Research Methods Correlation & Replication
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Association Verbs
verbs used in each case are association verbs
Bivariate Correlation
an association that involves EXACTLY two variables
Categorical Variable
values fall in either one category or another and are not numerical.
Quantitative Variable
values fall in a numerical category (use scatterplot)
Mean
the arithmetic average
Correlational Studies
involve measuring both variables and support an association claim
Experiments
have one variable manipulated which is appropriate for testing a causal claim
Association Claim
describes the relationship between two measured variables
Effect Size
describes the strength of a relationship between two or more variables
Replication
estimating the population association is to conduct the study again and find multiple estimates
Outlier
Extreme scores, ones that stand out from the rest
Restriction Range
if there is not a full range of score on one of the variables in the association, it can make the correlation appear smaller than it really is
Correction for Restriction of Range
estimates the full set of scores based on what we know about an existing, restricted set, and then recomputes the correlation
Curvilinear Association
the relationship between two variables is not a straight line
Covariance of Cause and Effect
The results must show a correlation, or association, between the cause variable and the effect variable
Temporal Precedence
The method must ensure that the cause variable preceded the effect variable, it must come first in time
Directionality Problem
when we don’t know which variable came first
Third-Variable Problem
when we come up with an alternative explanation for the association between two variables, that alternative is some lurking third variable
“nuisance” variables, outside variables
Spurious Association
the bivariate correlation is there, but only because of some third variable
External Validity
the size of the sample does not matter as much as the way the sample was selected from the population of interest
ask whether the association generalizes to other kinds of the same topic, for example like other kinds of praise (from teachers or other adults), ask if the study was randomly sampled
Internal Validity
There must be no plausible alternative explanations for the relationship between the two variables
longitudinal designs help establish temporal precedence and multiple-regression analysis helps rule out third variables, providing evidence for internal validity
Moderator
sub-group of people (external validity)
the variable can change the relationship between the other two variables by making it more intense or less intense
grouping, answers “for whom” or “in what situation”
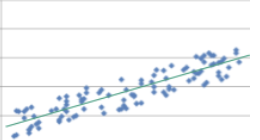
Homoscedastic

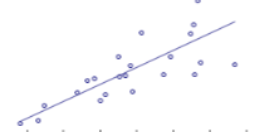
Heteroscedastic
Regression Equation
described the numeric relationship between the variables
Best fitting line
lets us predict scores of one variable given scores of the other in their measured units
Linear Regression
regression equation below predicts a dependent variable (DV) with one independent variable (IV)
Multivariable Regression
includes more than one predictor variable
Continuous Variables
betas represent slopes
Group Variables
beta’s represent difference scores to a reference level
Root mean squared error (RMSE)
provides a measure of the overall spread of data points away from the prediction (answers how much variability is left in Y)
R2
indicates the proportional gain in variability accounted for in predicting y from x rather than the mean of y
third-variable problem
is there a C variable that is associated with both A and B, independently?
Covariance
Do the results show that the variables are correlated?
Cross-sectional correlations
the correlation of variable when measured at the same time
Autocorrelations
the correlation of each variable with itself when measured at different times
Cross-Lagged Correlations
the correlation of an earlier measure of one variable with a later measure of another variable
interpreting intercept
value of dependent variable when all predictor variable are 0
interpreting beta
estimated difference in outcome for 1 level difference of predictor variable
Longitudinal Design
measures the same variables in the same people at several points in time
Multiple Regression
helps rule out some third variables and addresses internal validity concerns (does not establish causation)
Criterion Variable (dependent variable)
the variable researchers are most interested in understanding or predicting
Predictor variable (independent variable)
the variable that researchers are measuring for the study, change as the criterion variable is manipulated
Beta Basics
there is one beta value for each predictor variable, positive = positive r, zero = no relationship, higher = stronger relationship
P-Value
when greater than .05, the beta is considered not significant, and you can infer that its 95% CI DOES contain zero
coefficient b
represents an unstandardized coefficient
Pattern and Parsimony Approach
researchers can investigate causality by using a variety of correlational studies that all point in a single, causal direction
Parsimony
the degree to which a scientific theory provides the simplest explanation of some phenomenon
Mediator
between two of the variables in the study, why? (internal validity)
modifies the strength of the association between the independent (X) variable and the dependent (Y) variable
mechanisms, answers “why"?”
construct validity
appropriate to interrogate the construct validity of the variables in the study by asking how well each variable was measured
Statistical validity
ask about the point estimates and confidence intervals and ask whether the study has been replicated
Frequency
one measured variable
Association
multiple measured variables
causal
manipulated independent variables, measured dependent variable
data
a set of observations representing the values of some variable, collected from one or more research studies
Prediction/Hypothesis
a way of stating the specific outcome in the data that the researcher expects to observe if the theory is accurate
data
a set of observations representing the values of some variable, collected from one or more research studies
Theory
statement or set of statements that describes general principles about how variables relate to one another