Cell Division
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 1: Wednesday, August 27th: Lab Worksheet 1A: Cell Division; Week 3: Monday, September 8th
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Chromosomes are replicated for cell division during _______
mitosis
Chromosome number is reduced in half to produce haploid gametes for reproduction during _______
meiosis
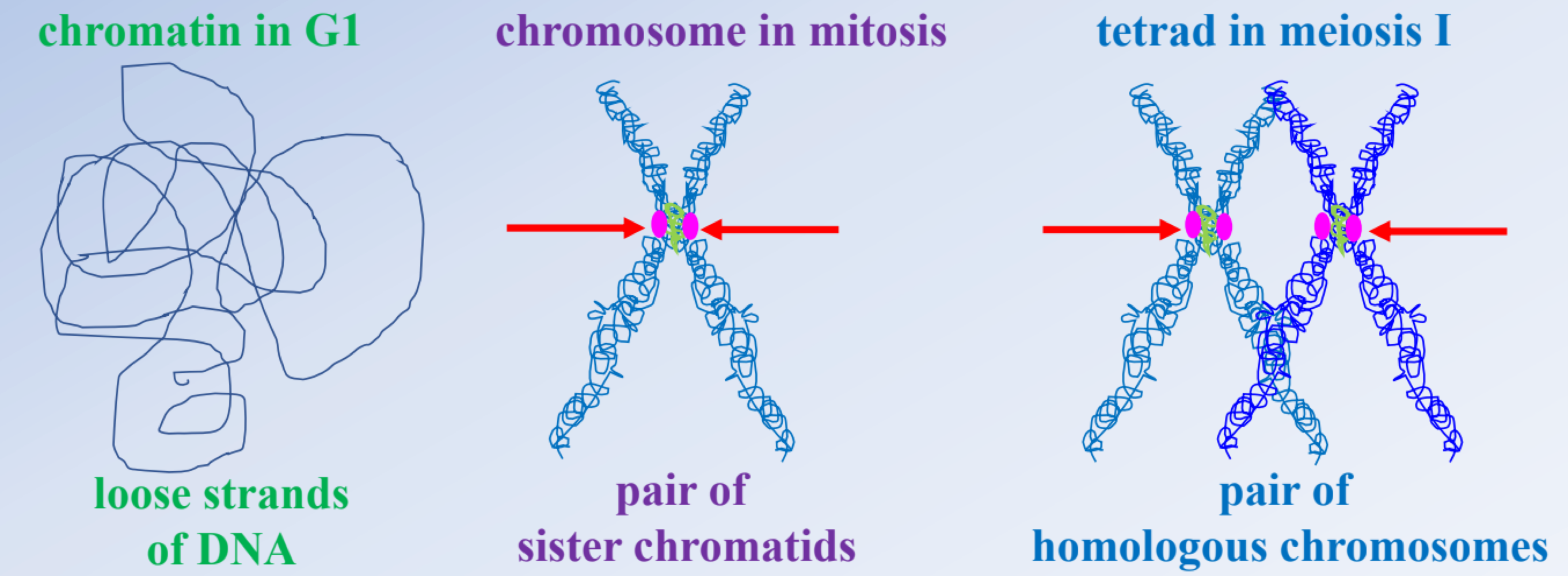
These chromosomes coil from loose strands of chromatin (DNA wrapped around histones), which involves the coordination between histone proteins, cohesin, and condensin. They also help hold sister chromatids together
eykaryotic chromosomes
_______ move chromosmes into position for cell division
spindle fibers
prokaryotes often have one _______ chromosome
circular
True or false: There aren’t any prokaryotes that have linear chromosomes
false. Borrelia burgdorferi have linear chromosomes
_______ hold prokaryote chromosomes in place
nucleoid associated proteins (NAPs)
true or false: fibers attach to centromere on either side of sister chromatids (+spindles bind to -kinetochore)
true
spindle fibers binding to chromosomes promotes _______, during which chromosomes are pushed to the cell center from either side to create _______. This ensures that chromosomes are in the right position for cell division
bi-orientation, tensional equlibrium (bipolarity)
_______ is when sister chromatids separate when they’re lined up properly, which is a good thing
disjunction
_______ is when fibers fail to attach to chromosomes, so the cell divides with an unequal chromsome number, which is a bad thing
nondisjunction
true or false: eukaryotic chromosome number differs among species, and correlates with the complexity of the organism
false. eukaryotic chromosome number differs among species, and doesn’t correlate with the complexity of the organism
true or false: eukaryotes that undergo sexual reproduction have an even number of chromosomes
true
true or false: if sex is determined by chromosome number rather than the X-Y system in humans, this number can be odd
true
among bees, the copies of chromosomes matter because haploid states produce females, but fertilization results in diploid zygotes, which produces males. this is referred to as a _______
haplodiploidy system
True or False: Mitosis occurs in eukaryotes and prokaryotes because they both have spindle fibers.
false. mitosis is unique to eukaryotes because prokaryotes lack spindle fibers.
