ARCL 228
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/248
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
1
New cards
forensic taphonomy
modifications made to the bone that are essentially natural
2
New cards
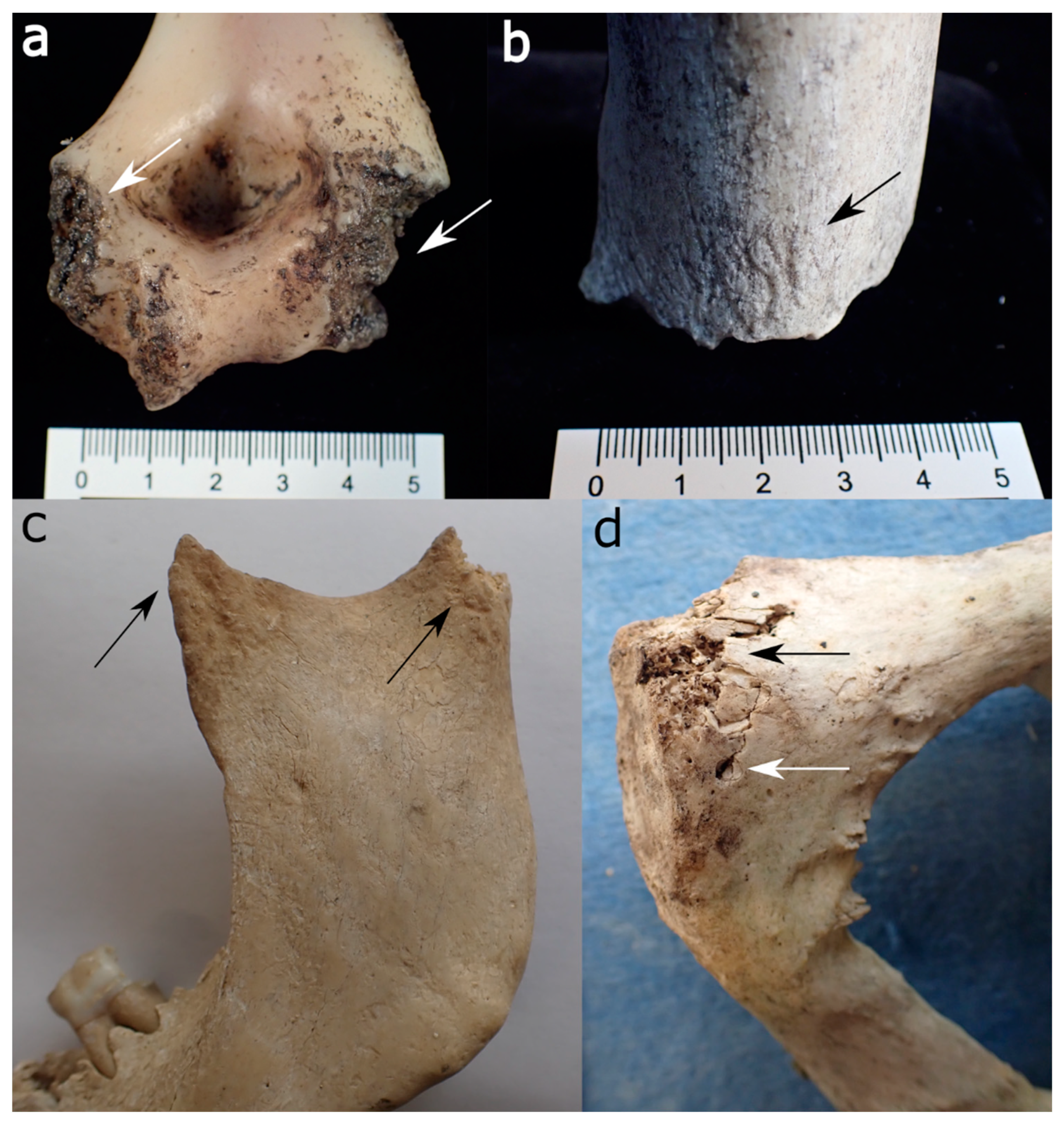
effects of animal scavenging
1. scattering/disarticulation of remains
2. pull limbs apart at torso, gnaw an epiphyses
3. break bones in particular pattern by trampling or chewing
- more than 80% of skeleton recovered = less than 6 months since dead
- less than 20% of skeleton recovered = more than 6 months since death
- rodents create parallel lines on bones
2. pull limbs apart at torso, gnaw an epiphyses
3. break bones in particular pattern by trampling or chewing
- more than 80% of skeleton recovered = less than 6 months since dead
- less than 20% of skeleton recovered = more than 6 months since death
- rodents create parallel lines on bones
3
New cards
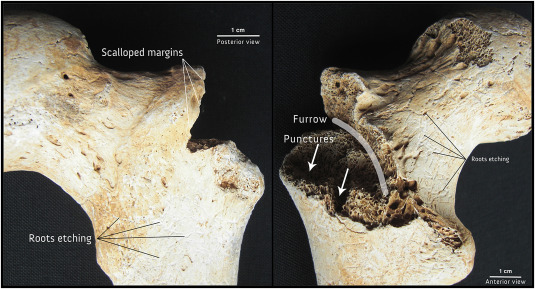
carnivore activity on bones
Chewing on bone
- puncturing
- pits (compressed cortical bone)
- scoring (parallel lines)
- furrows (sharp, deeper)
- excessive activity leaving V-shaped marks
- puncturing
- pits (compressed cortical bone)
- scoring (parallel lines)
- furrows (sharp, deeper)
- excessive activity leaving V-shaped marks
4
New cards
sequence of carnivore dismemberment
1. soft tissue of head and neck
2. ventral thorax opened, contents of chest eaten, followed by sternum/rib ends
3. upper limbs
4. lower limbs
5. thorax removed, ribs broken
6. long bones separated from each other
7. all bones disarticulated, scattered, chewed
2. ventral thorax opened, contents of chest eaten, followed by sternum/rib ends
3. upper limbs
4. lower limbs
5. thorax removed, ribs broken
6. long bones separated from each other
7. all bones disarticulated, scattered, chewed
5
New cards
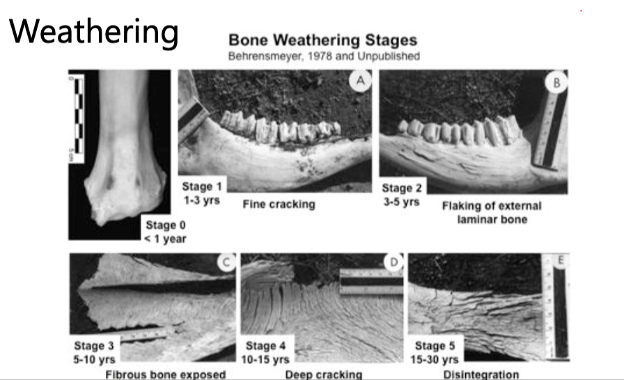
weathering
water hydrates bone, sun dries it out
6
New cards

burial damage
bone takes on qualities of burial environment
- soil colour permeates bone
- root etching
- erosion of cortical bone
- damage during recovery
- soil colour permeates bone
- root etching
- erosion of cortical bone
- damage during recovery
7
New cards
water transport phases
1. body sinks, travels away from initial point of insertion
- damage from body scraping, erosion of tissue
- damage from currents
2. body bloats, rises to surface
- body parts begin to separate
3. independent movement of individual body parts
- round segments can travel long distances
- ankles often detach
- flat bones stay closer to point of insertion
- damage from body scraping, erosion of tissue
- damage from currents
2. body bloats, rises to surface
- body parts begin to separate
3. independent movement of individual body parts
- round segments can travel long distances
- ankles often detach
- flat bones stay closer to point of insertion
8
New cards
Chronological age
birthdays
9
New cards
biological age
growth and development rate
- differs from chronological at actual birth
- differs from chronological at actual birth
10
New cards
socio-cultural age
sociological markers from progressing through social stages based on your roles and responsibilities
11
New cards
trajectory effect
dissociation of biological age and chronological age
- nutritional defects
- nutritional defects
12
New cards
fetal bone growth
starts at 8 weeks, birth occurs at 40 weeks
13
New cards
juvenile bone growth
1. in-utero to 5 years: very rapid (triples in size)
2. 5 to puberty: gradual plateau
3. 14-16: spikes again
- individual and sex dependent
2. 5 to puberty: gradual plateau
3. 14-16: spikes again
- individual and sex dependent
14
New cards
prenatal
conception to birth
- embryo: 1-10 weeks
- fetus: 10 weeks to birth
- birth: 40 weeks, skeleton formed at 32 weeks
- embryo: 1-10 weeks
- fetus: 10 weeks to birth
- birth: 40 weeks, skeleton formed at 32 weeks
15
New cards
infancy
when baby is nursing
- perinate: time of birth
- neonate: first 4 weeks after birth
- infant: birth to 1 year
- perinate: time of birth
- neonate: first 4 weeks after birth
- infant: birth to 1 year
16
New cards
childhood
weaning (2-5) to puberty
- early childhood: 1-4 years
- late childhood: 5-10 years
- early childhood: 1-4 years
- late childhood: 5-10 years
17
New cards
adolescence
puberty to end of growth
- early: 11-14 years
- late: 15-17 years
- early: 11-14 years
- late: 15-17 years
18
New cards
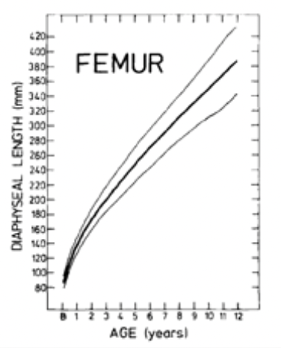
ageing using long bone length
lengths can estimate how long child has been in utero
- varies between people because no everyone is the same
- varies between people because no everyone is the same

