GP- intestines, liver, and bile ducts
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
maldigestion and malabsorption;
hyperperistaltism. hypoperistaltism, ileus, obstruction
the 2 main categories of intestinal disorders are secretory function disorders, which includes ________, and motor function disorders, which includes ________
maldigestion
malabsorption
what are the 2 types of secretory disorders of the intestines?
hyperperistaltism
hypoperistaltism
ileus
obstruction
what disorders are categorized as motor function disorders of the intestines?
-tenesmus
-colic
-constipation
-diarrhea
what are the 4 main possible clinical signs of intestinal disease?
the incomplete digestion or lack of division of great molecules
what is maldigestion?
enzymes (there is a decreased amount of enzymes)
with maldigestion, which factor of the intestines is not functioning correctly- enterocytes or enzymes?
dogs (especially small dogs)
maldigestion is more common in _______ (dogs or cats)
diarrhea
because if there is a lack of division/fractioning of molecules, there will be an increased osmotic pressure in the intestinal lumen, which causes water to move into the lumen.
what major clinical sign is produced by maldigestion? why?
-diet with high fat+protein and no fiber
-food allergy or lactose intolerance
-poorly digestive lacteal replacers
-exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)
-liver disease
-dehydration
-anemia
what are possible etiologies of maldigestion?
because the pancreas produces lipases and amylases that are necessary for digestion
why can exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) cause maldigestion?
because the liver produces bile, which is necessary for fat digestion. it also synthesizes other important enzymes for digestion
why can liver disease cause maldigestion?
maldigestion
because the pancreas produces lipases and amylases that are necessary for digestion
does exocrine pancreas insufficiency cause malabsorption or maldigestion?
maldigestion
because the liver produces bile, which is necessary for fat digestion. it also synthesizes other important enzymes for digestion
does liver disease cause malabsorption or maldigestion?
maldigestion
which secretory disorder- maldigestion or malabsorption is related to the decrease of enzymes in the intestines?
insufficient nutrient assimilation due to the impairment or decrease in absorption or nutrient transport through the intestinal
what is malabsorption?
not always
are maldigestion and malabsorption linked (appear together)?
malabsorption
disorders that affect the intestinal mucosa coating (villi) will cause ________ (maldigestion or malabsorption)
disorders affecting the intestinal mucosa coating:
-infections
-parasites
-inflammation
-neoplasia
-drugs
decrease in intestinal absorption capacity:
-intestinal blood flow deficiency
-enterocyte processing defects
-congenital disorders
-villus atrophy
-endocrinopathy
what are the possible etiologies of malabsorption?
diarrhea
a disorder that decreases the intestinal absorption capacity will cause what major clinical sign?
-intestinal blood flow deficiency
-enterocyte processing defects
-congenital disorders
-villus atrophy
-endocrinopathies
what types of diseases decrease the intestinal absorption capacity and therefore cause malabsorption?
it causes malabsorption because it affects the mucosal coating/villi
how does a lymphoma (neoplasia) on the intestinal mucosa cause diarrhea?
we cannot. they have the same clinical signs
clinically, how can we differentiate malabsorption and maldigestion?
diabetes, hypothyroidism
what endocrinopathies can cause malabsorption?
-diarrhea
-steatorrhea
-weight loss
-ravenous appetite or anorexia
-abdominal distension
-meteorism
what are the clinical signs of malabsorption and maldigestion? (they both have the same signs)
malabsorption
the presence of a parasite on the intestinal mucosa will cause ________ (malabsorption/maldigestion)
maldigestion and/or malabsorption
a decreased blood flow to the intestines will cause ________ (malabsorption/maldigestion)
because the body won't have enough iron and vitamin B12 to make RBCs
why can malabsorption or maldigestion cause anemia?
because the body won't have enough calcium and vitamin D
why can malabsorption or maldigestion cause osteomalacia?