in mitosis, fibers attach to _______ sides of the chromosome to separate _______
both, sister chromatids
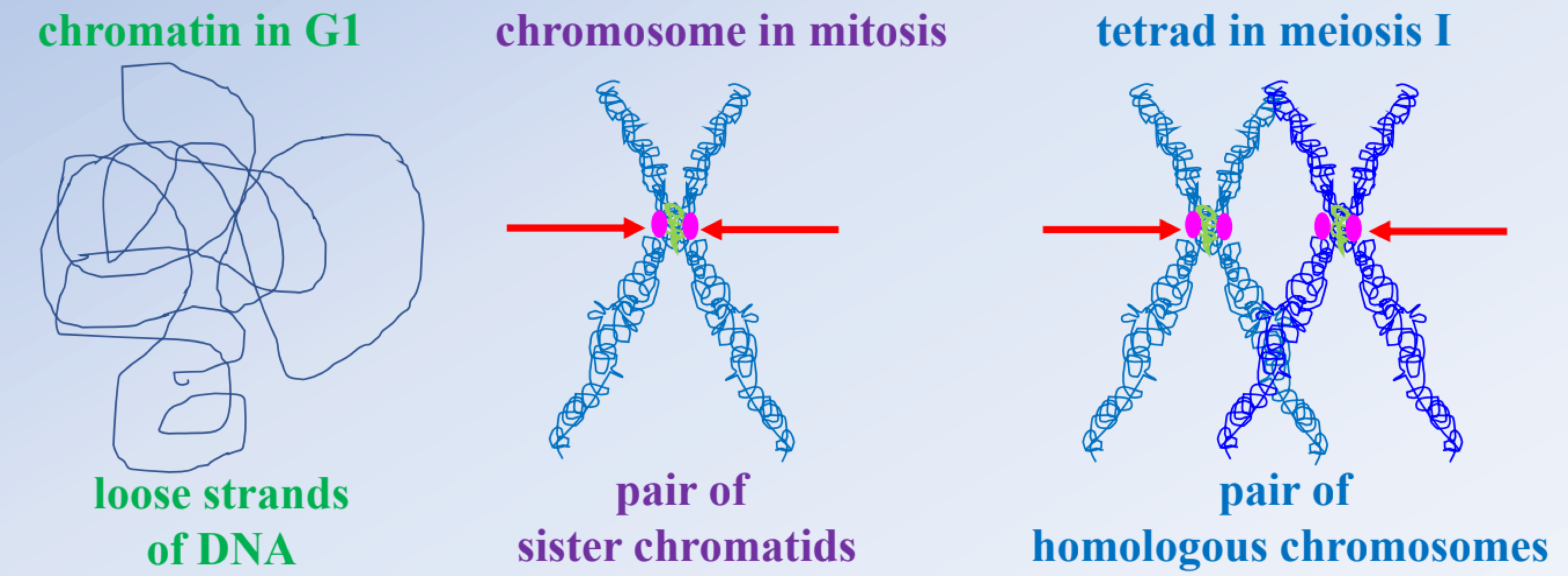
in meiosis 1, fibers attach to _______ of each chromosome to separate _______
one side, homologs
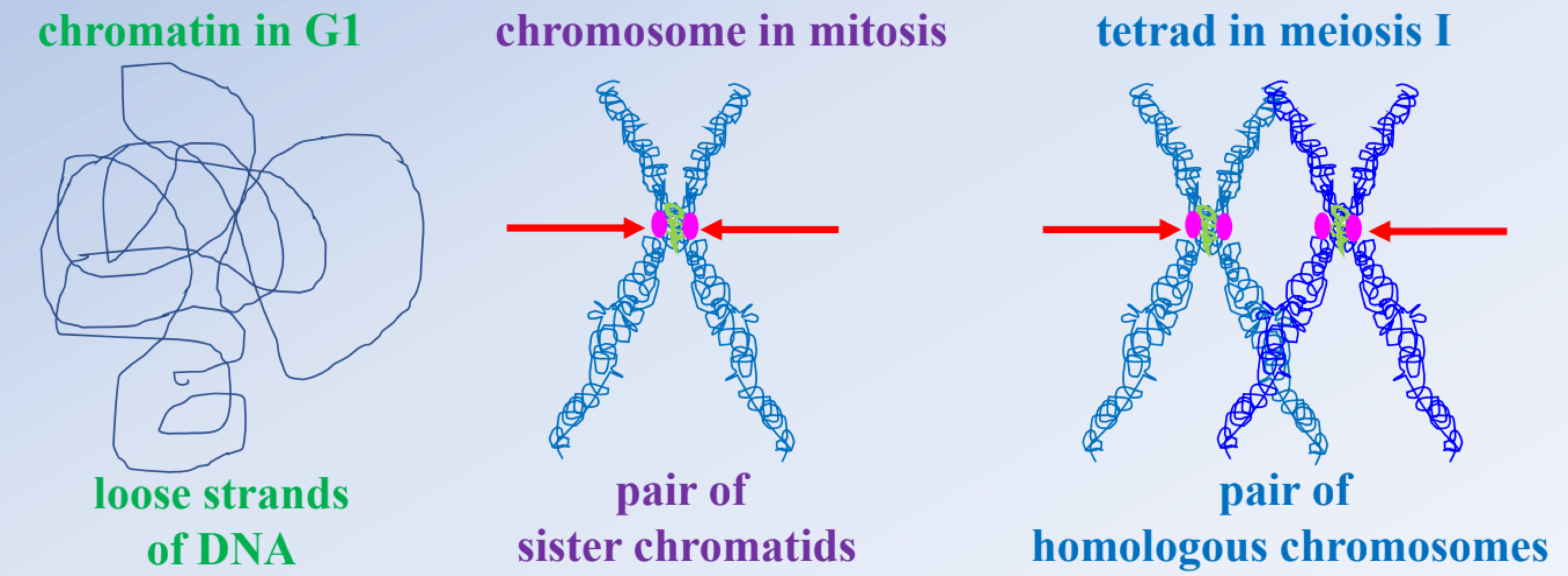
in meiosis 2, fibers attach to _______ to separate homologs into _______
both sides, sister chromatids
when the cell is preparing for DNA synthesis, replicating DNA, and growing, it is in
Interphase (G1, S, G2)
this phase of interphase involves cell growth, organelle production, and division enzyme production
G1 phase
This phase of interphase involves the duplication of the centromere, then DNA (p and q arms), them centrosomes
S phase
this phase of interphase involves more growth, more energy generated, more enzymes made, and cohesion digestion
G2 phase
this checkpoint of interphase ensures the cell is healthy and ready for division; cyclin proteins adn kinases must be readily available to mediate cell passage through check points
G1 checkpoint
this checkpoint of interphase ensures DNA replication forks are stable
S checkpoint
this checkpoint of interphase ensures DNA was replicated proerly during S phase
G2 checkpoint
this checkpoint of interphase ensures spindles are attached for disjunction
M checkpoint
true or false: ignoring checkpoints can lead to unregualted cell growth
true
when chromosomes are dividing, the cell is in _______
M phase
true or false: after mitosis, cells have to stay active
false. after mitosis, cells can move to G0 (resting state)
what stage of cell division is this?
interphase
during this phase of mitosis:
chromosomes condense and are in random fashion
the nuclear membrane and nucleolus condense
spindle fibers begin to form from microtubule-organizing centers (MTOC)
replicated chromosomes move to opposite sides
prophase
what stage of cell division is this?
