Multicellular Primary Producers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Macroalgae produce approximately ____ of the oxygen in our atmosphere
25%
Compared to unicellular algae, macroalgae are _________ and __________..
Structurally more complex, have more elaborate reproduction
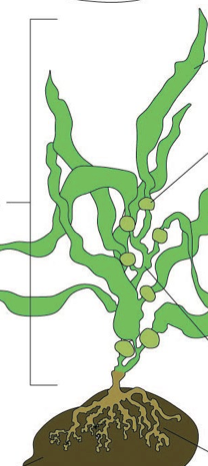
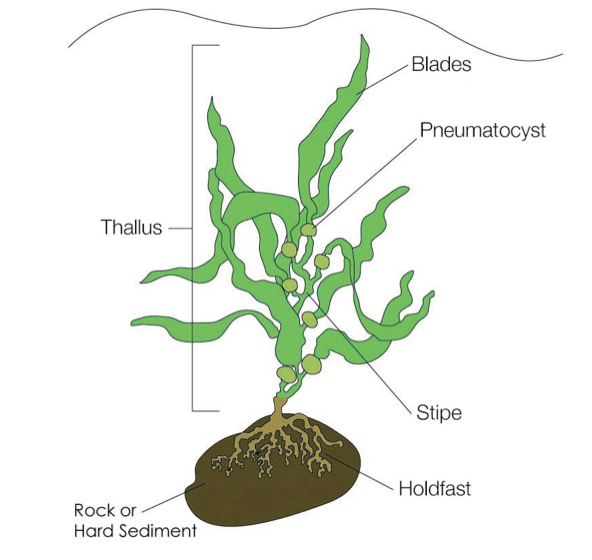
Label in order from top arrow to bottom.
Blades, Pneumatocyst, Thallus, Stipe, Holdfast, Rock or Hard Sediment
Seawater is about ______ more dense than air.
1000 times
Archimedes Principle states that
a body immersed in fluid is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
Buoyancy of seawater allows marine organisms to have ______ and allows the presence of ______.
reduced structural materials, planktonic communities
Seaweeds in the phylum _____ are termed green algae.
Chlorophyta
Seaweeds in the phylum ______ are termed red algae.
Rhodophyta
Coralline red algae are important _____
reef builders
Brown algae are in the Phylum ________
Phaeophyta
__________ is a genus of brown algae often found in large, floating rafts on the surface of the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea.
Sargassum
Invasive species of macroalgae are often transported via ________________ on vessels.
ballast water, the aquarium trade, fouling growth
__________ is an example of a genus of macroalgae invasive to the Mediterrean.
Caulerpa
True vascular plants that live completely underwater in the ocean are _______.
seagrasses
Seagrasses are valuable as: ________________.
sediment stabilizers, habitat for marine life, tourism
Seagrasses are consumed by large animals such as ___________.
manatees and green sea turtles
Seagrasses are threatened by _____________.
eutrophication, dredging, boating, and commercial fishing.
Plants that grow well in salt water are termed ________.
halophytes
Saltmarsh grasses cannot tolerate ________ for long.
complete submersion
An important species of saltmarsh grass in Louisiana is _______commonly called ______.
Spartina alterniflora, smooth cordgrass
One of the most important saltmarsh zones for juvenile marine organisms is the _______.
edge
Louisiana is losing its coastal wetlands due to: ______________.
subsidence, erosion, sea-level rise, and sediment starvation
________ are trees and shrubs adapted to living in seawater and brackish water along tropical and subtropical coasts.
Mangroves
Mangrove seedlings are called _______ and they ______ on the tree.
propagules, germinate
In South Louisiana, ______are expanding to replace smooth cordgrass.
black mangroves
Marine microbes produce approximately ____ of the oxygen in our atmosphere
50%