Jeppesen 01A - Reciprocating Engines
1/415
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
416 Terms
1483
What year did Leonardo da Vinci conceived a flying machine he called the aerial screw?
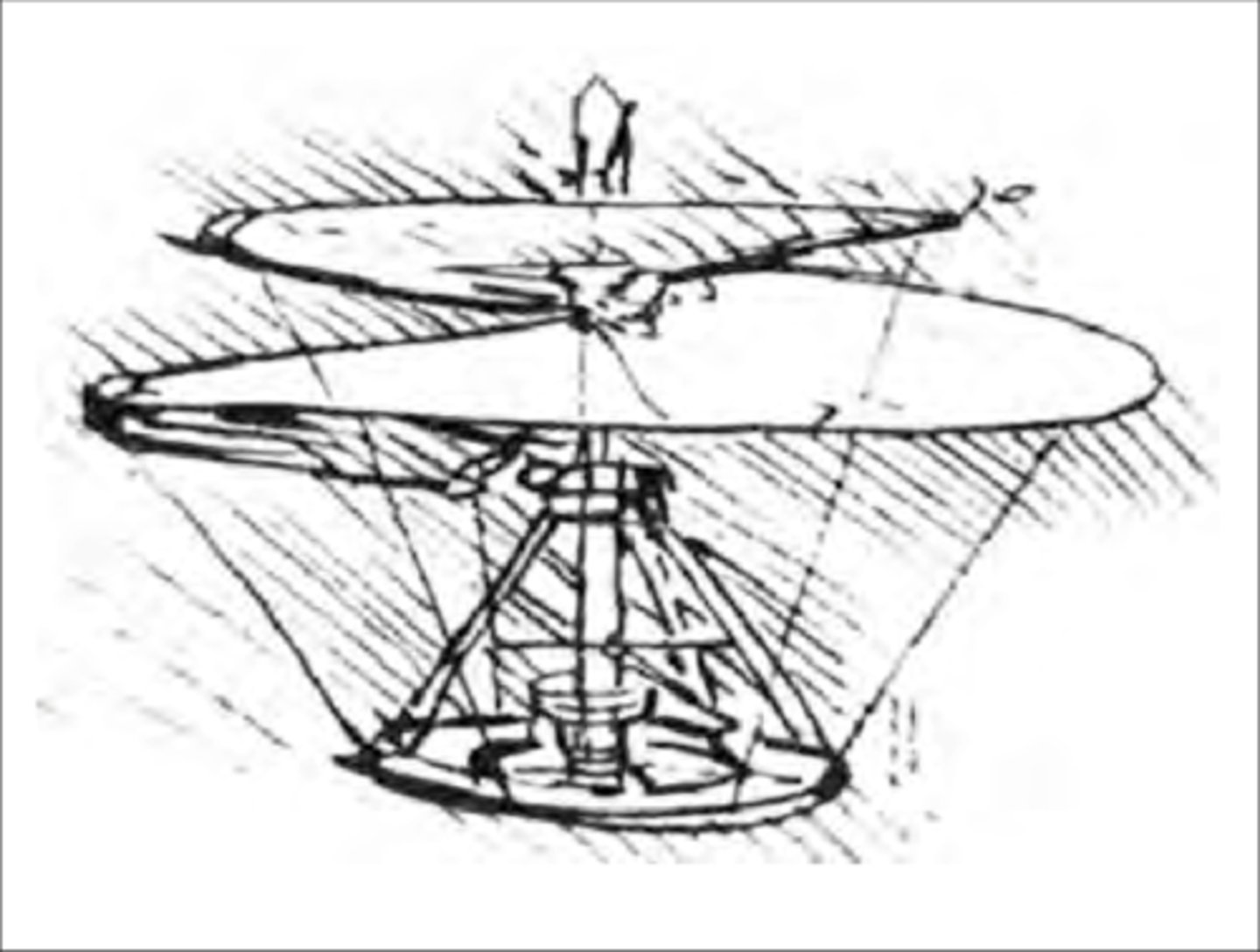
1791
The first patent for a heat engine was not taken out until _____ by John Barber.
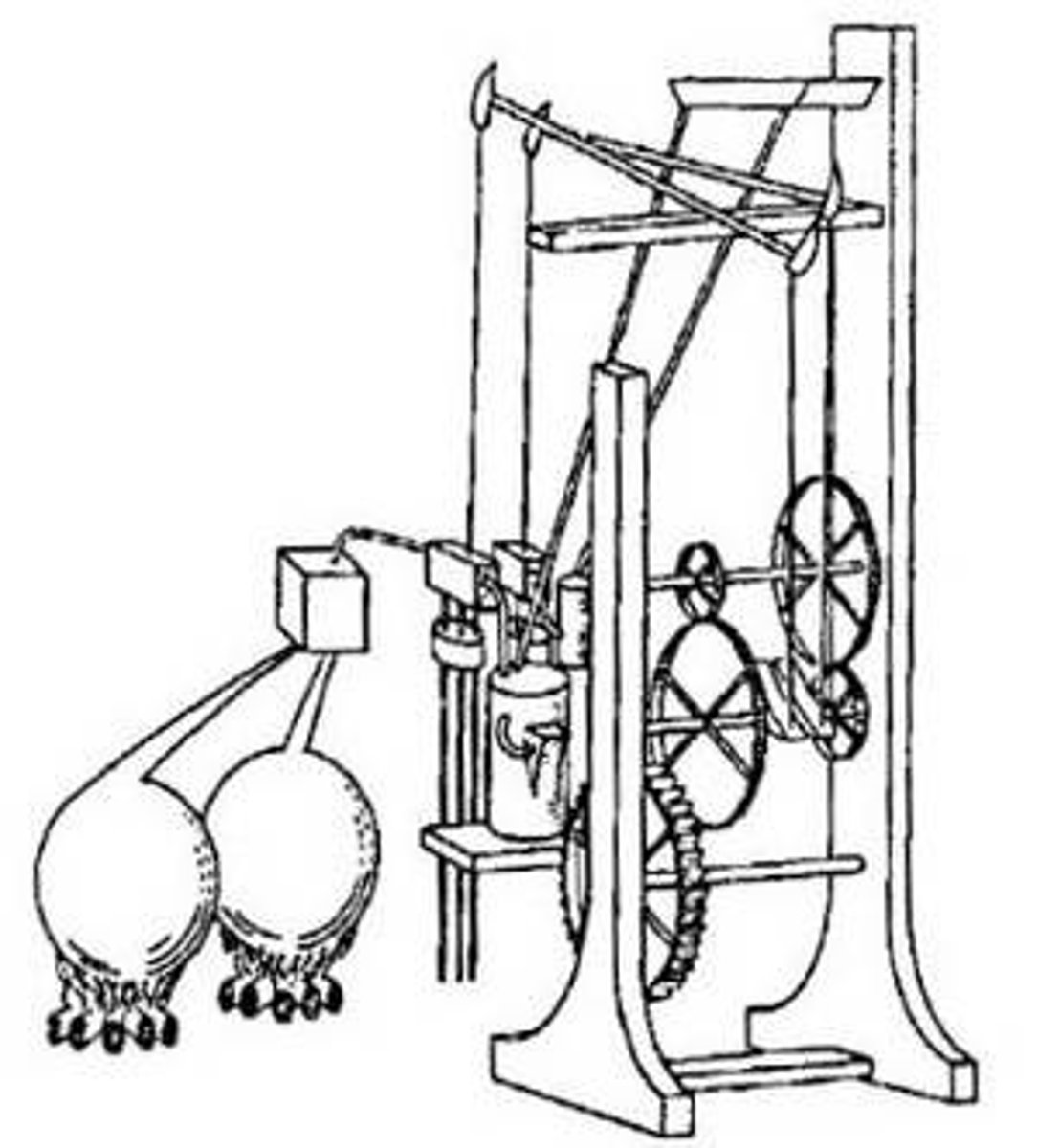
1860
What year did a truly practical piston engine was built by Etienne Lenoir of France?

Lenoir's engine
This is the first practical piston engine that employs a battery ignition system and natural gas as fuel which was used to operate industrial machinery such as lathes.
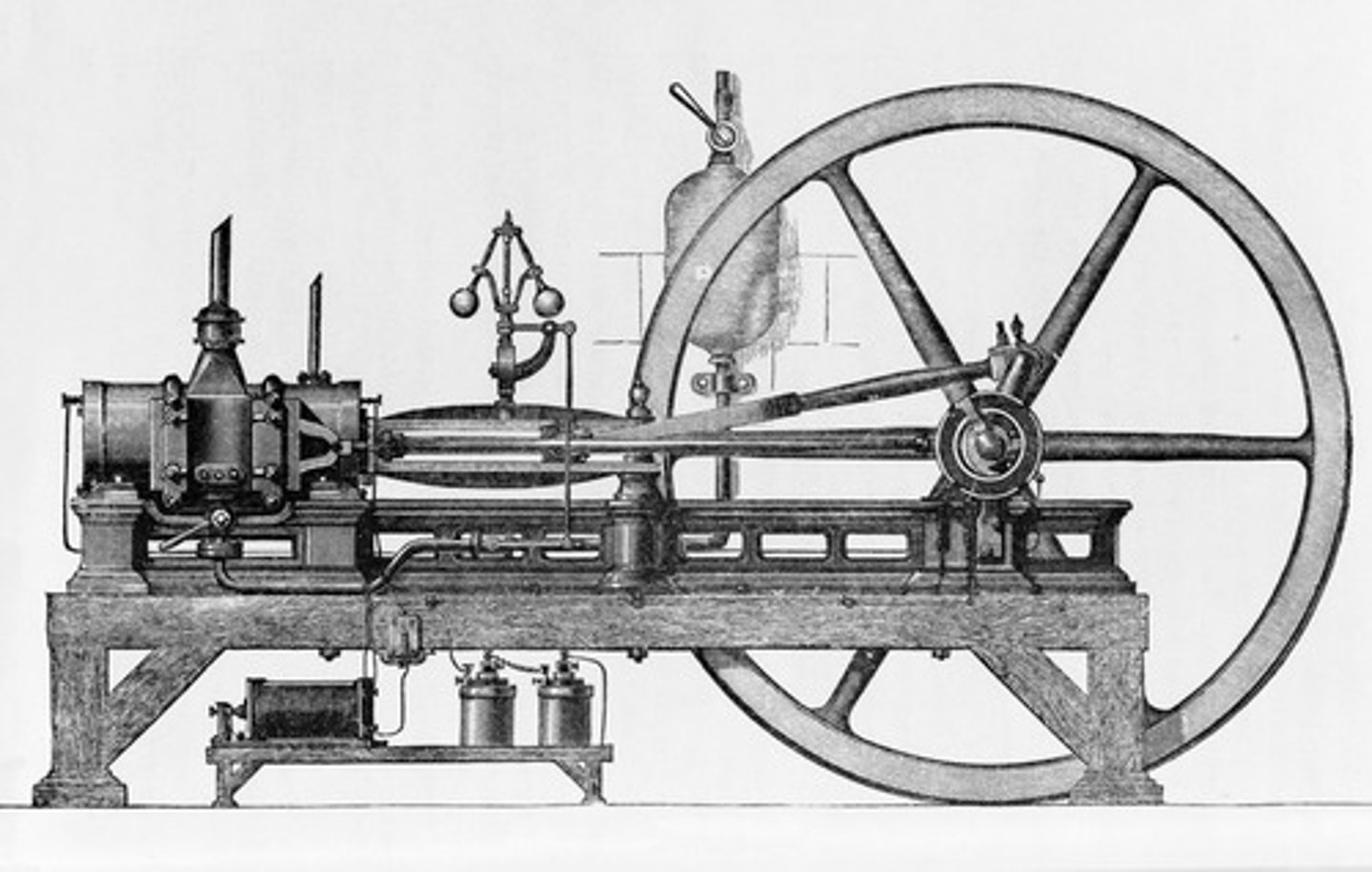
1876
What year did the major breakthrough in piston engine development came when Dr. August Otto developed the four-stroke, five-event cycle which is the operating cycle used by most modern reciprocating aircraft engines?

Heat energy
All heat engines convert _______ into mechanical energy by taking in a specific volume of air and heating it through the combustion of a fuel.
Mechanical energy
When heat engines convert heat energy into mechanical energy, the heated air expands, creating a force that is converted into ________ to drive a propeller or other device.
Reciprocating engine
The most common type of heat engine is the ________.
Reciprocating engine
Derived their name from the back-and-forth, or reciprocating movement of their pistons. It is this reciprocating motion that produces the mechanical energy needed to accomplish work.
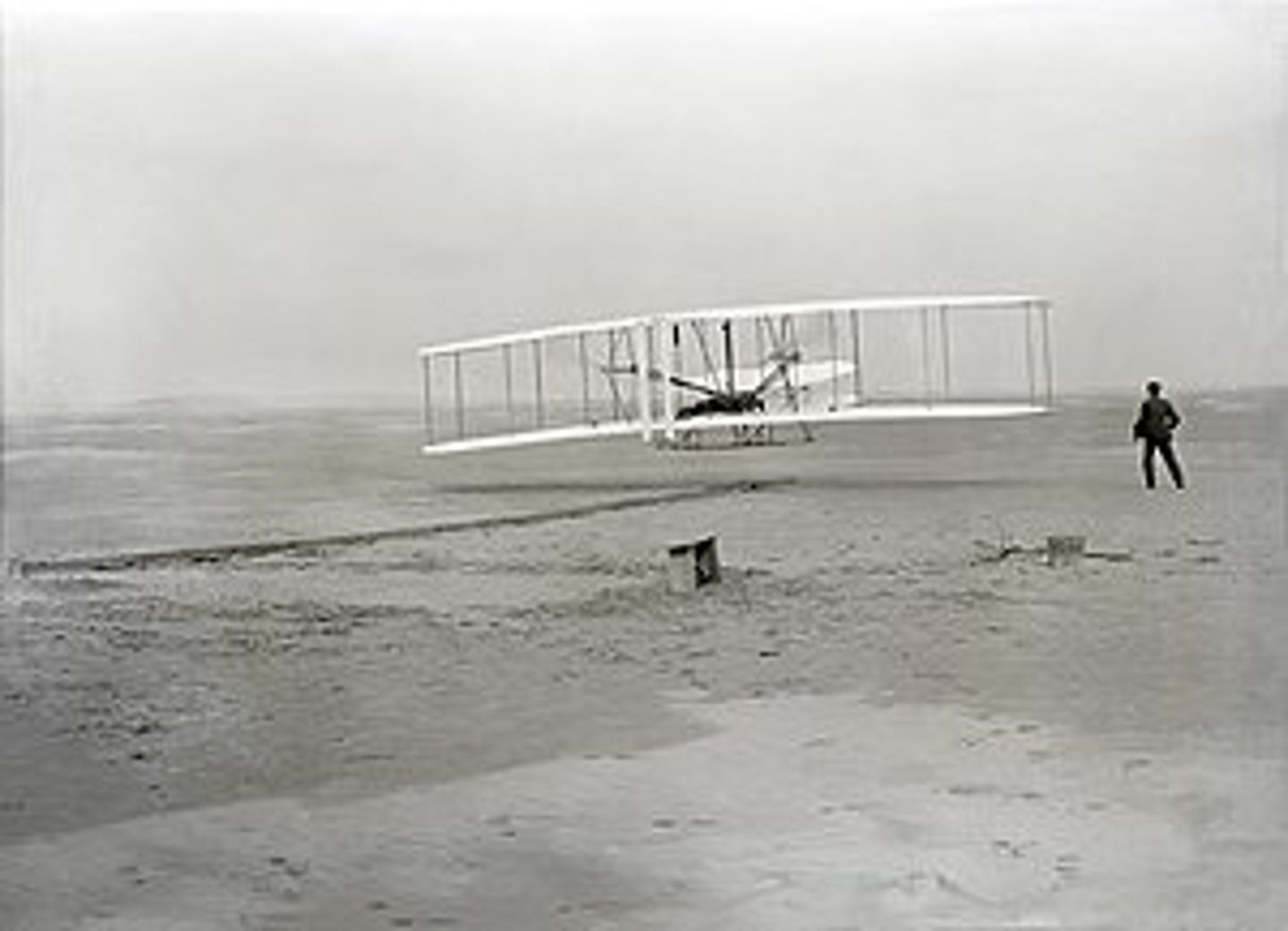
Four-cylinder in-line engine
What type of reciprocating engine did the Wright Brothers used for their Wright Flyer I?

Cylinder arrangement with respect to the crankshaft
The two most common means of classifying reciprocating engines are by _______ and the method of cooling.
Method of cooling
The two most common means of classifying reciprocating engines are by cylinder arrangement with respect to the crankshaft and _______.
Radial engine
Consists of a row, or rows of cylinders arranged radially about a central crankcase.