prophase
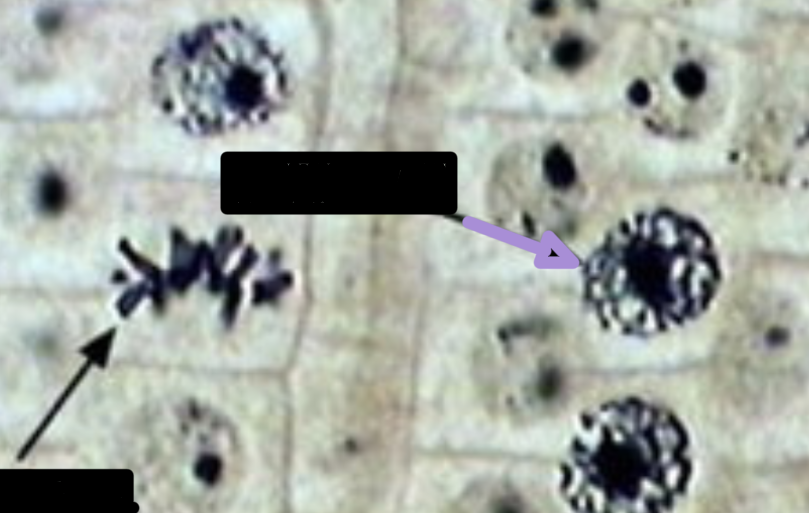
during this phase of mitosis:
microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) of the centrosome creates spindle apparatus
spindle fibers attach to both kinetochores of sister chromatids
the nuclear membrane and nucleolus completely dissolves
prometaphase
what stage of cell division is this?
prometaphase
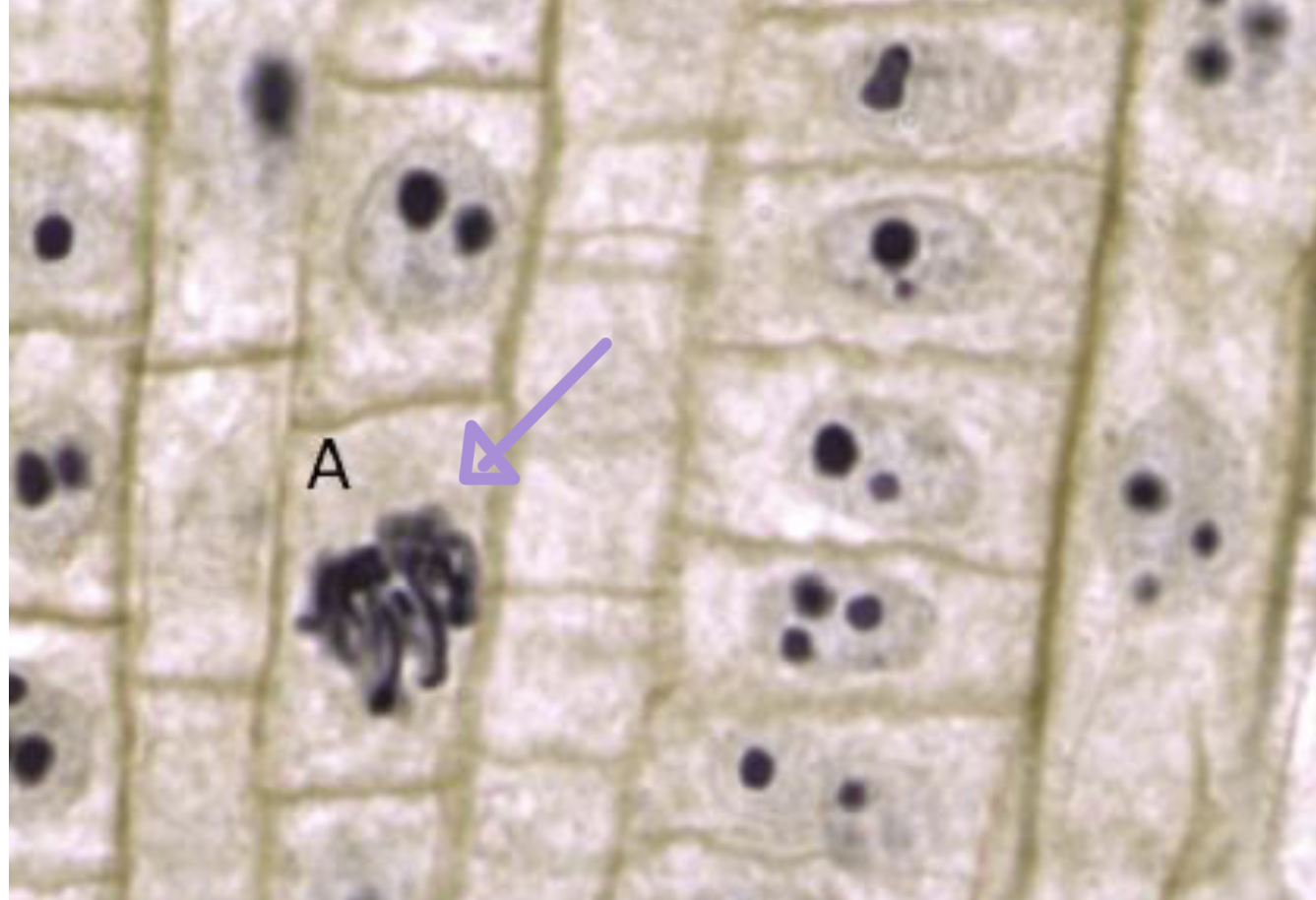
during this phase of cell division:
spindle fibers lengthen and align the sister chromatids in the middle of the cell with the involvement of bi-orientation
the cell clears M checkpoint once balance is detected, and the last of cohesin is digested
metaphase
what stage of cell division is this?