19
New cards
standard error
accounts for differences in bone length between each person
20
New cards
ageing using the skull
- Sphenoid and mastoid fontanelle: after birth
- Posterior fontanelle: 6 months
- Anterior fontanelle: 1-2 years
- Metopic suture: 2-4 years
- Posterior fontanelle: 6 months
- Anterior fontanelle: 1-2 years
- Metopic suture: 2-4 years
21
New cards
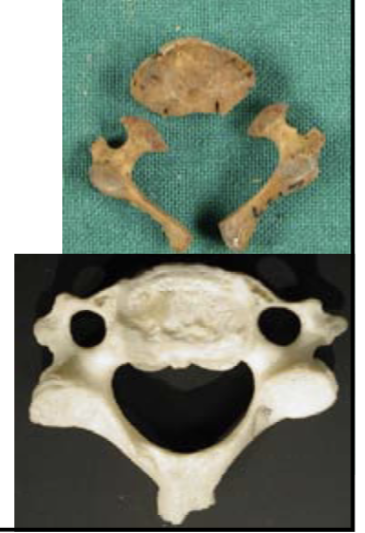
ageing using vertebral arches
2 years: neural arches fuse together
3-4 years: pedicals fuse to neural arches
3-4 years: pedicals fuse to neural arches
22
New cards
ageing using sacrum
2-6 years: neural arches fuse
12-14 years: lateral element fuses
12-25+ years: sacral vertebrae fusees
12-14 years: lateral element fuses
12-25+ years: sacral vertebrae fusees
23
New cards
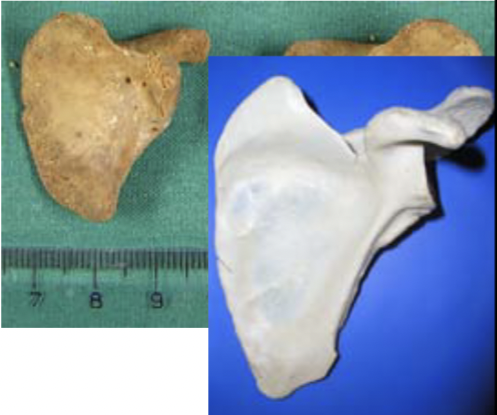
ageing using scapula
18-20 years: acromion process fuses
16-17 years: coracoid process fuses
15-20 years: rim of glenoid fossa fuses
16-17 years: coracoid process fuses
15-20 years: rim of glenoid fossa fuses
24
New cards
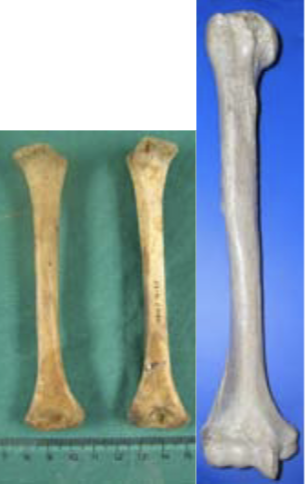
ageing using humerus
14-21 years: hemeral head fuses (F=14-19, M=16-21)
11-18 years: distal epiphysis fuses (F=11-15, M=14-18)
13-18 years: medial epiphysis fuses (F=13-15, M=16-18)
11-18 years: distal epiphysis fuses (F=11-15, M=14-18)
13-18 years: medial epiphysis fuses (F=13-15, M=16-18)
25
New cards
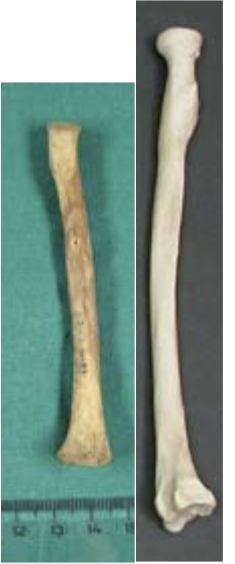
ageing using radius
11-17 years: radial head fusing (F=11-13, M=14-17)
14-20 years: distal epiphysis fusing (F=14-17, M=16-20)
14-20 years: distal epiphysis fusing (F=14-17, M=16-20)
26
New cards
ageing using ulna
12-16 years: olcranon fuses (F=12-14, M=13-16)
15-20 years: ulnar head fuses (F=15-17, M=17-20)
15-20 years: ulnar head fuses (F=15-17, M=17-20)
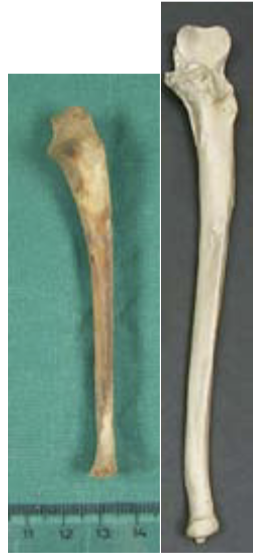
27
New cards
ageing using hand and wrist
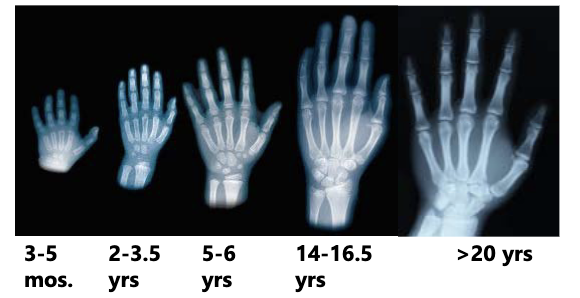
28
New cards
ageing using femur
12-19 years: femoral head fusing (F=12-16, M=14-19)
14-18 years: greater trochanter fusing (F=14-16, M=16-18)
16-17 years: lesser trochanter fusing
14-18 years: distal epiphysis (F=14-18, M=16-20)
14-18 years: greater trochanter fusing (F=14-16, M=16-18)
16-17 years: lesser trochanter fusing
14-18 years: distal epiphysis (F=14-18, M=16-20)
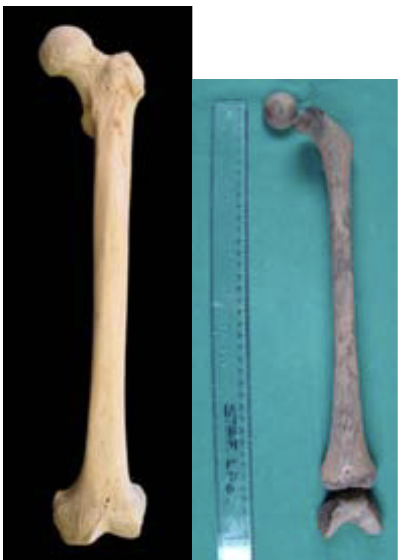
29
New cards
ageing using tibia
13-19: tibial plateau fusing (F=13-17, M=15-19)
14-19: distal epiphysis fusing (F=14-16, M=15-18)
14-19: distal epiphysis fusing (F=14-16, M=15-18)
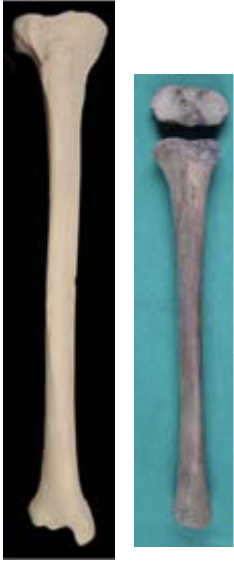
30
New cards
ageing using patella
appears at 3-6 years
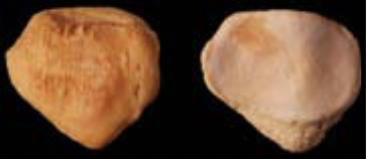
31
New cards
ageing using fibula
12-20 years: proximal epiphysis fusing (F=12-17, M=15-20)
12-18 years: distal epiphysis fusing (F=12-15, M=15-18)
12-18 years: distal epiphysis fusing (F=12-15, M=15-18)