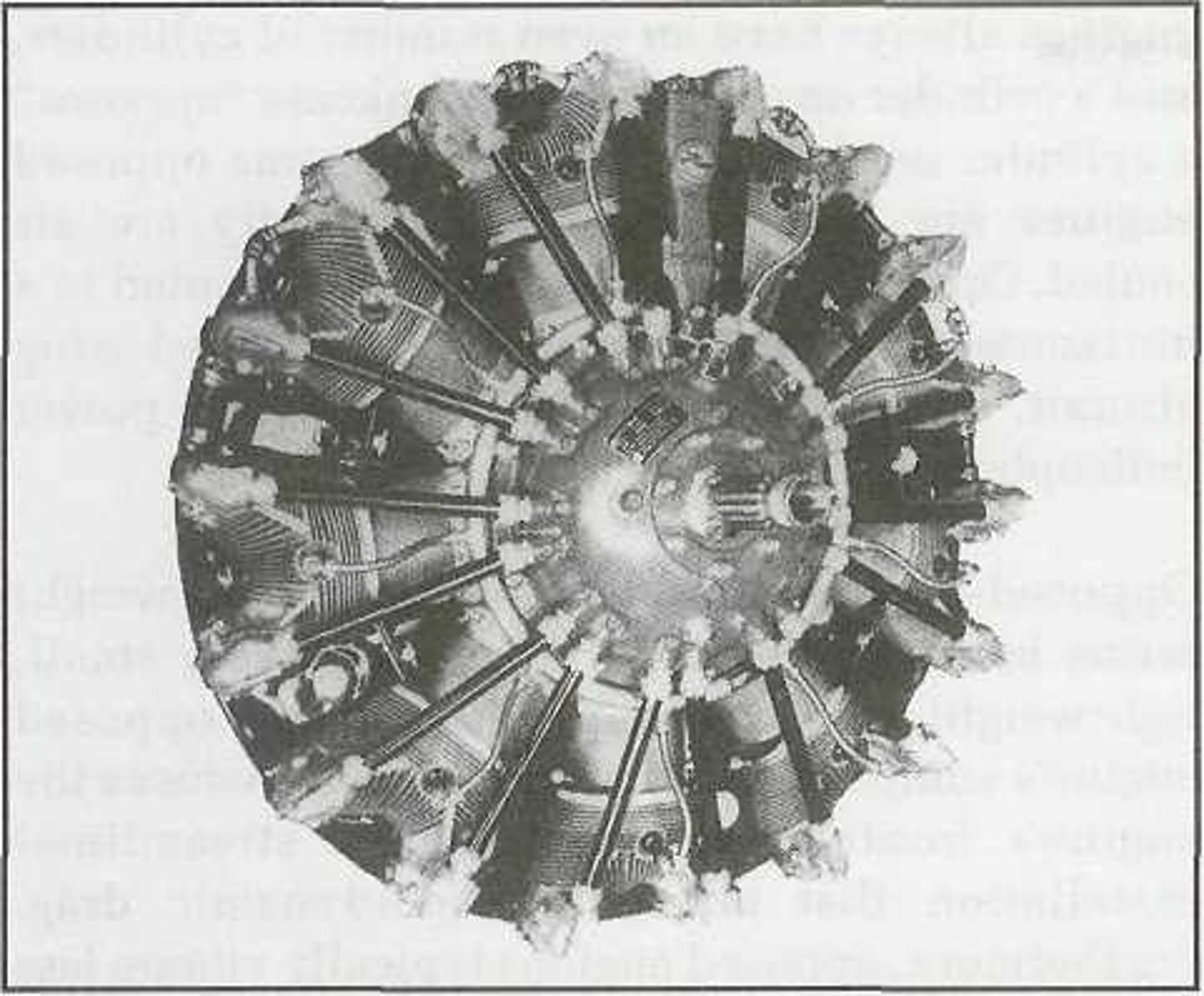
Rotary-type
The two basic types of radial engines include the ______ and the static-type.
Static-type
The two basic types of radial engines include the rotary-type and the ______.
Rotary-type
What type of radial engines were used almost exclusively because they produced the greatest horsepower for their weight during World War I?
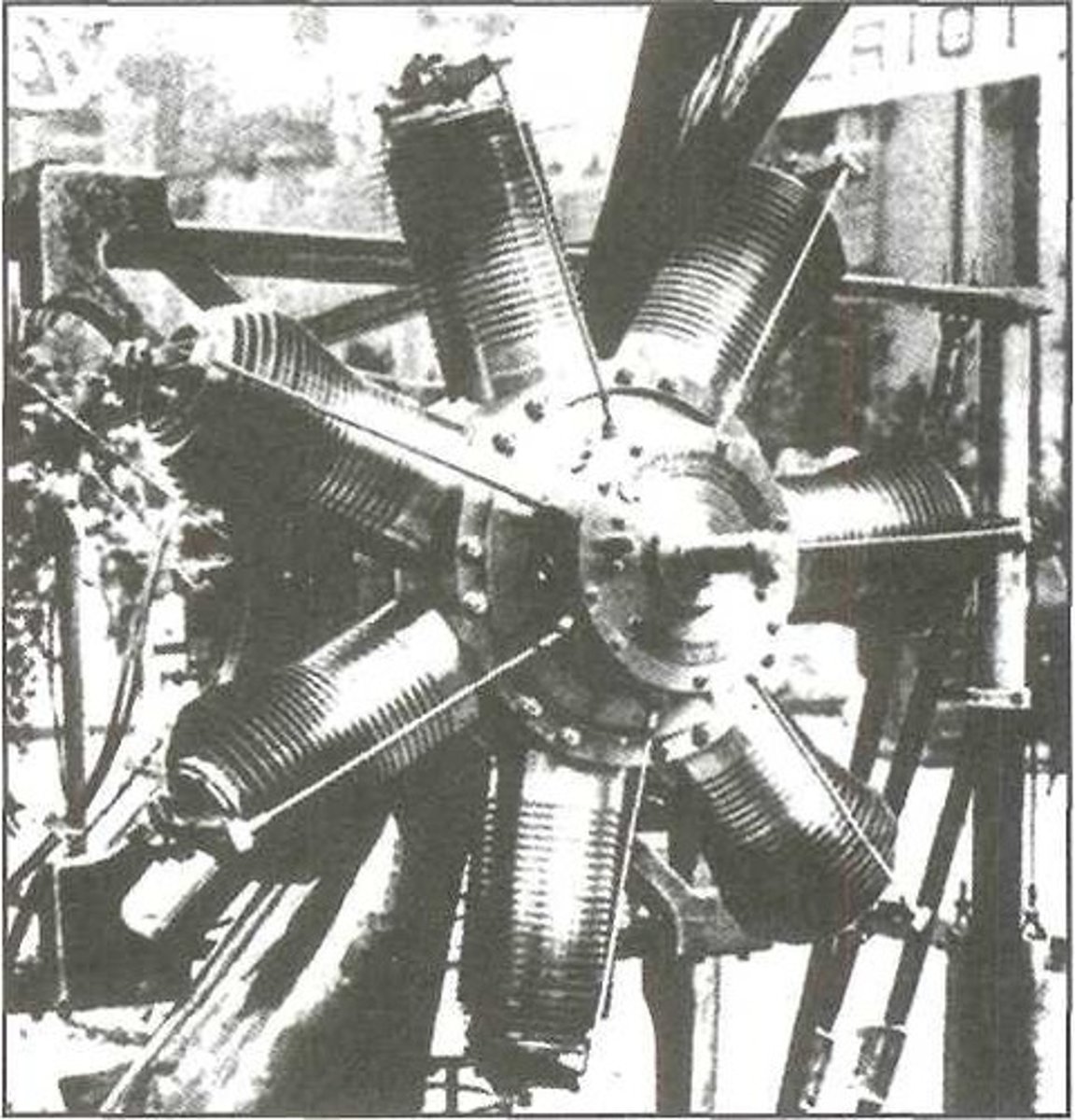
Crankshaft
The cylinders of a rotary-type radial engine are mounted radially around a small crankcase and rotate with the propeller, while the ______ remains stationary.
Torque effect
The biggest disadvantage rotary-type radial engines possessed was that the ______ produced by the large rotating mass of the propeller and cylinders made aircraft somewhat difficult to control.
Static-type
In the late 1920s, the Wright Aeronautical Corporation, in cooperation with the U.S. Navy, developed a series of five-, seven-, and nine-cylinder ______ radial engines. These engines demonstrated reliability far greater than any other previous designs.
Crankcase
Static-type radial engines differ from rotary-type radial engines in that the ______ is bolted to the airframe and remains stationary. This dictates that the crankshaft rotates to turn the propeller.
Static-type
Outstanding reliability coupled with a high power-to-weight ratio made these radial engines ideal for powering early military and civilian transport aircraft.
Single-row
A typical radial engine configuration consists of five to nine cylinders evenly spaced on the same circular plane with all pistons connected to a single crankshaft.
Multi-row
To further increase a radial engine's power, while maintaining a reasonable engine frontal area, ______ radial engines were developed.
Double-row
One of the most common multiple-row radial engines consisted of two single row engines in line with each other connected to a single crankshaft. This type of engine is sometimes referred to as a ______ radial engine and typically has a total of 14 or 18 cylinders.
Staggered
To help cool a multiple-row radial engine, the rear rows of cylinders are ______ so they are behind the spaces between the front cylinders. This configuration increases the amount of airflow past each cylinder.
Pratt and Whitney R-4360
It was the largest practical radial engine used in aviation which consisted of 28 cylinders arranged in four staggered rows of seven cylinders each and developed a maximum 3,400 horsepower.
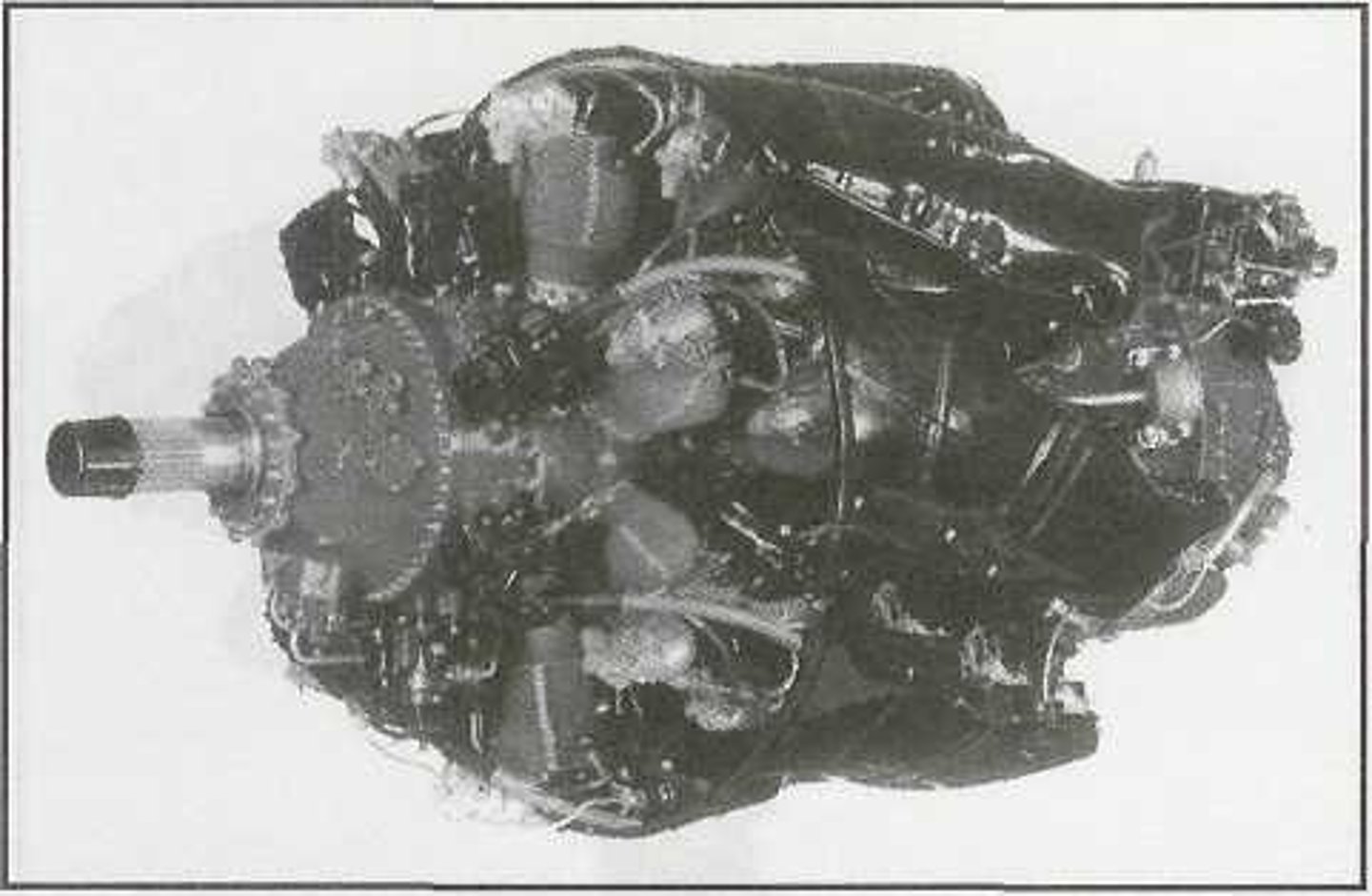
In-line engine
This generally has an even number of cylinders that are aligned in a single row parallel with the crankshaft. This engine can be either liquid-cooled or air cooled and the pistons can be located either upright above the crankshaft or inverted below the crankshaft.
In-line engine
This engine has a comparatively small frontal area and, therefore, allows for better streamlining. Because of this, they were popular among early racing aircraft.
Propeller ground clearance
An advantage of the in-line engine is that, when mounted with the cylinders inverted, the crankshaft is higher off the ground, allowing greater ______ which permitted the use of shorter landing gear.
In-line engine
These engines were used primarily on tail-wheel aircraft, where the shorter main gear provided for increased forward visibility on the ground.
In-line engine
These engines have relatively low power-to-weight ratios and when air-cooled, the rearmost cylinders receive relatively little cooling air and so were typically limited to only four or six cylinders.
V-type engine
These engines have cylinder arranged around a single crankshaft in two in-line banks that are 45, 60, or 90 degrees apart.
V-type engine
These engines had a reasonable power-to-weight ratio while retaining a small frontal area.
Inverted V-type engine
The cylinders on a V-type engine could be above the crankshaft or below it, in which case the engine is referred to as a _______.
V-type engine
These engines provide an excellent combination of weight, power, and small frontal area.
V-type engine
These engines had 8 or 12 cylinders and were either liquid-cooled or air cooled.
Opposed-type engine
These engines are the most popular reciprocating engines used on light aircraft.
Opposed-type engine
They always have an even number of cylinders, and a cylinder on one side of a crankcase "opposes" a cylinder on the other side.
Air-cooled
While some opposed engines are liquid-cooled, the majority are ______.
Opposed-type engine
These engines are typically mounted in a horizontal position when installed on fixed-wing aircraft, but can be mounted vertically to power helicopters.
Opposed-type engine
These engines have high power-to-weight ratios because they have a comparatively small, lightweight crankcase.
Aerodynamic drag
An opposed engine's compact cylinder arrangement reduces the engine's frontal area and allows a streamlined installation that minimizes ______.
Opposed-type engine
Typically vibrate less than other engines because its power impulses tend to cancel each other.
Power lever
The Porsche Flugmotoren (PFM) 3200 is a direct descendant of the 214 horsepower engine used in the Porsche 911 sports car. It utilizes a single engine control called a ______. This control automatically governs the throttle, mixture, and propeller pitch settings. This reduces pilot workload and, at the same time, maintains the engine's peak performance for the given conditions.
