Health assessment review day1
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chaoter 1,2,3,8 and 14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Assessment
Collecting subjective and objective data
Diagnosis
Analyzing subjective and objective data to make and prioritize professional clinical judgments (client concerns, collaborative problems, or referral)
Planning
Generating solutions, developing a plan, and determining which outcomes need to be met first
Implementation
Taking action. Prioritizing and implementing the planned interventions
Evaluation
Assessing whether outcomes have been met and revising the plan if the interventions did not make a difference
Scope and standards of practice
Collect data in a system manner, prioritizes data collection; involves the patient and the family.
Used EBP assessment techniques
Synthesis data and document findings
Derives diagnoses based on assessment date
Purpose of health assessment
Collect subjective and objective data to determine a clients overall level of functiong to make a professional clinical judgment (nursing diagnosis)
Framework for assessment
History of present health concern (chief complaint)
personal health history
Family history
Lifestyle and health practices
Initial comprehensive assessment
Collection of subjective and objective data about the clients perception of health of abll body parts or systems, past med history, family history and health practices
Ongoing or partial assessment
Collecting data after initial comprehensive assessment (E.g reassessment or shift assessment)
Focused/problem-oriented assessment
Assessing a particular client problem
Emergency Assessment
Vary rapid assessment in life threatening situations (E.g ABC’s, chest pain)
Steps of health assessment
Collection of subjective data
collection of objective data
validating assessment data for accuracy
Documenting data
prep for assessment
review client record first (gives info about the client like education level and occupation; background info like do they have chronic disease, ADL difficulty)
Educate yourself. about diagnoses, tests
Avoid premature judgments (chronic disease, alcohol abuse)
Get supplies for assessment
Collecting subjective data
Biographical info (name,DOB, etc)
History of present health concern (feeling, physical symptoms)
Personal health history
Family health history
health and lifestyle practices
Collecting objective data
Physical characteristics
Body functions (vitals)
appearance
behavior
measurements
results of labs/tests
Validation of data
Ensures that assessment process isn’t ended before all relevant data is collected
Steps of Analysis
Identify abnormal data and strengths
Cluster that data
draw inferences and identify problems
propose possible nursing diagnoses
check for defining characteristics
confirm or rule out nursing diagnosis
document conclusion
Factors affecting health assessment
Client’s culture (taboos), family, community (poverty) and spirituality (preferences)
Subjective data
Symptoms, feelings, perception, desires, preferences, ideas, beliefs, values
Personal info obtained in an interview that is elicited and verified by the client.
Provides clues to various problems and risk problems
Interviewing
Needed so that you can obtain a valid nursing health history.
Establish rapport and trusting relationship so that you can get client info
pre-interaction of interview phase
review client data from medical record
beginning of the interview
introduction, privacy ensure, nurse relaxes client
Closing of the interview
Condcuting, summarizing areas of concerns or importance, client asks any questions
introductory phase of interview
pre-intro: review health record, explain purpose of interview, ensure HIPPA (client confidentiality), make sure client is comfortable and has privacy, develop trust and rapport with verbal/nonverbal skills.
try to sit down with patient
Working phase of interview
Get biographical data, hx of present health concern, past health hx and family hx, review of body systems, lifestyle and health practices, listening and observing client, collaborating with client to identify problems and goals
summary/closing phase of interview
Should not end abruptly, summarize info obtained in working phases, validate problems and goals, identifying/discussing possible plans to resolve client problem, ask about client concerns/ further questions.