32
New cards
ageing using foot
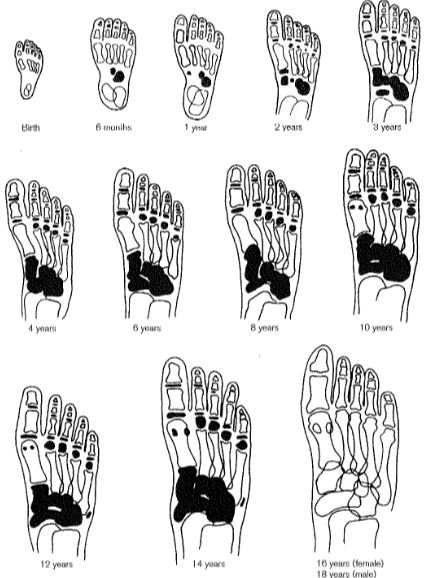
33
New cards
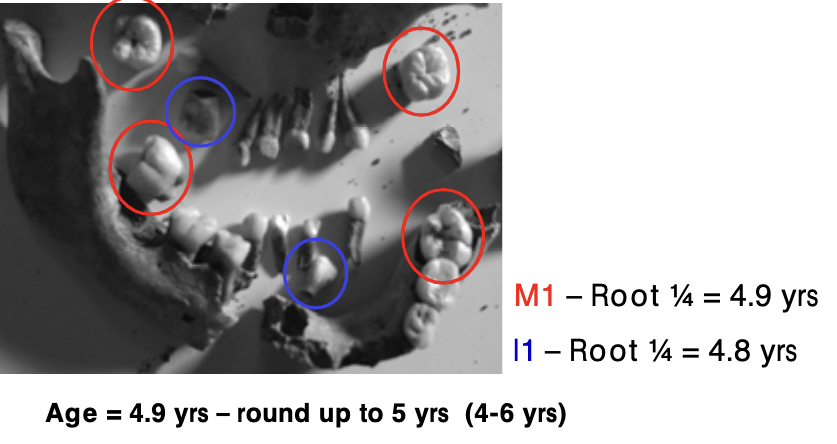
ageing using teeth
- ex. M1 Tooth: 1/4 length grown = 4.9 years
- ex. I1 Tooth: 1/4 length grown = 4.8 years
- ex. I1 Tooth: 1/4 length grown = 4.8 years

34
New cards
tooth eruption
adult or deciduous teeth as they are being exposed through gum line
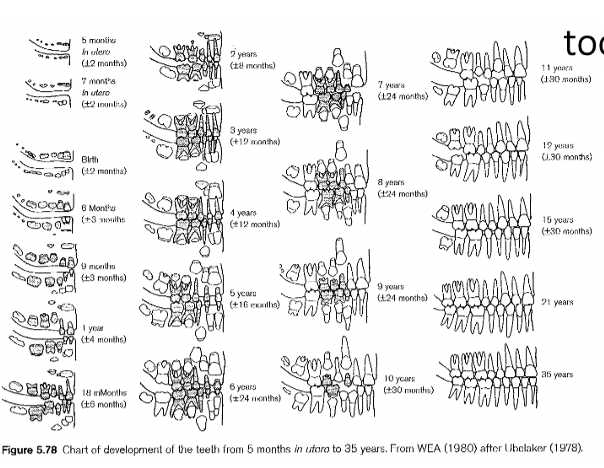
35
New cards
adult age
1. young adult: 20-35 years
2. middle age: 35-50 years
3. old adult: 50+ years
2. middle age: 35-50 years
3. old adult: 50+ years
36
New cards
bones that fuse in adulthood
1. clavicle: 16-30 years (manubrium end)
2. sternum: 40 years (xiphoid process, sternal body)
3. sacrum: 25 years (sacral element 1-2)
4. os coxa: 27 years (pubic symphysis), 17-23 (iliac crest)
2. sternum: 40 years (xiphoid process, sternal body)
3. sacrum: 25 years (sacral element 1-2)
4. os coxa: 27 years (pubic symphysis), 17-23 (iliac crest)
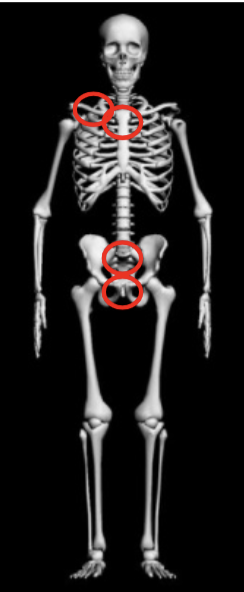
37
New cards
adult bones breaking down
- pubic bone - pubic symphysis, auricular surface (gets more holey, coarser, striations, more stable joint)
- ilium
- ribs - surface bone, surface contour, rim contour
- cranial sutures (fill with bone)
- ilium
- ribs - surface bone, surface contour, rim contour
- cranial sutures (fill with bone)
38
New cards
pubic symphysis degradation
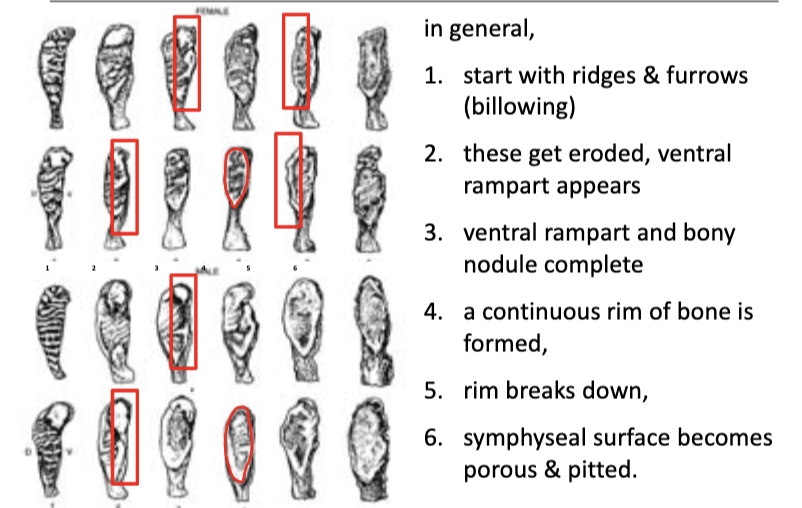
39
New cards
rib degradation
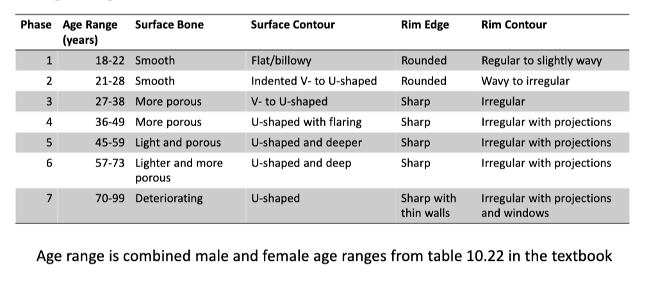
40
New cards
primary sex characteristics
genitals
41
New cards
secondary sex characteristics
skeletal and phenotypic forms that develop during puberty
42
New cards
female secondary sex characteristics
- mechanisms necessary for childbirth
- juvenile growth rate faster
- juvenile growth rate faster
43
New cards
male secondary sex characteristics
- taller on average
- muscle attachments larger
- muscle attachments larger
44
New cards
estimating sex
more sexually monomorphic than other species
- pelvis: correct 90-95% of the time
- skull: correct 80-90% of the time
- long bones: correct
- pelvis: correct 90-95% of the time
- skull: correct 80-90% of the time
- long bones: correct
45
New cards
sex estimate with nuchal area
m: rugged, may have hook
f: smoother, rarely have hook
f: smoother, rarely have hook
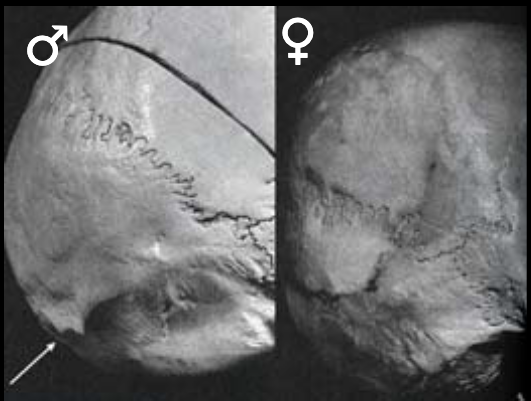
46
New cards
sex estimate with mastoid process
m: large, projecting
f: small, non-projecting
f: small, non-projecting
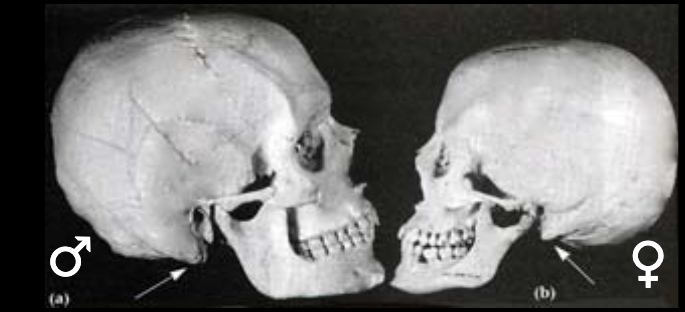
47
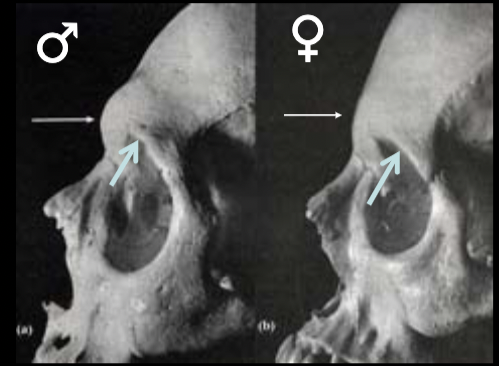
New cards
sex estimate with brow ridges
m: large
f: small to none
f: small to none
48
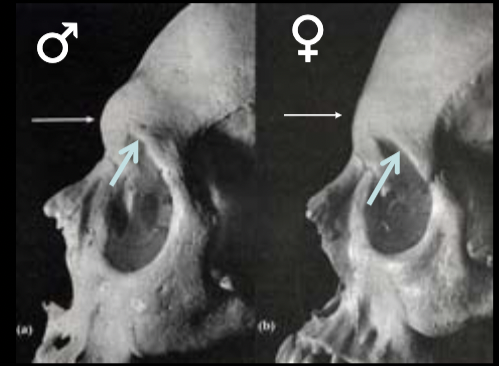
New cards
sex estimate with supraorbital margin
m: rounded
f: sharp
f: sharp
49
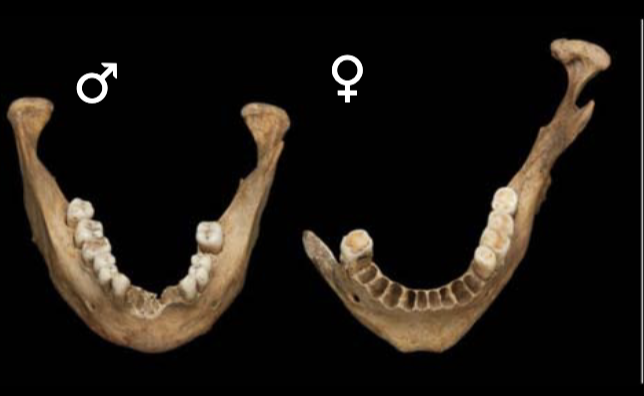
New cards
sex estimate with mental eminence
m: broad or square
f: pointed
f: pointed
50
New cards
discriminant function equation
M1: cranial length
M2: cranial breadth
M3: bizygomatic diameter
M4: mastoid process length
M2: cranial breadth
M3: bizygomatic diameter
M4: mastoid process length