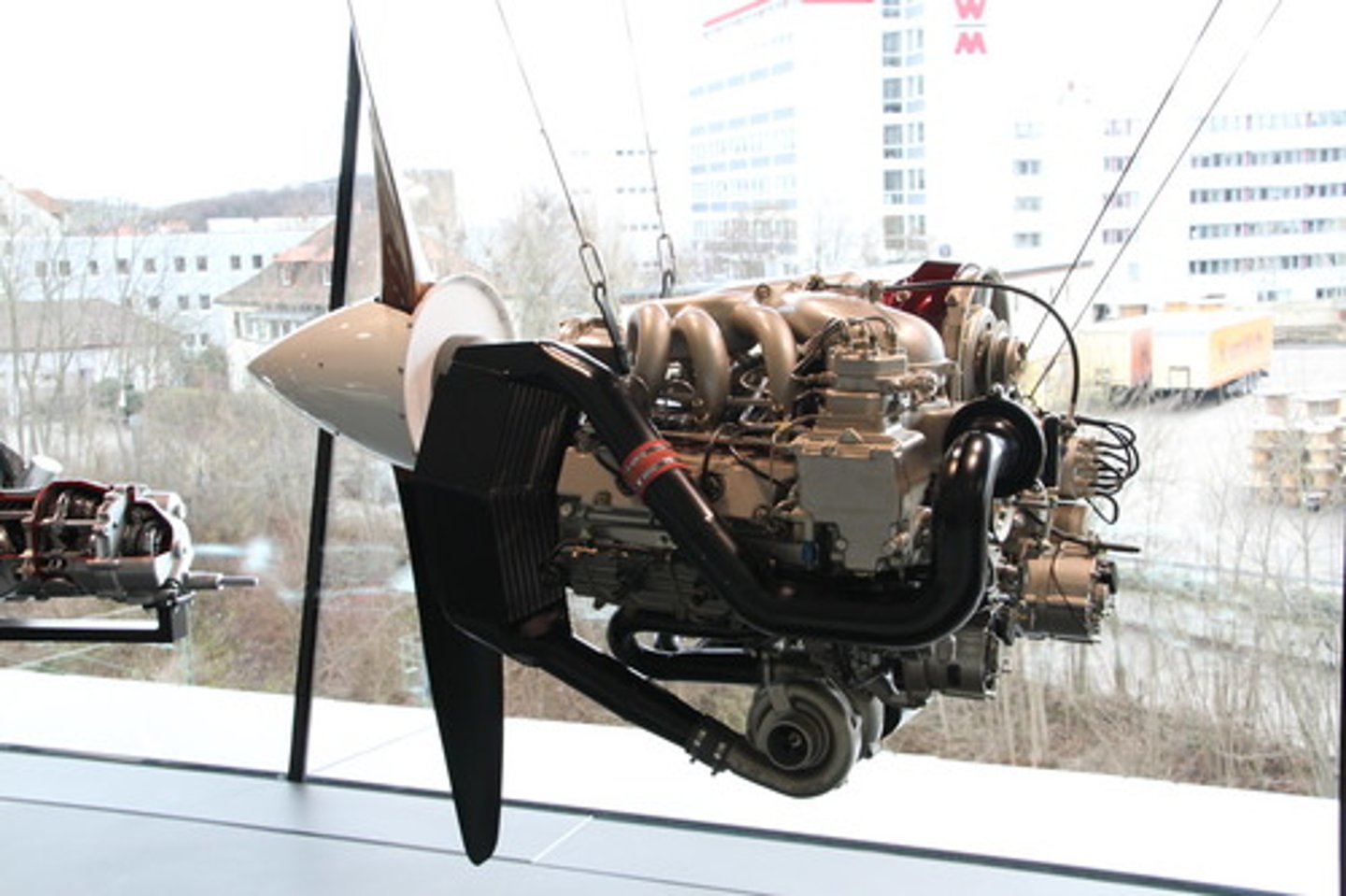
Opposed-type engine
This engine combines a good power-to-weight ratio with a relatively small frontal area. It powers most light aircraft in use today.
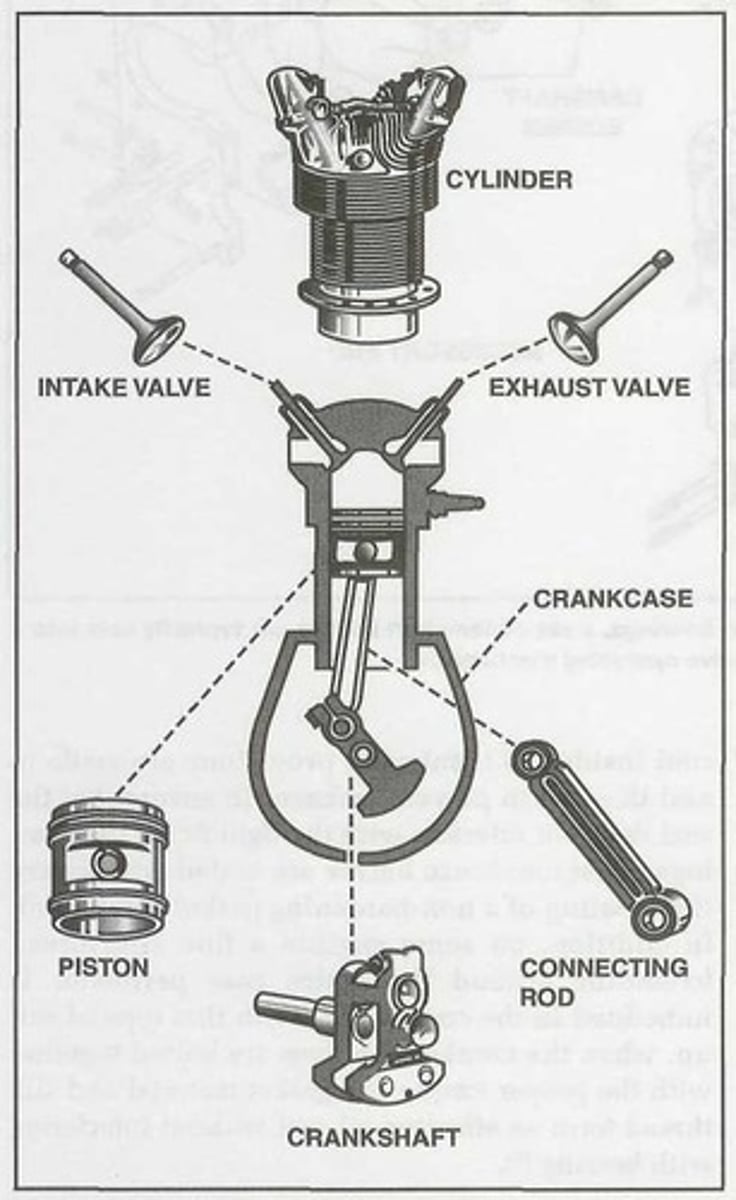
Cylinder
The ______ forms a chamber where the fuel/air mixture is compressed and burned.
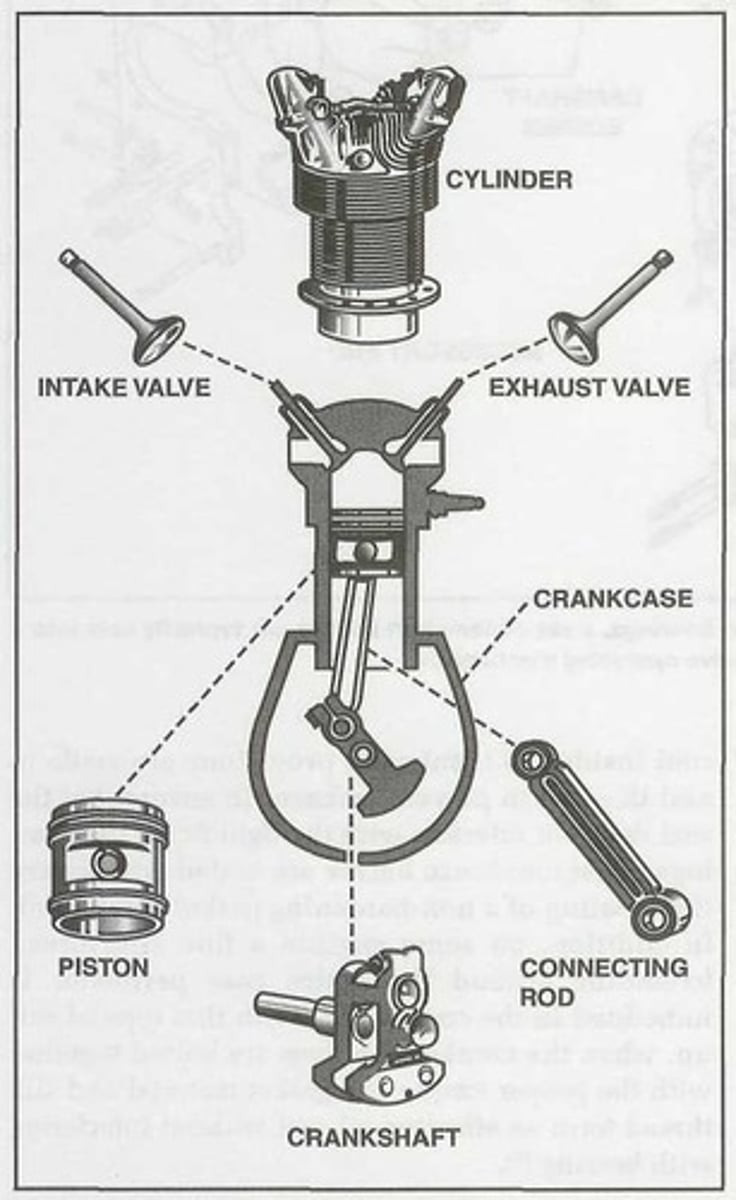
Piston
The ______ compresses the fuel mixture and transmits the power produced by combustion to the crankshaft through the connecting rods.
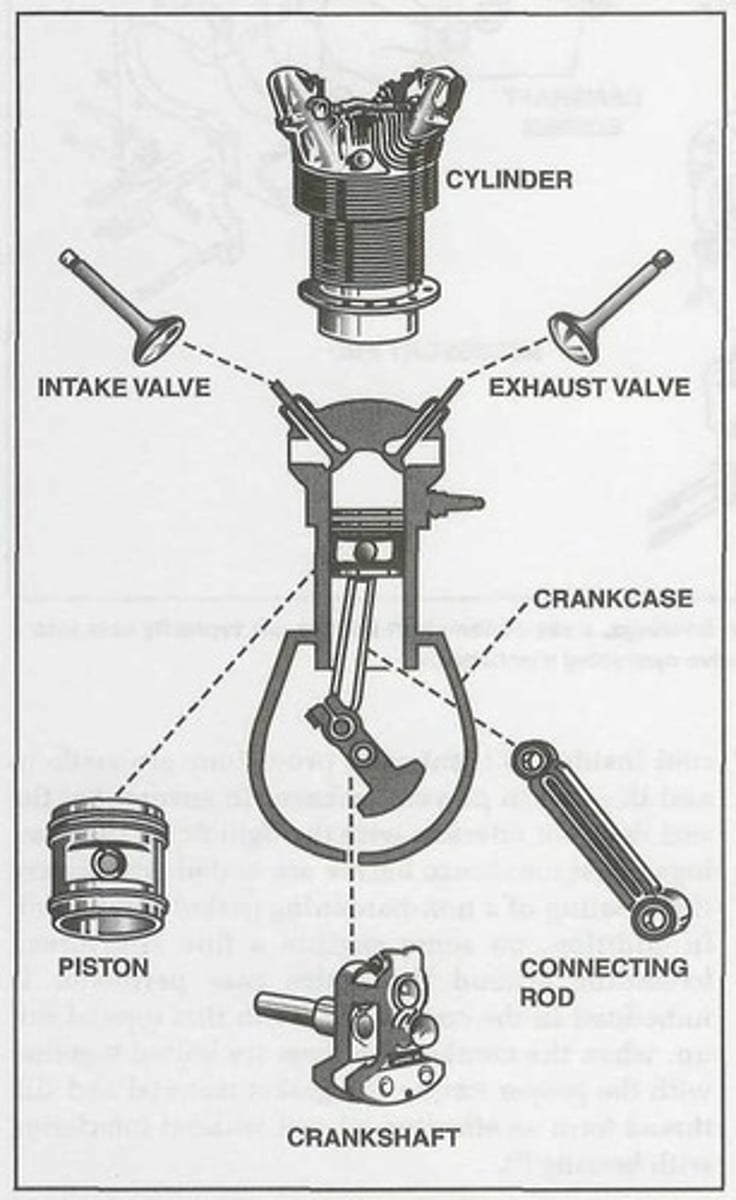
Cylinder
The intake valve allows the fuel/air mixture into the ______ while the exhaust valve lets the exhaust gases out of the ______.
Crankcase
It is the foundation of a reciprocating engine.
Crankcase
It contains the engine's internal parts and provides a mounting surface for the engine cylinders and external accessories.
Crankcase
It provides a tight enclosure for the lubricating oil as well as a means of attaching a complete engine to an airframe.
Bending moments
To remain functional, a crankcase must be capable of absorbing forces and still maintain its integrity. For example, due to the internal combustion forces exerted on the cylinders and the unbalanced centrifugal and inertial forces inflicted by a propeller, a crankcase is constantly subjected to ______ which change continuously in direction and magnitude.
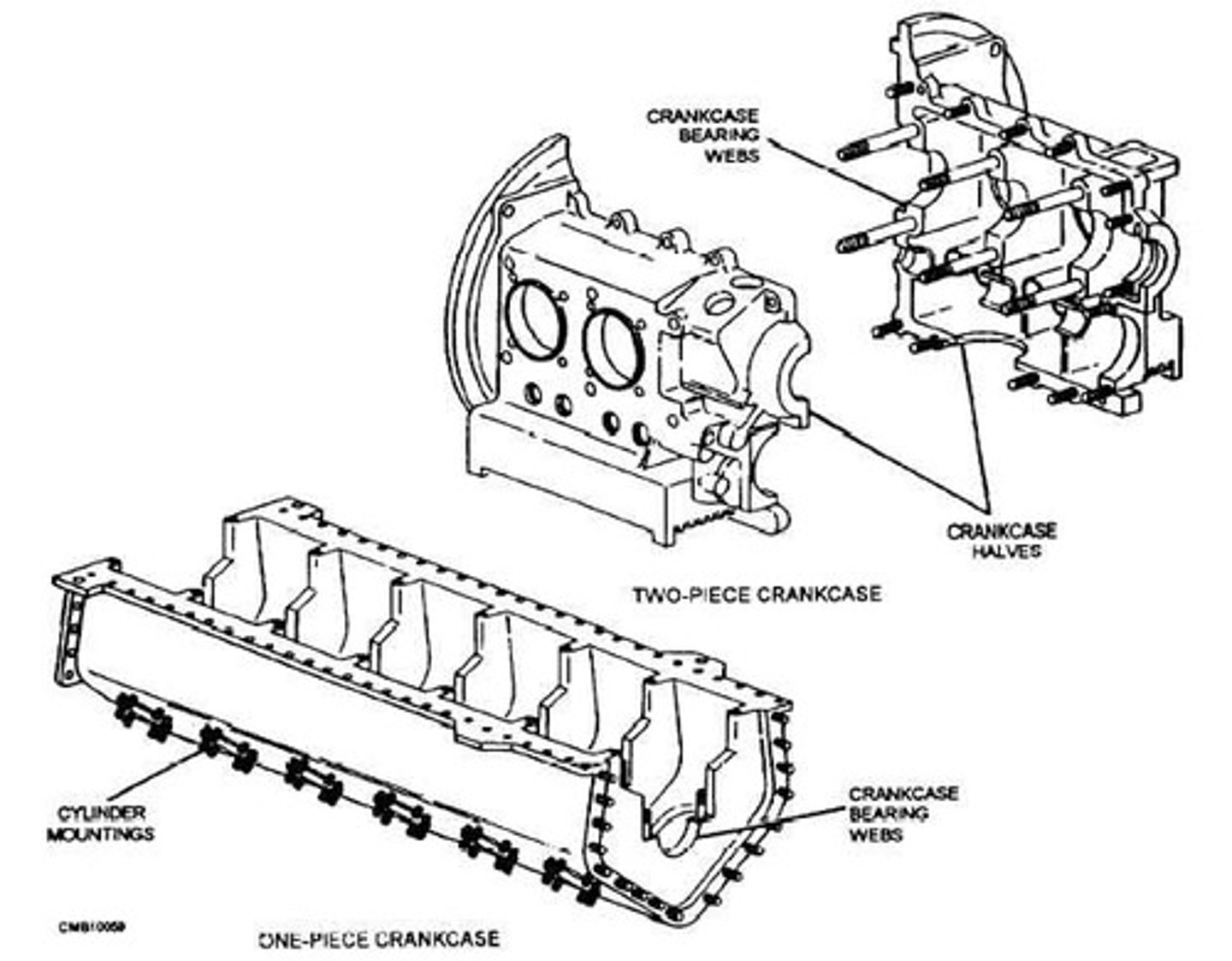
Two pieces
Today, most crankcases consist of at least _______; however, there are some one-piece and up to five-piece case assemblies.
Cast aluminum alloy
To provide the strength and rigidity required while maintaining a relatively light weight, most aircraft crankcases are made of ______.
Cast aluminum alloy
A typical horizontally opposed engine crankcase consists of two halves of _______ that are manufactured either with sand castings or by using permanent molds.
Permanent mold process
Crankcases manufactured through the ________, or per-mamold, as it is called by some manufacturers, are denser than those made by sand casting.
Permanent mold process
Crankcases that underwent this process have denser construction that allows to have thinner walls than a sand cast crankcase and exhibit less tendency to crack due to fatigue.
