Business Theme 1
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Market growth
The increase in demand or sales for a particular product or service, or the overall increase in the size of a market. Usually measured on an annual basis.
Market size
The overall size (value or volume) or demand for a specific market.
Market share
The proportion of total sales in a market held by a particular business, product, or brand. It's often expressed as a percentage and indicates how a business is performing compared to its competitors.
Risk
Possibility that things will go wrong, can be managed through contingency planning.
Examples of risk: Business investments, risk of a product breaching health and safety regulations.
Uncertainty
The unpredictable and uncontrollable events that affect business.
Examples of uncertainty: Sales success for a new product launch.
Niche market
Smaller segment of a larger market where customers have specific needs and wants requiring differentiated products.
Mass market
The largest part of a market where there are many similar, undifferentiated products offered by competitors.
Market research
Gathering and analysis of research to help support the implementation of marketing strategy. Provides insight into things such as competitor strategies and customer needs and wants.
Product orientation
Business develops products based on what it is good at doing.
Market orientation
Business responds to customer needs and wants - designs products accordingly.
Why is market orientation linked to marketing success?
• Markets are more dynamic - e.g technology which shortens product life cycles
• Customers are expecting a higher level of service and are able to share experiences on social media
• Barriers to market entry are getting lower - many new entrants utilising online and mobile technology
Primary research definition + benefits and drawbacks
Data collected first-hand for a specific research purpose.
Benefits:
• Directly focused on research objectives
• Kept private - not publicly available
• More detailed insights and specific to the business
Drawbacks:
• Time consuming and costly
• Risk of survey bias
• Sampling may not be representative
Secondary research definition + benefits and drawbacks
Data that already exists and which has been collected for a different purpose.
Benefits:
• Often free and easy to obtain
• Good source of market insights
• Quick to access and use
Drawbacks:
• Can quickly become out of date
• Not tailored to business needs
• Specialist reports are often quite expensive
• Can be accessed by competitors
Examples of primary resesrch
• Focus groups - potential customers share detailed views on a product or market.
• Observation - watching how consumers behave, works well in retail.
• Surveys - low cost, capture views of existing and potential customers.
• Telephone interviews - provides quick feedback, potential customers are often wary of being called and can give short answers.
• Test marketing - involves selling a new product in a small section of the market to assess customer reaction. Can predict how a new product will be received.
Examples of secondary research
• Published market research reports
• Internal transactional data
• Official statistics
• Trade associations
• Media reports
• Competitor materials
Quantitative research definition and methods of obtaining it
• Based on numerical data
• Addresses questions such as “how many?” “how often?” “who?” “when?” and “where?”
• Based on larger samples, therefore more statistically valid
Methods of obtaining:
• Various forms of survey: telephone, postal, face to face and online
Benefits and drawbacks of quantitative research
Benefits:
• Data relatively easy to analyse
• Numerical data provides insights into relevant trends
• Can be compared with data from other sources, e.g. competitors, history
Drawbacks
• Focuses on data rather than explaining why things happen
• Doesn’t explain the reasons behind numerical trends
• May lack reliability if the sample size and method is not valid
Qualitative research definition and methods of obtaining it
• Based on opinions, attitudes, beliefs and intentions
• Answers questions such as “why?” “would?” and “how?”
• Aims to understand why customers behave in a certain way or how they may respond to a new product or service
Methods of obtaining:
• Focus groups
• Interviews
Benefits and drawbacks of qualitative research
Benefits:
• Essential for important new product development and launches
• Focused on understanding customer needs, wants, expectations = very useful insight for a business
• Can highlight issues that need addressing - e.g. why customers don’t buy
• Effective way of testing elements of the marketing mix - e.g. new branding, promotional campaigns
Drawbacks:
• Expensive to collect and analyse - requires specialist research skills
• Based around opinions - always a risk that sample is not representative
Sampling definition + benefits and drawbacks
Sampling involves the gathering of data from a sample of respondents where the results should be representative of the population or target market.
Benefits:
• Even a relatively small sample (if representative) can provide useful research insights
• Using sampling before making marketing decisions can reduce risk and costs
• Flexible and relatively quick
Drawbacks:
• Biggest risk = sample is unrepresentative of population which leads to incorrect conclusions
• Risk of bias in research questions
• Less useful in dynamic markets
What is data mining and what are its benefits?
