Psychology 107 (fall 2023)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
1
New cards
Psych definition
the scientific study of the mind
2
New cards
inductive reasoning
taking info from a small group and generalizing
3
New cards
William Wundt (lifespan and accomplishments)
(1832-1920) Started the first psych lab in Germany (1879), studied introspection
4
New cards
E.B. Titchener
(1867-1927) Introspective method; Structuralism - basic structure and content of human mind
5
New cards
William James
(1842-1910) 1st US psychologist, stream of consciousness (tracing back to how you started thinking of something), functionalism - interaction between the mind and environment
6
New cards
Psychoanalytic approach
Unconcious mind, early childhood experiences, Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) used psychoanalysis, Erik Erikson revised freud’s views
7
New cards
Behavioral Approach
observing and controlling behavior, directly observable and measurable, would ask: how do we learn to be anxious in certain situations? People: Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), John Watson (1878-1958), B.F. Skinner (1904-1990), Albert Bandura (1925-2021) formed the social cognitive theory which is measuring the response of an organism to a stimulus
8
New cards
Humanistic Approach
Potential for good in humans, Key figures: Carl Rogers (1902-1987), Abraham Maslow (1908-1970), would say: you have the potential to understand your anxiety
9
New cards
Cognitive approach
Mind active and aware, Key figure: Noam Chomsky (1928-present)
10
New cards
Multicultural and Cross Cultural Approach
descriptive science, differences between cultural groups, key figures: Francis Sumner (1895-1954), George Sanchez (1906-1972), Kenneth Clark and Mamie Phipps
11
New cards
Mary Calkins
(1863-1930) degree in psychology at Harvard was denied by the university
12
New cards
Margaret Washburn
First female PHD (1894)
13
New cards
Biopsychological approach
brain and nervous system related to behavior and mental process, neuroscience, would ask: how do levels of certain neurotransmitters contribute to anxiety levels?
14
New cards
Evolutionary Approach
adaptation and survival of the fittest
15
New cards
Positive Approaches
Valuable experiences, positive individual traits, positive values
16
New cards
APA
American Psychological association, founded 1892
17
New cards
APS
American association for psychological science, founded 1988
18
New cards
Why do we need psychological science?
Without it we would have biases
19
New cards
Hindsight bias
I knew it all along
20
New cards
False consensus affect
tendency to think more people agree with us
21
New cards
Overconfidence
We think we’re better than we are
22
New cards
Step 1 of the Scientific Method
Observe phenomenon - choose the problem to study
23
New cards
Step 2 of the Scientific Method
Generate hypothesis, operational definitions
24
New cards
Step 3 of the Scientific Method
Collect data - who will you study? population then sample then random sample, which research methods will you use?
25
New cards
Step 4 of the Scientific Method
Analyze data - connect findings back to the hypothesis, reliability
26
New cards
Step 5 of the Scientific Method
Summarize data and evaluate theory - larger scientific community reviews and evaluates
27
New cards
3 types of research
descriptive, correlational and experimental
28
New cards
Clinical or case study
In depth look at one person, conducted when something rare happens
29
New cards
Pros of case study
Deep understanding of phenomenon
30
New cards
Cons of case study
Lack of generalizability
31
New cards
Observation
Observing and recording behavior, describing not explaining
32
New cards
Naturalistic observation
behavior in natural setting
33
New cards
Pros of naturalistic observation
more accurate data
34
New cards
Cons of naturalistic observation
no control over environment
35
New cards
Laboratory observations
Observe behavior in a controlled setting
36
New cards
Pros of laboratory observation
controlled setting
37
New cards
Cons of laboratory observation
participants are aware they’re being observed, setting is unnatural
38
New cards
Observer bias
observer skews observations
39
New cards
inter-rater reliability
poor agreement between observers
40
New cards
Pros of Surveys
cost effective
41
New cards
cons of surveys
social desirability - people say whats socially acceptable, under representative sampling
42
New cards
Archival research
using existing records to answer research questions
43
New cards
pros of archival research
saves time and money
44
New cards
Cons of archival research
No control over data, inconsistency between data sets
45
New cards
Difference between structuralism and functionalism
structuralism is the contents of the mind while functionalism is the behavior of the mind
46
New cards
Correlational research
describes the association between two variables; the correlational coefficient (r) is positive or negative and the closer it is to 1 the stronger the association
47
New cards
Confounding variable
third unknown variable that affects both variables
48
New cards
Longitudinal design
data gathered repeatedly over time
49
New cards
Cross sectional
data gathered once in time
50
New cards
Experimental group
group who receives the IV
51
New cards
Control group
does not receive the IV
52
New cards
Pros of experiment research
shows cause and effect, controlled conditions, no need to wait for occurrences to happen naturally
53
New cards
Cons of experimental research
cannot study some natural behaviors experimentally
54
New cards
External validity
do the results generalize to the real world
55
New cards
Internal validity
extent to which changes in DV are due to manipulation of the IV
56
New cards
Can you have both internal and external validity?