metaphase
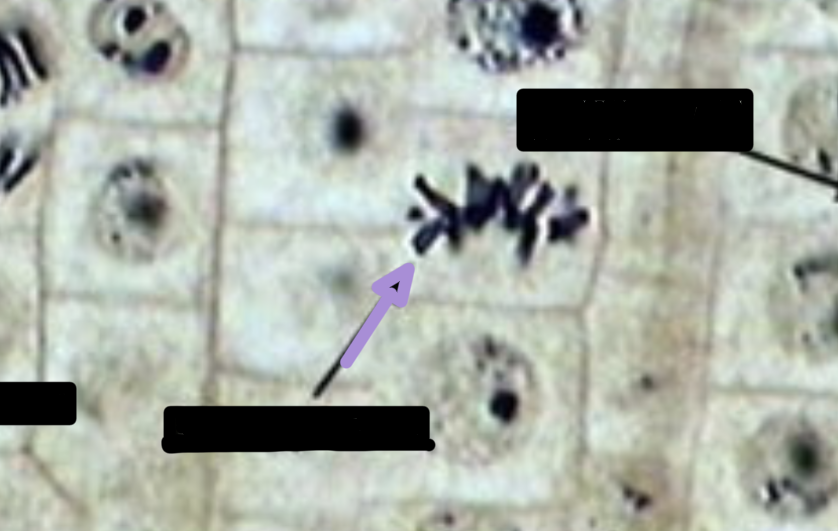
during this phase of cell division:
46 pairs of sister chromatids separate
microtubules disassemble and pull a set of now 46 daughter chromosomes back to opposite sides
anaphase
what stage of cell division is this?
anaphase
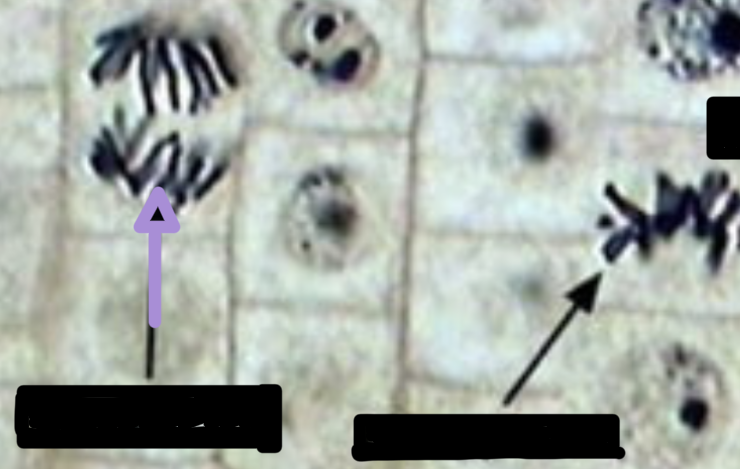
during this phase of mitosis:
daughter chromosomes relax into chromatin
two nuclei form around each set of daughter chromosomes in a single cell
ER rebuilds the nuclear membrane around them, which leads to cell division
telophase
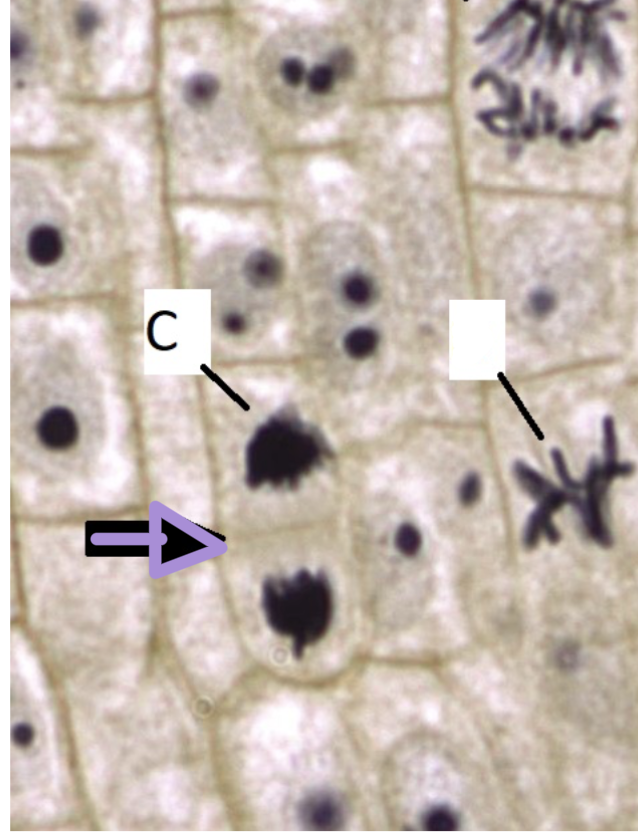
what stage of cell division is this?
telophase
during this phase of cell division:
the cell divides in half to form two new cells by a cleavage furrow for animals, or a cell plate for plants
two daughter diploid cells are created
cytokinesis
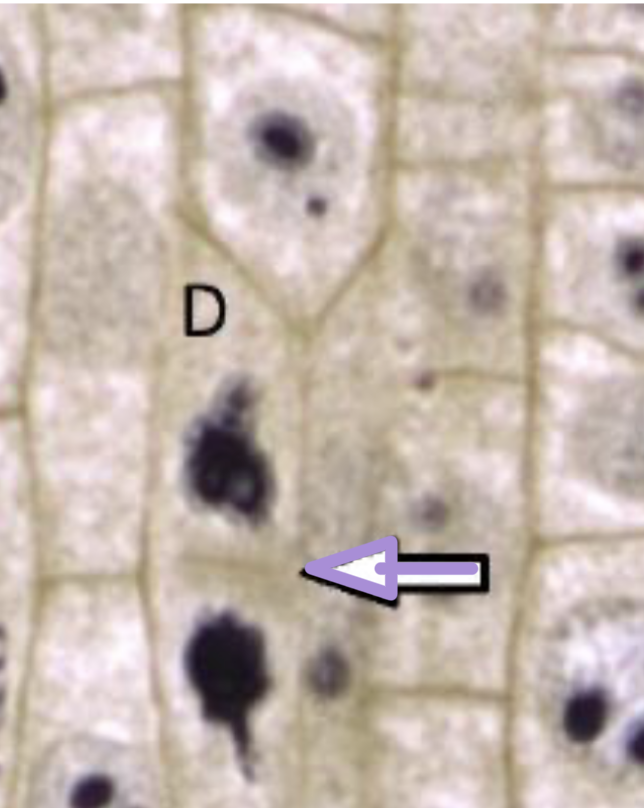
what stage of cell division is this?
