StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.4.2 DNA and protein synthesis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is meant by the genome? (1)
Complete set of genes and non-coding DNA in a cell
What is meant by the proteome? (1)
The full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce
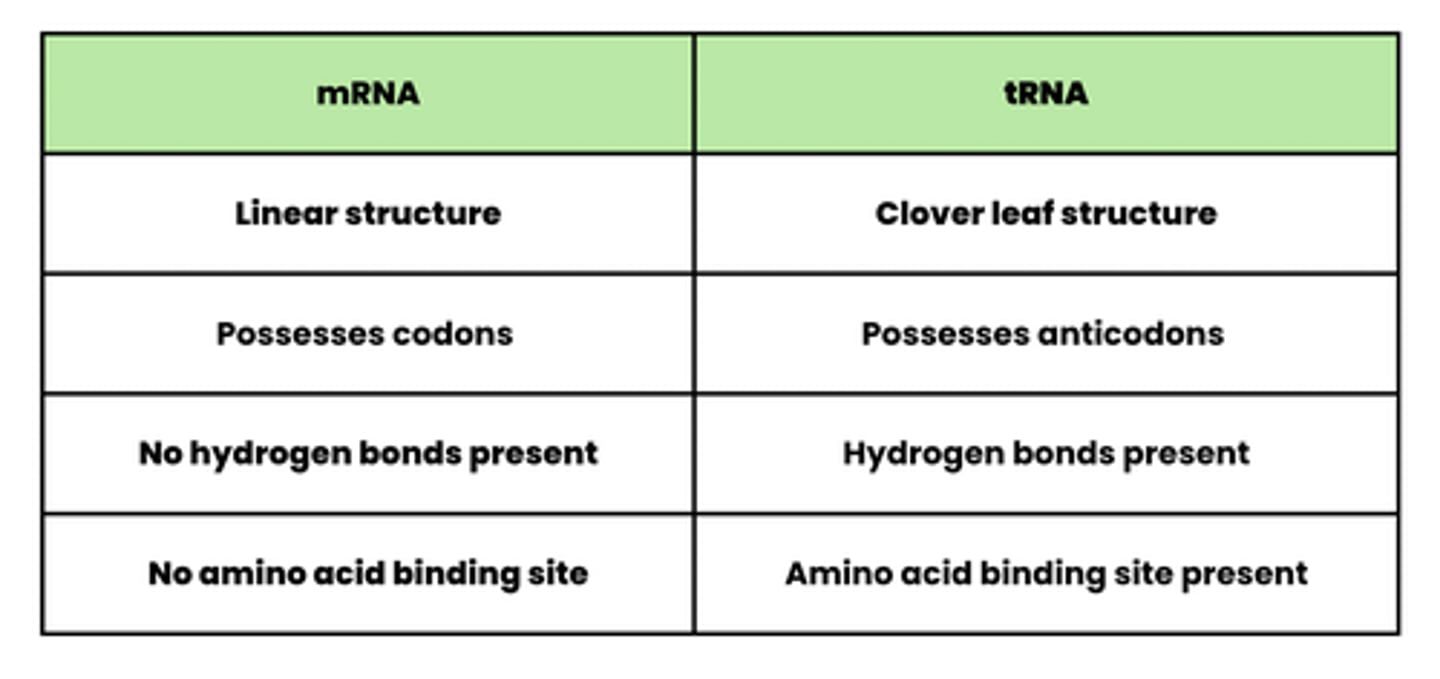
What are the features of the structure of mRNA? (2)
- It has a linear structure
- It possesses codons
What are the features of the structure of tRNA? (4)
- It has a clover leaf structure
- Possesses anticodons
- Contains hydrogen bonds
- It has an amino acid binding site
Compare the structures of mRNA and tRNA
What is transcription? (1)
The production of mRNA from DNA
What is the difference in bases between DNA and mRNA? (1)
mRNA uses Uracil instead of Thymine
What is the difference in the process of transcription in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes? (2)
- In prokaryotes, transcription results directly in the production of mRNA from DNA
- In eukaryotes, transcription results in the production of pre-mRNA
- This is then spliced to form mRNA
Describe the process of transcription in eukaryotes
1. DNA helicase unwinds the double helix and breaks the hydrogen bonds between DNA bases
2. One DNA strand will act as the template strand
3. Free RNA nucleotides align by complementary base pairing (uracil is used instead of thymine)
4. RNA polymerase joins adjacent RNA nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds
5. This forms pre-mRNA
6. Which is then spliced (removal of introns) to form mRNA
How does splicing of pre-mRNA into mRNA work? (1)
Removes introns (non-coding DNA)
What is translation? (1)
The production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA
Describe the process of translation
1. mRNA binds to ribosomes
2. tRNA anticodons bind to complementary codons on mRNA strand
3. tRNA brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome
4. Amino acids are then joined together by peptide bonds using ATP
5. tRNA is released and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to form the polypeptide
Describe the role of a ribosome in the production of a polypeptide (3)
- Acts as a binding site for mRNA
- Allows tRNA with anticodons to bind
- Catalyses the formation of peptide bond between amino acids