because the body won't have enough thiamine, B1, cobalamin, and vitamin B12, which are necessary for neurological development
how can malabsorption/maldigestion lead to neurologic lesions?
because the body won't have enough calcium and the animal will be dehydrated due to the diarrhea
how can malabsorption/maldigestion lead to muscular weakness?
because the body does not have enough proteins, so the water moves into tissues
why can malabsorption or maldigestion cause edema?
because the body will not have enough thrombin and vitamin K, which cause clotting factor deficiencies
why can malabsorption or maldigestion cause hemorrhage?
because they have diarrhea, which causes loss of water, and they have decreased nutrient absorption
why do animals with malabsorption or maldigestion lose weight?
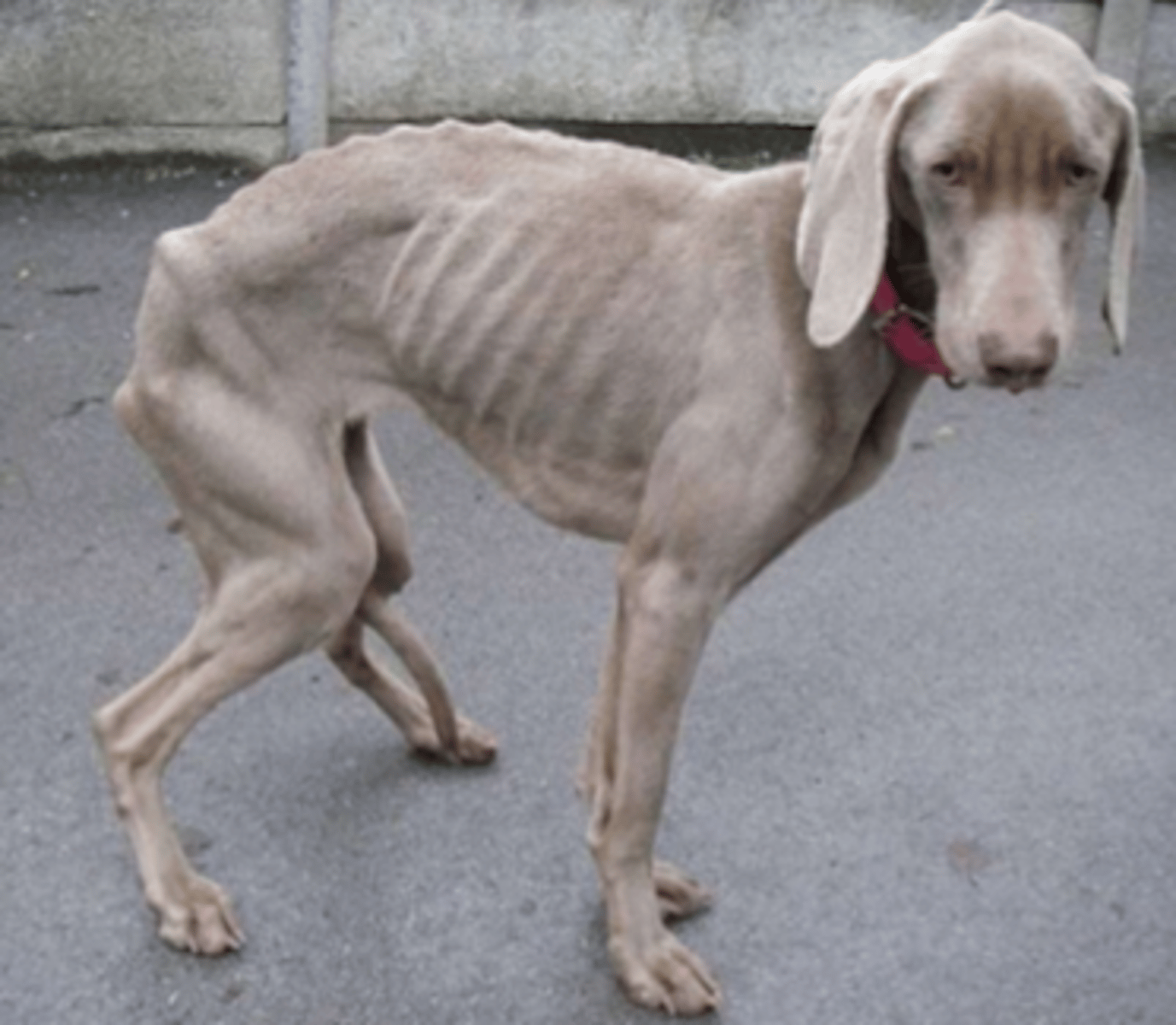
because the oncotic pressure is decreased due to hypoalbuminemia, so the water moves from the blood to the abdomen
why do animals with malabsorption or maldigestion commonly have abdominal distention?
