CLS 306 BB lecture 11
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN)?
incompatibility between maternal antibodies and fetal RBC antigens
maternal antibodies destroy fetal RBCs
What is the medical condition caused by maternal antibody destruction of fetal RBCs called?
Erythroblastosis Fetalis (EF)
When can HDFN occur?
In utero (prepartum) and after birth (postpartum)
What antibody class causes HDFN?
IgG
crossed placenta
What condition can develop in the fetus due to severe EF?
Hydrops Fetalis (HF)
anemia
edema
cardiac failure
death
What are the three classifications of Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus & Newborn (HDFN)?
ABO: most common. mother incompatibility w/ baby
Rh: anti-D most common or caused by other Rh abs
Other (non-Rh immune antibodies): rare. jk, K, Fy, S
What is a common reason mothers develop anti-K antibodies?
Previous multiple blood transfusions
Why is anti-K especially important in HDFN?
second most common cause of severe HDFN
what are the major dangers of HDFN during pregnancy (in-utero/prepartum)?
Severe fetal anemia
Fetal heart failure
Fetal death
What happens to the fetus in HDFN during pregnancy?
Maternal IgG antibodies attack fetal RBCs, causing fetal anemia and potentially Hydrops Fetalis (HF)
What is released when fetal RBCs are destroyed in HDFN?
Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
Why is unconjugated bilirubin less harmful in utero?
It is cleared through the mother’s liver via the placenta, preventing bilirubin buildup in the fetus
What blood bank tests are performed at the first obstetrical visit?
ABO, Rh (including Du), and Antibody Screen (ABS)
What is done if the initial antibody screen is negative?
Repeat ABS at ~24 weeks
What is done if the antibody screen is positive?
Perform Antibody Identification (Ab ID)
If antibody is IgG, perform an antibody titer
What should be done with maternal samples when antibodies are detected?
Retain all maternal samples
How are maternal antibody titers monitored?
Perform periodic titers
> 1:32 is considered clinically significant
Run previous and current samples in parallel
What does an increase in maternal antibody titer indicate?
Increased risk and severity of HDFN
What additional testing may be done if maternal antibody titer is high?
Amniocentesis to test fetal cells (amniocytes) for antigen presence
Why may the father be tested in regards to prenatal care?
To verify whether he is antigen positive, helping assess fetal risk
When is amniocentesis performed in suspected HDFN?
When maternal antibody titers are elevated and HDFN is suspected
What is amniocentesis and when is it done?
Removal of amniotic fluid from the womb, typically at 18–20 weeks gestation
What does amniotic fluid bilirubin indicate?
Severity of HDFN
How is bilirubin measured in amniotic fluid?
Using a spectrophotometer scanning increasing wavelengths to detect absorbance at 450 nm
What does an increase in ΔOD₄₅₀ indicate?
Rising bilirubin levels → worsening severity of HDFN
What does the Queenan curve for ΔOD₄₅₀ show in HDFN monitoring?
amniotic fluid bilirubin levels (ΔOD₄₅₀ at 450 nm) with gestational age to assess severity of HDFN
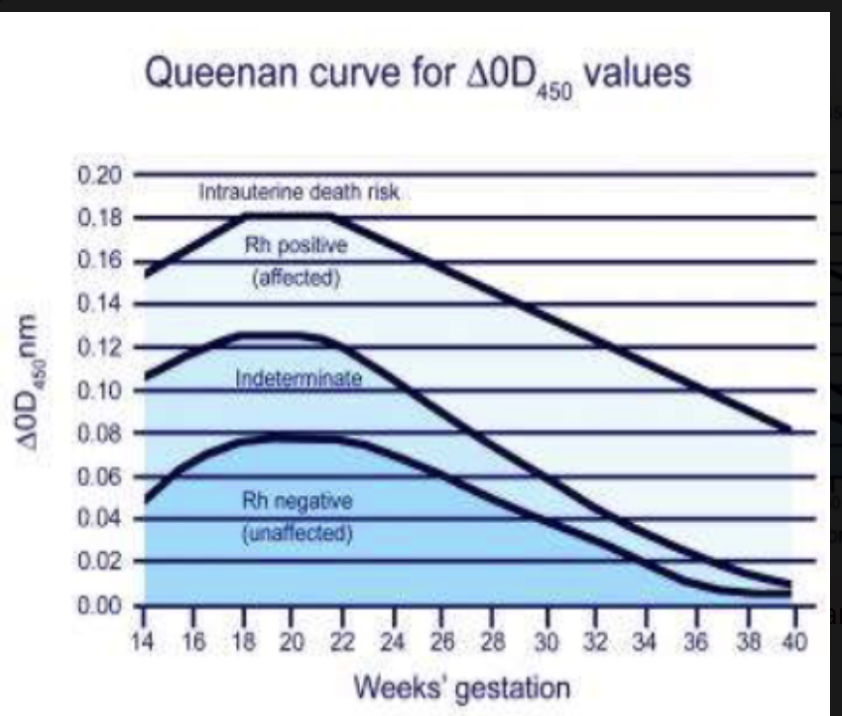
Higher ΔOD₄₅₀ = more hemolysis = more severe HDFN
What is an intrauterine transfusion (IUT)?
direct transfusion of blood to the fetus to treat severe HDFN–related anemia
When is intrauterine transfusion indicated?
