Circadian Rhythms & Sleep (8)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what’s the difference between ultradian, circadian, infradian, and circannual?
Each of those terms refers to the length of a cycle of SOMETHING
Ultradian (< day)
ex. 2-4 hr vole feeding cycles, sleep cycles go in 90 minutes
Circadian (about a day)
Infradian (> day)
ex. estrous, menstrual cycles
Circannual (about a year)
ex. squirrel’s body weight, hibernation, seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
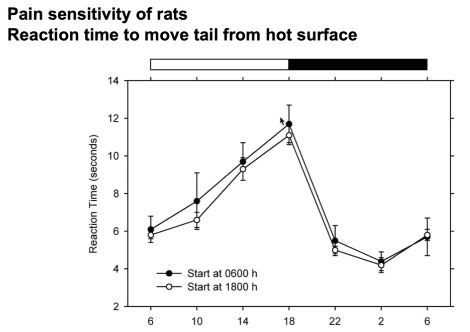
how does pain sensitivity change in rats throughout the day? how do we know this?
Method
measured the reaction time of rats to move tail away from hot surface
Pain Sensitivity Changes
least sensitive around 6pm, most sensitive at 2am
shows that pain sensitivity changes based on time of day
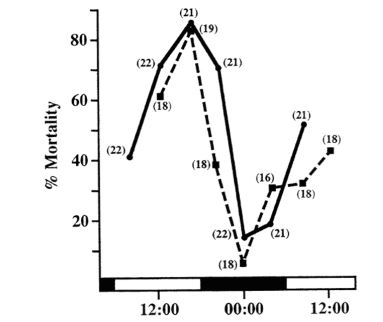
Explain the injection of the toxic dosages injected in rats and how their mortality fluctuated
The mortality of rats being injected by deadly poison was different based on time of administration
what does the melatonin cycle look like?
During the day time, virtually no melatonin
During night time, melatonin spikes
what are some consequences related to Circadian Rhythms?
Public safety
People have to work during times when their body tells them to SHLUMP
ex. Exxon oil spill, gas release in India
Medical Interventions
certain drugs have more effectiveness dependent on time of administration
ex. child chemotherapy effectiveness changes based on time of day
Experimental control
can affect outcome of research so account for it
Educational policy
delay start of school day leads to positive effect in learning
Shift-work
more likely to cause accidents late at night
they be suffering
Physiology
what is the history of discovering the existence of an internal endogenous clock?
DeMarain: plant experiments in 1700s
plants opened leaves during day and closed them at night
Demarain wanted to know if its light-dependent so it put it in a cellar and it still opened and closed
concluded that it came from within plant
Aschoff bunkers
put people into bunkers as an experiment
they kept their rhythms even when isolated from outside
Blind people
not aligned with day-night but they still show sleep-wake cycles
DD (animal studies)
studied in animals in complete darkness
how long does it take a hamster to get over jetlag?
Actogram shows a gradual shift toward day-night cycle
takes about 5 days to adapt free-wheel running behavior (4 hr delay)
what part of our eyes relates to our circadian rhythm?
We have a specialized visual system called ipRGC (intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells)
contain melanopsin
Describe the Transcription-translation feedback loop (TTFL)
per1 transcribed → per1 translated → goes to cytoplasm and forms dimers → dimer goes to nucleus and inhibits transcription → degrades so inhibition is released (loops again)
what is advance sleep phase syndrome? what gene was a determiner is having ASPS?
makes you go to sleep earlier. affects your sleep phase
mutation in hPer2 gene will result in ASPS
what is the SCN? what happens when you lesion it? what happens when you isolate the SCN in vitro?
SCN was theorized to be crucial for circadian rhythm
information from eyes made a pitstop at SCN (right above optic chiasm)
When lesioned . . .
healthy animals will lose free-running cycle
they start running sporadically
When in vitro . . .