fat in the feces
the feces will appear brightly colored
what is steatorrhea?
increased intestinal peristalsis
what is hyperperistaltism?
diarrhea
what is the major clinical sign of hyperperistaltism?
hypoperistaltism
the condition of decreased intestinal motility is called...
-stress
-hyperthyroidism in cats
-neurological disorder, affecting the parasympathetic NS
what are the main reasons an animal might have hyperperistaltism?
because the thyroid hormone regulates the speed of metabolism, so a patient with hyperthyroidism will have hyperperistaltism, which causes diarrhea
cats with hyperthyroidism commonly have diarrhea. why is this?
-ileus (failure of intestinal propulsion)
-obstruction
-lead poisoning
what are the main causes of hypoperistaltism?
the failure of intestinal propultion, due to smooth muscle paralysis or mechanical reasons (obstruction)
what is ileus?
the acute failure of intestinal propulsion without mechanical obstruction
it is caused by either adynamia or a vascular problem
what is paralytic ileus?
adynamia- loss of muscle strength
due to postsurgical conditions, peritonitis, uremia, or hypocalcemia
vascular problems
what can cause paralytic ileus?
the loss of muscle strength.
causes:
after surgery (postsurgical)
peritonitis
uremia
hypocalcemia
what is adynamia? what are the causes of intestinal adynamia?
the acute failure of intestinal propulsion due to a mechanical obstruction
mechanic ileus is....
extraluminal obstructions:
-adhesions
-visceral location changes
-intususception, strangled hernia
-abdominal neoplasia
intramural obstructions:
-neoplasia of the intestinal wall
-intestinal wall inflammation
intraluminal obstructions:
-enteroliths
-phytobezoars
-foreign bodies
what can cause mechanic ileus?
foreign bodies
the most common cause of mechanical ileus is...
mechanical;
hypo;
constipation
these are all causes of ________ ileus, which will cause ______peristaltism, characterized by what main clinical sign?

constipation
what is the main clinical sign of hypoperistaltism?
hypoperistaltism
is ileus linked with hyper or hypo peristaltism?
complete
which is more severe to the animal- a partial or complete intestinal obstruction?
weight loss
what are the clinical signs produced by a partial intestinal obstruction?
partial intestinal obstruction
this causes hypoperistaltism, which probably caused the animal to have weight loss and constipation OR diarrhea
when performing an abdominal surgery, we notice intestinal abnormality. what is this? what clinical signs did the animal probably have?