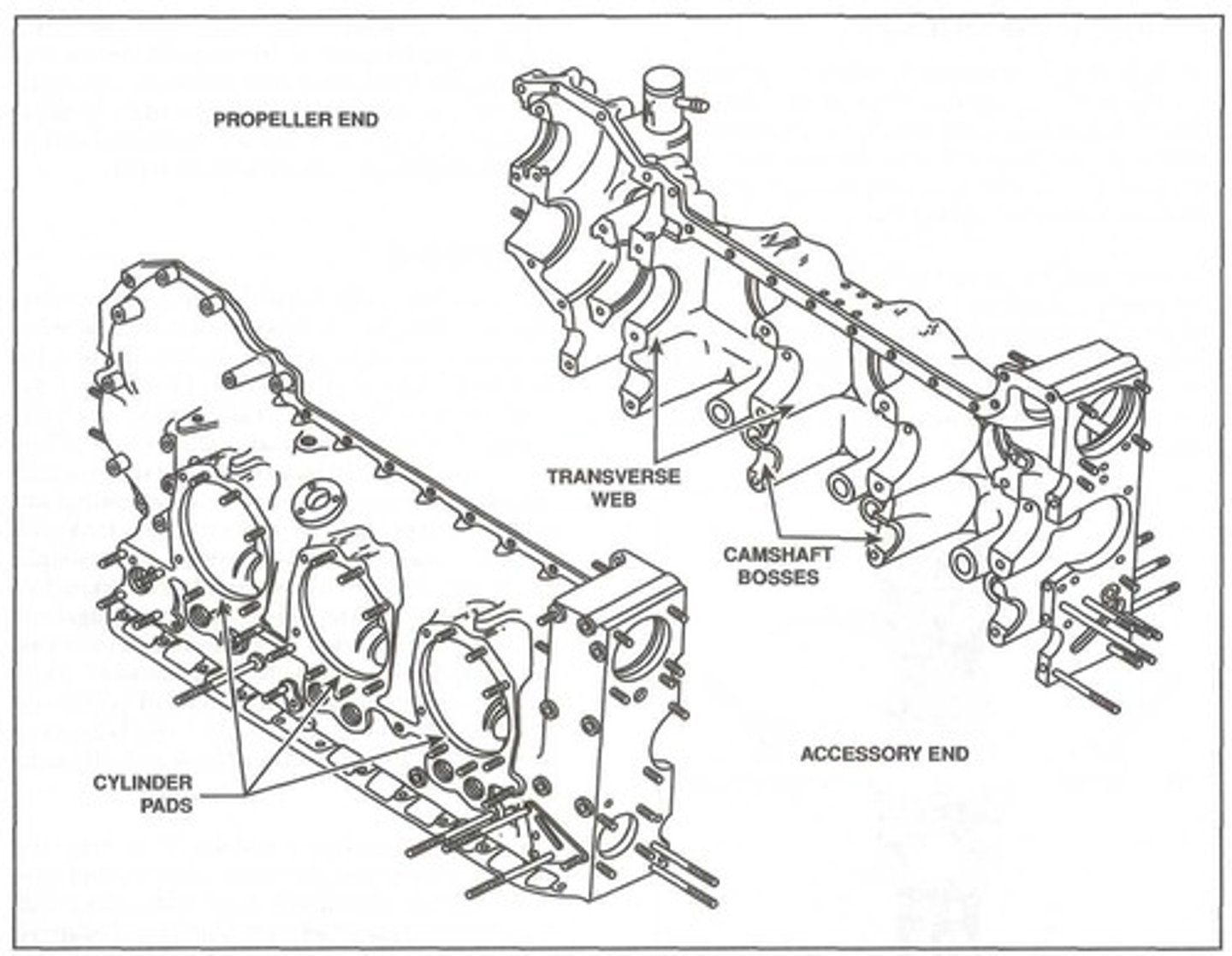
Cylinder pad
Most opposed crankcases are approximately cylindrical, with smooth areas machined to serve as a _______.
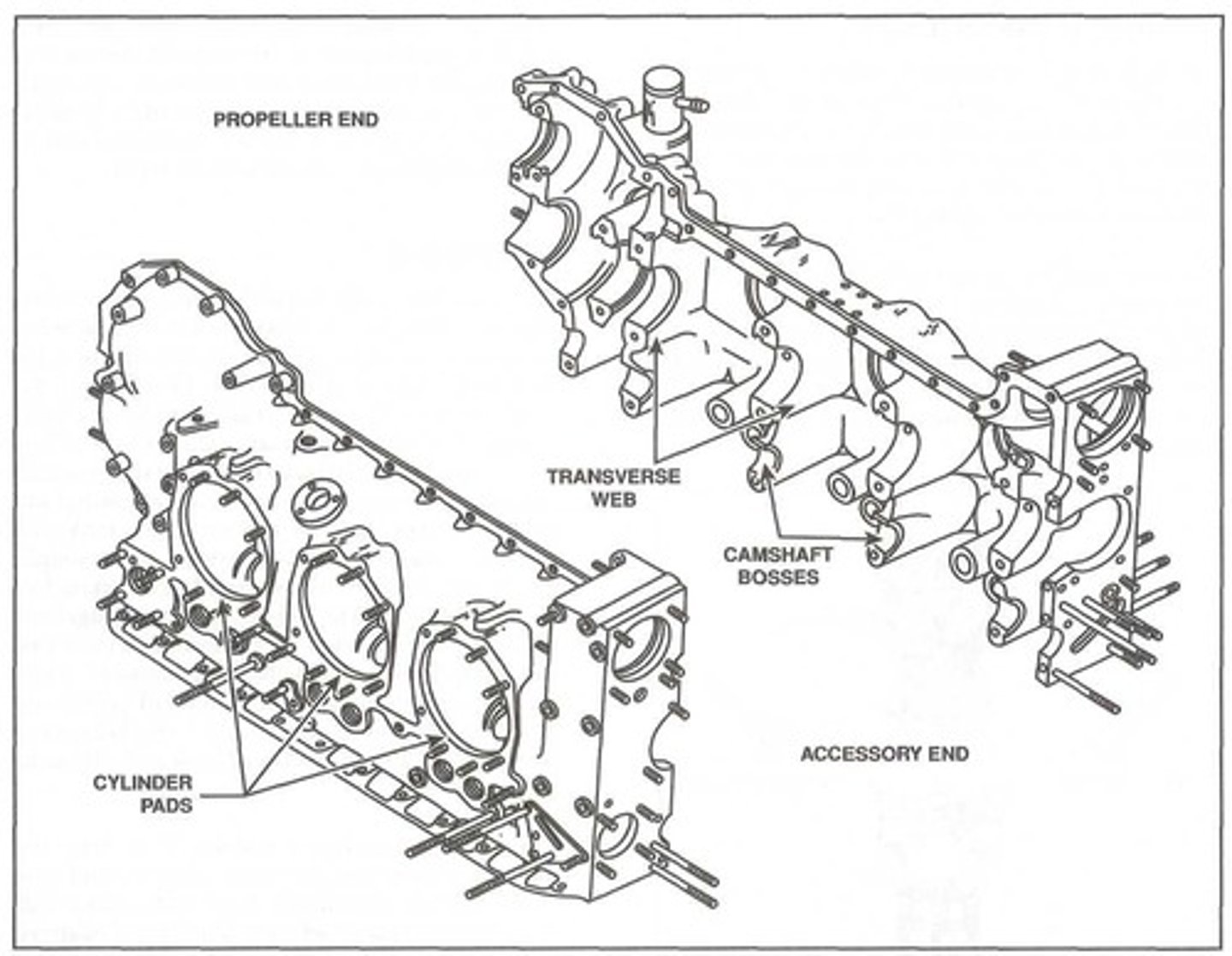
Cylinder pad
It is simply a surface where a cylinder is mounted to a crankcase.
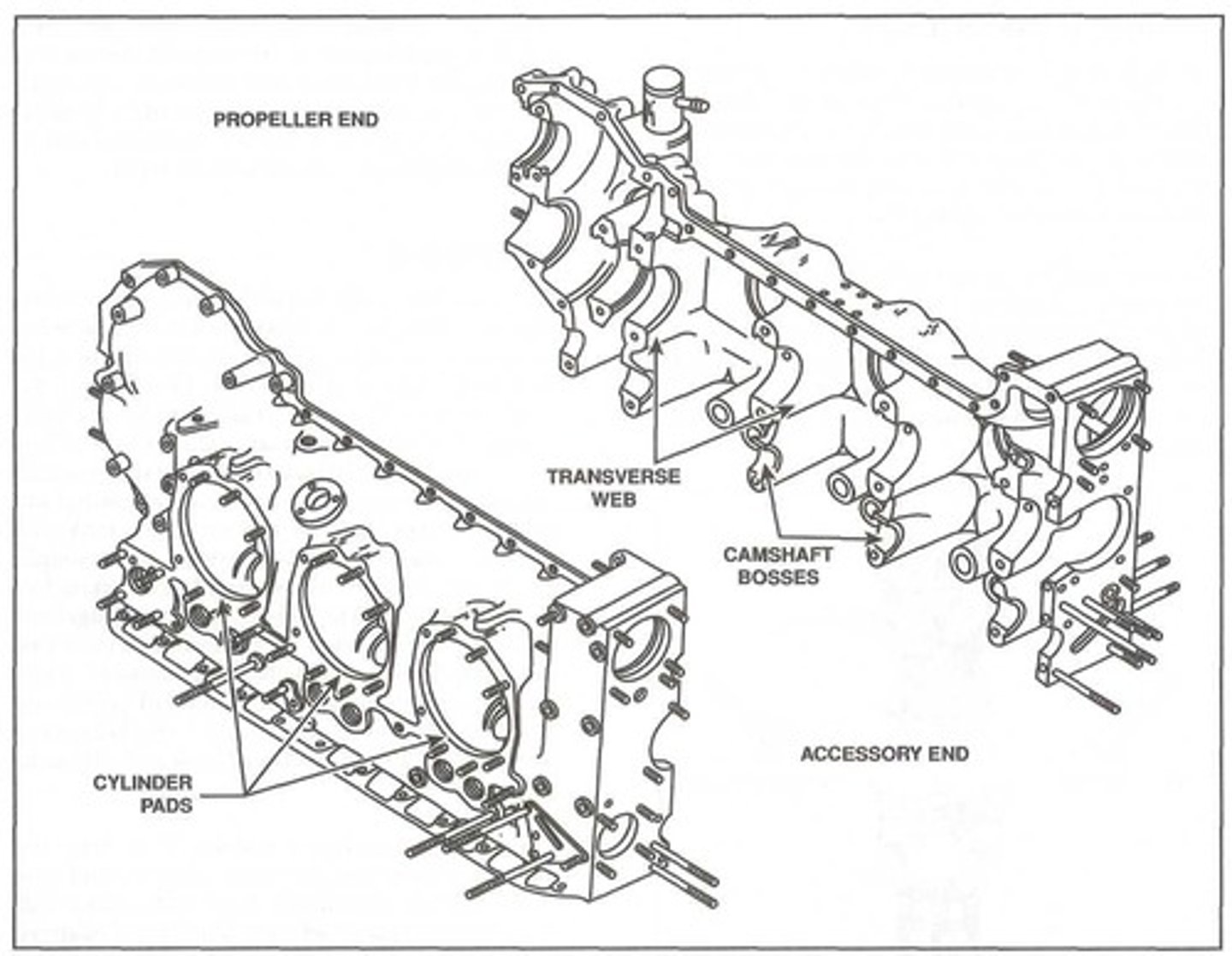
Transverse webs
To allow a crankcase to support a crankshaft, a series of _______ are cast directly into a crankcase parallel to the case's longitudinal axis.
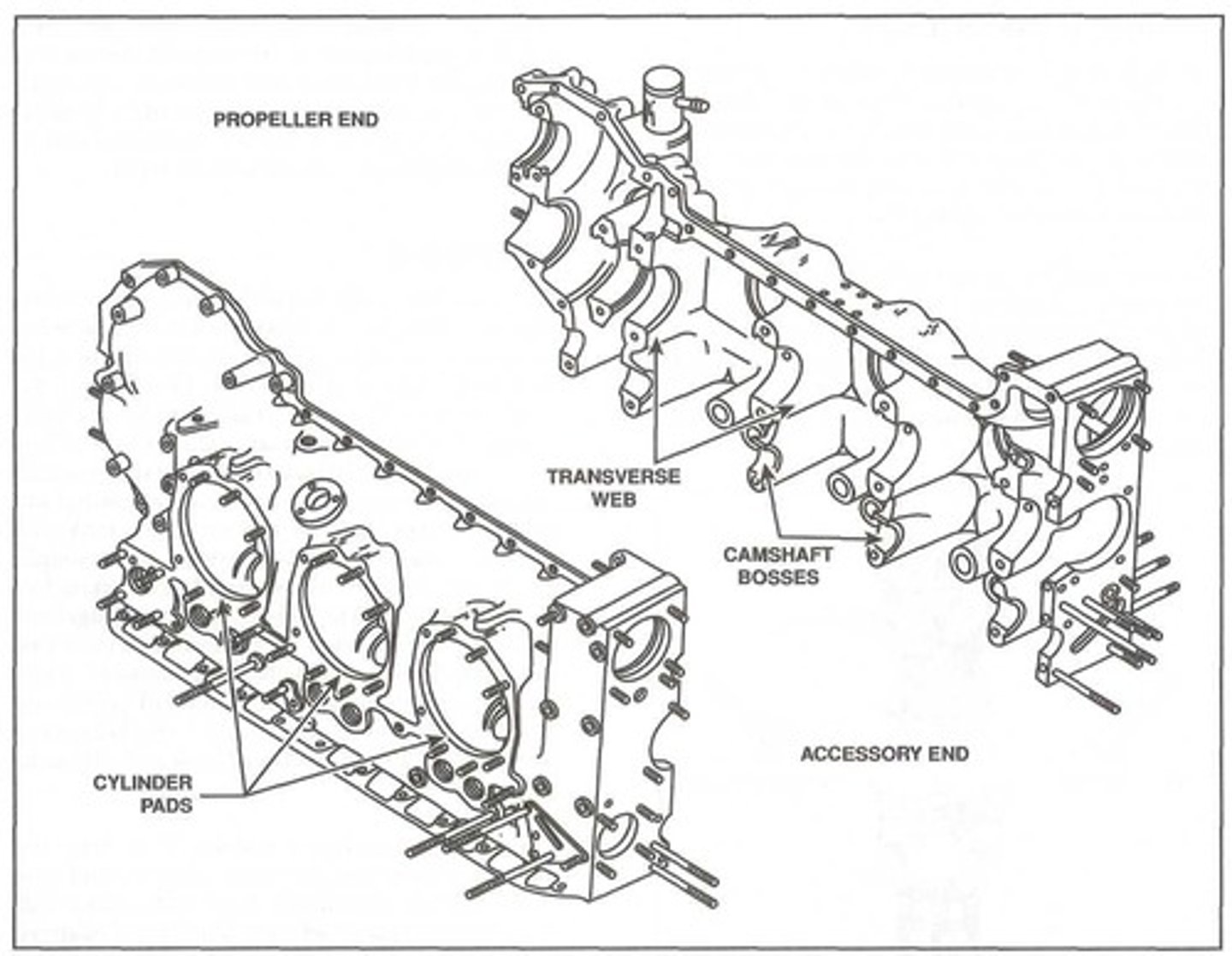
Transverse webs
These webs form an integral part of the crankshaft structure and, in addition to housing the bearings that support the crankshaft, the webs add strength to the crankcase.