When one or more of the following are present:
Fetal hydrops on ultrasound
Fetal Hgb < 10 g/dL (severe anemia)
High ΔOD₄₅₀ on Liley graph or Queenan curve (severe hyperbilirubinemia)
What are the blood product requirements for an intrauterine transfusion (IUT)?
RBCs
< 5 days old
CPDA-1 or AS-3 preservative (no mannitol)
Antigen-negative to corresponding maternal alloantibody
O neg
CMV-negative or *leukoreduced (“CMV-safe”)
Hemoglobin S–negative
Irradiated
AB FFP (if plasma is required)
Why are CPDA-1 or AS-3 used for IUT RBCs?
They lack mannitol, a diuretic that is unsafe for fetuses/neonates
What are the dangers of HDFN after birth (postpartum)?
Continued maternal antibody RBC destruction
Severe anemia → may cause cardiac failure
Hepatomegaly
Splenomegaly
Jaundice due to immature neonatal liver → accumulation of unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin; Hyperbilirubinemia (toxic)
Kernicterus if untreated unconjugated bilirubin → severe neurologic damage/retardation, potentially death
How is neonatal hyperbilirubinemia treated in HDFN?
Phototherapy (460–490 nm): Converts unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin into less lipophilic, less toxic isomers that can be excreted
unconjugated/indirect bilirubin sensitive to strong light
Exchange transfusion: Indicated when Hgb < 10 g/dL or bilirubin ≥ 20 mg/dL to rapidly remove bilirubin and maternal antibodies
if phototherapy doesnt work
What is a neonatal exchange transfusion?
postpartum treatment that replaces the neonate’s blood to remove unconjugated bilirubin and maternal antibodies and stop ongoing hemolysis
When is exchange transfusion chosen over phototherapy?
When phototherapy fails to control rising bilirubin
When maternal antibodies are rapidly destroying fetal RBCs
What are the clinical triggers for neonatal exchange transfusion?
Hemoglobin < 10 g/dL
Total bilirubin ≥ 20 mg/dL
How is exchange transfusion performed in neonates?
Via umbilical cord access or peripheral extremities, depending on age
What RBC characteristics are required for neonatal exchange transfusion?
< 5 days old
CPDA-1 or AS-3 (no mannitol)
Antigen-negative to maternal alloantibody
O neg
CMV-negative or leukoreduced
Hgb S neg
Irradiated
What plasma is used in neonatal exchange transfusion? Why can Rh type be disregarded for plasma?
Universal plasma donor
Contains no anti-A or anti-B antibodies
Prevents plasma incompatibility
Plasma contains no RBCs, therefore no Rh antigens
Why is the neonatal exchange transfusion performed slowly?
to avoid:
Clinically significant hemodynamic shifts
Metabolic abnormalities
What vascular access routes are used for neonatal exchange transfusion?
UVC = Umbilical Venous Catheter
UAC = Umbilical Arterial Catheter
What are the beneficial effects of a 2-volume exchange transfusion?
Removes ~50% of bilirubin
Removes 80–90% of sensitized infant RBCs
Removes 80–90% of maternal incompatible antibodies
Replaces incompatible RBCs with compatible RBCs
What is ABO HDFN?
most common form of HDFN, caused by maternal ABO antibodies reacting with fetal RBCs
When can ABO HDFN occur?
First pregnancy and subsequent pregnancies — no prior exposure required
what is the most common ABO combination causing HDFN?
Type O mother (IgG anti-A,B) with a Type A neonate
(Type B neonate is less common)
How severe is ABO HDFN compared to Rh HDFN?
Usually milder than Rh HDFN
What symptoms are typically seen in ABO HDFN?
Mild to moderate jaundice
Is maternal prenatal testing predictive of ABO HDFN?
No — prenatal testing is usually not predictive
What is the purpose of the cord blood work-up?
To evaluate the newborn for HDFN and identify maternal antibodies attached to fetal RBCs
What tests are performed on the mother postpartum?
Repeat ABO/Rh
Antibody Screen (ABS)
(Usually done at hospital admission prior to delivery)
What tests are performed on the baby in a cord blood work-up?
ABO/Rh typing (including weak D)
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
What does a positive IgG DAT in the newborn indicate?
