Photosynthesis in C3, C4, and CAM Plants
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Why do plants close their stomata on hot, dry days?
To conserve water, but this limits access to carbon dioxide and reduces photosynthesis
What is the effect of closing the stomata on oxygen and carbon dioxide?
It reduces carbon dioxide intake and causes oxygen to build up.
What process is favored when stomata are closed, and why is it considered wasteful?
Photorespiration is favored, as it consumes energy and releases CO2 without producing useful sugars.
How does CO2 fixation occur in most plants (C3 plants)
CO2 is fixed by rubisco, forming a three-carbon compound, phosphoglycerate.
What happens during photorespiration?
Rubisco adds O2 instead of CO2 in the Calvin Cycle, producing a two-carbon compound.
What are the consequences of photorespiration?
It consumes O2 and organic fuel, releases CO2, and does not produce ATP or sugar.
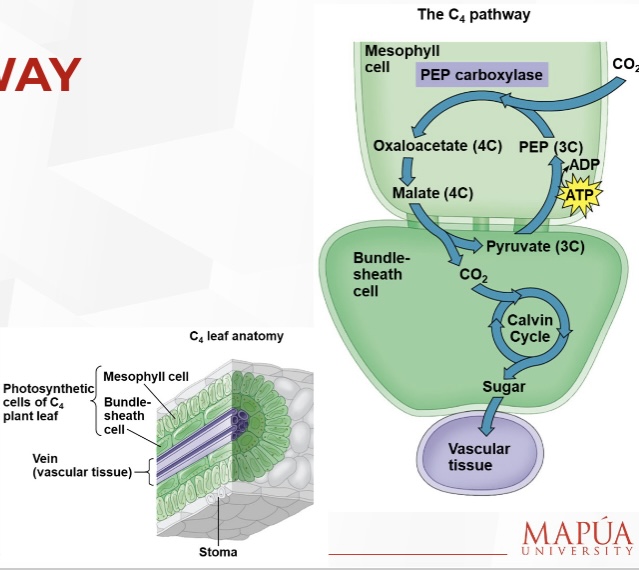
How do C4 plants minimize the cost of photorespiration?
They incorporate CO2 into four-carbon compounds in mesophyll cells.
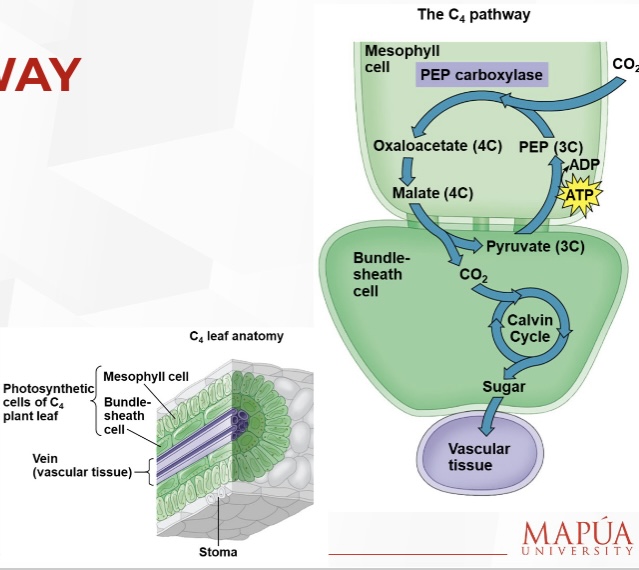
What enzyme is required for the C4 pathway?
The enzyme PEP carboxylase is required to incorporate CO2 into four-carbon compounds.
What is crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)?
CAM is a process some plants use to fix carbon, including succulents.
How do CAM plants fix CO2?
CAM plants open their stomata at night to incorporate CO2 into organic acids.
What happens during the day in CAM plants?
The stomata close, and CO2 is released from organic acids for use in the Calvin cycle.