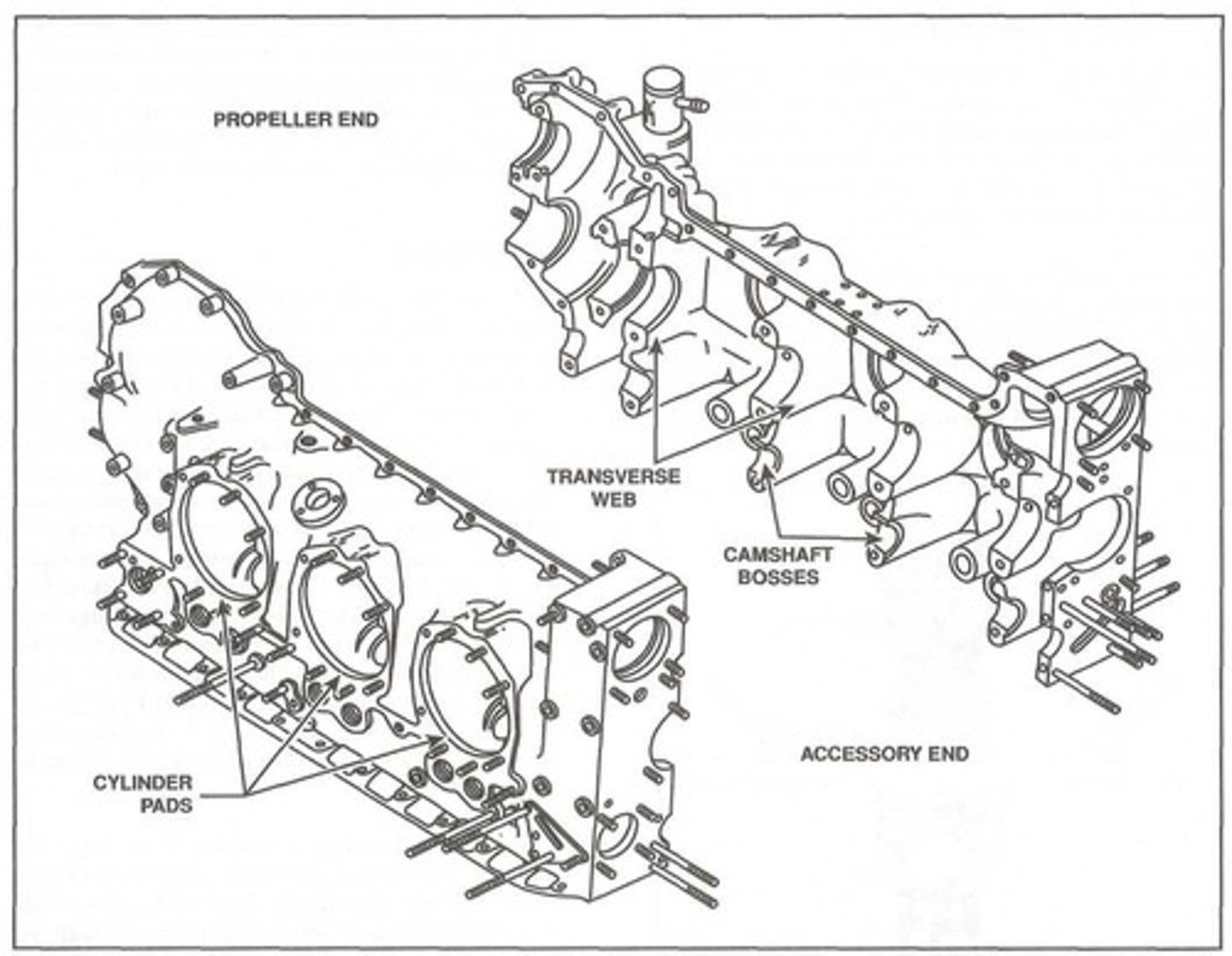
Camshaft bosses
In addition to the transverse webs that support the main bearings, a set of ________ are typically cast into a crankcase. These bosses support the camshaft which is part of the valve operating mechanism.
Case halves
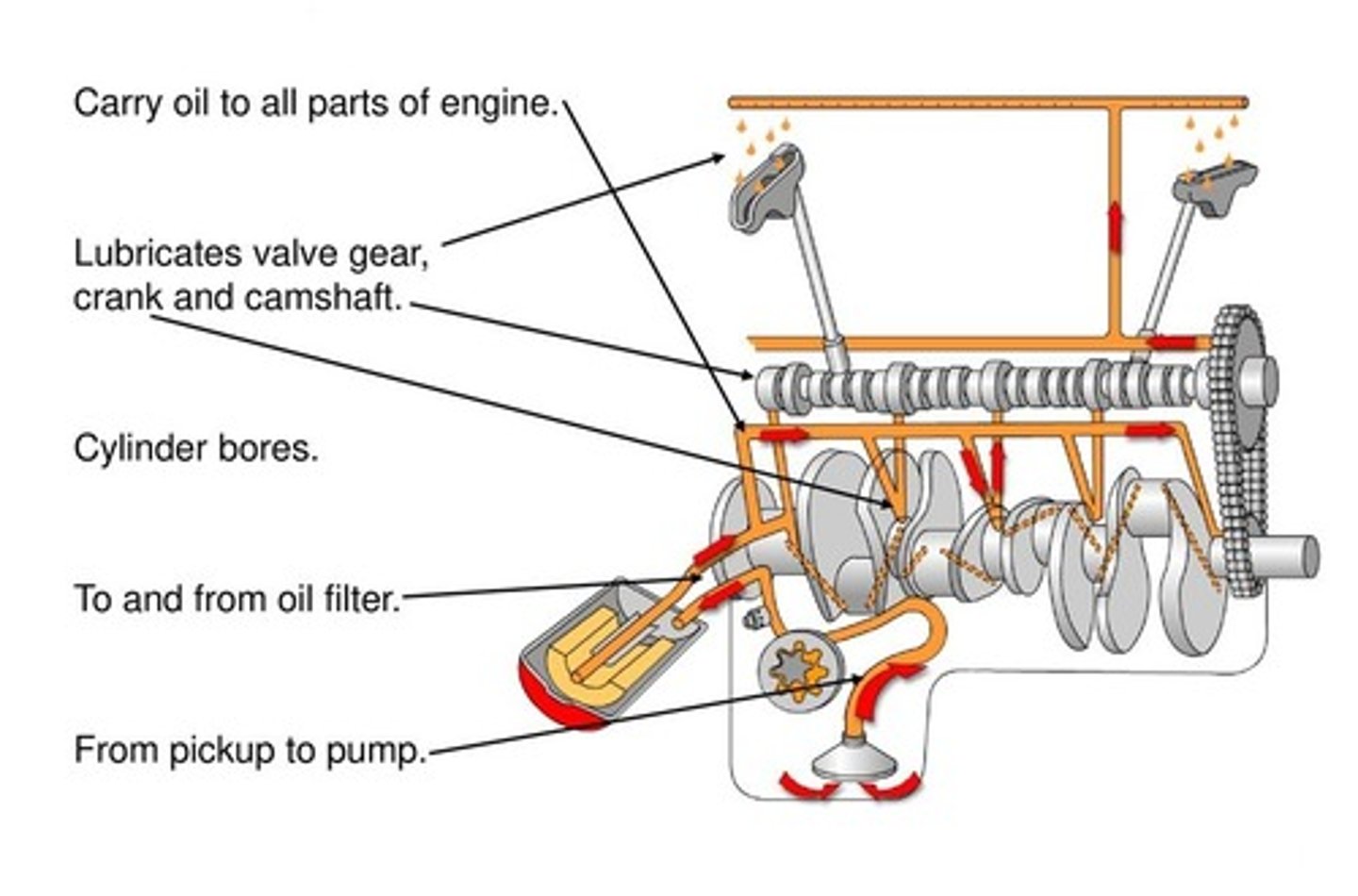
The crankcase is also an integral part of the lubrication system. Oil passages are drilled throughout the _______ to allow lubricating oil to be delivered to the moving parts housed within the crankcase.
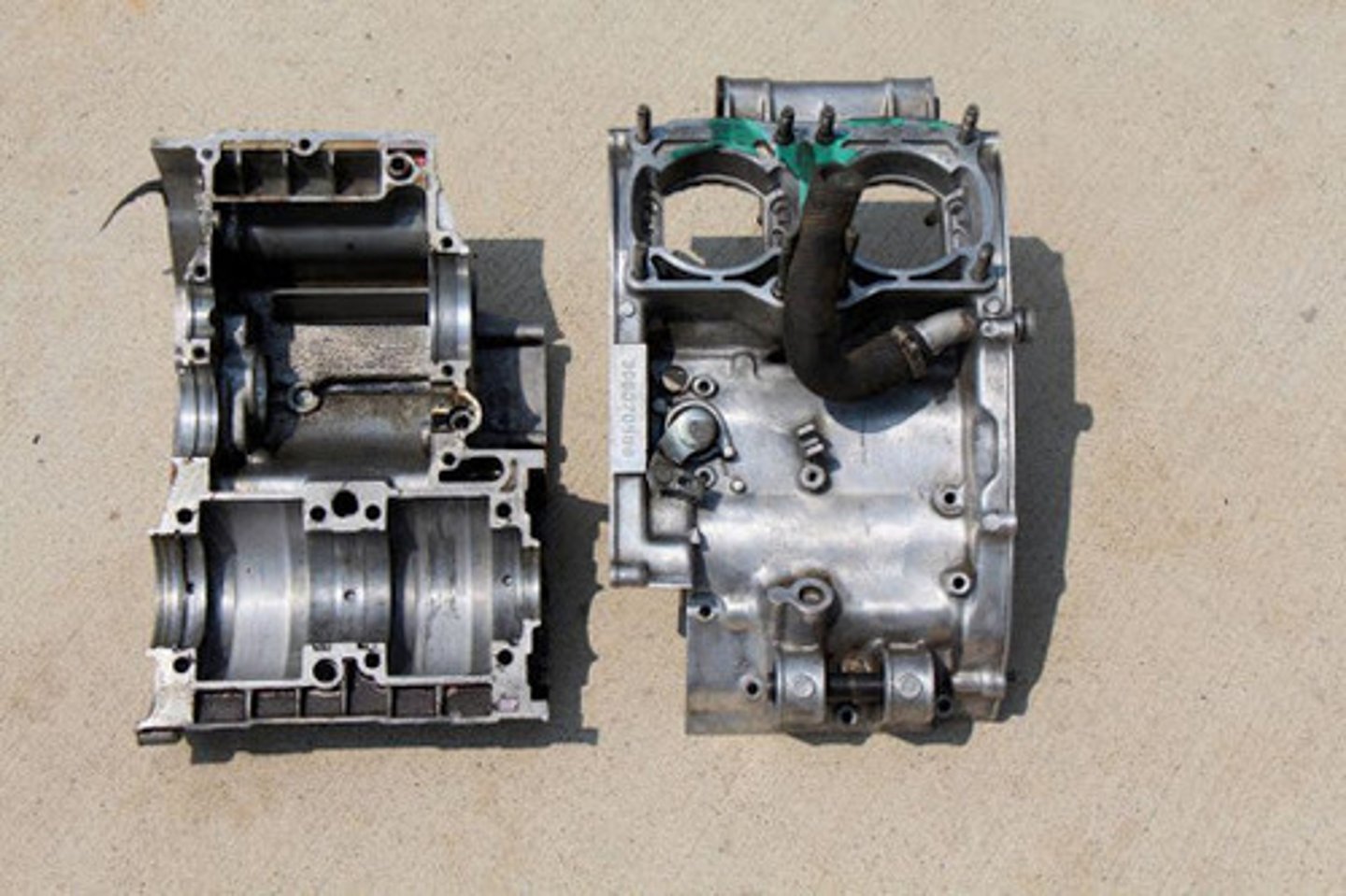
Oil galleries
_______ are machined into the case halves of the crankcase to scavenge, or collect, oil and return it to the main oil tank or sump.
Crankshaft bearings
Most crankcase halves split vertically and are aligned and held together with studs and bolts. Through bolts are typically used at the _______ while smaller bolts and nuts are used around the case perimeter.
Case perimeter
Most crankcase halves split vertically and are aligned and held together with studs and bolts. Through bolts are typically used at the crankshaft bearings while smaller bolts and nuts are used around the ________.
Non-hardening gasket compound
Since the oil supply in most modern horizontally opposed engines is carried inside the crankcase, provisions are made to seal the case to prevent leakage. To ensure that the seal does not interfere with the tight fit for the bearings, most crankcase halves are sealed with a very thin coating of a _________.
Silk thread