The process of searching and analysing a large batch of data in order to identify patterns and extract useful information
Benefits:
• Quick and automated
• Large data sets can be analysed = reduced need for sampling
• Data can be linked (e.g. transactional data with customer profiles)
Market segmentation + examples
Involves diving a market into parts that reflect different customer needs and wants.
Examples:
• Demographic - e.g. age, gender, lifestyle, religion
• Income
• Behavioural - based on ways customers use or respond to a product and the benefits they seek
• Geographical
Benefits and drawbacks of market segmentation
Benefits:
• Focuses resources on parts of a market where the business can succeed
• Allows growth of market share or to “ride the wave” of fast-growing segments
• Helps with new product development - focused on needs of customers in the segment
• Helps make the marketing mix more effective, e.g. more targeted promotion
Drawbacks:
• Data about each market segment is not always available, up to date or reliable
• Doesn’t mean you can reach customers in it
• Markets are dynamic and so are their segments
Benefits and drawbacks to market mapping
Benefits:
• Helps spot gaps in the market
• Useful for analysing competitors
• Encourages use of market research
Disadvantages:
• Just because there is a “gap” doesn’t mean there is demand
• Not guaranteed success
• How reliable is the market research?
What is product differentiation and what does it allow a business to do?
The act of distinguishing a product/service from competitors to make it more attractive to a particular target market.
Allows a business to:
• Compete effectively - hard to copy, creates competitive advantage
• Protect and build a brand - build intangible value and strengthen customer loyalty
• Add more value - strong differentiation allows the charge of a higher price, higher profit margins
What is demand and how is a demand curve drawn?
Demand is the quantity that customers are willing and able to buy at a given price in a given period of time.
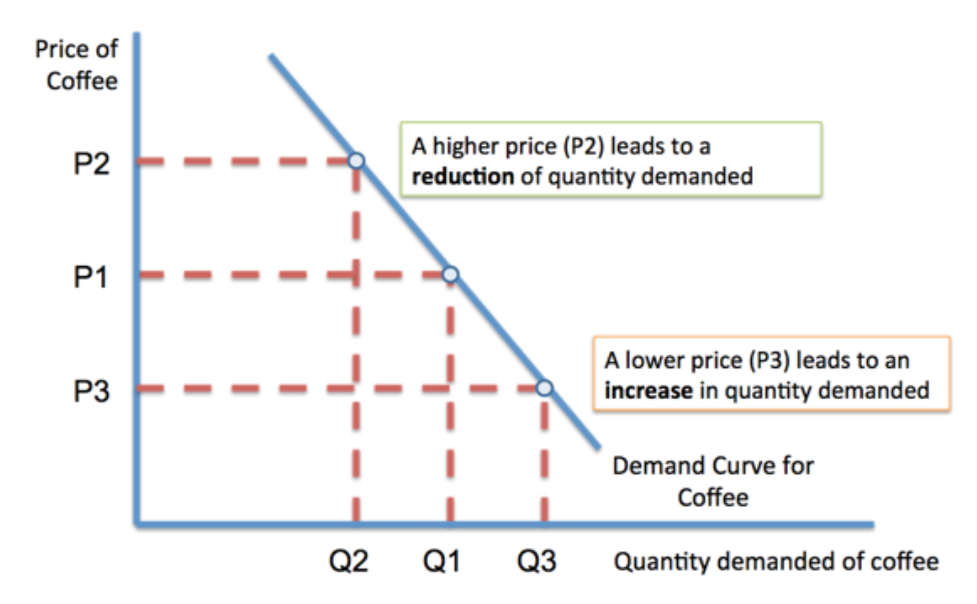
What causes a change in demand?
• Price - depends on PED
• Incomes - for inferior goods, demand will fall as consumers choose better alternatives that are now affordable
• Fashions, taste and preferences
• Advertising and branding
• External shocks - sudden and often significant change in the external environment
• Seasonality
What is supply and how is a supply curve drawn?
Supply is the quantity of a good or service that a producer is willing and able to supply onto the market at a given price in a given time period.