nonverbal communication
appearance —> should be proffesional (uniform/ID)
Demeanor —> Warm, professional
Facial expressions —> neutral, friendly
silence —> allows client to reflect
Lisening —> active listening
Posture —> same level as client (open posture_
Attitude —> nonjudgmental and accepting
nonverbal communication to avoid
too much/little eye contact
being in personal space(<2-3 ft)/distant
Standing —> makes pT feel inferior
verbal communication
Open-ended questions statements (how?/ What?/ Tell me) —> Use these three first
Close-ended communication (when?/ Did?) —>useful to keep the interview on course and clarify info from open open-ended Q’s
Laundry list —> list of words ( is pain sharp, dull, radiating, etc)
Rephrasing —> Clarifying information client said and allows reflection
Well-placed phrases —> “Yes, go on” Encourages client to continue
Inferring —> may elicit more data and verify existing data. DO NOT LEAD THE CLIENT TO UNTRUE STATEMENTS
Providing information —> Give the client information as questions and concerns arise
verbal communication to avoid
Biased or leading questions, rushing through interview, reading questions, FALSE ASSURANCES, ADVICE, using authority, professinal jargon, talking to much, interrupting, “ WHY QUESTIONS”
Older adult considerations for obtaining data
May be frail or health, assess hearing and if decreased speak slowly and face client, trust is KEY
Cultural considerations
reluctance to share personal info
differences in language/ non verbal
variation in disease/illness
variation in time orientation
family role
Working with interpreter
prepare ahead of time, nurse must be present, be patient with the patient, speak clearly/slowly, pause to allow interpreter to translate, avoid side convos with interpreter, use trained interpreter (no patient family/friends), NO CHILDREN
Anxious clients
work in a simple, organized format
explain your role and purpose
ask simple, concise questions
avoid being anxious
Take your time, DO NOT RUSH
decrease external stimuli (close door, TV, etc)
Angry clients
approach in calm, reassuring, in control manner
let them vent
avoid arguments or touching client
obtain help from other health care professionals
give personal space
depressed client
express interest in client
do not communicate in upbeat, encouragingmanner
manipulative clients
provide structure and set limits, obtain an objective opinion from other colleagues
discussing sensitive issues
be aware of your own opinions
Ask simple question in nonjudgmental way
allow client time to vent
if you are not comfortable you may make referral
Seductive clients
set firm limits, encourage more appropriate methods
complete health history
identify relevant problem
blueprint for physical exam
explain purpose.
what to get out of health history
bio data, reasons for seeking health care, history of present health car, past health history, family history, review of system, lifestyle, developmental level
Biographical data
name, address, DOB, phone, gender, PCP, race, languages, educational level, occupation, significant others, religion or spiritual practices,
COLDSPA - Character
Description (what does it feel like)
COLDSPA - Onset
When did it start
COLDSPA - Location
Where is it? Does it radiate?
COLDSPA - Duration
How long does it last? does it recur and is it constant/intermittent?
COLDSPA - Severity
Intensity, how much does it bother you
0-10 on pain scale
Associated factors/affect the client
Other symptoms/ how does it affect ADLS
Past history
Childhood - present
illnesses, chronic illnesses, medications, surgeries/ hospitalizations, accidents/injuries, history of ain, emotional or mental problems.
Family history
Genetic condition and others, as many relatives as possible, draw genogram if possible
Review body systems
skin/nails/hair, head and neck, eyes, ears, mouth/throat/nose/sinuses, thorax/lungs, breats/lymph/heart/neck vessels, abdomen, genitlia, anus/rectum/prostate, musculoskeletal, neuro
SUBJECTIVE DAYA ONLY and use lay (common) terminology
document description of health status and denial of any problems
Lifestyle and health practices