cytokinesis
true or false: meiosis interphase is different from mitosis interphase
false. meiosis interphase is the same steps as mitosis interphase
_______ involves tetrad synapse, cross-over in holliday junctions, and chromosome separation from diploid to haploid
meiosis 1
during this phase of cell division:
the phase is prolonged
pairs of homologous chromosomes line up side-by-side (synapsis) to form a tetrad
SPO11 makes double-stranded DNA breaks for allelic changes between homologs
synapsis crossing-over occurs
spindle fibers attach again
prophase 1
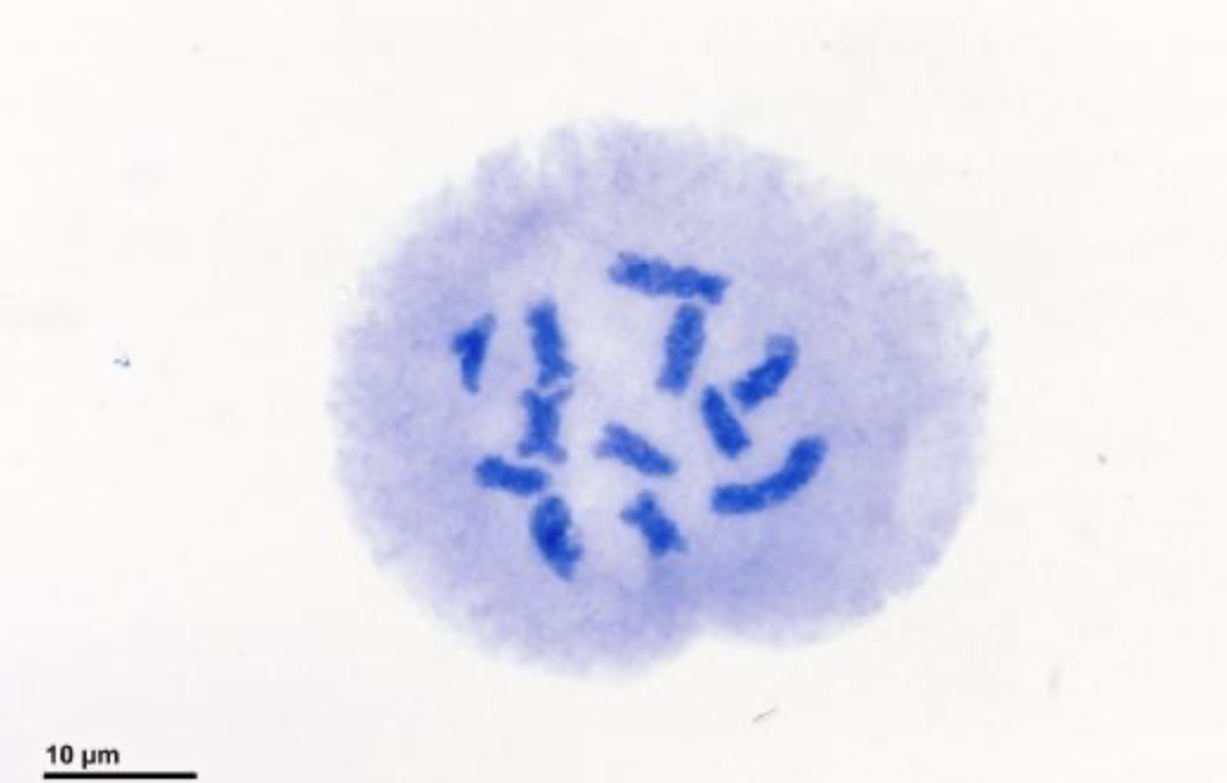
what stage of cell division is this?
prophase 1
_______ holds tetrads together during prohase 1. they’re then held by chiasmata
synaptonemal complex (SC)
true or false: during meiosis, cells go through a prometaphase stage
false. during meiosis, cell don’t go through a prometaphase stage because spindle fibers are already attached during prophase
during this phase of cell division:
spindle fibers bind to the outer sides of the recombined tetrads
recombined tetrads are pushed to cell center and held together by spindle fibers (chiasmata prevents them from binding to the inner sides of tetrads like in mitosis)
metaphase 1
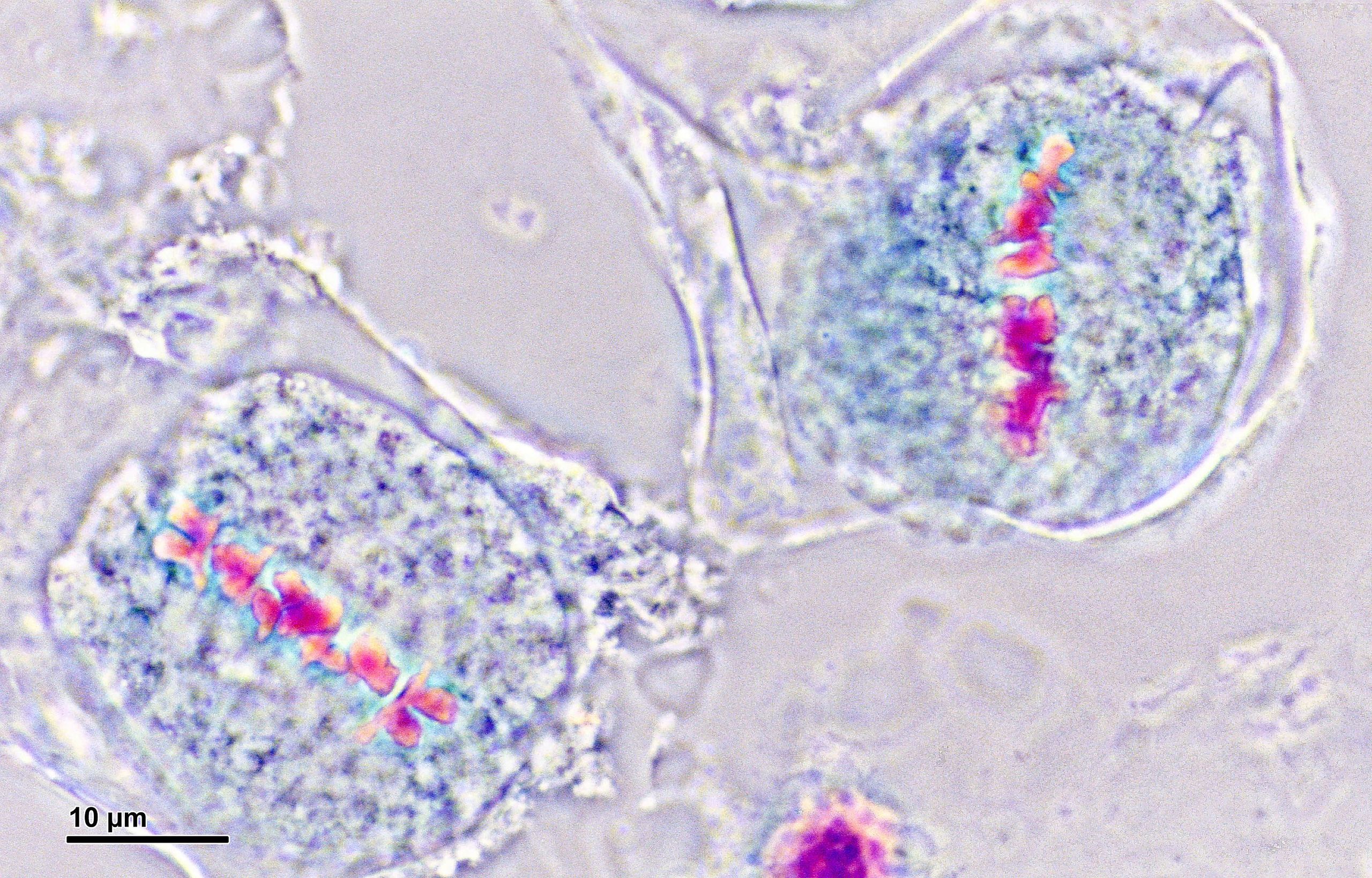
what stage of cell division is this?
