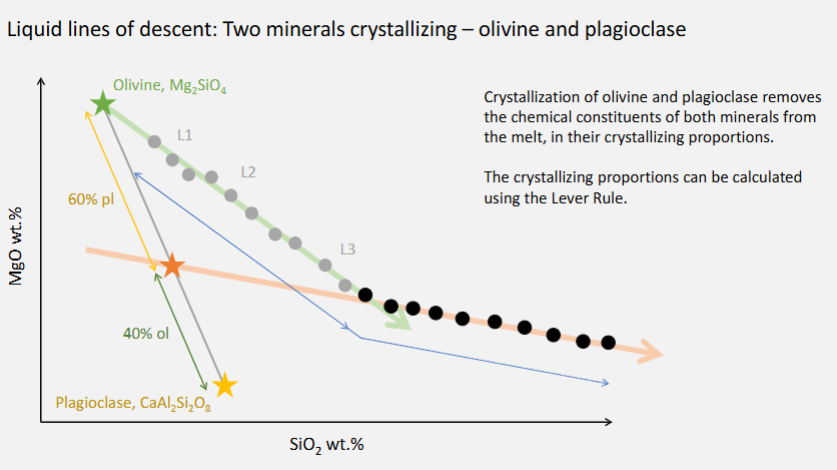
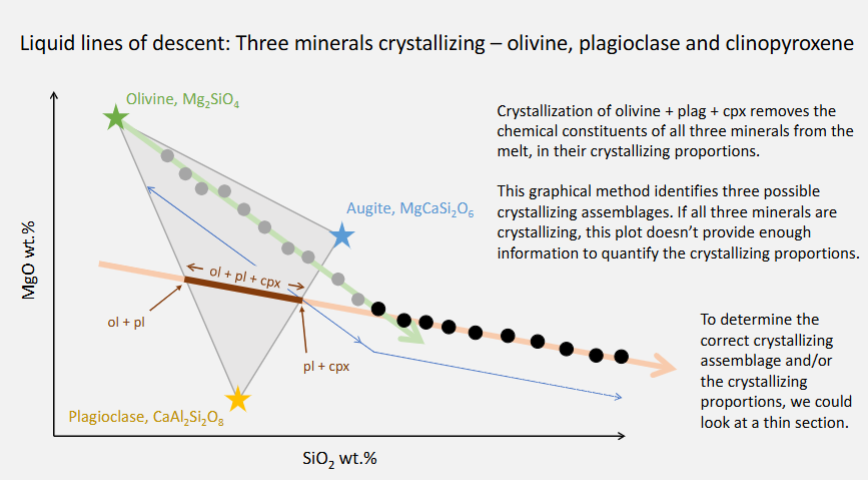
Interpret variation diagrams to provide qualitative descriptions of the crystallisation trends in igneous rock suites
From left to right, crystallising.
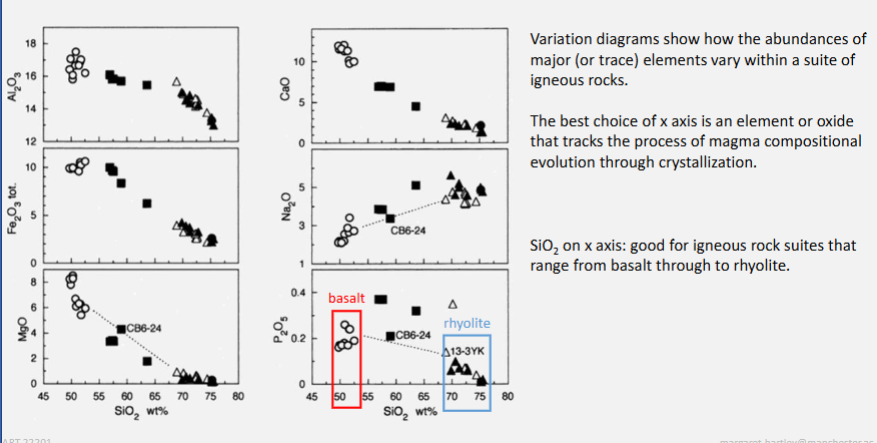
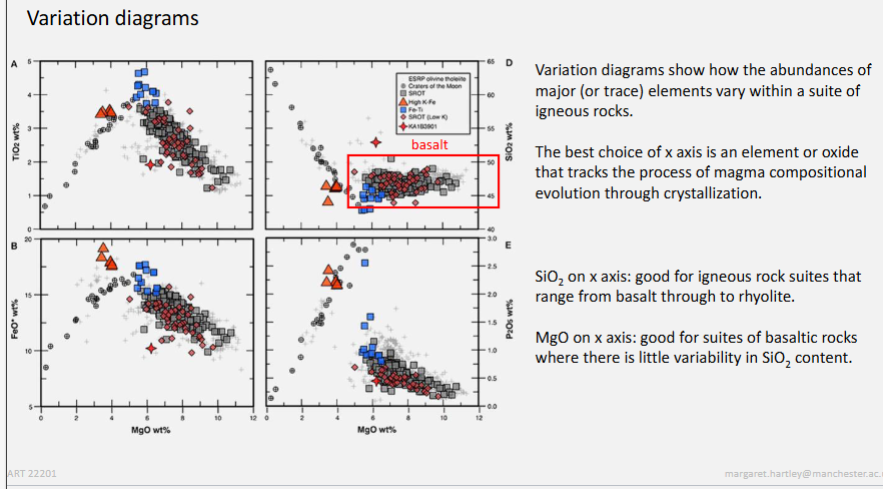
What does the presence of glass tell you about quickly the magma cooled?
Basalt glass only forms when cooling rates are extremely fast.
How does nucleation rate and growth rate relate to one another?