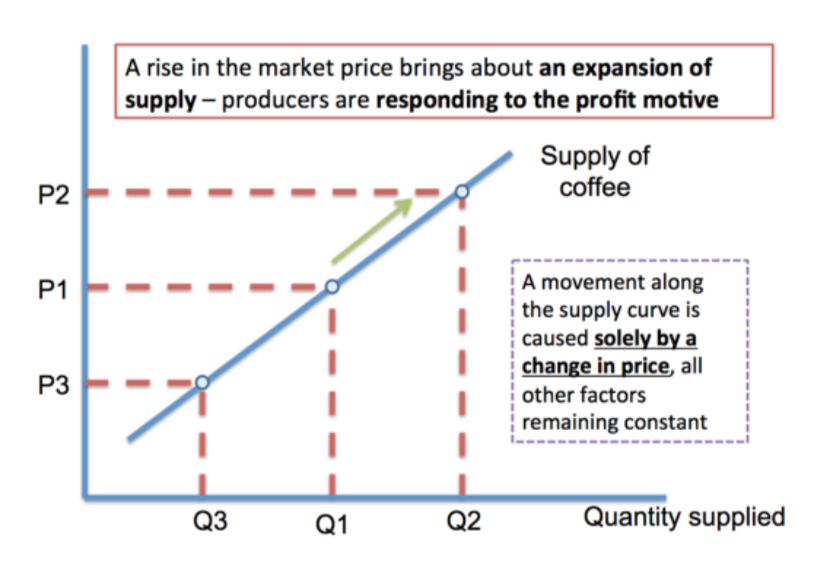
What causes a change in market supply?
• Costs of production - Higher unit costs cause an inward shift of supply e.g. a rise in wage rates or an increase in energy prices / other raw materials
• External shocks - e.g. economic downturn led to companies cutting back scale of operations
• New technology - encourages new market entrants and enable existing suppliers to become more efficient, thereby increasing their potential to supply.
• Taxation and subsidies - E.g. subsidies given for instillation of solar panels.
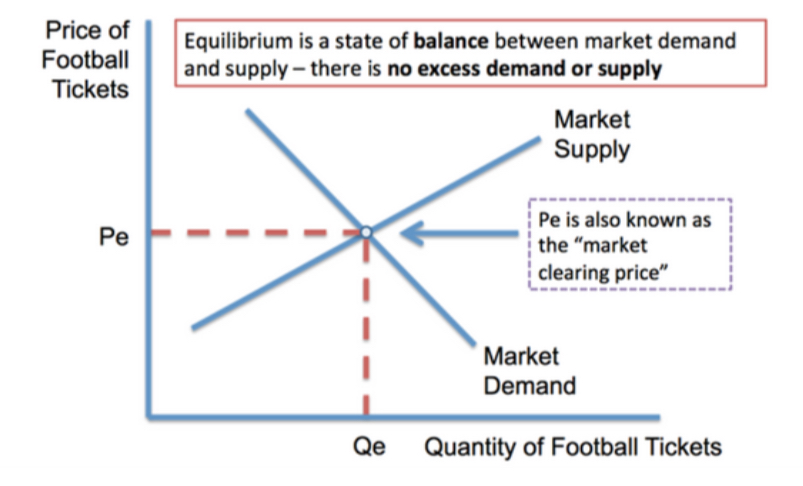
Equilibrium
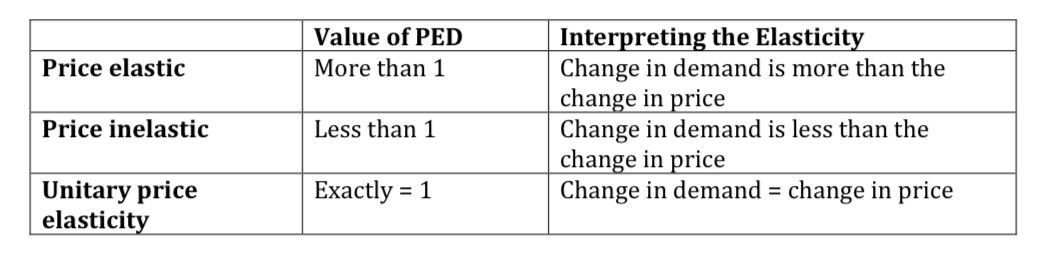
Elasticity
Measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in a relevant variable - such as price or income.