51
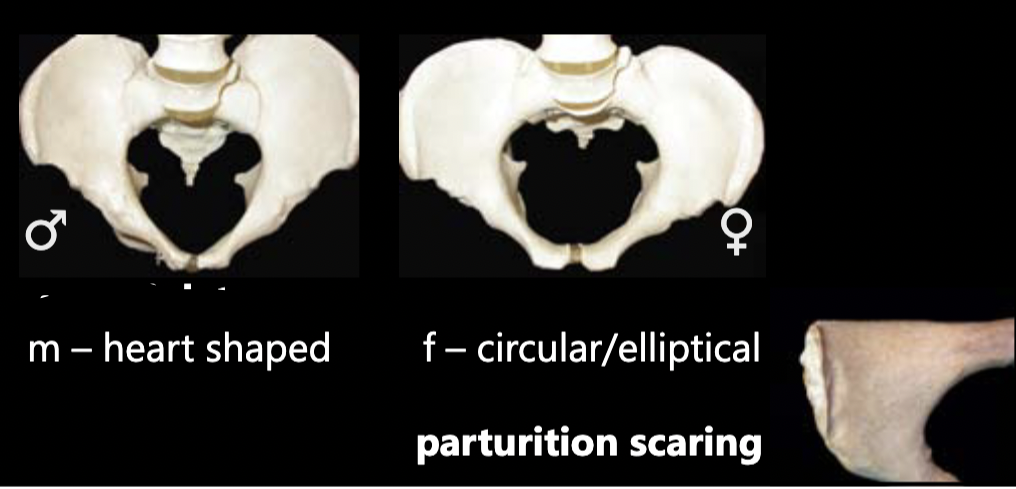
New cards
sex estimation using pelvic inlet
M: heart-shaped
F: circular/elliptical, parturition scarring
F: circular/elliptical, parturition scarring
52
New cards
sex estimation using subpubic angle/concavity
M: narrow or V-shaped
F: wide or U-shaped
F: wide or U-shaped
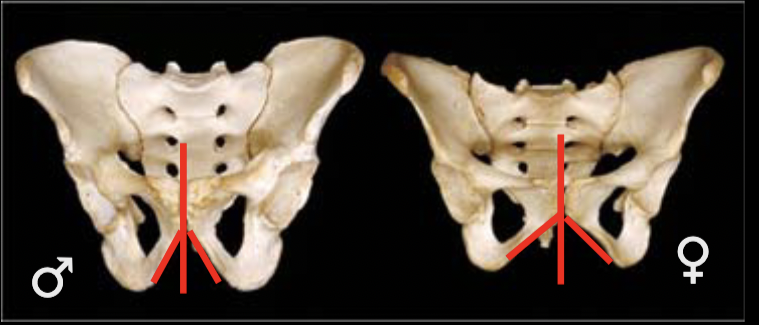
53
New cards
sex estimation using ilium
M: tall, denser
F: broad, thinner
F: broad, thinner
54
New cards
sex estimation using pubic bone
M: narrow, rectangular
F: broad, square
F: broad, square
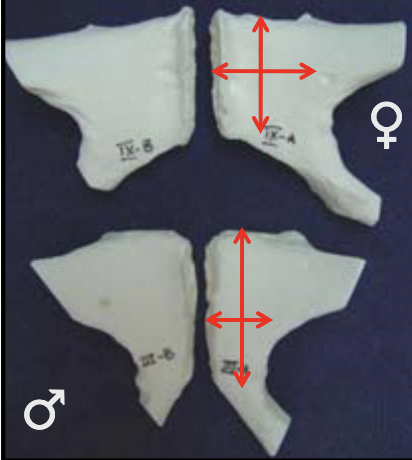
55
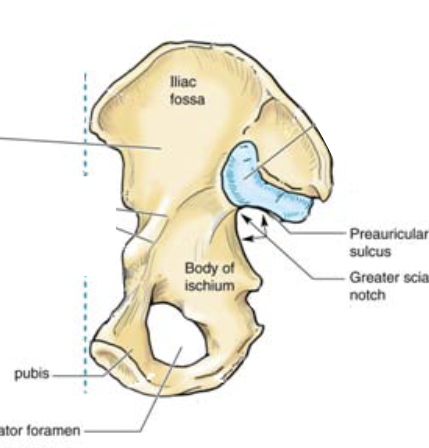
New cards
sex estimation using pre-auricular sulcus
M: absent/poorly developed
F: present/well-developed
F: present/well-developed
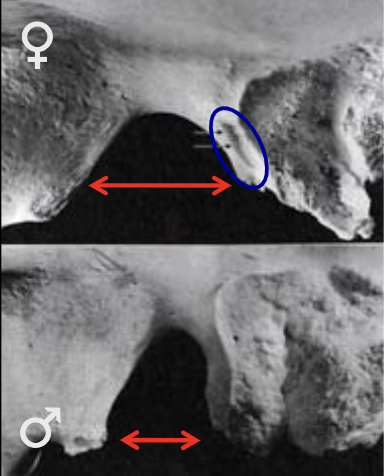
56
New cards
sex estimation using greater sciatic notch
M: narrow
F: wide
F: wide
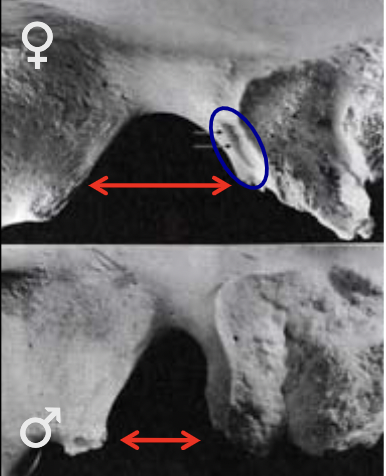
57
New cards
sex estimation using coxal bone
- ventral arc: M=slight/absent, F=strong
- subpubic concavity: M=convex, F=concave
- ischiopubic ramus ridge: M=broad/flat, F= narrow/crest-like ridge
- subpubic concavity: M=convex, F=concave
- ischiopubic ramus ridge: M=broad/flat, F= narrow/crest-like ridge
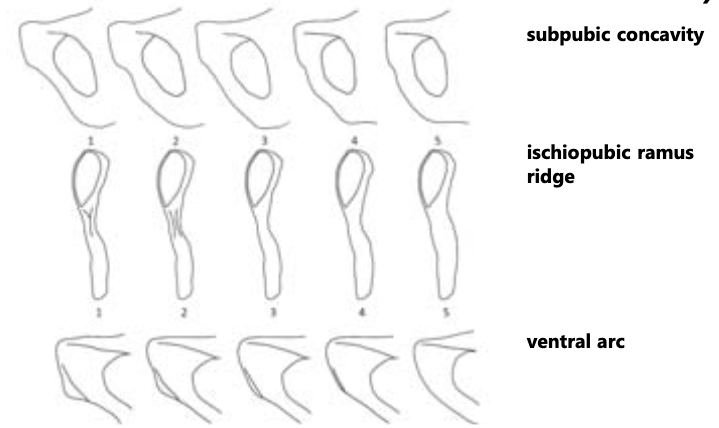
58
New cards
three main classifications of ethnicity (problematic)
black, white, asian
59
New cards
nose anthroposcopic traits
1. root
2. bridge: how far nose sticks out
3. spine
4. shape of lower boarder: edge of nostrils (sharp, flat, or no boarder)
5. shape of nasal aperture (tall, oval, heart-shaped)