metaphase 1
during this phase of cell division:
spindle fibers dissemble
recombined homologous chromosomes separate into only paternal or only maternal haploid sister chromatid sets to opposite poles (sister chromatids aren’t pulled apart)
anaphase 1
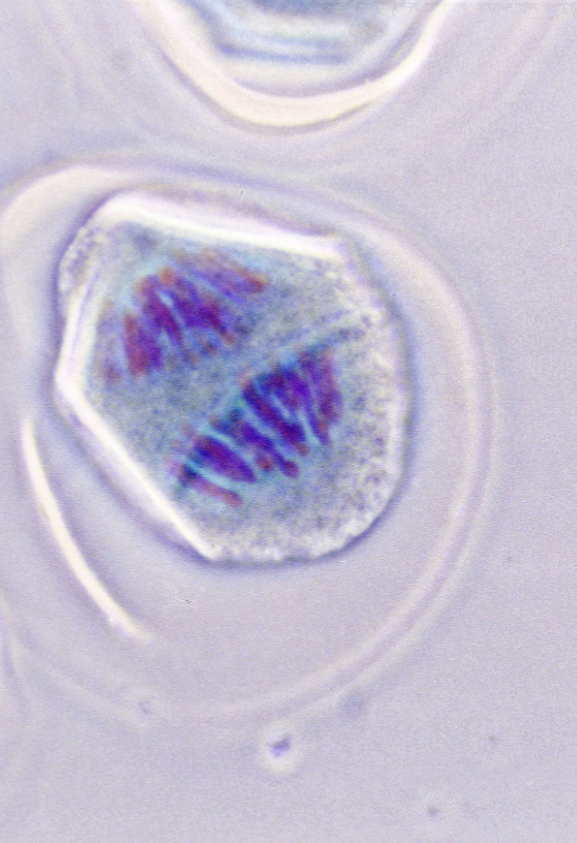
what stage of cell division is this?
anaphase 1
during this phase of cell division:
two nuclei form around each set of sister chromatids, which are enclosed by separate nuclear membranes
two recombined haploid cells are created
telophase 1
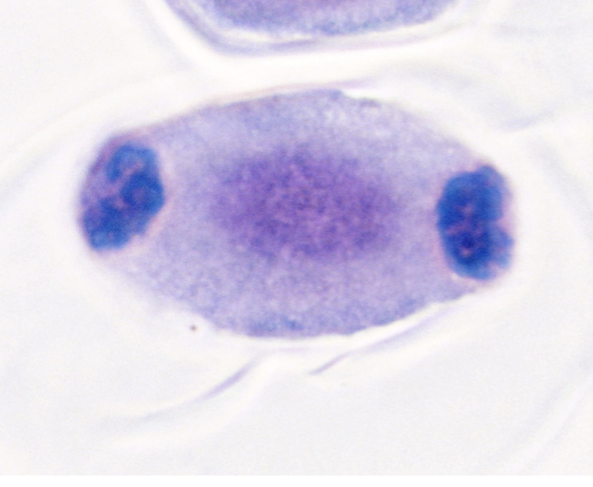
what stage of cell division is this?
telophase 1
chromosome reduction occurs _______ Meiosis 1, (before interkinesis) where homologous chromosomes are separated
after
haploid sister chromatids are seaprated in _______, which produces haploid gametes
meiosis 2
during this stage of cell division:
there’s no S phase
G1 and G2 phases are reduced
two haploid cells are preparing to divide
interkinesis
during this phase of cell division,
haploid cells made of recombined sister chromatids prepare to divide again
they condense and alighn at right angles at the plane of division of meiosis 1
spindle fibers attach
prophase 2
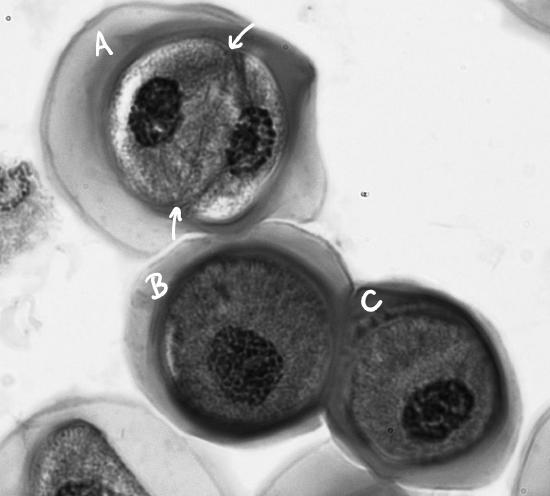
what stage of cell division is this?