PED =
% Change in quantity demanded /
% Change in Price
How to interpret PED
Factors that will influence the PED of a product
• Brand strength - Products with strong brand loyalty and reputation tend to be price inelastic
• Necessity - demand tends to be inelastic
• Habit - Inelastic
• Availability of substitutes - Demands for products that have lots of alternatives tend to be price elastic
• Time - Price changes tend to have less impact on demand over longer periods.
YED =
% Change in quantity demanded /
% Change in income
Luxury goods YED and examples
YED = more than 1
As income grows, more is spent on luxuries
Examples:
• Consumer goods
• Expensive holidays
• Branded goods
Necessities YED and examples
YED = less than 1 but more than 0
As income grows, less is spent on necessities
Examples:
• Staple groceries (e.g. milk)
• Own-label goods
Inferior goods
YED = less than 1
As income rises, demand falls due to consumers switching to better alternatives, substitute products become affordable.
Limitations of using elasticities
• Can be difficult to get reliable data on how demand changes in relation to price (although this is getting easier with the emergence of big data)
• Other factors affect demand (e.g. consumer tastes)
• Many markets subject to rapid technological change, making previous data less reliable
• Competitors will react - pricing decisions can’t be taken in isolation
Design Mix
• Function - The way the product works, is it reliable? does it do what it is supposed to?
• Cost - Does the design allow the product to be made and sold profitably? How much value is added during the production process?
• Aesthetics - How the product appeals to customers in terms of how it looks, feels etc. Based on the subjective judgement of the customer. Popular way to differentiate a product.
Features of products that focus on function in the design mix
• More predictable and stable demand
• Longer product life cycles
• Lower promotional costs
• Build reputation for quality based on reliability
• Economic manufacture through economies of scale
Features of products that focus on aesthetics in the design mix
• High added value
• Demand fuelled by customer aspiration
• Potentially shorter product life cycle
• Attracts imitation = need for design protection
• Need for greater promotional support
How the design mix is changing to reflect social trends
Sustainability
• Not damaging the environment
• Minimise waste in production
• Enable recycling or re-use
Ethical supply chains
• Consumers are increasingly interested in buying from “ethical” businesses
• “How” products are made is a key issue for many consumers
• There is potential for significant damage to a business reputation if issues are discovered in its supply chain
Waste minimisation
• Links to lean production
• Businesses address this issue by ensuring products are recyclable and production has minimum waste.
Marketing mix
• Price
• Product
• Place
• Promotion
Used to:
• Forecast future sales trends
• Help with market targeting and positioning
• Help analyse and manage the product portfolio
The product life cycle
• Development - often complex and time consuming, absorbs significant resources, high cost, high failure rate so businesses may use a test launch.
• Introduction - Likely to be low sales, low capacity utilisation and high unit costs, usually negative cash flow.
• Growth - Fast growing sales helped by wider distribution, rise in capacity utilisation should lower unit costs, cash flow may become positive, attracts new entrants to the market.
• Maturity - Slower sales growth, intense competition, high capacity utilisation, strongly positive cash flow, weaker competitors begin to leave the market
• Decline - Falling sales, market saturation, decline in profits and weaker cash flows, more competition leave, decline in capacity utilisation as they switch capacity to alternative products.
Extension strategies
• Lowering the price
• Changing promotion (e.g. new promotional message)
• Changing the product - re-styling etc.
• Looking for alternative distribution channels
Criticisms of the product life cycle
• Shape and duration varies from product to product
• Difficult to recognise where a product is in its life cycle
• Length cannot reliably be predicted
• Decline is not inevitable
Product portfolio analysis
Assesses the position of each product or brand in a firm’s portfolio to help determine the right marketing strategy for each.
Most popular model is the Boston Matrix.
What does the Boston Matrix look like?