Since the oil supply in most modern horizontally opposed engines is carried inside the crankcase, provisions are made to seal the case to prevent leakage. To ensure that the seal does not interfere with the tight fit for the bearings, in addition to the gasket material, on some engines a fine ________ extending around the entire case perimeter is imbedded in the compound.
Gasket material and silk thread
When the crankcase halves are bolted together with the proper torque, this type of setup form an effective oil seal without interfering with bearing fit.
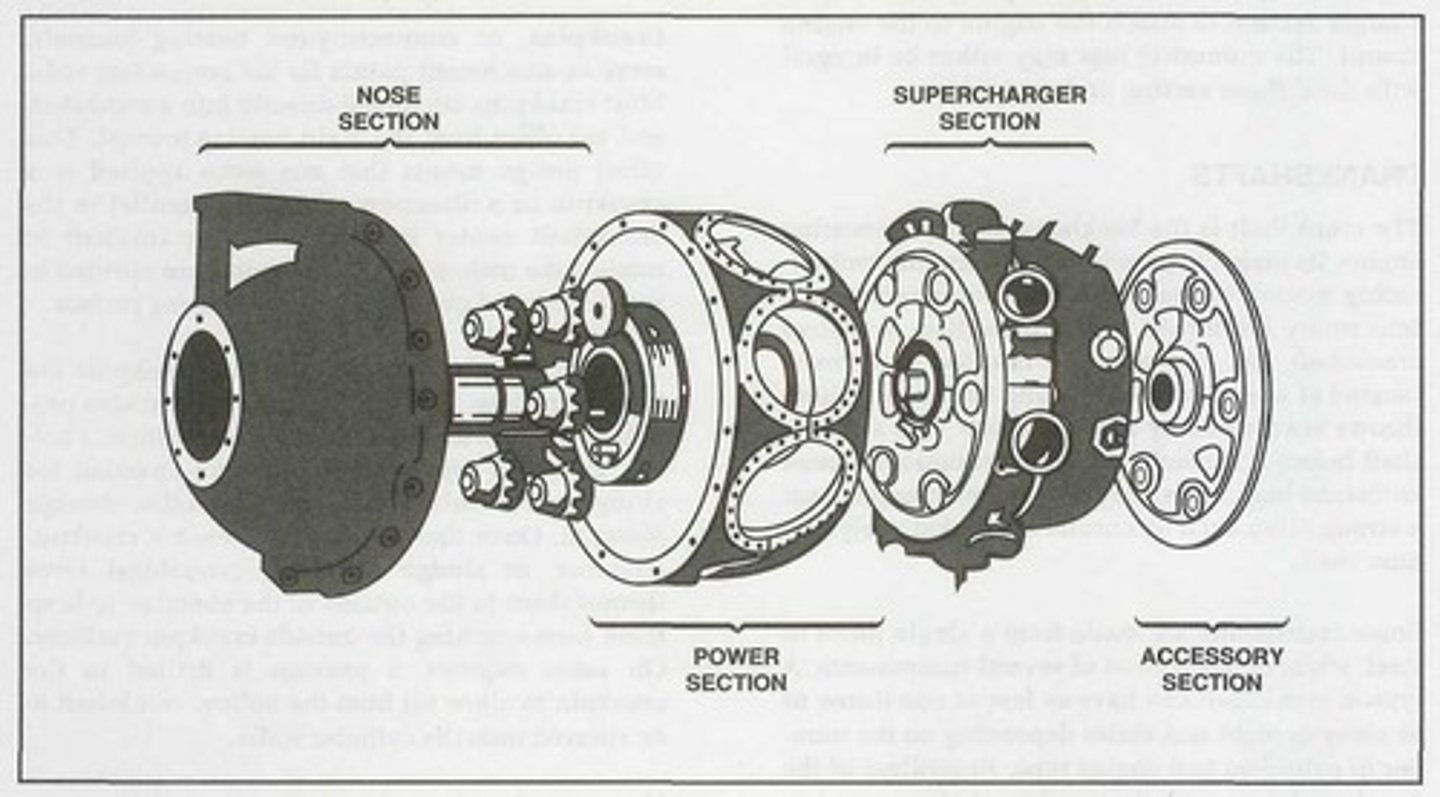
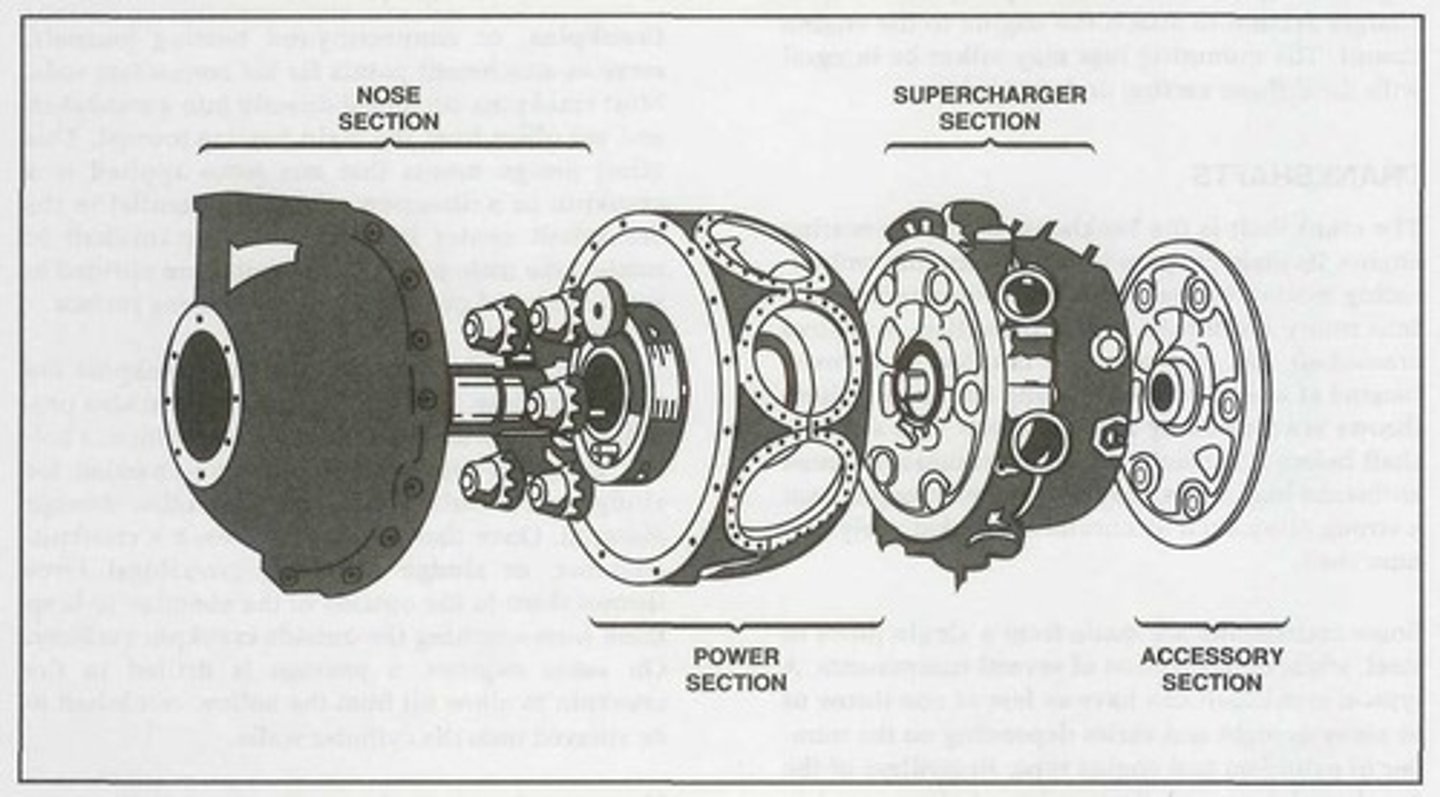
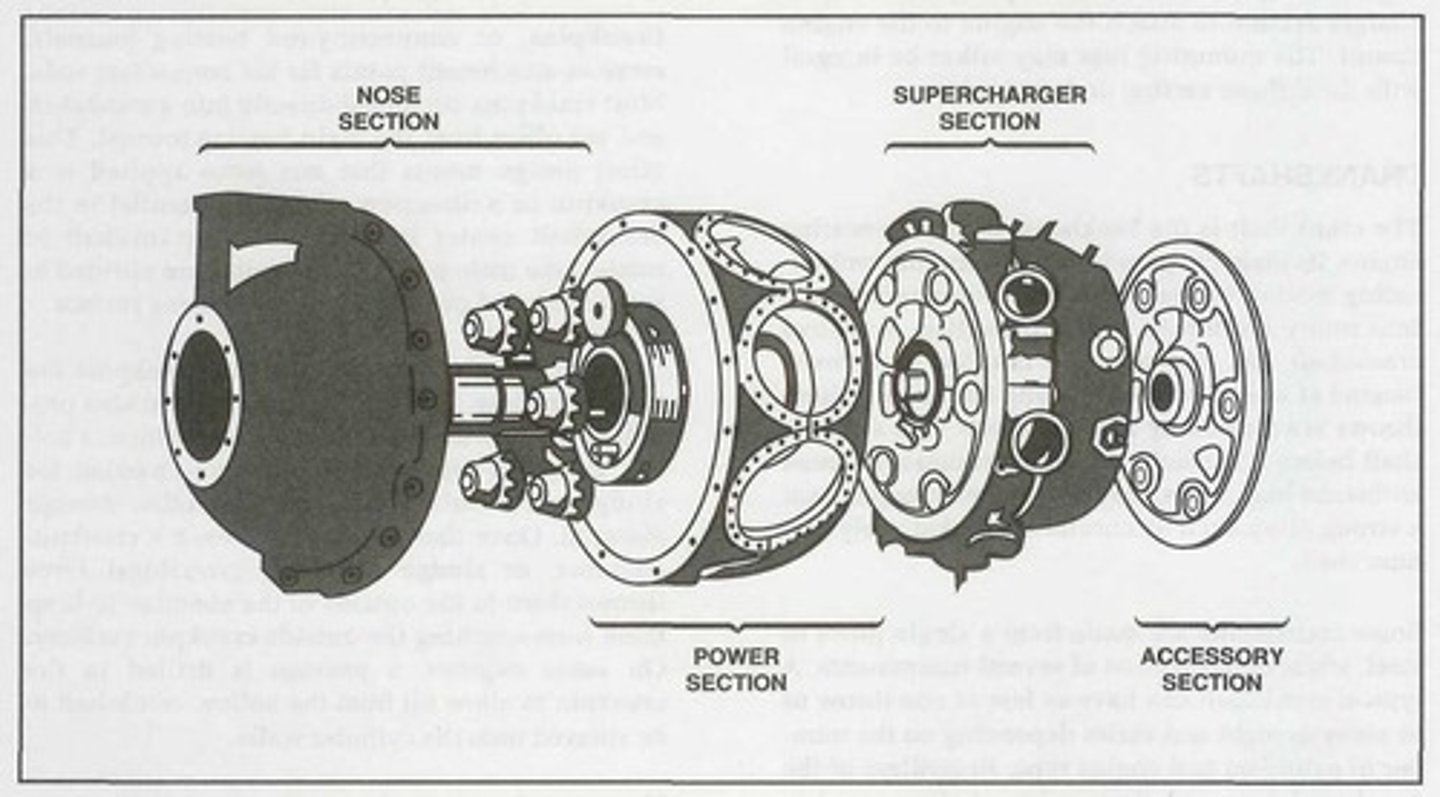
Nose section
It is mounted at the front of a radial engine crankcase and bolts directly to the power section. Typically made of an aluminum alloy that is cast as one piece with a domed or convex shape.
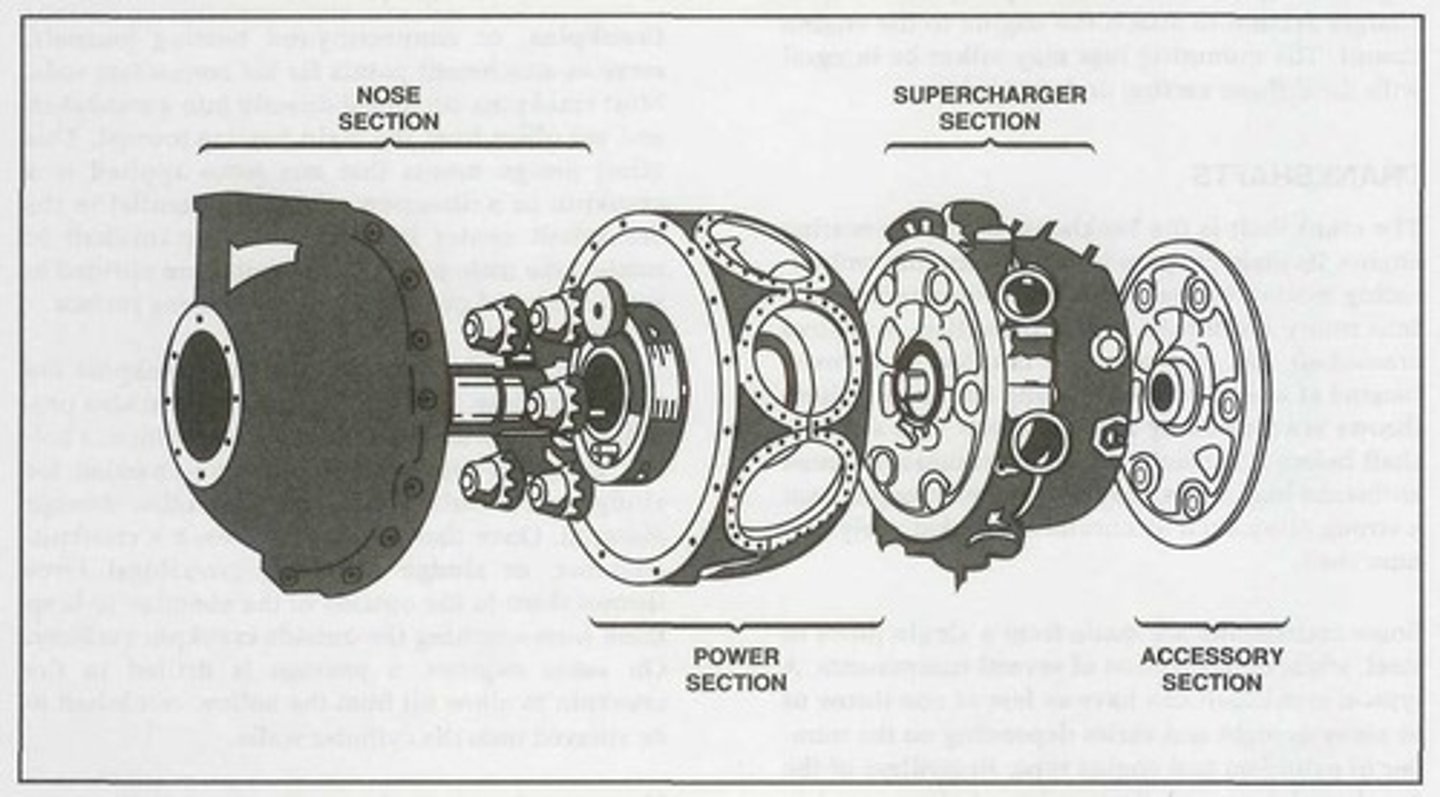
Nose section
For radial engine crankcases, it usually houses and supports a propeller governor drive shaft, the propeller shaft, a cam ring, and a propeller reduction gear assembly if required. In addition, it has mounting points for magnetos and other engine accessories.
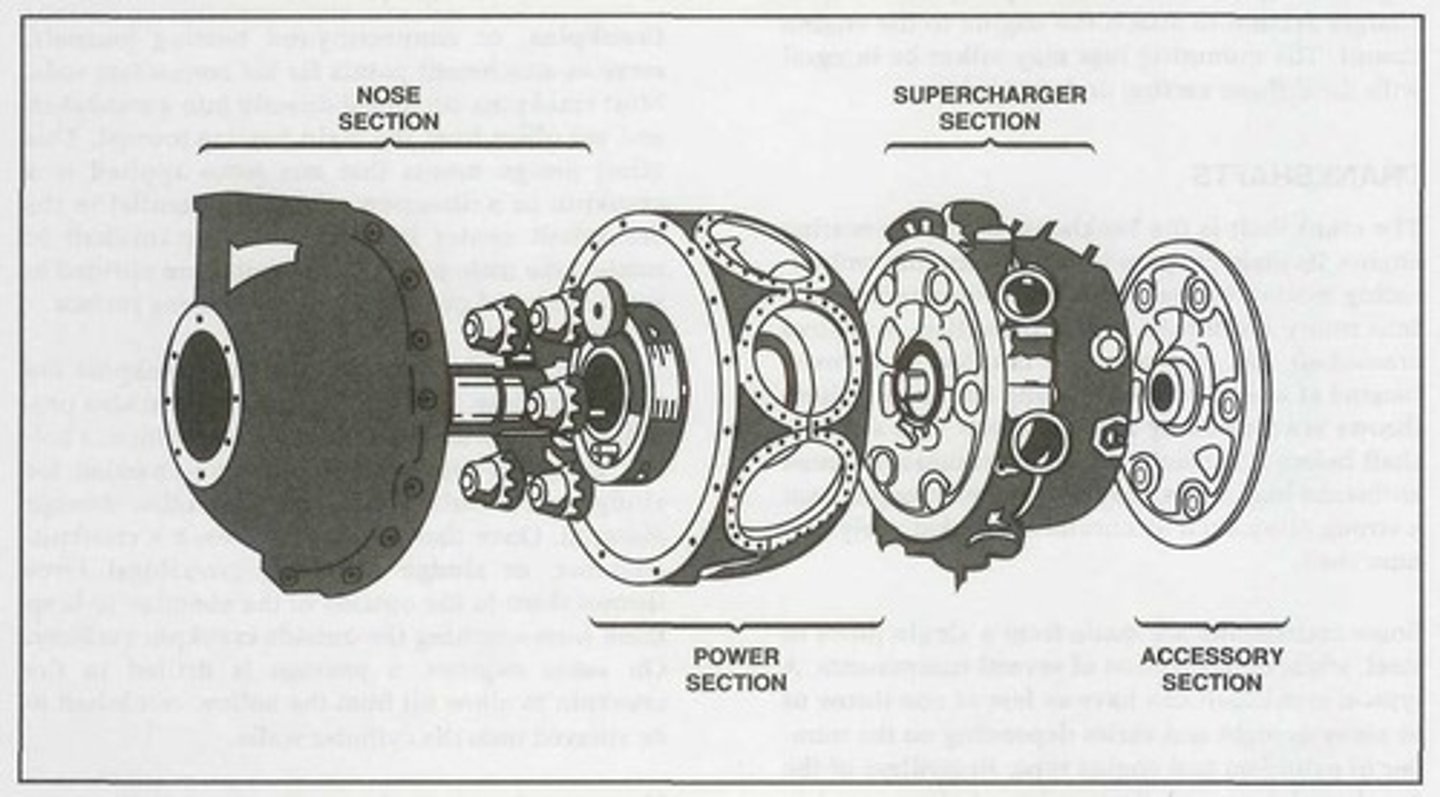
Power section
The second portion of a radial crankcase is referred to as the _______ and represents the section of the crankcase where the reciprocating motion of the pistons is converted to the rotary motion of the crankshaft.
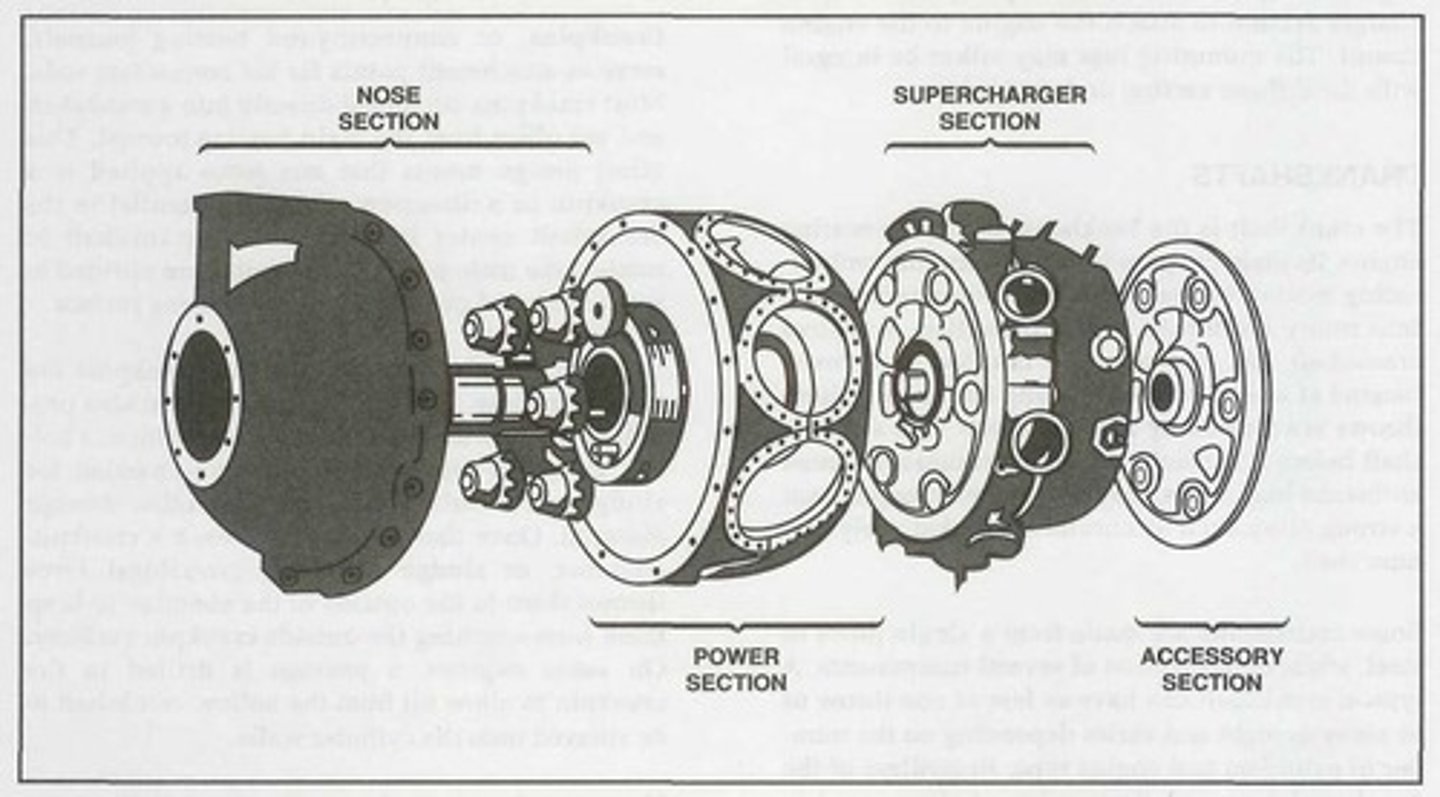
Power section
Like an opposed engine crankcase, this radial engine crankcase section absorbs intense stress from the crankshaft assembly and the cylinders.