2. bridge: how far nose sticks out
3. spine
4. shape of lower boarder: edge of nostrils (sharp, flat, or no boarder)
5. shape of nasal aperture (tall, oval, heart-shaped)
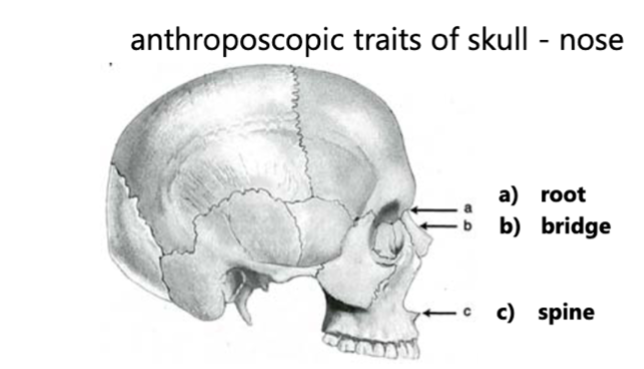
60
New cards
face anthroposcopic traits
- face width: narrow or wide
- eye orbit: angular, rectangular, rounded
- eye orbit: angular, rectangular, rounded
61
New cards
suture anthroposcopic traits
- sutures: patterns are complex and unique
- post-bregmatic depression (where coronal and sagittal suture meet): not always present
- post-bregmatic depression (where coronal and sagittal suture meet): not always present
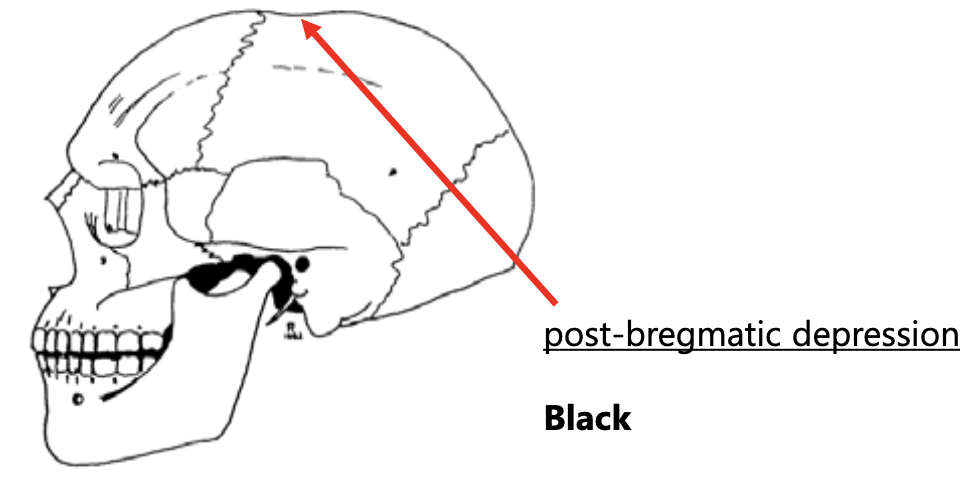
62
New cards
jaw and teeth anthroposcopic traits
- jaw shape: parabolic, elliptical, hyperbolic
- chin shape: small, large/pointed, blunt,
- teeth: crowding, gaps, incisor shapes
- chin shape: small, large/pointed, blunt,
- teeth: crowding, gaps, incisor shapes
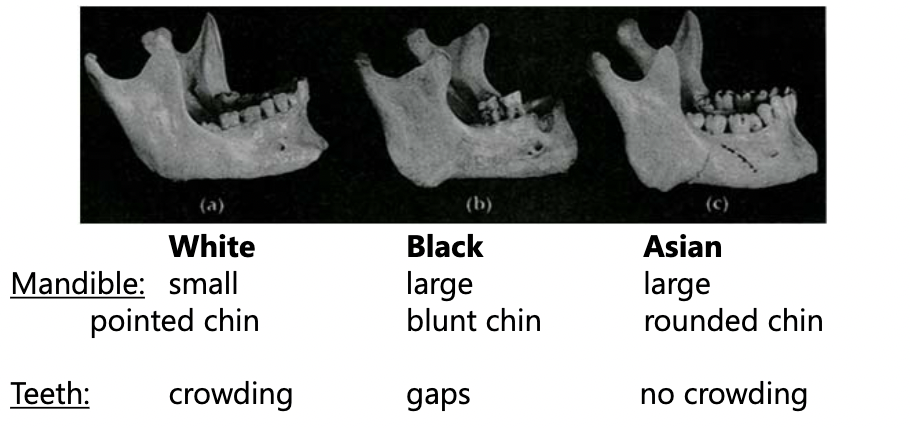
63
New cards
Carolus Linneas
created the Homo sapiens classification - white, black, dark, red
64
New cards
Johann Blumenbach
first to use comparative anatomy
- 5 categories: Mongolian, American, Caucasian, Malayan, Ethiopian
- 5 categories: Mongolian, American, Caucasian, Malayan, Ethiopian
65
New cards
sharp force trauma
wounds left on the bone from bladed instruments
* narrow focus, dynamic, slow-speed compressive
* sometimes resembles blunt force trauma
* narrow focus, dynamic, slow-speed compressive
* sometimes resembles blunt force trauma
66
New cards
SFT cleft
deep/wide v-shaped cut

