Chem 131 Exam 3 🤬
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hate
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
When is it appropriate to form double or triple bonds in a Lewis structure?
When the central atom does not have an octet of electrons
How many covalent bonds are usually formed by the element C?
four covalent bonds because it has four valence electrons and needs four more to complete its octet. (common pattern for atoms in Group 14)
State the number of valence electrons in a chlorine atom.
7
State the total number of valence electrons in O2.
12 (one oxygen has 6)
If the electronegativity difference is small the bond is
nonpolar covalent
Nonpolar Geometries (symmetric)
Linear, Trigonal Planar, Tetrahedral, Trigonal bipyramidal, Octahedral, Linear, Square planar
Polar Geometries (asymmetrical)
Bent, Trigonal pyramidal, Seesaw, T-shaped, Square pyramidal, Distorted octahedral
Bonding Order
Non-bonding - antibonding / 2
What elements can form an expanded octet?
silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
how many electron groups in AB2?
2
Steric # =
lone pairs + bonded atoms
2 bonds, 0 lone pairs, 180 degrees (AB2) (Ex: BeCl2, HgCl2, CO2)
linear
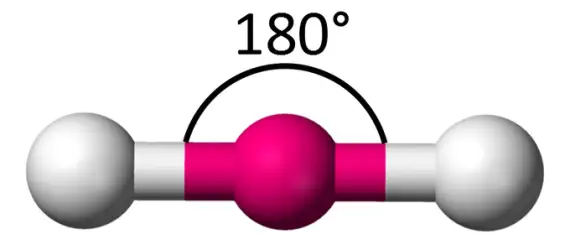
120 degreess, sp2, 3 bonds, 0 lone pairs (AB3) (Ex: BF3, CO32-, SO3)
trigonal planar
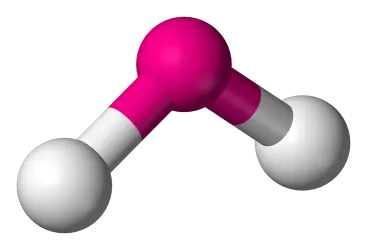
2 bonds, 1 lone pair, slightly less than 120 bond angle, AB2E type (Ex. SO2)
Bent/V-shaped
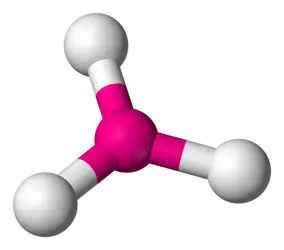
109.5 degrees 4 bonds, 0 lone pairs (AB4) (Ex: CH4, XeO4, PO43-) (OR 3 bonds, 1 lone pair for some electron geometries)
tetrahedral
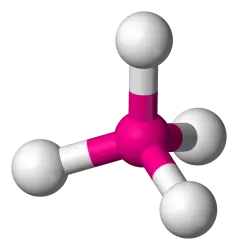
107.5 degrees, 3 bonds, 1 lone pair (AB3E) (Ex: NH3)
Trigonal Pyramidal
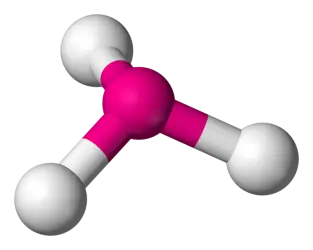
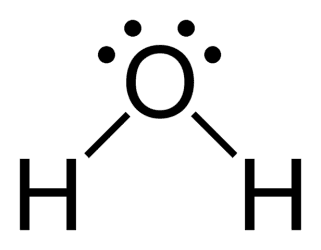
104.5 degrees 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs (AB2E2) (Ex: H2O)
Tetrahedral bent
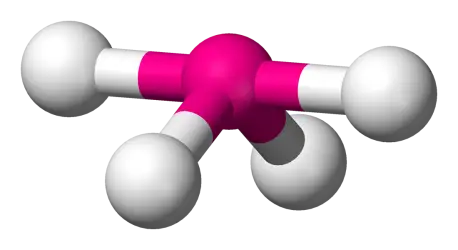
4 bonds, 1 lone pair (AX4E) (ex: SF4)
Seesaw
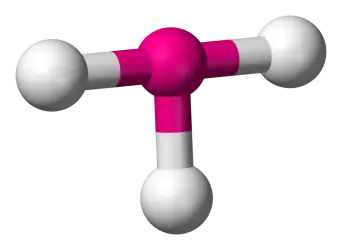
3 bonds, 2 lone pairs, about 90 bond angle, AB3E2 type Ex. ClF3
T-shaped
2 bonds, 3 lone pairs (AB2E3) (Ex: XeF2)
OR 5 bonds, 0 lone pairs
linear (trigonal bipyramidal)
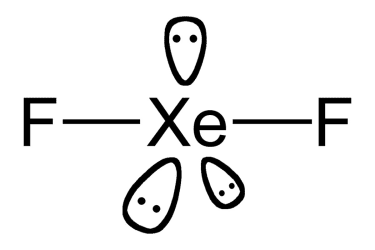
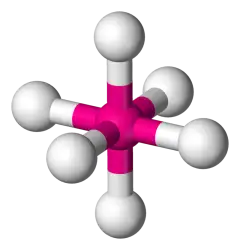
6 bonds, 0 lone pairs (AB6) (Ex: SF6)
Octahedral
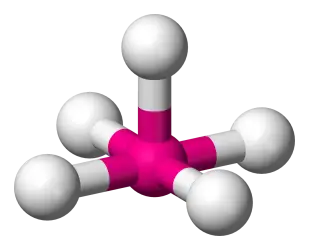
5 bonds, 1 lone pair, (AB5E) (Ex: BrF5)
Square Pyramidal
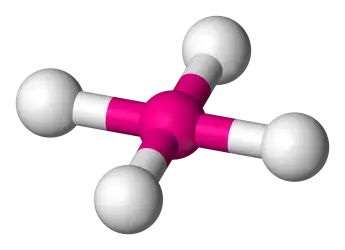
4 bonds, 2 lone pairs (AB4E2) (Ex: XeF4)
Square Planar
bent angle with one lone pair
~120 degrees
bent angles with two lone pairs
107.5 degrees
The orientation in space of an atomic orbital is associated with
the magnetic quantum number (m1)
When a bond is broken
energy is absorbed
When a bond is formed
energy is released
Nonpolar
symmetrical
polar
asymmetrical
s orbitals (sphere)
Helium and groups 1-2