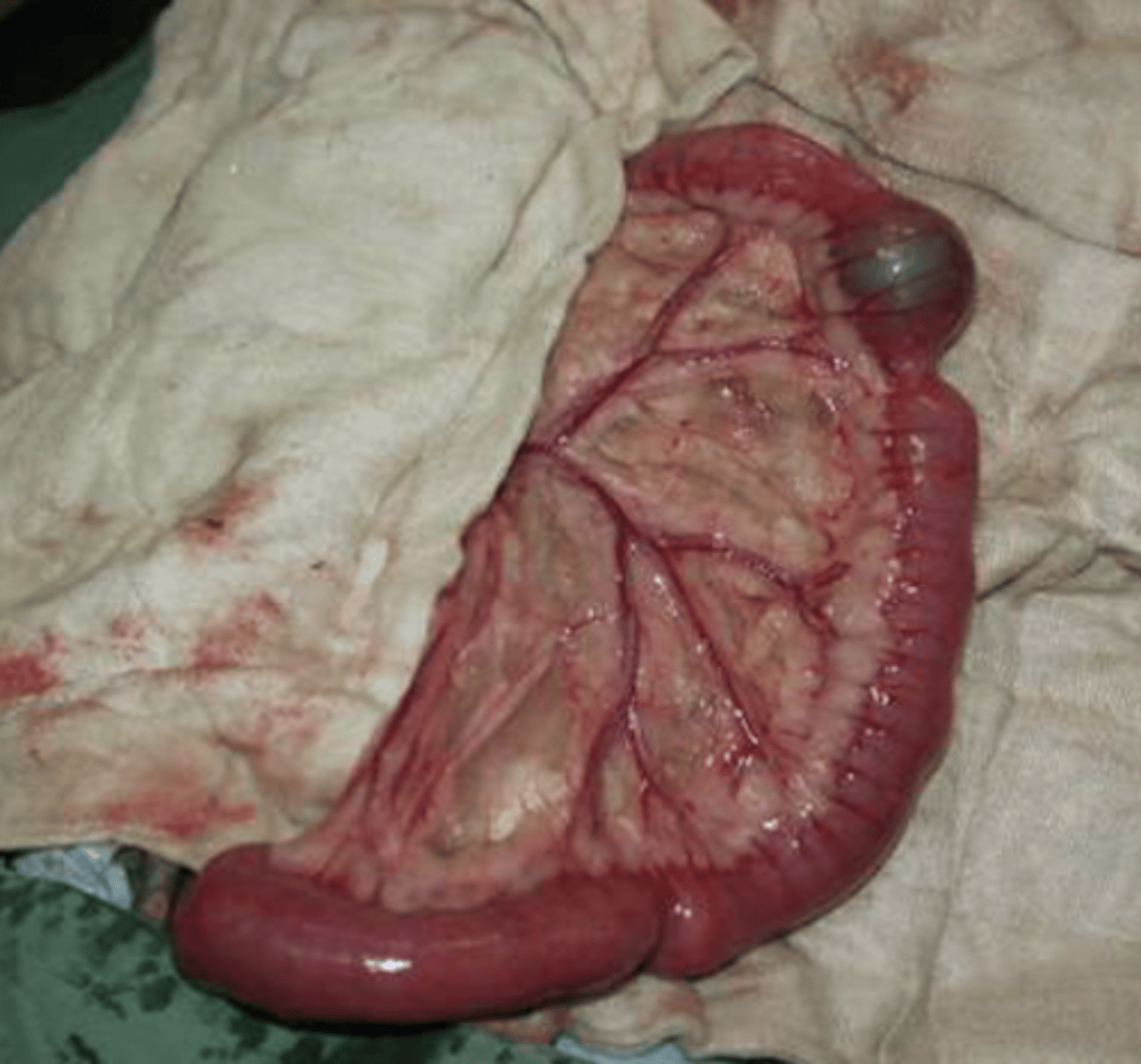
because the obstruction is only partial, so allows fluids to move through, but not many solids.
even though a partial intestinal obstruction causes hypoperistaltism, why might the animal suffering this have diarrhea?
vomit and alkalosis
because there will be abdominal distention, which causes vomiting, and vomiting leads to alkalosis (bc the animal vomits gastric acids)
the complete obstruction of the small intestine leads to what clinical signs? why?
because there will be abdominal distention, which causes vomiting. vomiting leads to dehydration, which can lead to hypovolemic shock (bc there is not enough blood volume due to lack of H20)
why can a complete obstruction of the small intestine lead to hypovolemic shock?