SCN showed evidence of maintaining clock-like features
measured by looking at the action potentials of SCN over a 24-hour period
how did researchers restore circadian rhythms in SCN lesioned rats?
they put methamphetamine in their water
what is the current model of the role of the SCN?
SCN sits atop a hierarchy of clocks
normally coordinates entire system
Additional, weaker clocks throughout brain/body
Normally dampen without SCN
Under permissive condition, these can be coordinated
Are individual cells of the SCN capable of maintaining a 24 hour period? How did we answer this question (two ways)?
Researcher put single SCN cells in vitro:
they grew cells on a micro-electrode plate
one cell has a circadian rhythm
different cells have different period etc.
Researcher switched from electrical recording (clock output) to clock-gene recording (gear of the clock)
used glow-in-the-dark protein from fireflies
attached to a clock gene
Results:
SCN increases/decreases in PER2 protein
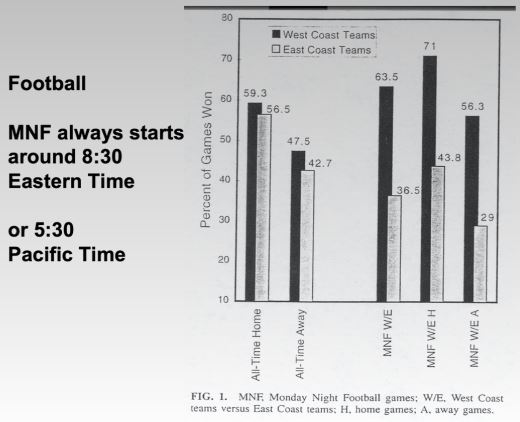
Why do West Coast Teams perform better during Monday night football?
Not because one team is better than the other
performance during the week is about even
Explanation
because of jetlag
how do dolphins and whales go to sleep?
They have specific sides of their brain sleep at a time
what are the characteristics of sleep?
Decreased activity
Lowered sensitivity to stimuli
how long does it take a newborn to develop a day-night cycle?
around 6 months
what is a chronotype? how does this change over time?
Chronotype: characteristic of your sleeping behavior
Larks: go to sleep hella early
Owls: go to sleep hella late
calculated by looking at midpoint between bedtime and wake up time
Chronotype as child is very low, peaks around 20 years old and decreases over time
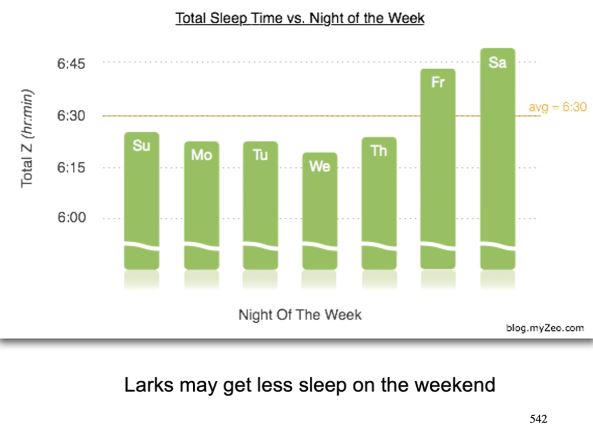
what is social jet lag?
No sleep during the week due to obligations
work, school, whatever
Extra sleep on weekends
to catch up
Could get even less sleep on weekends
go to party, go out, social occasions results in sleeping later
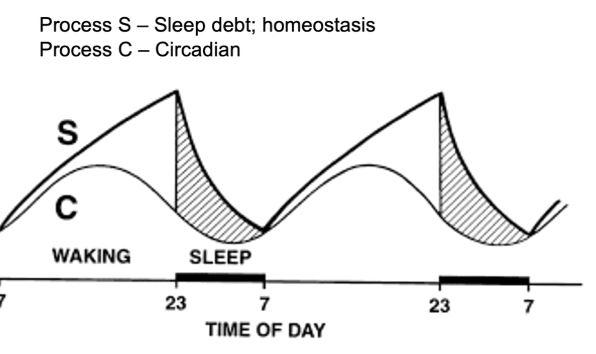
what is the difference between Process S vs Process C?