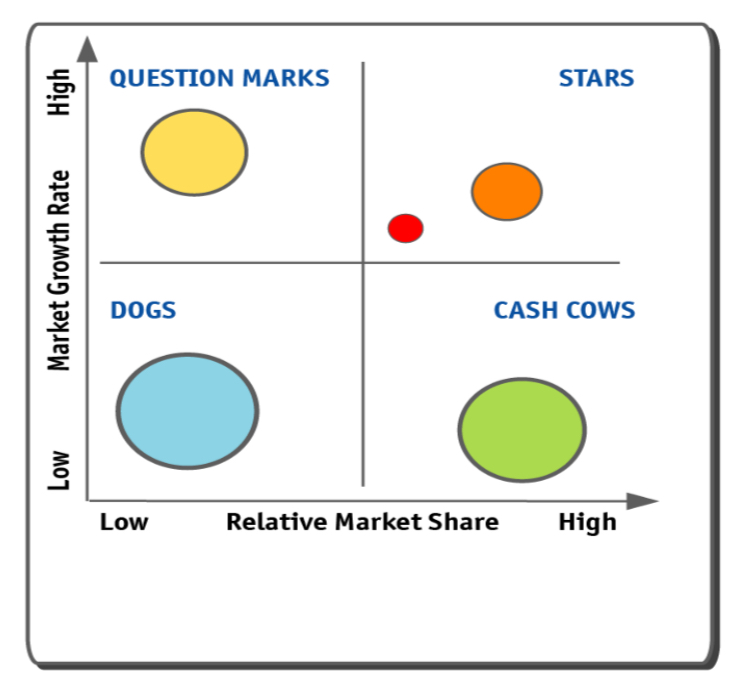
Categories of the Boston Matrix
• Question marks - Low market share in high growth markets. Suggests they have potential but need substantial investment.
• Stars - High growth products competing strongly against competition. Often need heavy investment to sustain growth, eventually growth will slow and if they keep their market share they will become a cash cow.
• Dogs - Low market share in low growth markets, rarely generate enough cash to break even, not worth investing in, usually sold or closed.
• Cash cows - Low growth products with high market share. These are mature, successful products with relatively little need for investment. Need to be managed for continued profit so that they generate the strong cash flow needed to invest in stars.
How valuable is the Boston Matrix?
+ Useful for analysing product portfolio decisions
- Only a snapshot of the current position
- Little or no predictive value
- Focus on market share and market growth ignores issues such as developing a sustainable competitive advantage
What is branding and what are the benefits of effective branding?
A brand is a product that is easily distinguished from other products so that it can be easily communicated and effectively marketed. A brand name is the name of the distinctive product.
Types of brand
• Product brand - brands associated with specific products. E.g. pot noodle
• Service brand - brands that add perceived value to services either delivered face-to-face or online. E.g. Vue
• Umbrella / family brand - brands assigned to more than one product, makes different product lines easily identifiable. E.g. Cadbury
• Corporate and own label brands - promoting a brand name of a corporate entity as opposed to specific products or services. E.g. Unilever
• Own label - example of corporate branding where retail outlets assign their corporate branding to a range of products. E.g. Tesco
• Global brand - Easily recognised and operating worldwide. Based on familiarity, availability and stability. E.g. Coca-cola
What is the promotional mix and its main elements?
The promotional mix is the promotional methods used to pursue marketing objectives.
Its main elements are:
• Advertising
• Sales promotion and merchandising
• Personal selling
• Public relations / publicity / sponsorship
• Direct marketing
Advertising definition + benefits and drawbacks
Paid for communication, e.g. mobile, tv, radio, social media
Benefits:
• Wide coverage
• Control of message
• Repetition means message can be communicated effectively
• Effective for building brand awareness and loyalty
Drawbacks:
• Expensive (especially in mass markets)
• Impersonal (less for online)
• One way communication
• Lacks flexibility
• Limited ability to close a sale
Personal selling definition + benefits and drawbacks
Promotion on a person-to-person basis, e.g. telephone, retail outlets
Benefits:
• High customer attention
• Customised message and interactive
• Opportunity to close the sale and be persuasive
Drawbacks:
• High cost
• Labour intensive
• Can only reach a limited number of customers
Sales promotion definition + benefits and drawbacks
• Tactical, point of sale material to stimulate purchases, e.g. free samples or coupons.