No
57
New cards
Experimenter bias
preconceived knowledge gets in the way of testing; smart rat vs. dumb rat example
58
New cards
Research participant bias
participants expectations change behavior
59
New cards
Solution to experiment bias
double-blind experiment
60
New cards
Ethnic gloss
assuming that all members of an ethnic group have the same characteristics
61
New cards
Central nervous system
brain and spinal chord, reflexes
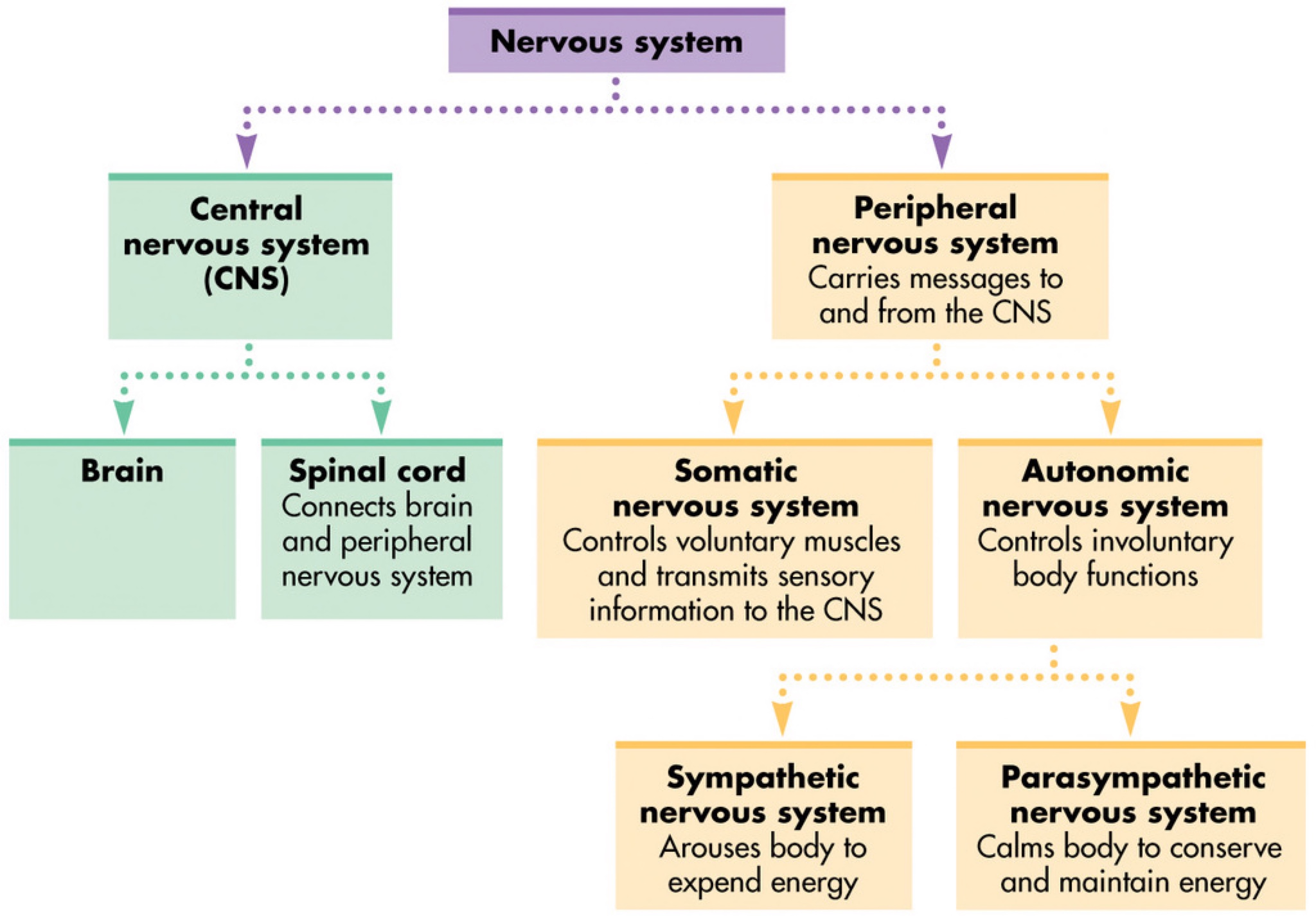
62
New cards
Peripheral nervous sytem
network of sensory nerves - connects cns to body
63
New cards
Afferent nerves
sensory nerves that carry info to the brain
64
New cards
Efferent nerves
carry info away from brain
65
New cards
Divisions of PNS
somatic system (controls skeletal muscles, voluntary activities), autonomic system (organs and glands, automatic functions)
66
New cards
Divisions of autonomic system
Sympathetic (arouses body) and parasympathetic (calms the body)
67
New cards
sensory neurons
carry info to CNS
68
New cards
motor neurons
carry info away from CNS
69
New cards
Interneurons
carry info to and away
70
New cards
Glial cells (glue)
keep neurons running smoothly
71
New cards
Soma
cell body
72
New cards
Dendrites
receive info from other neurons
73
New cards
Axon
carries info away from neuron
74
New cards
terminal buttons
on the end of the axon
75
New cards
synaptic vesicles
inside terminal buttons
76
New cards
neurotransmitters
inside of synaptic vesicles
77
New cards
myelin sheath
covers axons and speeds up connection
78
New cards
how do neurons carry info?