small intestine
vomit and alkalosis are signs of an obstruction of the _______
large intestine
acidosis is a sign of an obstruction of the _______
because an obstruction of the large intestine will cause gas distention (bc gas cannot pass). This will lead to metabolic acidosis because HCO3- will not be absorbed.
why does a complete obstruction of the large intestine lead to acidosis?
large
a complete obstruction of the ______ intestine leads to metabolic acidosis, and therefore, dehydration.
small
(large intestine obstructions do not cause vomiting)
an animal that is vomiting might have an obstruction in the ______ intestine.
when the blood supply of the intestine is completely cut off.
this leads to fluid accumulation, and therefore dehydration. it also causes ischemia, which causes ileus and mucosal detachment, which leads to the absorption of endotoxins. these all increase the HR, RR, Htc, PPT, and CRT to a point where the animal can DIE
what is complete strangulation of the intestine?
the sensation of the urgent need to evacuate the bowel (defecate)
what is tenesmus?
tenesmus
the urgent sensation of needing to evacuate the bowel is called....
colorectal disease:
IBD
histoplasmosis
clostridium
large intestine obstruction
neoplasia
perianal disease:
perianal gland inflammation
anal sac neoplasia
perianal hernia
perianal fistula
urogenital disease:
urinary bladder/urethra calculi
prostatitis/prostamegaly
neoplasia of the vagina/prostate
caudoabdominal mass
pelvic fracture
what types of diseases may be the cause of tenesmus?
perianal diseases (perianal hernia/inflammation)
tenesmus because it compresses the rectum
what is wrong with these dogs? what main clinical sign do they produce?
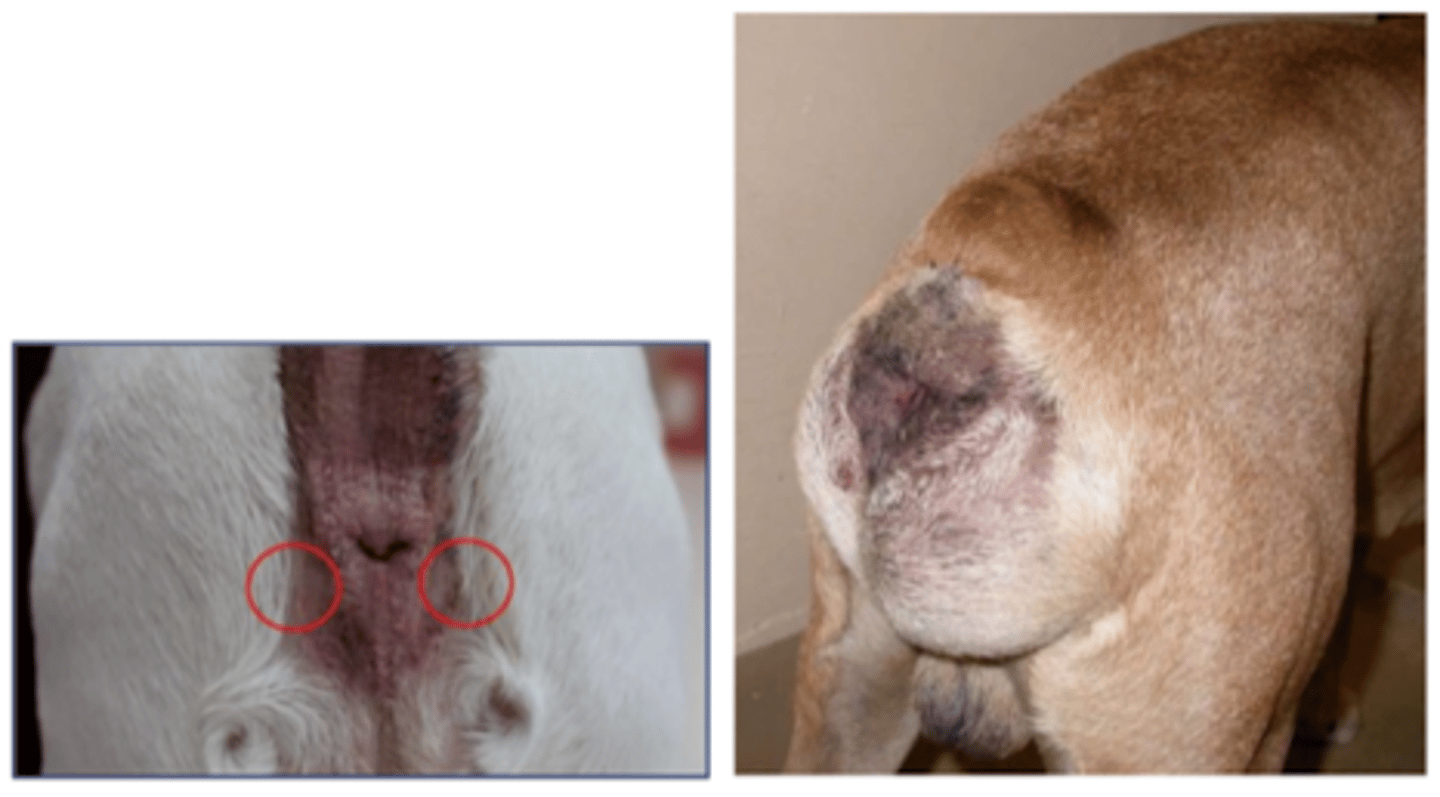
pelvic fracture
because the bone is compressing the rectum
what is wrong here? why might this cause tenesmus?

abdominal pain due to smooth muscle contraction in a hollow, tubular organ (in horses)
what is colic?
1. gallbladder