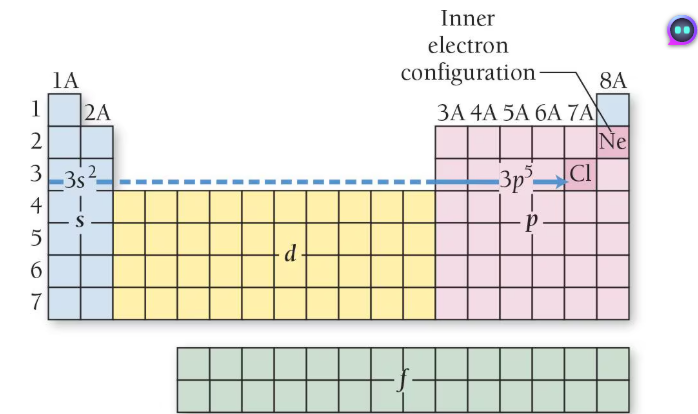
p -orbital (dumbell)
Groups 13-18
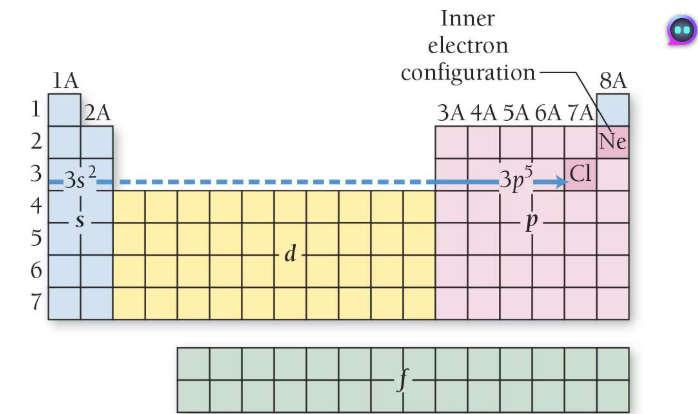
d orbital (clover)
Groups 3-12
f orbital (complex shape)
Groups 5-18 (lower levels)
Atomic Radius
Moving down: increases (size of outermost occupied orbital increases)
Moving across (left to right): decreases (Effective nuclear charge increases)
First ionization energy
Moving down: Decreasing (outermost electrons further away from nucleus)
Moving across (left to right): Increasing (Effective nuclear charge increases)
Electron affinity
Moving Up: Decreasing/more negative
Moving across (right): Decreasing/more negative (effective nuclear charge increases)
Metallic character
Moving Down: Increasing (ionization energy decreases)
Moving Across (right): Decreasing (ionization energy increases)
Ionization energy
Going Up: increases
Going Across (right): increases
Copper and Chromium Columns Exception Rule
remove s orbital electron and put it in p orbital
Bonds broken are positive because
energy is being absorbed
Bonds formed are negative because
energy is being released
To know which resonance structure is best,
you should follow a hierarchy of rules that prioritize stability: structures where all atoms have a full octet are most stable, followed by structures with the fewest formal charges. If a choice still needs to be made, the structure with negative formal charges on the most electronegative atoms and positive charges on the least electronegative atoms is preferable.
Hydrogen Bonding
Look for H directly bonded to N, O, F
C-C bond
low electronegativity
C-F bond
high electronegativity
London Dispersion Forces
weak, temporary attractions between molecules or atoms that result from the random motion of electrons. These forces occur in all molecules and their strength depends on the number of electrons, molecular size, and shape. Larger molecules with more electrons and greater surface areas have stronger London dispersion forces, leading to higher boiling points.
Intermolecular forces strength
ionic (metal) > hydrogen (H with N,O,F)> dipole-dipole (polar) > London dispersion forces (all)
If l is s,
0
If l is p
1
If l = d
2
if l = f
3
Steric Number (2-6)
depends on how many “collections” of bonds AND lone pairs there are surrounding the central atom
SN of 2
sp hybridization
SN of 3
sp2 hybridization
SN 4
sp3 hybridization
SN 5
sp3d
SN 6
sp3d2
Sigma bonds are ____ than pi
stronger
Only ___ bond is sigma. The other ones (if double or triple) are all pi bonds
one
What atom becomes the central atom
Least electronegative (further to the left)
Large boiling point
small size, strong forces, if molar mass is greater
Cr to Cr+
[Ar] 4s1 3d5 → [Ar] 3d5
(remove from s orbital and add to d)
Cu to Cu+
[Ar] 4s1 3d10 → [Ar] 3d10
(remove from s orbital and add to d)
magnetic quantum (ml) is related to
orientation of atomic orbitals in space
Fewer protons means
larger radius and weak pull