Ions; cell membrane is semi-permeable
79
New cards
Resting potential
neuron is not firing; negative inside, positive inside
80
New cards
Threshold
level at which the neuron fires from outside stimulation
81
New cards
Depolarization
neuron becomes more positive on the inside
82
New cards
Action potential
electrical signal that moves down the neuron; all or none - strength of stimulus does not affect speed of the action potential
83
New cards
synapse
junction between two neurons
84
New cards
first way that neurons communicate
electrical impulse converted to chemical energy
85
New cards
second way that neurons communicate
neurotransmitters released
86
New cards
third way that neurons communicate
neurotransmitters cross synapse
87
New cards
fourth way that neurons communicate
neurotransmitters bind to the receptor sites of the next neuron
88
New cards
reuptake
sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters
89
New cards
Acetylcholine
(ACh) muscle action, learning and memory
90
New cards
What can too little ACh cause?
alzheimers
91
New cards
Beta-endorphin
pain, pleasure
92
New cards
Dopamine
movement, mood, sleep, learning
93
New cards
What does too much dopamine cause
schizophrenia
94
New cards
What does too little dopamine cause?
Parkinson’s
95
New cards
Gaba
brain function, sleep
96
New cards
What does too little Gaba cause
anxiety
97
New cards
Glutamate
Learning and memory
98
New cards
What does too much glutamate cause
seizures
99
New cards
Norepinephrine
heart, intestines, alertness
100
New cards
What do lower levels of norepinephrine cause
depression