weight management and nutrition, sleep and rest, relationships, stress levels, education and work, meds/tobacco/alcohol/substance use, self-care
Collecting objective data exam prep
Provide comfort, warm tempature, free of interruption, quiet area with adequate lighting, firm examination table or bed, waist height bed to prevent stooping/bending, bedside table/tray to hold equipment
Standard precautions
Hand hygine, PPE for blood/bodily fluids
Gloves and gown
Client approach and prep
establish nurse-client relationship. Explain procedure/steps of physical exam. Respect clients requests/desires; sequence may vary with age or patient acuity
explain importance of exam
reassure client “i will listen in a number of places; that does not mean there is a problem”
Leave room and provide privacy, provide necessary container in case of need for sample
being with invasive procedures
explain procedure being with performed
explain why position change necessary, be organized, unnecessary position changes
Sitting position
Allows full expansion of lungs, good position for vitlas and exampining head, neck, lungs, chest, back, breasts, axillae, heart, vitals and upper extremities
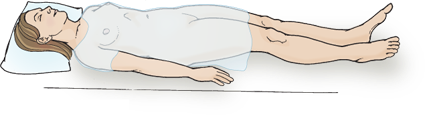
Supine
allows abdominal muscles to relax and provides easy access to peripheral pulse sites
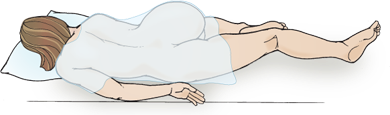
Dorsal recumbent
More comfortable than supine for clients with pain in back or abdomen. DO NOT ASSESS ABDOMEN IN THIS POSITION because abdominal muscles are contracted
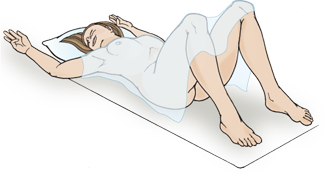
Sims position
Assess rectal and vaginal areas. Clients with joint problems and elderly may have difficulty assuming and maintaining this position
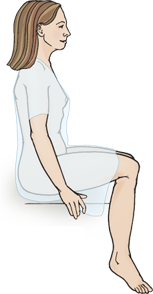
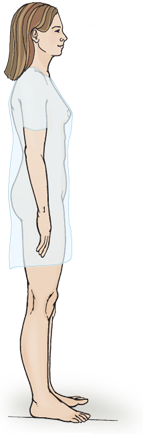
Standing position
Assess posture, balance and gait. Also useful for examining male genitalia
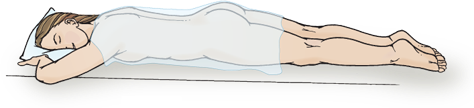
Prone
Assess hip joint. Clients with cardiac and respiratory problems cannot tolerate this position.
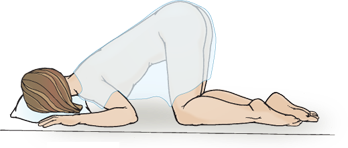
Knee Chest
examine rectum. Should be kept in this position for limited time as it can be embarrassing and uncomfortable. Elderly and clients with respiratory and cardiac problems cannot tolerate this.
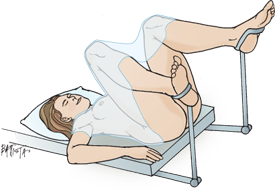
Lithotomy
Examine female genitalia, reproductive tracts and the rectum. Elderly can not assume this position. Keep client draped until needed and keep for limited time.
order of assessment? what is the one exception and why
Inspect-palpate-percuss- Auscultate
Abdomen is Inspection-Auscultate and palpate because if you palpate first you could increase gastric motility leading to false assessment.
Fingerpads for palpating
Fine discriminations like pulse, texture, size, consistency and crepitus.
Ulnar or palmar surface for palpating
Vibrations, thrills and fremitus
Doral (back) surface
temperature
Inspection
Have good lighting (sunlight best), loop and observe before touching, only expose oart being examine (drape other areas), note colo/patters/size/location, compare body parts for symmetry
Purpose of percussion
Elicit pain, determine location/size/shape, determine density (air, fluid or solid) detect abnormal masses, elicit reflexed using percussion hammer)
Hyper-resonance is heard
lung with emphysema
Resonance is heard
hollow sound heard over NORMAL LUNG
tympany is heard
drum sound heard over GASTRIC BUBBLE LIKE STOMACH
dullness is heard
thud like sound heard over ORGAN(NORMAL) OR PLEURAL EFFUSION (!!ABNORMAL!!)
flatness is heard over
bone or muscle
Diaphragm is used for
high-pitched sounds, Firm pressure (LUNG, BOWEL AND NORMAL HEART SOUNDS)
Bell is used for
low pitched sounds, light pressure (ABNORMAL HEART SOUNDS → MURMURS AND BRUITS)
Blunt percussion
Detect tenderness of organs (e.g kidney by placing one hand flat on body surface and using fist of other hand to strike the back of the hand. on the body surface.
Direct percussion
tapping of a body part using one or two fingertips to elicit possible tenderness (e.g tenderness over the sinuses)
indirect percussion
Most common and tapping done to feel for density of underlying structure.
solid tissue produces a soft tone, fluid produced louder tone and air is the loudest.