67
New cards
SFT wastage
removal of bone from inside of cleft
68
New cards
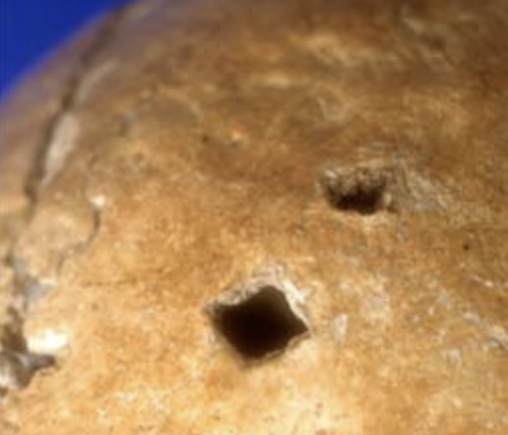
SFT punctures
penetrating wound
* captures shape of object
* captures shape of object

69
New cards
SFT striations
lines etched into bone from passage of blade
* parallel to cut mark
* perpendicular = chopping motion
* parallel to cut mark
* perpendicular = chopping motion

70
New cards
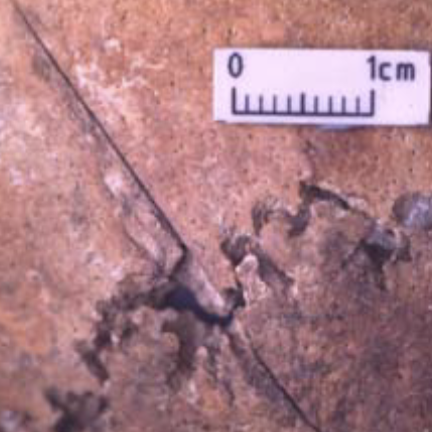
SFT incisions
gradually tapered v-shapes
* longer than they are wide
* longer than they are wide

71
New cards
wound analysis
1. Wound Description
* placement on skeleton
* type of wound
* size
2. Instrument Characteristics
* Type
* Blade
3. Direction of Force
4. Number of Traumatic Events
5. Sequence of Events
72
New cards
Antemortem Injury
healed sharp force trauma
* rounded edges
* rounded edges
73
New cards
Blunt Force Trauma
elevated level of impact, not high velocity
* characterized by radiating fracture lines
* type of instrument influences wound seen
* characterized by radiating fracture lines
* type of instrument influences wound seen
74
New cards
BFT instrument size
focused = smaller objects
diffused = wider objects
diffused = wider objects
75
New cards
BFT shape of instrument
cross-sectional outline
longitudinal configuration
* injury mimics shape of object
longitudinal configuration
* injury mimics shape of object
76
New cards
deformation
inbending and outbending at impact site
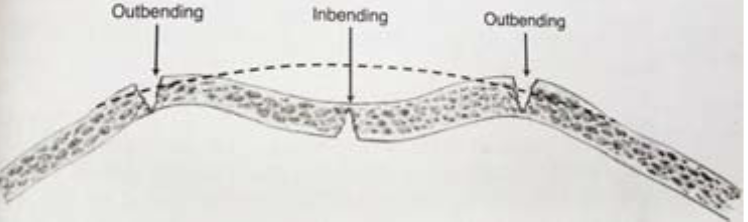
77
New cards
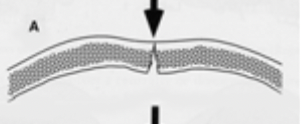
elastic bone fracture
incomplete - more resistant to forces, more collagen, most often inward bending
78
New cards
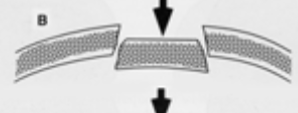
brittle bone fracture
complete fracture - whole sections of bone may fail
79
New cards
weak trabecular bone fracture
incomplete fracture - outer table fail, inner table might not

80
New cards
weak inner table
comminuted fracture - inner table fail, outer may not
81
New cards
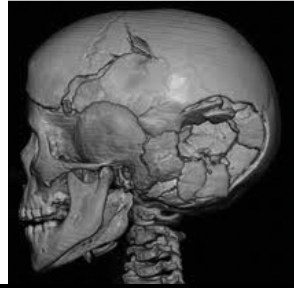
depressed skull fractures
break in cranial bone, depression towards brain

82
New cards
spiderweb skull fractures
radiating lines on outbent surface
* additional force used
* stop at suture or previous radiating line
* tend to have bone wedges in-between fractures
* additional force used
* stop at suture or previous radiating line
* tend to have bone wedges in-between fractures