Benefits:
• Effective to achieve a quick boost of sales
• Encourages customers to trial a product or switch brands
Drawbacks:
• Sales effect may only be short-term
• Customers may come to expect further promotions
• May damage brand image
PR definition and aims
Create goodwill towards an individual, business, cause or product.
Aims:
• Achieve favourable publicity
• Promote new products and enhance awareness
• Obtain favourable reviews
Direct marketing definition and its aims
Involves sending a promotional material through email, social media etc to individuals in aim to trigger a response, such as a purchase or enquiry.
Aims:
• Increase sales
• Build customer loyalty
Financial objectives vs Marketing objectives
Financial:
• Maximise profit
• Achieve a target level of profits / returns
• Improve cash flow
Marketing:
• Maintain/ improve market share
• Prevent competition
• Increase sales
• Build a brand
Benefits and drawbacks of cost based pricing
Benefits:
• Easy to calculate
• Profit on every product sold
Drawbacks:
• Doesn’t take competition into account
• Ignores PED
• Doesn’t guarantee customers will pay that price - therefore losing sales
Price skimming
• Setting a high price to maximise profits
• Aims to recover from development costs quickly
• Creates excitement amongst “early adopters”
• E.g. electronics
Price penetration
• Offering a low introductory price
• Aims to gain market share quickly, build customer usage and loyalty, build sales of higher-price related items
• Price can be increased once target market share is reached
Psychological pricing
Tricks people into believing the product is cheaper than it really is, e.g. 99p on the end.
Loss leaders
• Product advertised at a price below the normal price and even below cost to the seller
• Encourages customers to buy other full price products along with the loss leader product
• Draw in customers away from rivals
• Encourage people to buy complementary goods at full price
Dynamic pricing
Business sets flexible prices for products or services based on current market demands. E.g. surge pricing on Uber or amazon pricing
Purpose of distribution channels
• Provide a link between production and consumption
• Help gather market information
• Communicate promotional offers
Distributors and agents
Distributors:
• Sell on products and serve as a local sales point, usually specialise in an industry
• Offer products from many producers = greater choice
• Holds stock
Agents:
• Specialist type of distributor
• Tend to operate in a tertiary sector, e.g. travel or insurance
• Don’t hold stock
Reasons for indirect distribution
• Allows business to make use of resources elsewhere, less capital tied up on inventories
• Businesses may lack retail experience
• Customers may live too far away to reach directly or may be wide spread
Multi channel distribution channel benefits and drawbacks
Benefits:
• Allows more target segments to be reached
• Customers increasingly expect products to be available through more than once channel
• Enables higher revenues, e.g. customers can buy online if retailers have no stock
Drawbacks:
• Potential for channel conflict - e.g. competing with retailers by also selling online
• Can be complex to manage
• Danger that pricing strategy becomes confused in customers eyes
Staff as an asset (soft HRM)
• Treats employees as the most important resource in the business and a source of competitive advantage
• Concentrate on employee needs, e.g. roles, rewards, motivation.
• Strong and regular two way communication
• Competitive pay structure with suitable performance related rewards (e.g profit share, share options)
• Employees are empowered and take responsibility for
• Flatter organisational structure
• Suitable with a democratic leadership style
• Being too ‘soft’ when all employee benefits are added up can be costly
Staff as a cost (hard HRM)
• Treats employees simply as a resource of the business
• Identify workforce needs of the business and recruit and manage accordingly (hiring, moving, firing)
• Short term changes in employee numbers (recruitment and redundancy)
• Minimal communication, top down
• Little empowerment and delegation
• Taller organisational structures
• Suits autocratic leadership style
• More cost effective however a genuinely ‘hard’ approach will create higher absenteeism.
Outsourcing
Delegating one or more business processes to an external provider.
Employee representation benefits and drawbacks
Benefits:
• Increased empowerment and motivation
• Better decision making as employee experience is taken into account
• Lower risk of industrial disputes
Drawbacks:
• Time consuming - potentially slows decision making
•Conflict
• Managers may feel authority is being undermined
Trade unions
An organised association of workers in a trade formed to protect and further their rights and interests. Represents and negotiates on behalf of employees.