If nucleation rate is high, lots of crystals can grow; growth rate is low, so crystals can’t grow that big.
If no vesicles present what is likely formation environment?
NO vesicles so erupted under a confining pressure - most probably under water (as air would produce vesicles), e.g. tectonic environment at a mid-ocean ridge. or a subglacial eruption.
Quiz: What is true for equilibrium crystallisation?
Bulk chemical composition of system is always same.
System is closed: no mass enters or leaves the system as crystallisation proceeds.
A rock contains 40% augite, 40% plagioclase and 20% olivine, and has an average grain size of 4 mm. How would you classify this rock? Type your answer into the box.
Olivine Gabbro
Correct. The rock is an olivine gabbro. The rock is coarse-grained, and contains the essential minerals plagioclase and augite, so it is a gabbro. Olivine is a type mineral, which is added in front of the root name to give the full rock classification.
A volcanic rock contains 58% SiO2, 5% Na2O and 2% K2O. Using an appropriate chemical classification scheme, how would you classify this rock?
latite, trachyandesite, trachyandesite/latite
The most appropriate classification scheme is the volcanic TAS diagram on p12 of the Practical Reference Handout. A composition of 58% SiO2 and 7% Na2O+K2O plots in the trachyandesite field.
A rock contains 70% hornblende (containing 39% SiO2) and 30% plagioclase (containing 55% SiO2). Which two of the following terms correctly describe this rock? You will need to refer to the Practical Reference Handout.
Ultramafic and melanocratic.
Hornblende is a mafic mineral, and plagioclase is a felsic mineral. A rock containing 70% hornblende and 30% plagioclase will have a colour index of 70% and therefore be melanocratic. The acidity is calculated as 70% x 39 + 30% x 55 = 43.8 = ultramafic.
A rock is made up of 15% alkali feldspar, 10% quartz, 75% plagioclase. According to the QAPF classification scheme, which one of the following rock types is it?
Quartz monzodiorite
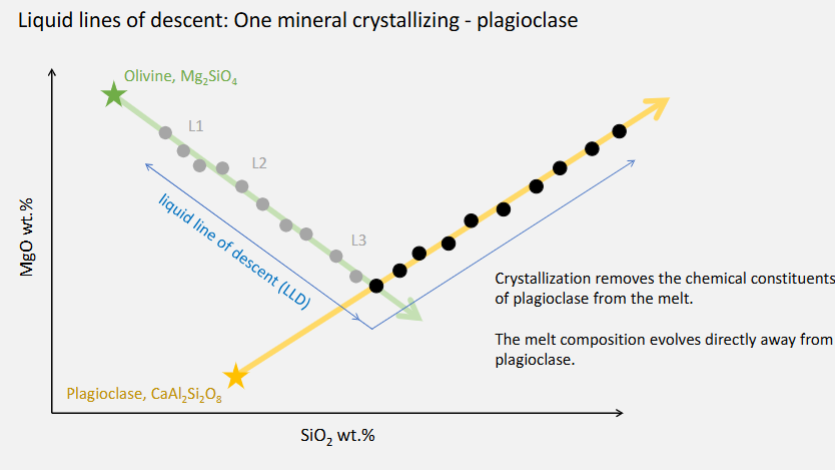
Which of the following statements are NOT true of a liquid line of descent? Select all that apply.
For most igneous rock suites it shows increasing MgO concentration with fractionation.
MgO tends to decrease during fractionation, as initially Mg-rich minerals such as olivine are removed from the melt.

Granular
Which of the following could occur as essential or type minerals in basalt? Select all that apply. You may wish to refer to the Practical Reference Handout.
Augite, Olivine, Plagioclase
Put basalt, komatiite, andesite, rhyolite in order of increasing SiO2
Lowest Komatiite
Basalt
Andesite
Highest SiO2 Rhyolite

1st to have crystallised black squares.
Then, red rectangles
Then green polygons.
Last to have crystallised large blue polygons.
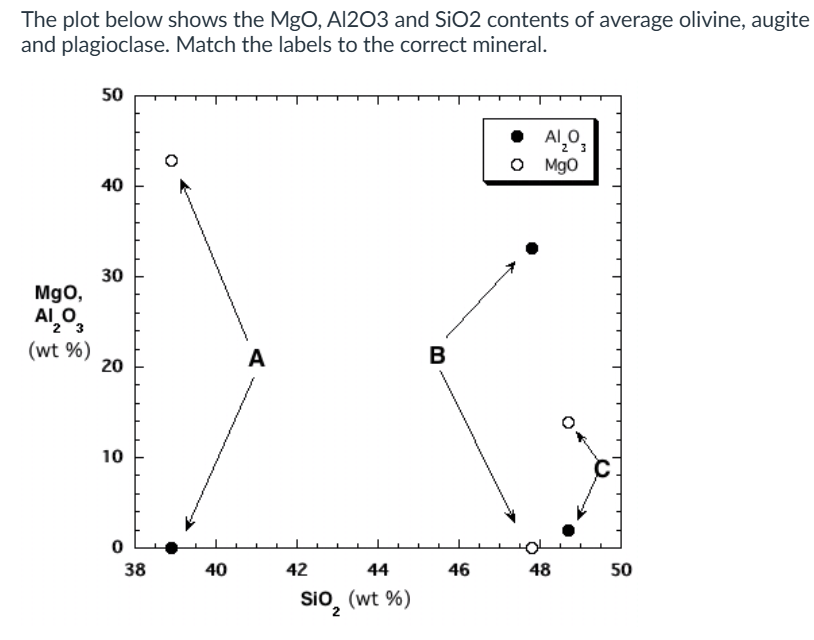
A - olivine
B - Plagioclase
C - Augite