83
New cards
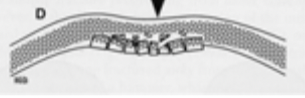
skull bone wedges
concentric fracture lines and bone wedges forced inward
84
New cards
hinge skull fractures
incomplete fracture on one side of depression
* outward bending not completely separating
* outward bending not completely separating
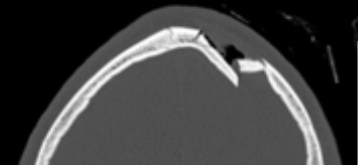
85
New cards
face fractures
3 areas (denser to weaker facial sections - buttressing)
1. alveolar ridge
2. malar eminences
3. nasofrontal processes
1. alveolar ridge
2. malar eminences
3. nasofrontal processes
86
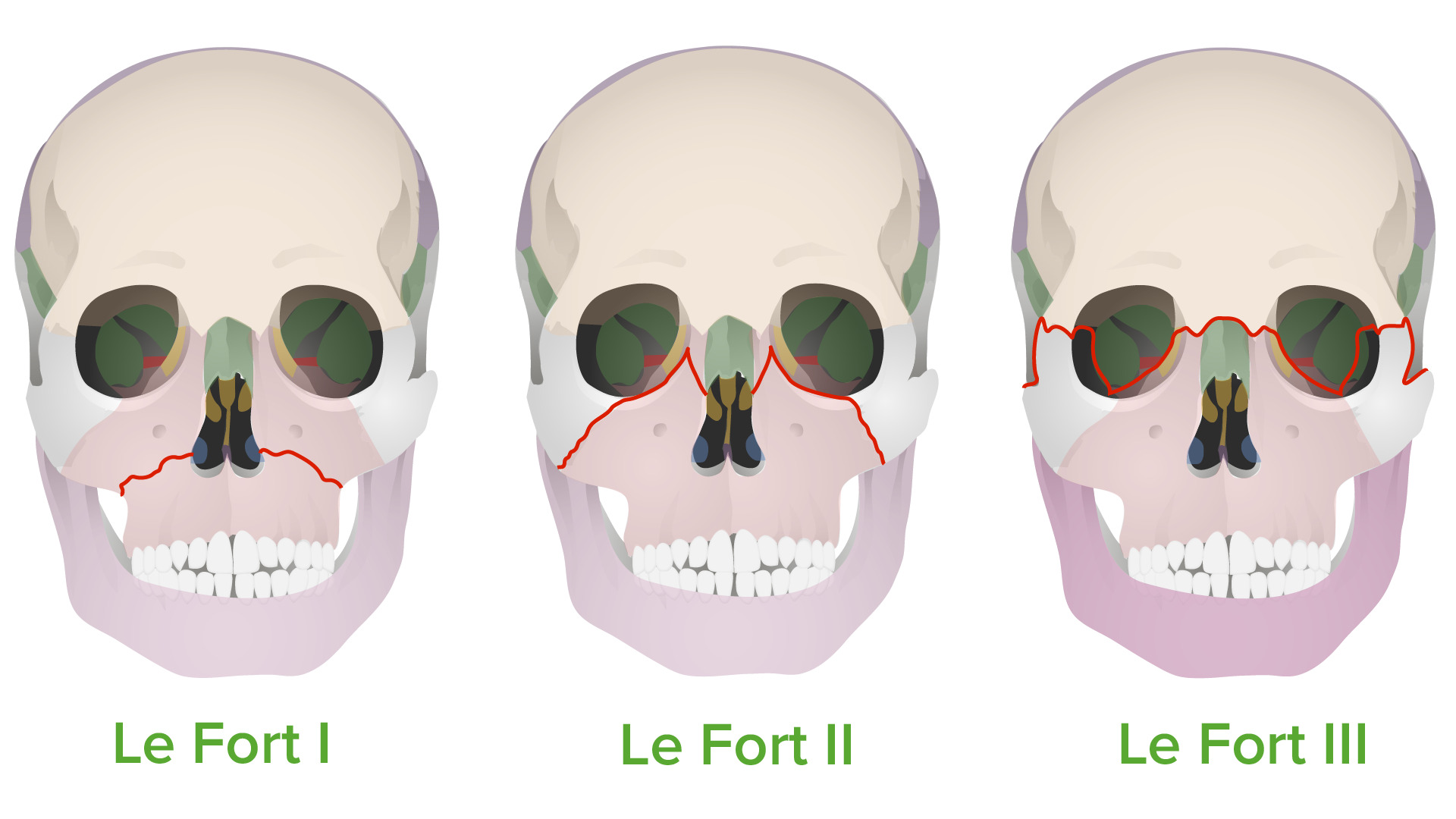
New cards
lefort fractures on the face
LeFort 1: between alveolar and nasofrontal
LeFort 2: between nasofrontal and malar
LeFort 3: below anterior temporal and midfrontal
* most frequently occurs in high-speed car accidents or falls, or striking the face directly with a rigid object
LeFort 2: between nasofrontal and malar
LeFort 3: below anterior temporal and midfrontal
* most frequently occurs in high-speed car accidents or falls, or striking the face directly with a rigid object
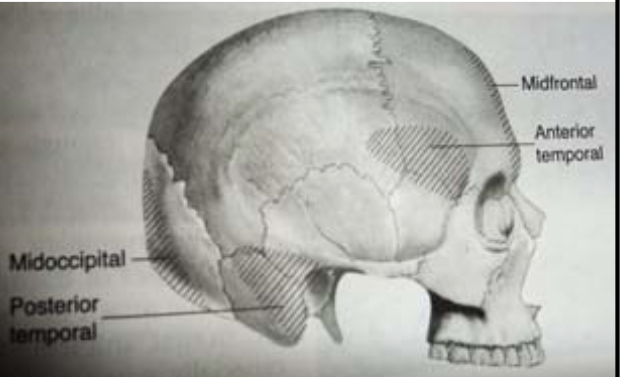
87
New cards
cranial vault fractures - 4 areas of buttressing
1. Midfrontal
2. Midoccipital
3. Posterior temoral - mastoid process
4. Anterior temporal - above sphenoid
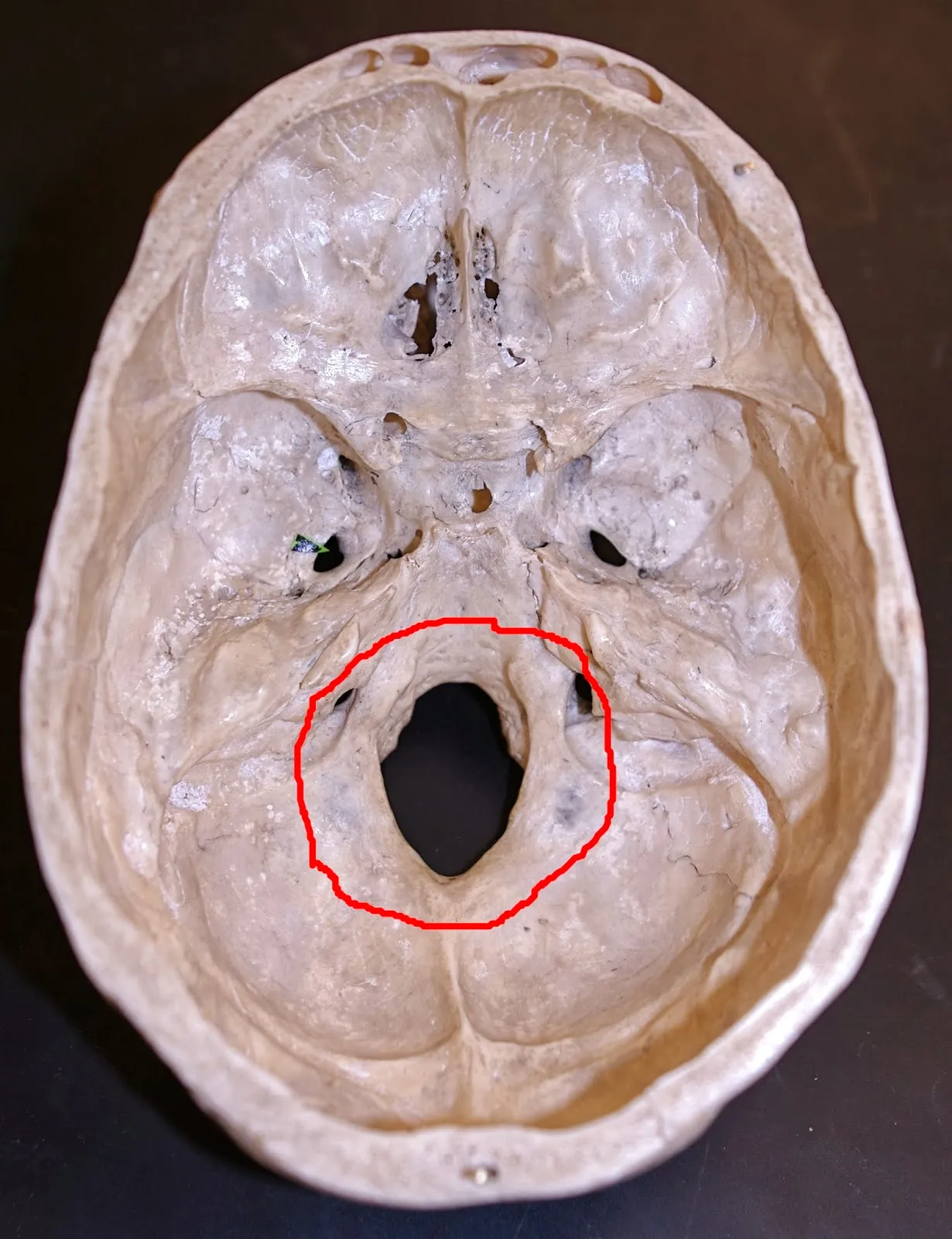
88
New cards
ring fractures
falling backwards on hard surface, jumping from large heights and landing on feet
* skull base fracture
* spine shoved into crania
* skull base fracture
* spine shoved into crania
89
New cards
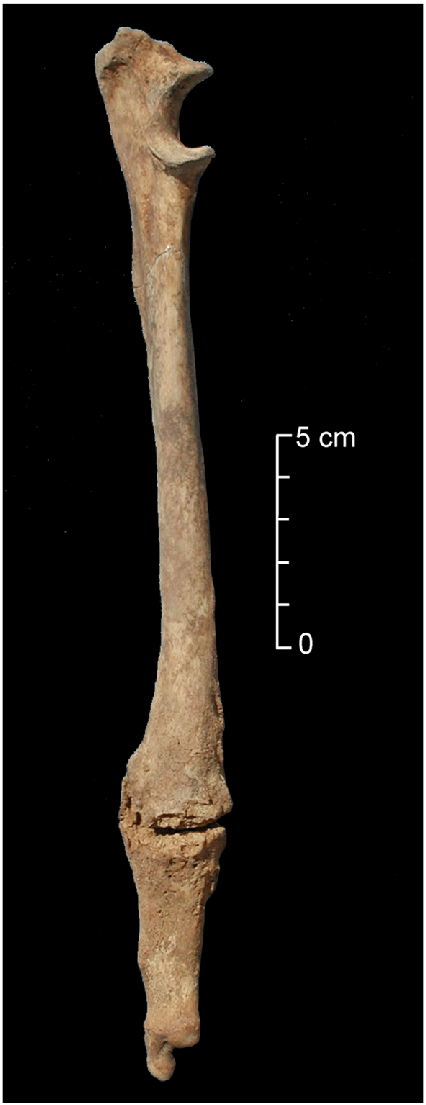
long bone BFT
* complete fractures
* bone wedges
* parry fractures (when you block trauma with your arm)
* bone wedges
* parry fractures (when you block trauma with your arm)

