B3 Genetics
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
sexual reproduction
variation in offspring
requirement to find a mate
asexual reproduction
no variation if offspring
rapid reproductve cycle
no need to find a mate
meiosis
cell division the reduces the number of chromosomes by half it produces four non identical haploid sex cells (gametes)
structure of DNA
polymer made of two strands
strands are coiled to form a double helix shape
how are strands of DNA linked together
complementary base pairs
bases are joined together by weak hydrogen bonds
what are nucleotides in DNA
building blocks of DNA
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, phosphate group, and one of the for bases
what are the four base in DNA and how do they pair
A and T
C and G
genome
the genome is the entire DNA of an organism
It contains all the genetic information needed for growth, development and functioning
gene
a gene is a section of a DNA molecule
It codes for a specific protein that carries out a particular function in the body
how to extract DNA from fruit
mash up fruit
add salt and washing liquid
heat
filter and keep liquid
cool
add cold ethanol
how does order of bases affect proteins
order of bases determines order of amino acids in a protein
role of amino acids in proteins
building blocks of proteins
sequence of amino acids determines portends structure and function
how are amino acids ordered
DNA are red in codons (groups of 3)
Each codon codes for a specific amino acid
what happens after amino acids are assembled
the chain of amino acids folds into a specific shape
the shape determines the protein function, such as forming enzymes
why is the shape of a protein important
shape of protein = function of protein
enzymes the shape determines their active site and ability to catalyse reactions
stages of protein synthesis
dna instructions: DNA has a code that tells the cell how to make proteins.
mRNA copy: The cell makes a copy of the DNA code called mRNA
mRNA to ribosomes: The mRNA travels to the ribosome.
amino acids: tRNA brings the correct amino acids to the ribosome.
protein chain: The ribosome links the amino acids together to form a protein.
folding: the protein chain folds into a specific shape to work properly
Gregor Mendeleev key discoveries
principles of inheritance through pea plants
genes come in pairs
some traits are dominant some are reccesive
chromosome
long coiled structure made of DNA that contains many genes
gene
small bit of DNA that carries code for something
allele
different variations of the same gene (dominant or reccseive)
homozygous
two identical alleles for a gene
heterozygous
two different alleles for a gene
genotype
combination of alleles for a particular gene
phenotype
physically observable trait
gamete
sex cell
zygote
fertilised egg from when two gametes combine
monohybrid inheritance
the study of how one characteristic is passed from parent to offspring (use punnet squares)
how is the sex of an offspring determined
combination of sex chromosomes from each parent
females = XX
male = XY
ABO blood groups
I^A
I^B
i
I^A + I^A or i = A
I^B + I^B or I = B
I^A + I^B = AB
i + Ii= O
what cause sex linked genetic disorders
disorders linked to genes on the X chromosomes
e.g colour blindness, hemophillia
how do sex linked disorders affect females
female have two X chromosomes
need two recessive alleles to show the disorder
with one recessive alleles female are carriers
draw out a punnet square of a 50/50 chance of done having hemophillia
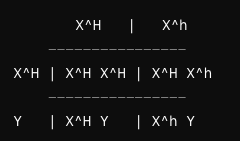
are most phenotype (physical) feature influenced by a single gene or multiple genes
multiple
genetic variation
differences in characteristics due to genetic factors
mutations
genes from parents
environmental variation
differences in characteristics caused by an organisms environment
acquired characteristics like tattoos
human genome project
global research that mapped out all the genes in the human genome
outcomes of human genome project
complete DNA sequence
genetic testing in medicine
personalised medicine
gene therapy
what causes genetic variation in a population
mutations