chemistry topic 6b and 10.9 (haber process)
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Haber procces 10.9, reversible reactions and le chateliers principle 6b
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what is a reversible reaction
where the products of the reaction can react with themselves to produce original reactions
(represented with reversible arrow)
what is a closed system
where none of the reactants or products can escape and nothing else can get in
equilibrium always reached if reversible reaction is taken place in closed system
what does it mean if a reaction has reached equilibrium
if a reaction is at equilibrium it doesn’t mean the amount of reactant and product is the same
if it lies to the right the concentration of products is greater than reactants
if it lies to the left the concentration of reactants is greater than the products
what is an endothermic reaction
chemical process that absorbs energy from its surroundings
what is an exothermic reaction
chemical process that releases energy to its surroundings
reversible reactions endo and exothermic
if the reaction is endothermic in one direction it is exothermic in the over. the energy absorbed by the endothermic reaction is the same to the energy released by the exothermic reaction
what is le chateliers principle
the idea that if you change the conditions of reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract the change. so the effect of any changes to a system can be predicted.
altering temperature, pressure, concentration of the reactants can alter the yield of the reaction - making sure you end up with more of the product (and less reactant)
what happens to the yield if you change the temperature
raise the temp - yield of endothermic reaction increases and yield of exothermic reaction decreases
reduce temp - yield of exothermic reaction increases and yield of endothermic reaction decreases
what happens if the pressure is changed
affects reactions where reactants and products are gases
lots reactions have greater volume on one side. greater volume = more gas molecules
raising pressure favours reaction which produces less volume
lowering pressure favours reaction which produces more volume
what happens if the concentration is changed
if you change concentration of reactant or products the system will no longer be at equilibrium so the system will respond to bring itself back to equilibrium
if you increase concentration of reactant the system tries to decrease it by making more products
if you decrease concentration of product the system tries to increase it by reducing amount reactants
what is used to make ammonia in haber process
nitrogen and hydrogen gas
where does the nitrogen and hydrogen come from
nitrogen is obtained easily from air which is 78% nitrogen
hydrogen comes from reacting natural gas (methane) with steam. it can also come from crude oil
symbol equation for ammonia reaction
𝑁2+3𝐻2⇌2𝑁𝐻3
what is the haber process carried out in
reaction vessel
200atm means 200 atmospheres
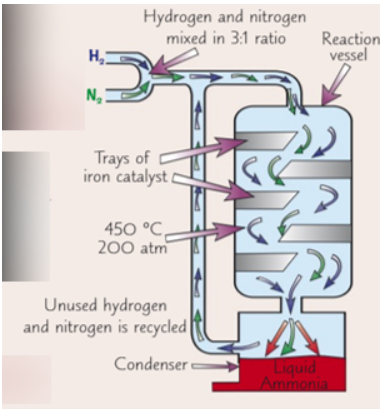
how the haber process works
hydrogen and nitrogen pumped into the compressor through the pipes mixed in 3:1 ratio
the gases are pressurised to 200atm in the compressor
the gases are pumped in a tank with trays of iron catalysts at 450c. in this condition some of the hydrogen and nitrogen will react to form ammonia
the unreacted/unused hydrogen and nitrogen are recyled by being fed back through the pipes to be put back into the tank with catalyst
in the condenser the ammonia turns from gas to liquid and can be removed from reaction vessel
what conditions are used in the haber process
450c
200 atm - pressure
iron catalyst
what is a factor in choosing the conditions
cost, energy and availability
as the reaction is reversible , the temperature and pressure conditions used are a compromise between yield and rate
temperature in the haber process
the forward reaction is exothermic so increasing the temp will move equilibrium the wrong way (away from ammonia toward h2 and n2) so the yield of ammonia would be greater in low temperature
but lower temp means lower rate of reaction. so temp is increased anyway - for reasonable rate of reaction
450c is a compromise between maximum yield and speed of reaction
pressure in haber process
higher pressure favours forward reaction (4 molecules on left , 2 on right) this moves equilibrium towards ammonia away from n2 and h2. so higher pressure increases yield of ammonia. high pressure also increases rate of reaction
the pressure is set to as high as possible to give best yield, without making plant to expensive - so 200 atm
iron catalyst in haber process
makes reaction go faster so it reaches equilibrium faster. but catalyst doesn’t change the amount of prroducts and reactants
without the catalyst the temp would have to be raised more to get a quick enough reaction - this would reduce the percentage yield and mean higher energy costs.
why do we need ammonia
to make nitrogen based fertilisers which grow our food
exam q. explain why 450c is used in the haber process
450°C is a compromise between percentage yield, rate of reaction, and cost.
The forward reaction is exothermic, and so the reaction should be done at a low temperature to get a high yield.
The reaction will be faster at higher temperatures because the particles will have more energy, and so will be more likely to collide with enough energy to react.
Generating high temperatures is expensive, so we can't use a very high temperature
exam q. explain why 200atm is used in the haber process
200 atm is a compromise between percentage yield, rate of reaction, and cost.
There are fewer molecules of product than reactant, so a higher pressure will result in a larger yield
The reaction will be faster at higher pressures because the particles are closer together and so will be more likely to collide and react.
Generating high pressures is expensive, so we can't use a very high pressure.