prophase 2
during this stage of cell division:
recombined haploid sister chromatids line up at the cell center
spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores on both sides of the centromeres
metaphase 2
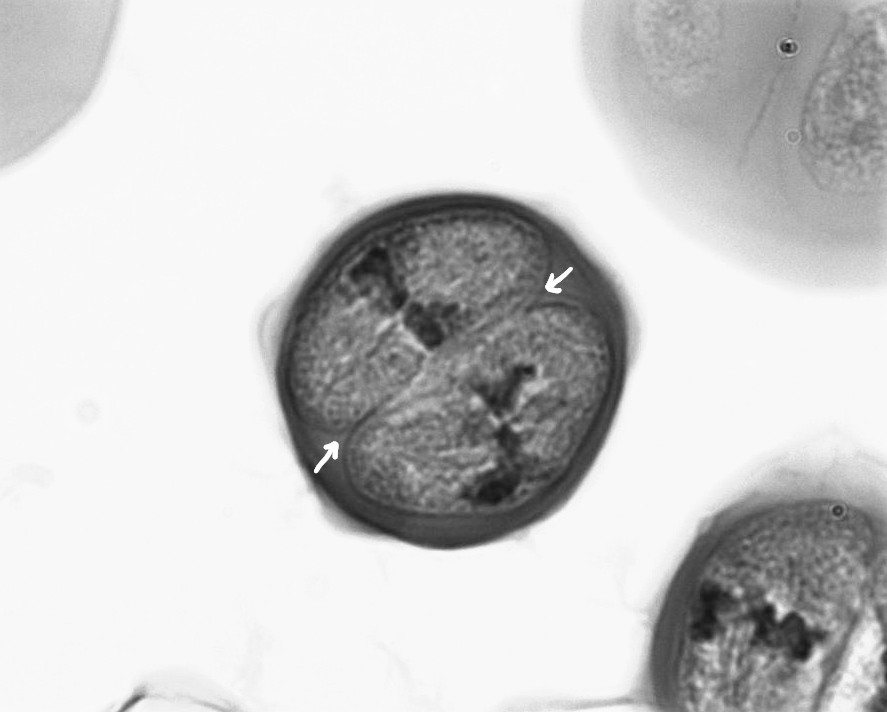
what stage of cell division is this?
metaphase 2
during this phase of cell division:
sister chromatids separate
cohesin is digested
spindle fibers break down
chromatids separate into haploid daughter chromosomes and are pulled apart
anaphase 2
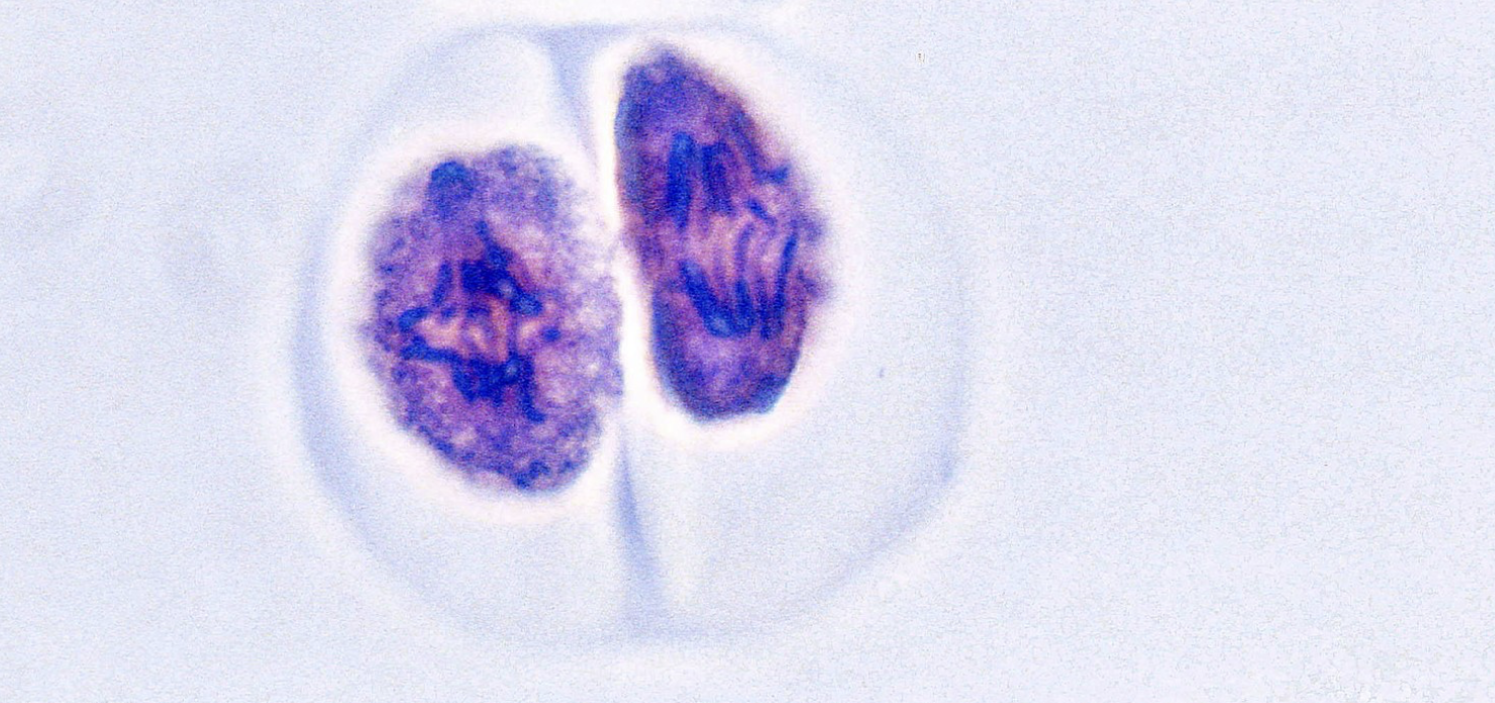
what stage of cell division is this?