Process S: sleep debt; homeostasis
all-nighter accumulates sleep debt that requires MORE sleep to decrease
Process C: Circadian
This rhythm is still in place even after an all-nighter you will feel more energy the next day
what method did researchers use to induce total sleep deprivation (TSD) in rats?
Method
they put rats in a pot of water standing on a small platform. Everytime they went to sleep they fell in the water, meaning they couldn’t sleep
Results
They all died within 11-32 days from various causes
causes of death include: skin diseases, weight
How does sleep deprivation affect performance in cognitive assessments? what research did we do to conclude this?
Research
Had four groups sleep in lab: total sleep dep, 4h, 6h, and 8h
Results
Total sleep deprivation resulted in poor performance on cognitive tasks
8 hours in bed group (6.5 hours sleep) results in slightly decreased performance over 2-week span
6 hour group showed significant progressive decrease in cognitive performance
after 2 weeks comparable to 24 hour sleep deprived person
4 hour group sees comparable performance to 24 hour sleep deprived person in one week
Self-Reported Sleepiness Score
6 and 4-hour group self-report decent sleep score in spite of decreased cognitive performance
suggests they are not aware of how bad it is
what type of EEG waves are associated with being awake?
Alpha waves
relaxed arousal
Beta waves
attentive arousal
what type of EEG waves are associated with Stage 1 and Stage 2 sleep?
Stage 1 Sleep
theta activity
Stage 2 Sleep
Sleep spindle: transient burst of synchronized potential
K-complex: transient, high amplitude spike; response to sounds
Stage 3 Sleep (slow wave sleep)
Delta Activity
Stage 4 Sleep (slow wave sleep)
Delta Activity
REM sleep
theta & beta activity
characterized by:
rapid rolling eye movement
desynchronized EEG
skeletal muscle atonia
shuts down motor activity
associated with REM behavioral disorder where person moves around in sleep
dreaming
what are the sleep disorders discussed in lecture?
Insomnia
Sleep talking/walking
Night terrors
REM Behavioral Disorder
Sleep Paralysis
muscle atonia while conscious
what are the different types of insomnia?
Insomnia
onset, maintenance, or terminal insomnia
Chronic Insomnia
difficulty concentrating
memory problems
auto accidents
inability to enjoy family / social relationship
2 fold greater risk for major depression
Fatal Familial Insomnia
prion mutation
stop sleeping within 18 months
possible insomnia cause of death?
what is narcolepsy? why does this happen? what does the anatomy of narcoleptic brain tell us?
Characterized by suddenly falling asleep
Narcolepsy in dogs . . .
showed a mutation of orexin/hypocretin receptor
Anatomy of Narcoleptic Human Brains show . . .
sections of brain show that narcoleptic brains do not have mRNA for hypocretin
suggests lack of hypocretin is cause of narcolepsy
what’s a good treatment for people with sleep apnea?
CPAP: continuous airway pressure
mask that puts pressure on your respiratory passages so you don’t stop breathing
what neurotransmitters are involved in our sleep cycles?
Norepinephrine
alerts large areas of brain
Serotonin
Acetylcholine
keep cortex alert
Histamine
keeps us awake
Adenosine
caffeine acts on this
alerting effect
What amount of each neurotransmitter is released during REM?
REM
ACh high
NE low
5-HT low
what are some theoretical purposes to sleep?
physiological restoration
memory and learning
metabolic processes
temperature regulation
ground squirrels de-hibernate to sleep
what studies have we done to conclude if sleep is essential in consolidating learning?
Study
had participants learn finger tapping task and measured improvement before and after sleeping
after sleeping they improved their ability to do task
Another Study
Found a positive correlation between % stage 2 NREM4 sleep and % improvement
Weaknesses of Studies
only measured on specific, simple task
definitely can learn without sleep
sleep stages still largely based on correlations