Temperature
Oral —> under tounge and next to frenulum, wait until a beep is heard
Axillary —> hold thermometer under axilla until beep
Temporal —> place thermometer on forehad while pressing scan, gently stroke across the temporal artery, then point to behind the ear
Bodu temperature is lowest in the morning and and highest in evening.
Hypothermia (cold , hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism or starvation) is less than 96 and hyperthermia (bacterial infections, malignancies, trauma and various blood/endocrine/immune disorders) is more than 100.
Pulse rate
Radia pulse —> use pads of 1st and 2nd fingers and lightly palpate radial artery on lateral aspect of wrist. Count for full minute if irregular
Apical —> use stethescope in mitral position on 5th intercoastal space, left midclavicular line for 1 minute
0 = absent
1+ = weak (easy to obliterate)
2+ = normal (obliterate with moderate pressure)
3+ = bounding (unable to obliterate or firm prssure_
Respirations
Count rise and fall of chest for 30 seconds and multiply x2. Acknowledge rate, rhythym and depth
Vitals BP
Dominant arm first or arm with no IV acess. Pt in sitting position, legs uncrossed. Papate brachial artery. Measure BP cuff (80% of arm circumference and wrap cuff on brachial artery. Use stethoscope with diagphram. with bulb in dominant hand inflate until beat disappears. listen for systolic and then diastolic.
Factors affecting BP
Cardiac output (more the heart pumps the greater the pressure)
Peripheral vascular resistance (increase in resistance in vascular system like people with circulatory disorders will increase BP)
Circulating blood volume (an increase in volume will increase blood pressure. Sudden drop in blood pressure may indicate a sudden blood loss like internal bleeding.
Viscosity (thicker blood = increased BP like polycythemia)
Elasticity of vessell walls (Increase in stiffness of walls will increase BP like athlersclerosis)
5th vitals
pain
order of BP
first tempature → pulse rate → respirations →blood pressure →pain
choosing correct route of measuring tempature
temporal unless sweating profusely
tympanic unless ear infection and pain
rectal ONLY for adults who need very accurate temperature
Oral unless pT just consumed hot or cold drink
Axillary for everyone especially with an altered immune system
Avoid before taking BP
High reading = smoking, caffine, upto 1 hour prior, excercise, anxiety, anger, cuff too small or lose, arm belofw heart level, legs crossed, client holding arm up
low reading = Noisy environment, cuff to large, poor placement of stethescope, arm placed above heart
older adult considerations for vitals
can have same normal tempature but they will feel cold
RR will be 15-22
have higher bP
Function of skin
protects the underlying tissues and structures from microorganisms, physical trauma, ultraviolet radiation, and dehydration.
temperature maintenance, fluid and electrolyte balance, absorption, excretion, sensation, immunity, and vitamin D synthesis.
1st layer of sin
Epidermis: Completely replaced every 3-4 weeks; Contains melanin and keratin-forming cells
2nd layer of skin
Dermis: Very vascular, thin, supportive layer consisting mainly of collagen; Enables skin to resist tearing; Resilient elastic tissue
3rd layer of skin
Subcutaneous: Loose connective tissue; Stores fat as an energy reserve; Provides insulation to conserve internal body heat
Sebaceous glands
Attached to hair follicls and secrete a oily substance that waterproofs the hair/skin.
Eccrine vs aprocrine sweat glands
Eccrine —> secretes sweat and thermoregulation
Aprocrine —> associated with hair follicles in axillae, perineum and breast areolae; Nonfunctional until puberty they Secrete a milky sweat; Interaction of sweat and skin bacteria produces body odor
vellus vs terminal hair
vellus hair is “peach hair” all over the body
terminal hair is longer, darker, and coarser like the scalp and eyebrows. Puberty initiates. the growth of terminal hair over the axillae, perineum, and legs.
Nails
Hard, transparent plates of keratinized epidermal cells
Melanoma
most serious type of skin cancer; biggest risk is sun exposure or UV radiation
Basal cell carcinoma
skin cancer that is Most commonly seen on sites with moderate skin exposure (e.g upper trunk or womens lower leg)