Role:
• Protect and improve the real incomes of their members
• Provide job security
• Lobby for better working conditions
Industrial action
• Work to rule - employees follow strict conditions of their employment contract and don’t work voluntary overtime
• Overtime ban
• Go-slow - employees work at slowest possible pace
• Strike
Damage to business:
• Lost sales and profits from lost output
• Damage to customer satisfaction
Damage to Employee:
• Lost pay
• Potential loss of jobs in an attempt to cut costs
Work councils
Formal group of employees representing a workforce in discussions with their employers.
• Focus on business objectives and performance
• Workforce planning issues
• Employee welfare issues
• Compliance with legislation
Methods of settling industrial disputes
Conciliation:
• Used when an employee is making a specific complaint against employer
• Conciliator discusses issues with both parties to help them reach an understanding of each others positions
Arbitration:
• Alternative to a court of law
• Held in private and voluntary, both parties must agree
• Impartial outsider makes decision on dispute based on evidence presented by parties
Mediation:
• Involves an independent, impartial person helping two or more individuals reach a solution acceptable to everyone
• Best used early in an industrial dispute
Internal recruitment methods + benefits and drawbacks
Jobs given to already employed staff, Promotion and reorganisation
Benefits:
• Cheaper and quicker
• People already familiar with business and how it operates
• Provides opportunities for promotion with in business
Drawbacks:
• Business already knows the strengths and weaknesses of candidates
• Limits number of potential candidates
• No new ideas
• Resentment amongst candidates not chosen
• Creates another vacancy
External recruitment methods + benefits and drawbacks
Job centres, job advertisements, recruitment agencies
Benefits:
• Outside people bring new ideas
• Larger pool of workers to find the best candidate
• People have a wider range of experience
Drawbacks:
• Longer process
• More expensive
• Selection process may not be effective enough to reveal best candidate
On the job training method + benefits and drawbacks
Demonstration, coaching/close working, job rotation to gain wider experience, group projects
Benefits
• Generally cost effective
• Employees actually productive
Drawbacks
• Quality depends on ability of trainer and time available
• Bad habits may be passed on
• Potential disruption to production
Off the job training methods + benefits and drawbacks
Day or part time attendance at college, professional development courses, online training
Benefits
• Wider range of skills or qualifications to be obtained
• Learn from outside specialists
• Employees start job more confidently
Drawbacks
• More expensive
• Lost working time
• New employees may still need some induction training
• May leave for better jobs with new skills and qualifications
Span of control
Number of subordinates a manager is directly responsible for.
Span of 7 = wide
more independence
Span of 3 or below = narrow
closer supervision and effective communication, more layer in hierarchy
Suitable span depends on:
• Experience and personality of the manager
• Nature of business, is close supervision needed?
• Culture, e.g. democratic management may operate wider spans of control
Tall vs flat structure
Tall
many layers of hierarchy and narrow spans of control
opportunities for promotion
longer communication time
more layers = more staff = higher cost
Flat
few layers of hierarchy and wide spans of control
less promotion opportunities but staff are given greater responsibility
verbal communication improved
fewer layers = less staff = lower costs
Delayering benefits and drawbacks
Benefits
lower management costs
faster decision making
shorter communication paths
Drawbacks
wider spans of control could be too wide
potential loss of management expertise
Matrix structure definition + benefits and drawbacks
Where individuals work across teams and projects as well as within their own department or function.
Benefits
Improves communication between departments
Greater motivation amongst team
Shares resource across departments
Drawbacks
Divided loyalties as they report to two lines of managers
Difficult to co ordinate
Takes time to get used to working in matrix structure
Centralised decision making benefits and drawbacks
Decisions rest with senior management at the centre of a business
Benefits
Prevent other parts of the business from being too independent
Easier to co ordinate and control from centre, e.g. budgets
Easier to achieve economies of scale
Quicker decision making
Drawbacks
Local and junior managers often closer to customer needs
Lack of authority down the hierarchy may reduce motivation
Decentralised decision making benefits and drawbacks
Decision making spread out to include more junior managers in the hierarchy.
Benefits
Decisions made closer to customer
Improved level of customer service
Improve motivation
Drawbacks
Not necessarily strategic
Harder to ensure consistent practices and policies at each location
Diseconomies of scale, e.g. duplication of roles
Delegation + benefits and drawbacks
Assignment to others of the authority for particular functions, tasks and decisions.