90
New cards
wound analysis
1. Wound description
* Placement on skeleton, bones being impacted
* Type of fractures
2. Estimate size of instrument
3. Estimate shape of instrument
4. Estimate direction of blows
5. Estimate force
6. Estimate number of blows
* Flaking on edge of fracture = multiple blows to same area
7. Estimate sequence of trauma
* First blow will have greater range of radiating fracture lines
* Fracture line that extends the most without being impeded will be first line
8. Miscellaneous estimations
* Intrinsic factors of bones, combination of tools used, different shaped trauma indicating different weapon areas, health issues
91
New cards
BFT ribs
most common cause of rib fractures
* direct pressure on ribs = break
* direct pressure on ribs = break
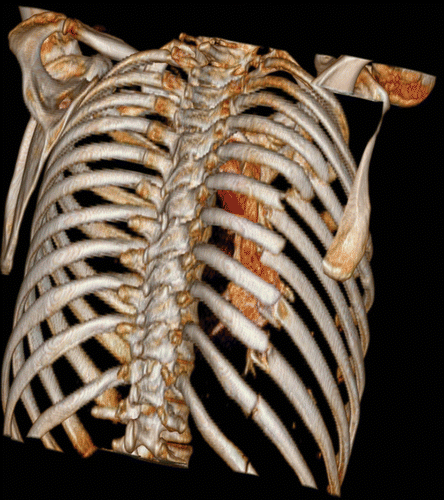
92
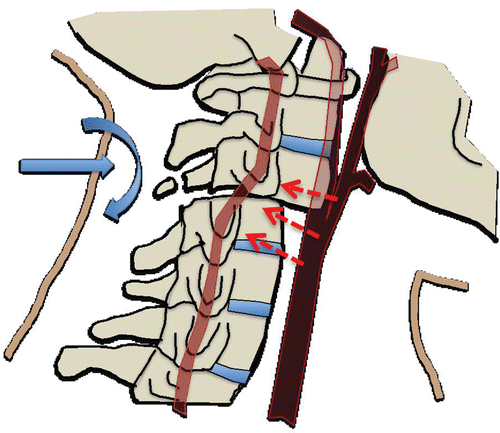
New cards
BFT vertebrae
most often caused by car accidents - also assault, hanging injuries, sport injuries
93
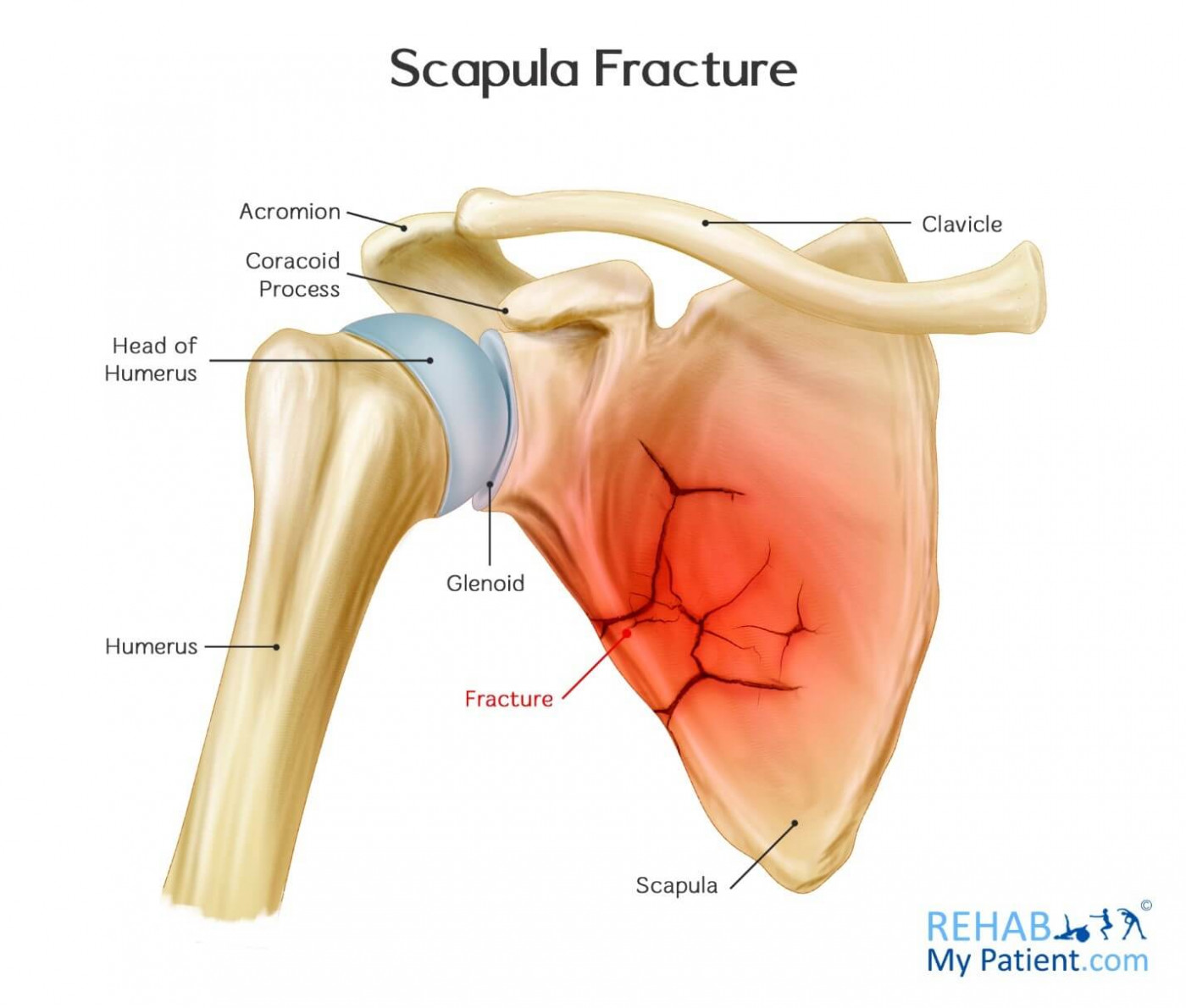
New cards
BFT scapula
caused by significant BFT - 75% car accidents
94
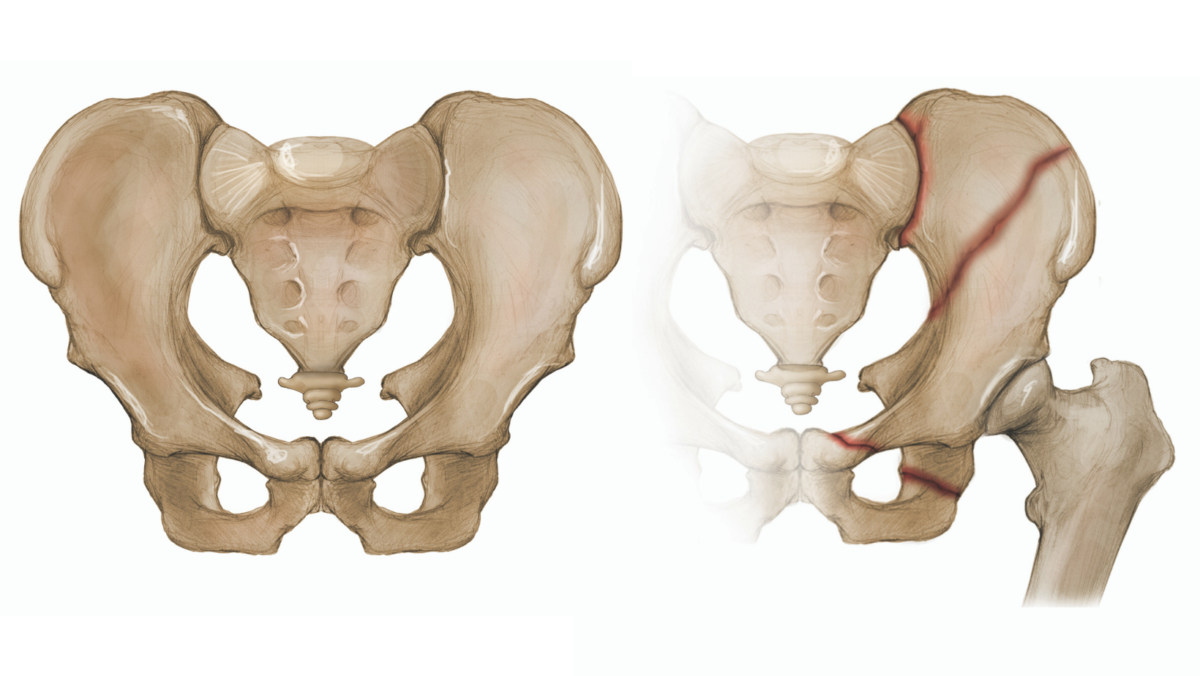
New cards
BFT pelvis
uncommon in instance of BFT (8-9%) - often car accidents/being hit by a car
95
New cards
burning - stage 1
pugilistic posture
* initial evaporation of moisture in body
* heat induced bending of limbs at joints
* initial evaporation of moisture in body
* heat induced bending of limbs at joints

96
New cards
burning - stage 2
soft tissue modification
* flesh chars/splits
* hair burns off
* expulsion of cooked internal organs
* larger muscles take longer to burn off
* flesh chars/splits
* hair burns off
* expulsion of cooked internal organs
* larger muscles take longer to burn off
97
New cards
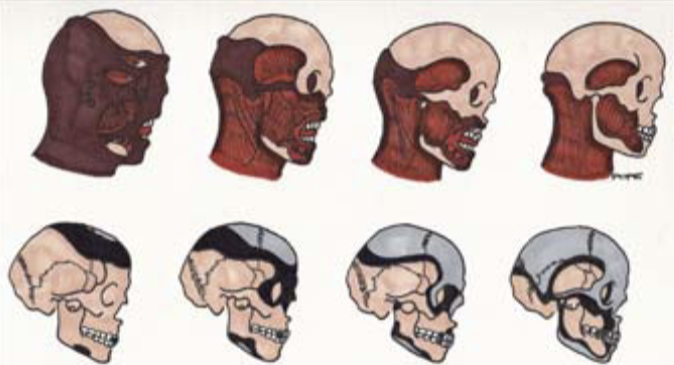
burning - stage 3
bone modification
* collagen chars first
* bone reduced to mineral
* denser bones take longer to modify
* collagen chars first
* bone reduced to mineral
* denser bones take longer to modify
98
New cards
bone burning colour change
* Low Temperature (200-700 C): yellow brown to darker yellow brown to black
* High Temperature (+800 C): dark grey to lighter grey/blue to white (calcination)
* High Temperature (+800 C): dark grey to lighter grey/blue to white (calcination)

99
New cards
bone burning bone cracking
* crescent shaped along diaphysis - transverse cracking on long bones
* shape relates to speed bone is drying out
* shape relates to speed bone is drying out
100
New cards
bone burning hydrated bone
longitudinal breaks