2. intestine
3. urethra/ureter
colic in horses is due to problems in what 3 anatomical structures?
difficult, infrequent, or absent bowel movements, generally associated with dry/hard stools in the colon or rectum
constipation is....
constipation
the term for difficult, infrequent, or absent bowel movements is...
increased
because food is accumulating, and the large intestine continues to absorb water, so the feces becomes harder and more difficult to push
constipation is characterized by an _________ (increased/decreased) intestinal transit time
cats
what animals frequently suffer from megacolon, induced by constipation?
megacolon
because the accumulated food distends the colon.
in cats, what result does constipation commonly produce?
a dilated colon, common in cats and due to constipation. it causes smooth muscle contraction disorders, leading to hypomotility. it is irreversible if it is chronic.
what is megacolon?
constipation
hard, dry stools accumulated in the colon/rectum
what do we see here?
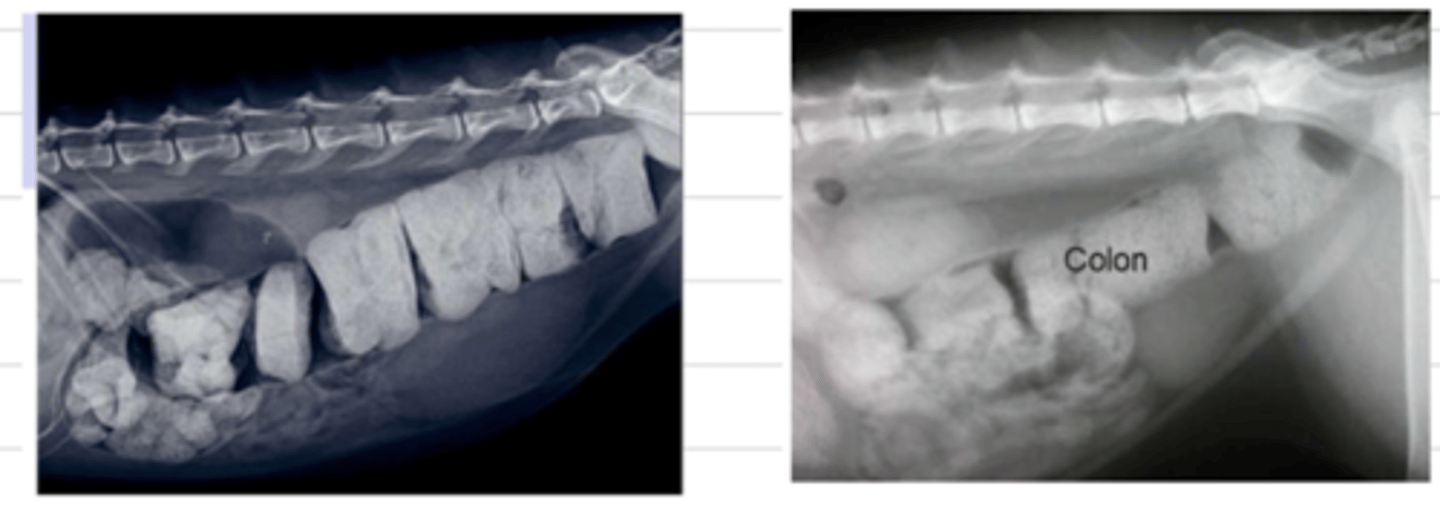
-diet poor in fiber
-decreased water consumption (dehydration)
-physical inactivity
-painful defecation (bc the animal will avoid defecating)
-mechanical obstruction of the colon
-neuromuscular disease
what are the possible causes of constipation?
-low volume, dry, hard stools
-tenesmus
-hematoschezia
-perianal swelling
-appetite loss
-whimpering
what clinical signs are typical of constipation?
NO, it is common (especially in cases of constipation) because the rectum easily bleeds
is hematoschezia in dogs a very worrying sign?
diarrhea
the most common sign of a GI disorder is...
the abnormal increase of frequency of defecation, with loose or watery stools, due to increased water content
what is diarrhea?
-osmotic
-secretory
-increased mucosal permeability
-motility disorders
what 4 different physiopathologic mechanisms can mediate diarrhea?