Benefits
Reduces management stress and workload
Allows senior management to focus on key tasks
Subordinates are empowered and motivated
Drawbacks
Depends on quality and experience of subordinates
Harder in a smaller firm
May increase workload and stress of subordinates
Taylor’s motivational theory (scientific management)
Identify efficient workers and train remaining workers to work like them, workers are payed based on productivity (e.g. piece rates)
Believe workers are motivated by money
Managers should maintain close control and supervision over employees
Autocratic style of management
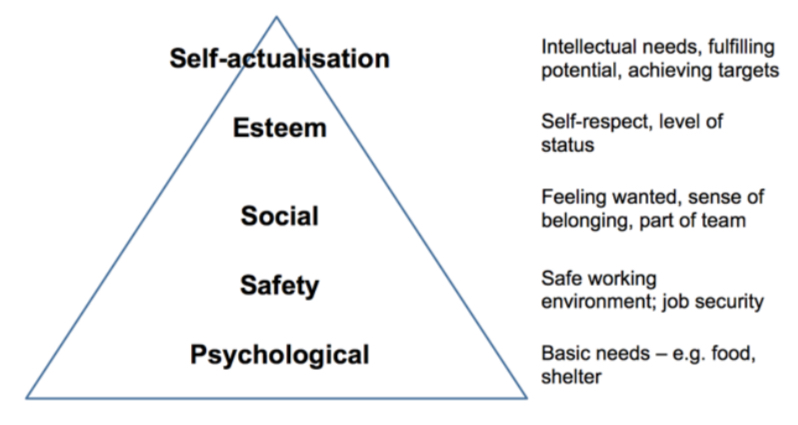
Maslow (Hierarchy of Needs)
Lower level of needs needs to be met before a worker is fully motivated by the opportunity of having the next need up in the hierarchy satisfied
Business should offer different incentives to workers in order to help them fulfil each need
Herzberg (Two factor theory)
Suggests two key factors in workplace motivation:
Motivators
Factors that directly motivate people to work harder
E.g. giving responsibility, recognition for good work, opportunities for promotion
Hygiene (maintenance) factors
Factors that can de-motivate if not present but do not actually motivate employees to work harder
E.g. pay, working conditions, job security
Herzberg use job enrichment and empowerment
Mayo (Human relations theory)
Workers are not just concerned with money but need their social needs met
Believes workers are best motivated by better communication between managers and workers, greater manager involvement in employees working lives and by working in groups or teams.
Fits with paternalistic management style
Employee engagement vs Employee motivation
Employee engagement
Employee is positive about their work
Thinks hard about how to improve
Engaged with fellow employees
Employee motivation
Employee has a will to work due to work incentives and satisfaction from work itself
Financial vs non financial incentives
Financial
Wages
Commission
Performance related pay
Profit sharing
Share options
Fringe benefits
Non financial
Job empowerment
Praise
Promotion
Job enrichment
Job enlargement
Performance related pay benefits and drawbacks
Paid to employees who meet certain targets
Benefits
Senior managers can easily monitor and assess individual employee performance during appraisal process
Setting targets for employees helps makes sure they are focused on company objectives
Drawbacks
Discourages team based approach and creates rivalry between managers
Can be difficult to accurately measure worker performance
Incentives may not be large enough to motivate employees
Piece-rate payments benefits and drawbacks
Pay per item produced in a certain time
Benefits
Requires low levels of manager supervision
Encourages high speed production
Good incentive for workers motivated by pay
Drawbacks
Workers are focused on quantity not quality
Repetitive and de-motivating
Workers are used to one method of production and may resist change
Commission
Usually linked to achievement of sales
Higher rate offered once sales targets are achieved
Benefits
Clear link between sales and remuneration
Drawbacks
Sales may be influenced by factors outside of employee control (e.g. mature product, customer service)
Authoritarian leadership style
Manager holds power
Communication top down and one way
Use of rewards and penalties
Very little delegation
Links to McGregor theory X approach
Democratic leadership style
Focus of power and leadership is with the group as a whole
Employees have greater involvement in decision making
Emphasis on delegation and consultation
Trade off between speed of decision making and better motivation and morale