anaphase 2
during this phase of cell division:
two nuclei form around each set of haploid daughter chromosomes
the second set of cell division occurs
telophase 2
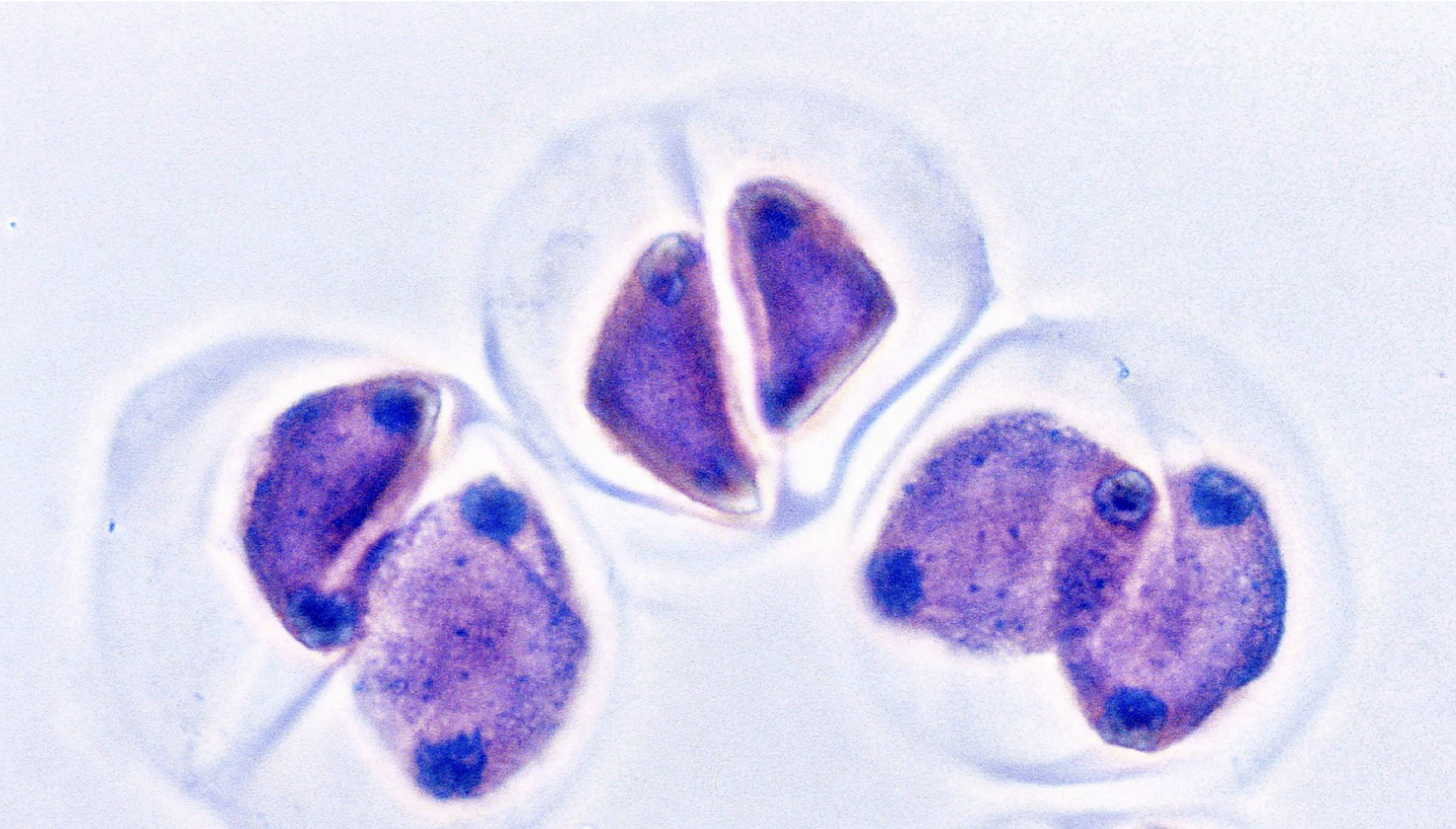
what stage of cell division is this?
telophase 2
during this phase of cell division:
four recombined haploid gametes in human males are produced
and one big oocyte and three degenerated cells in females are produced
cytokinesis
cohesin and _______ prevent sister chromatids from separating during mitosis and meiosis
shugoshin
_______ digests cohesion to allow anaphase to begin
separase
cohesion is only left between the centromeres during _______; and lasting until _______
metaphase, metaphase 2
meiosis produces gametes that then undergo _______ after zygote formation during fertilization.
mitosis
during zygote formation, sperm binds to ZP3 receptors on a hardened membrane surrounding the oocyte that prevents additional fertilization, which is referred to as the _______
zona pellucida
during zygote formation, sperm binding to an oocyte causes an _______ reaction that releases digestive enzymes so sperm can eat through the oocyte’s plasma membrane
acrosomal
true or false: during zygote formation, the mother cell provides organelles and cytoplasm
true
during zygote formation, the zygote goes through duplicative mitotic divisions (cleavage) to form 2, then 4, then 8, then 16 cells—all of which are a _______ and undifferentiated.
morula
during zygote formation, the morula develops into a 32-cell stage that forms a _______ and creates a fluid-filled hollow center.
blastula
during zygote formation, there’s an increase in size to accomodate the increasing number of cells
false. there’s no increase in size, so cells shrink to accommodate the increasing number
blastulation involves cell migration, and _______, which leads to three primal cell layers: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm
gastrulation
during zygote formation, the three primal cell layers, which differentiate and end in _______, when the neural plate transforms into the neural tube
neurulation
sexual differentiation begins around _______, wheras fetus formation begins by the end of _______
week 6, week 8
one chromosome and a copy of the same chromosome, which is created during Mitosis S-Phase, is defined as a pair of ____
sister chromatids
chromosomes that are identical to sister chromatids, but separated and independent during mitosis anaphase, are defined as _______
daughter chromosomes
4 chromatids that consist of one chromosome from each parent and their copies are defined as _______ and are present during meiosis prophase 1
tetrads
chromatin (DNA + histones) is coiled by _______
condesin