diarrhea caused by absorption disorders, which increases the non-absorbed substances, leading to an increased in osmotic pressure, and therefore more water in the stool.
what is osmotic diarrhea?
osmotic diarrhea
what type of diarrhea is associated with an absorption disorder?
-increased food intake
-sudden food change
-maldigestion
-malabsorption
what can cause osmotic diarrhea?
make the animal fast for 24 hours
(12 hours for very young animals)
what is the treatment for osmotic diarrhea?
diarrhea due to secretion disorders, caused by an imbalance in ion transport throughout the epithelium
what is secretory diarrhea?
-toxins
-viruses that injure the mucosa (parvovirus, coronavirus)
-enteritis
what 3 etiologies are associated with secretory diarrhea?
osmotic diarrhea
diarrhea that is caused by unabsorbed substances in the intestines is called....
secretory diarrhea
diarrhea that is caused by a problem with electrolyte transport throughout the intestinal epithelium is called...
osmotic diarrhea
what type of diarrhea can be treated by fasting?
-inflammation
-infection
-neoplasia
-ulcer
what etiologies can cause diarrhea due to increased mucosal permeability?
hypermotility leads to diarrhea because if there is an increased intestinal transit speed, there is decreased absorption, leading to an increase in osmotic pressure and therefore water moving to the intestines
why do motility disorders lead to diarrhea?
brown, green, orange, clayish
diarrhea resulting from a small intestine problem has what color?
large intestine
if an animal has mucus in their diarrhea, we can conclude that there is a problem where in their GI tract?
small
a disorder in the ______ intestine will cause a very increased volume of diarrhea
small intestine
does melena indicate a problem in the small or large intestine?
large
(only small intestine if it is ACUTE)
does hematochezia indicate a problem in the small or large intestine?
small intestine
it is associated with malabsorption and maldigestion
steatorrhea is a sign of a disorder where in the GI tract?