Maternal IgG antibodies are coating the baby’s RBCs
What is an elution and why is it performed?
procedure uses baby rbcs + supernatant media
Removes antibody from baby’s RBCs using heat or chemicals
The antibody is recovered in the supernatant for antibody identification
Antibody identified is of maternal origin
How is ABO HDFN confirmed using an eluate?
Test the eluate against A₁ and B reagent cells
Why do some hospitals avoid elution testing in newborns?
Requires large blood volume
Risk of iatrogenic anemia (anemia caused by excessive blood draws)
Can ABO HDFN be prevented?
No (unlike Rh HDFN)
What is the most common treatment for ABO HDFN?
Phototherapy for hyperbilirubinemia/jaundice
When is an exchange transfusion indicated in ABO HDFN?
When bilirubin ≥ 20 mg/dL
Which antibodies cause Rh0(D) HDFN?
Anti-D (most common)
Other Rh antibodies: anti-C, anti-c, anti-E, anti-e
How severe is Rh0(D) HDFN compared to other types?
most severe form of HDFN
What are the major clinical consequences of Rh0(D) HDFN?
Severe fetal/neonatal anemia
Severe hyperbilirubinemia/jaundice
Risk of kernicterus
Which pregnancies are usually affected by Rh0(D) HDFN?
2nd or subsequent pregnancies after maternal alloimmunization at 1st pregnancy
What events can cause maternal sensitization leading to Rh0(D) HDFN?
Prior delivery
Miscarriages or abortions
Prenatal fetal–maternal hemorrhage
Which antibodies can cause Rh HDFN, and how severe are they?
Anti-D: most common; mild → severe
Anti-E: usually mild
Anti-c: mild → severe
Anti-e: rare
Anti-C: rare
Antibody combinations (e.g., anti-c + anti-E): can be severe
What prenatal tests are performed on the mother for Rh HDFN?
ABO & Rh typing (including Du)
Antibody Screen (ABS)
What is done if the maternal antibody screen is positive?
Antibody ID
Antibody titer
Optional: father’s antigen status
IgG subclass determination if indicated
How are Rh antibody titers monitored during pregnancy?
Establish initial titer
Repeat every ~4 weeks
Run previous and current samples in parallel
When is further fetal testing indicated in Rh HDFN?
When antibody titer is > 1:32
What fetal tests are used when Rh antibody titers are high?
MCA-PSV Doppler ultrasound (noninvasive; predicts fetal anemia)
Amniocentesis (less commonly used)
What postpartum tests are performed on the mother?
Repeat ABO/Rh and ABS
If ABS positive → Antibody ID
weak anti-D:
May be due to antepartum Rh Immune Globulin (RhIG)
Must verify OB history
if due to RhIG: Report as “passive anti-D”, not alloanti-D
What tests are performed on the baby postpartum?
ABO/Rh typing (including weak D)
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
What is the purpose of elution testing in Rh HDFN?
Removes antibody from neonatal RBCs
Identifies maternal antibody using antibody ID panel cells
What postpartum laboratory testing is performed for Rh0(D) HDFN?
Qualitative test: Fetal Hgb Screen / Rosette Test
detect D-positive fetal cells in a D-negative mother
Quantitative test: Kleihauer–Betke (KB) Test
Measures the amount of fetal blood in maternal circulation
Maternal blood is acid-treated and stained
Fetal RBCs resist acid and stain; maternal RBCs become “ghost” cells
Count fetal cells among 2,000 maternal cells
Fetal blood volume = (# fetal cells × maternal blood volume) ÷ 2,000
What is Rh Immune Globulin (RhIG)?
A pharmaceutical drug of anti-D antibodies
given to Rh neg moms known to be neg for allo anti-D + exposed to Rh+ rbcs
How is RhIG administered?
Intramuscular injection
pre-measured 1 mL syringe with attached needle
When is the micro-dose RhIG given and what does it cover?
Indications: abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy
Administration: ≤ 12 weeks gestation (antepartum)
Dose: 50 μg anti-D
Protects against 2.5 mL Rh+ RBCs or 5 mL Rh+ whole blood
When is the full-dose RhIG given and what does it cover?
Indications: amniocentesis, cordocentesis, abdominal trauma, antepartum hemorrhage, postpartum
Administration:
After abortion/miscarriage >12 weeks
≥ 28 weeks gestation (antepartum)
Within 72 hours postpartum if infant is Rh+ or Rh unknown
Dose: 300 μg anti-D
Protects against: 15 mL Rh+ RBCs or 30 mL Rh+ whole blood
How is the number of RhIG vials calculated postpartum?
Fetal cell volume (from KB test) ÷ 30 = number of syringes
< 0.5 → round down (e.g., 2.2 → 2)
≥ 0.5 → round up (e.g., 2.7 → 3)
The calculation is an estimate — adding +1 vial ensures adequate protection