One-piece
A radial engine power section can be either one, two, or three pieces. A _______ power section usually consists of a solid piece of aluminum alloy.
Split
A radial engine power section can be either one, two, or three pieces. A ______ power section is typically manufactured from aluminum or magnesium and then bolted together.
Power section
As with an opposed engine crankcase, a radial engine ______ section contains machined bosses that rigidly support the crankshaft bearings and the crankshaft.
Cylinder pad
Cylinders are attached around the perimeter of the radial engine power section to machined _______.
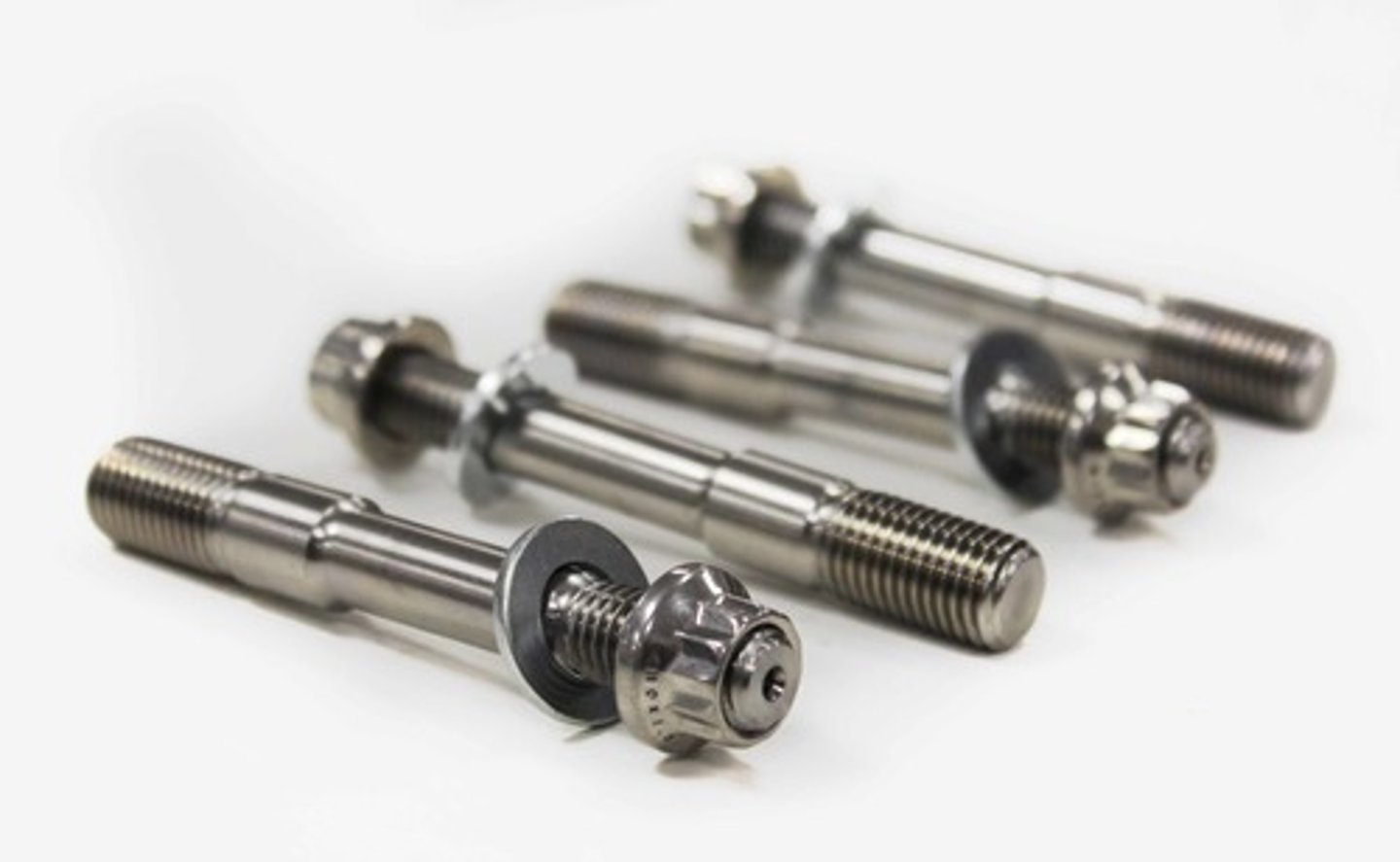
Studs
_______ are installed into threaded holes in the power section to provide a means of retaining the cylinders.

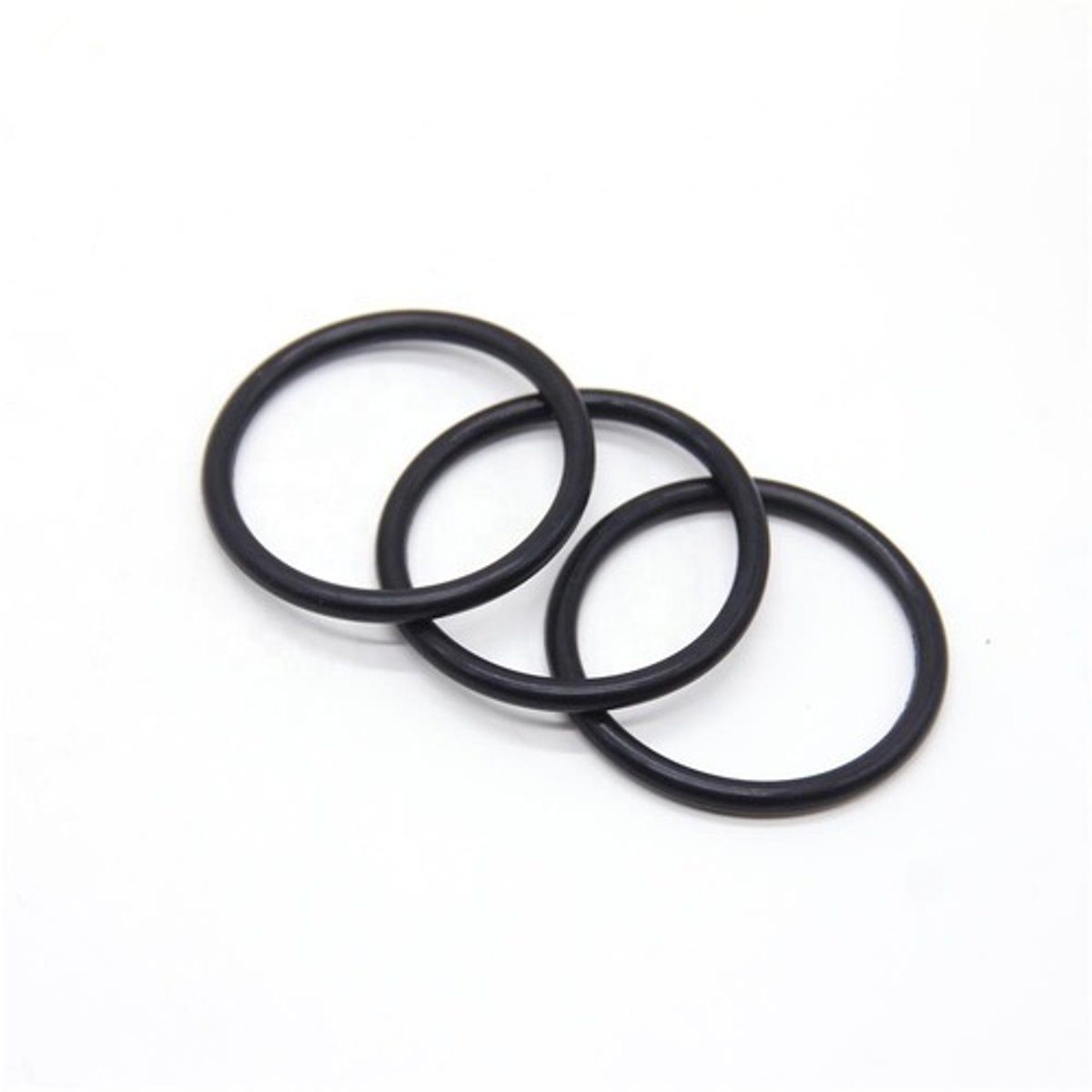
O-ring
The inner circumference of a cylinder pad is sometimes chamfered or tapered to permit the installation of a large rubber ______ around the cylinder skirt. This ______ effectively seals the joint between the cylinder and the cylinder pads.

Supercharger section
The diffuser or ________ is located directly behind the radial engine power section and is generally made of cast aluminum alloy or magnesium.
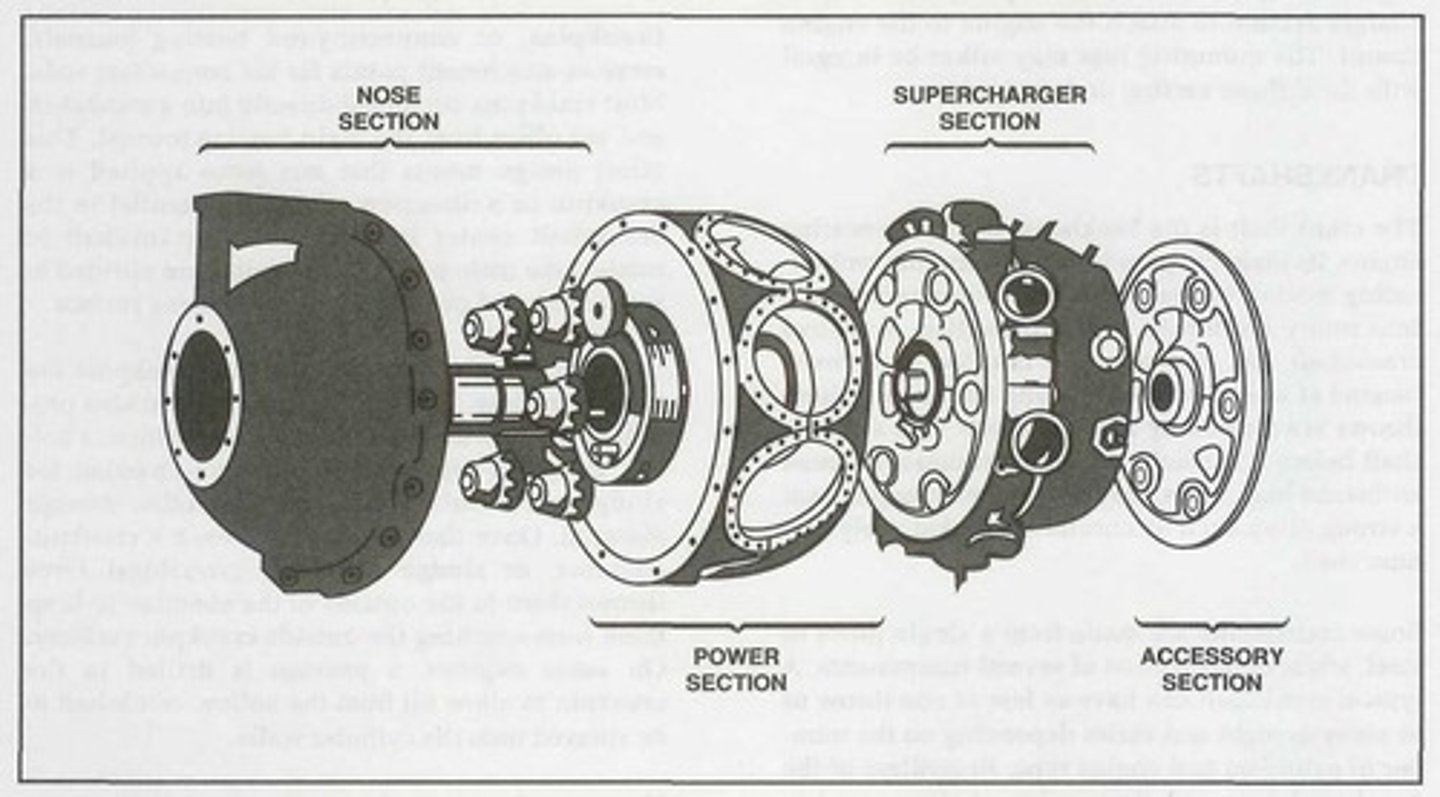
Supercharger section
This radial engine crankcase section houses the supercharger and its related components.
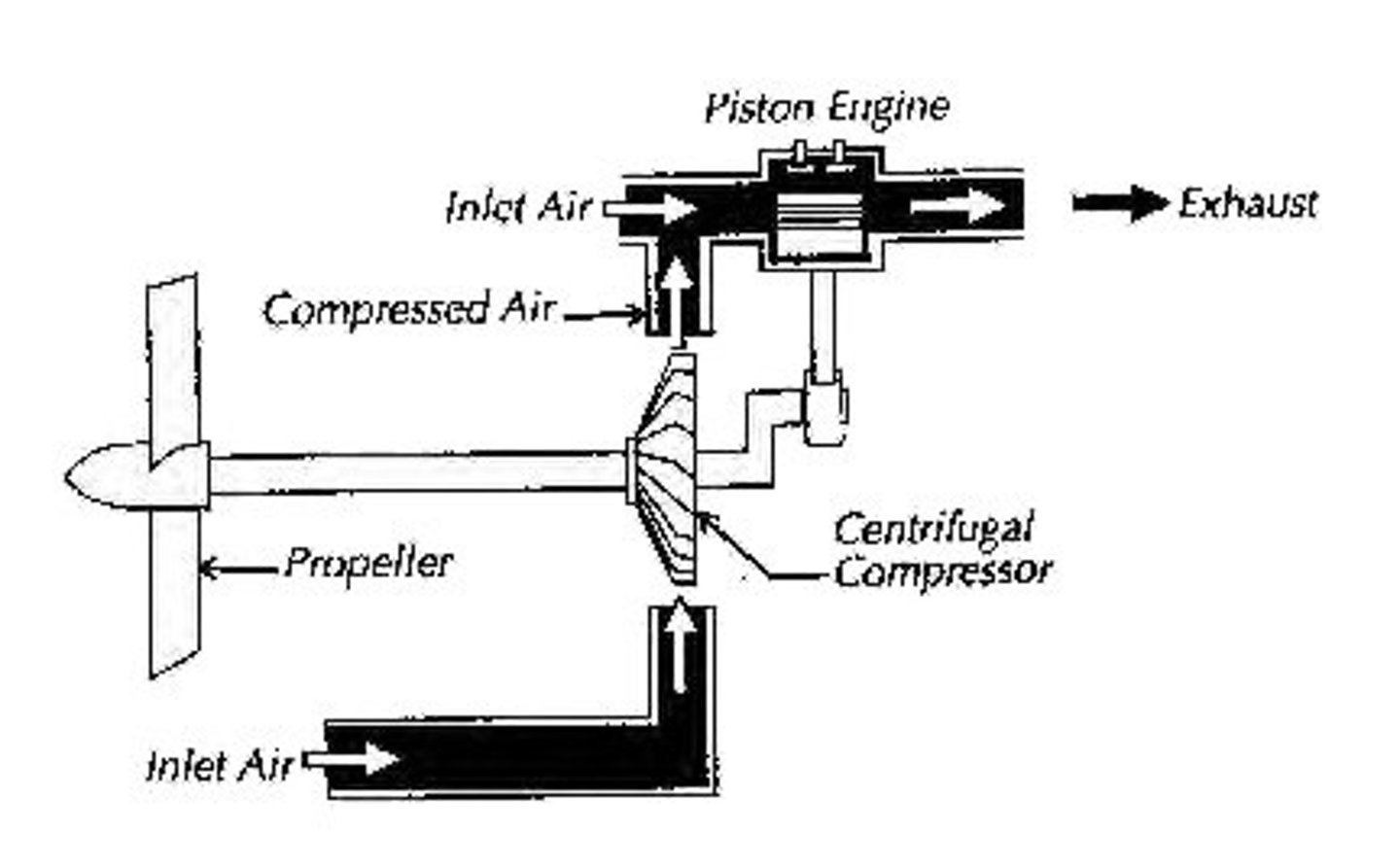
Supercharger
It is an engine accessory that is used to compress air and distribute it to the engine's cylinders.
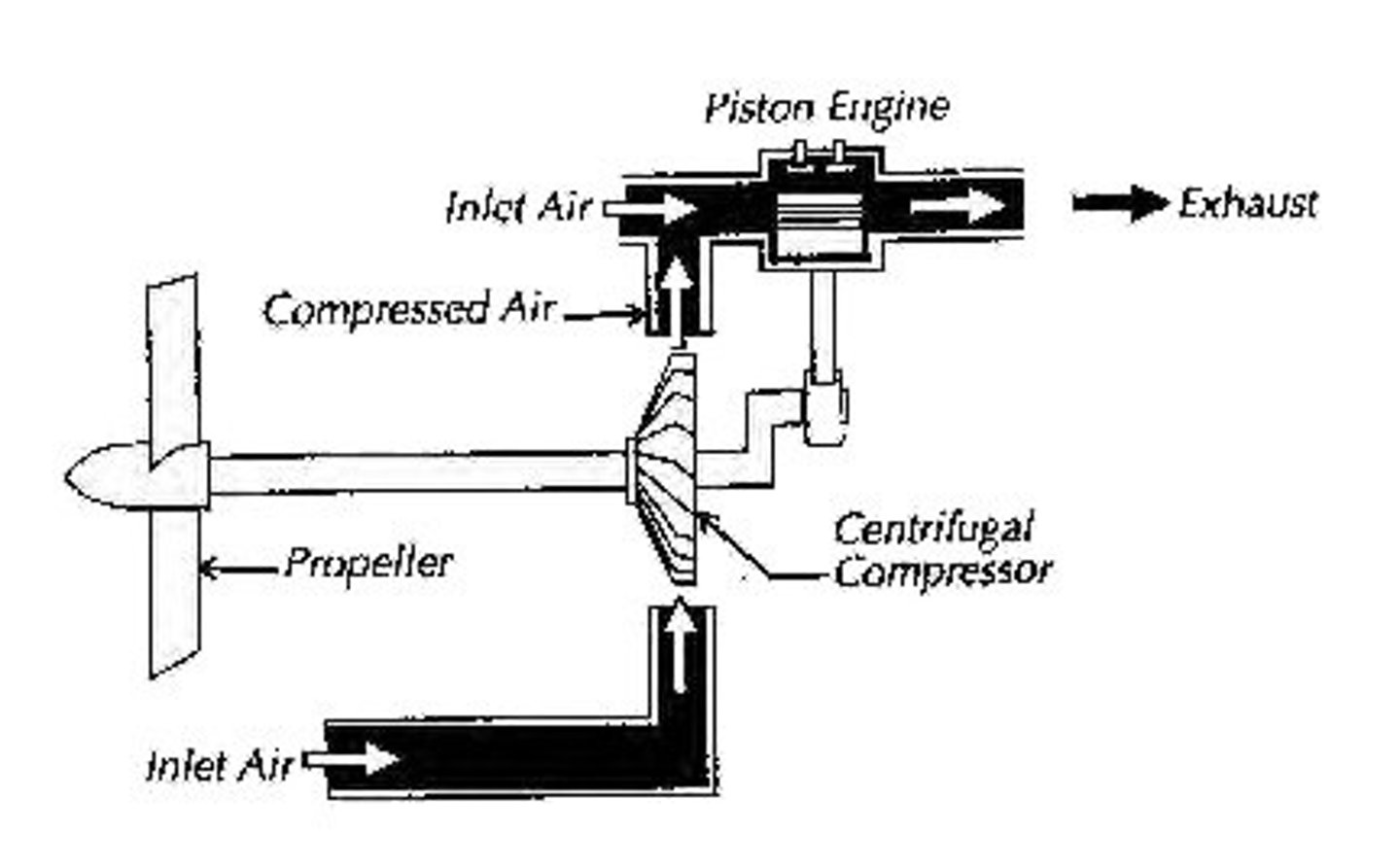
Supercharger
This engine accessory's compression increases the air density so the engine can operate at high altitudes and still produce the same amount of power as it would at sea level.
Mounting lugs
The radial engine supercharger section incorporates _______ to secure the engine assembly to the engine mounts.
Accessory section
The _______ is usually cast of either an aluminum alloy or magnesium. On some engines, it is cast in one piece and then machined to provide a means for mounting accessories such as magnetos, carburetors, pumps, starters, and generators. However, on other engines, it consists of an aluminum alloy casting and a separate cast magnesium cover plate on which the accessories are mounted.
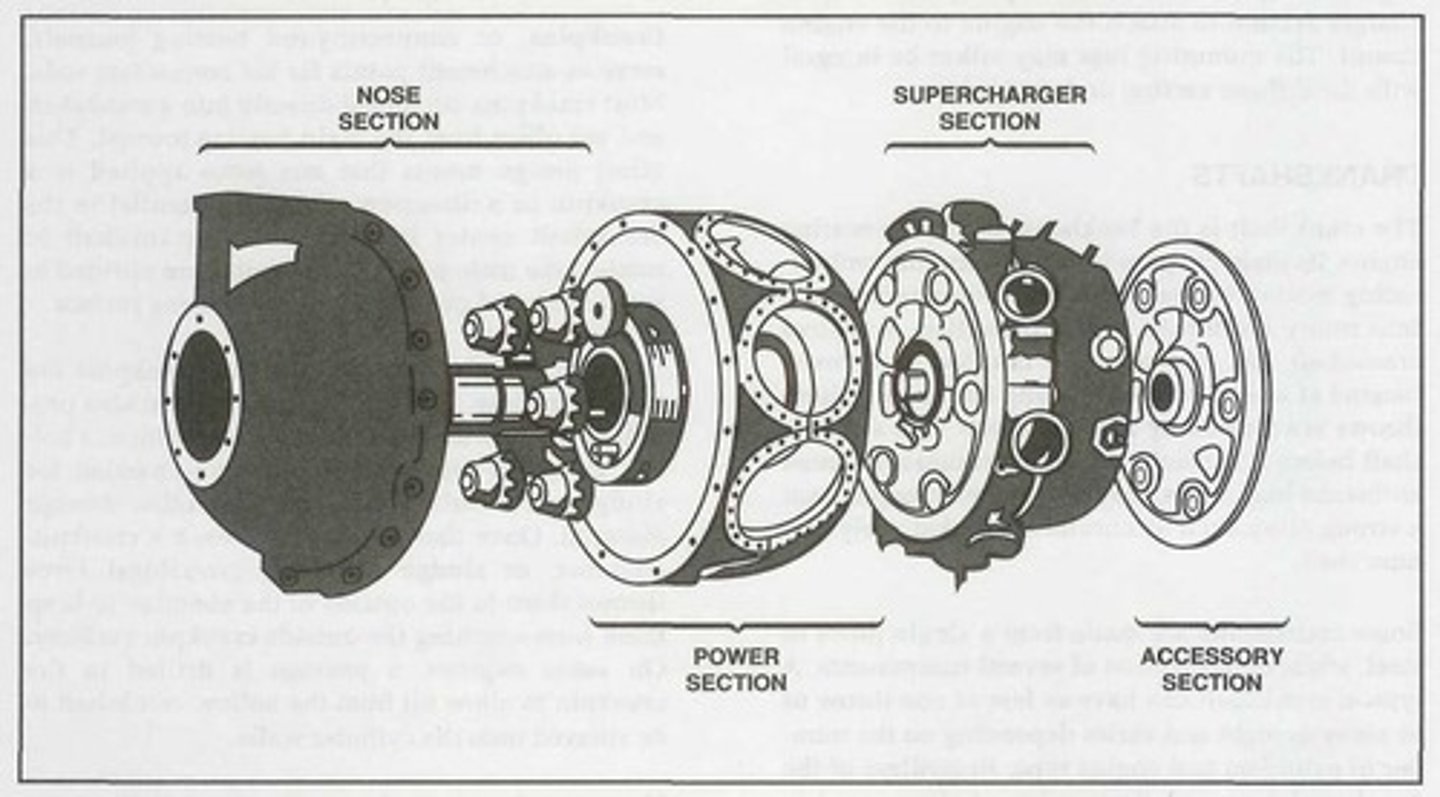
Accessory section
This radial engine section houses gear trains containing both spur- and bevel-type gears that drive various engine components and accessories.
Spur-type
_______ gears are generally used to drive more heavily loaded accessories or those requiring the least play or backlash in the gear train.

Bevel-type
_______ gears permit angular location of short stub shafts leading to the various accessory mounting pads.

Mounting lugs
For opposed engines, mounting points, sometimes called _______, are typically cast as part of the crankcase. However, some of it may be a bolt-on addition.
Mounting lugs
As a general rule, lower-horsepower engines use _______ that are cast into the crankcase, while higher-powered engines employ ________ that are bolted to the crankcase.
Mounting lugs
On all engines, ________ support the entire powerplant including the propeller and, therefore, must be designed to withstand various engine, centrifugal, and g-loading conditions.
Supercharger section
Mounting lugs for radial engines are spaced about the periphery of the ______ to attach the engine to the engine mount. The mounting lugs may either be integral with this section or detachable.
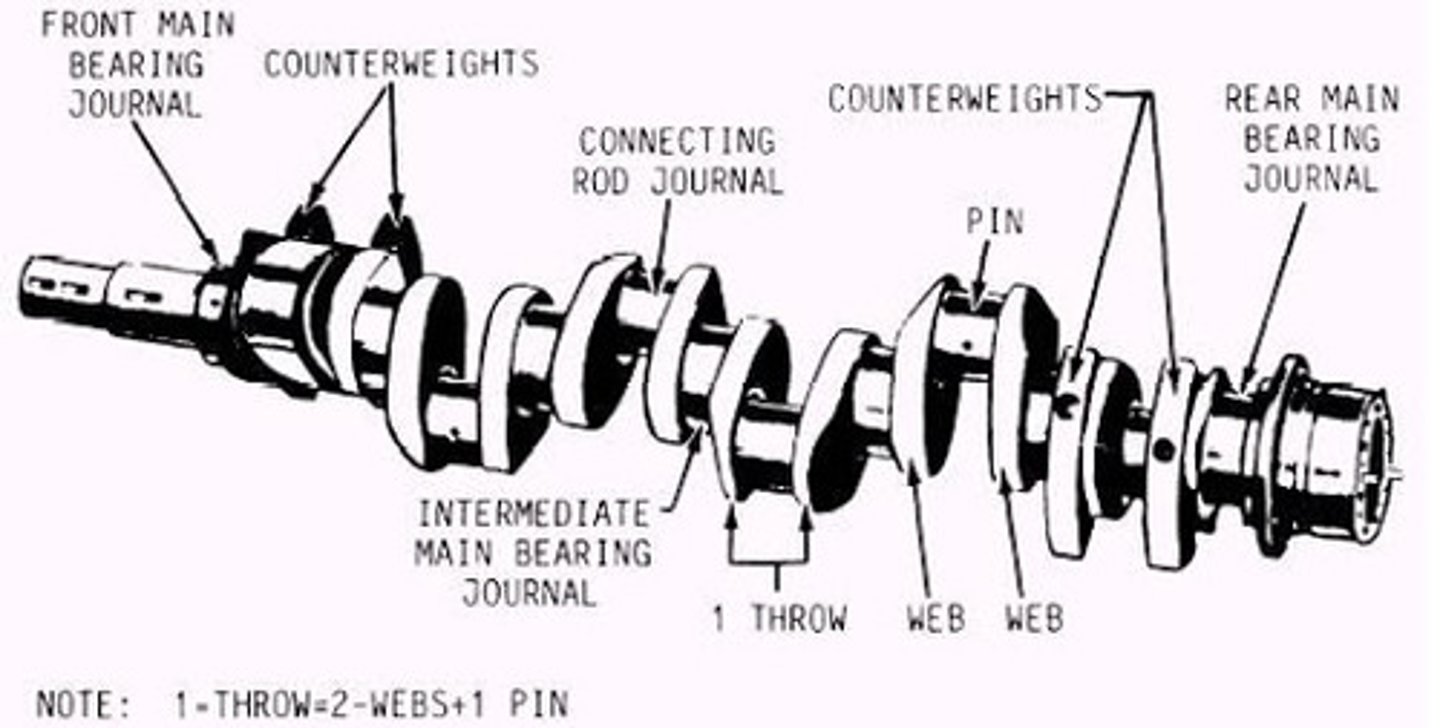
Crankshaft
It is the backbone of a reciprocating engine.
Crankshaft
Its main purpose is to transform the reciprocating motion of the pistons and connecting rods into rotary motion to turn a propeller.
Chromium-nickel molybdenum steel
A typical crankshaft has one or more cranks, or throws, located at specified points along its length. These throws are formed by forging offsets into a crankshaft before it is machined. Since crankshafts must withstand high stress, they are generally forged from a strong alloy such as _______.
Cylinder
Some crankshafts are made from a single piece of steel, while others consist of several components. A typical crankshaft can have as few as one throw or as many as eight and varies depending on the number of ______ and engine type.
Engine vibration
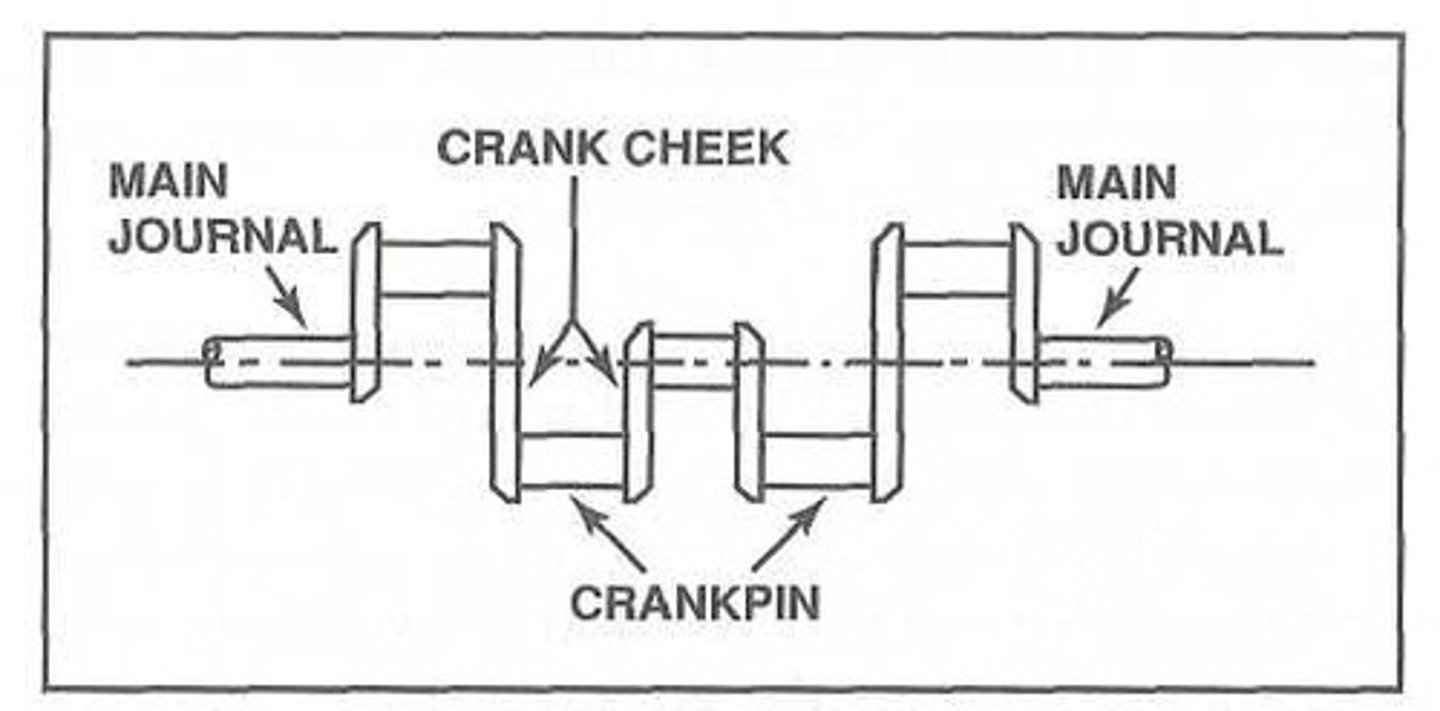
Regardless of the number of throws or the number of pieces used in construction, all crankshafts utilize the same basic parts. These parts include the main bearing journal, the crankpin, and the crank cheek. In addition, although they are not true parts of the crankshaft, counterweights and dampers are often installed on many crankshafts to reduce _______.
Main bearing journals
The _______, or main journals, represent the center line of a crankshaft and support the crankshaft as it rotates in the main bearings.
2
All crankshafts require at least _____ main journals to support the crankshaft, absorb the operational loads,and transmit stress from the crankshaft to the crankcase.
Nitriding
To help minimize wear, most main bearing journals, or crank journals, as they are sometimes called, are hardened through ________ to resist wear.