TOPIC #6: Understanding chance
1/14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the prosecutor’s fallacy?
a mistake in statistical thinking, where it is assumed that the probability of a random match is equal to the probability that the defendant is innocent.
What is chance (frequentist defintion)
the percentage of time a certain event is expected to happen if the same process is repeated long term.
what are the basic properties of chance?
P(impossible event) = 0, P (certain event) = 1
P(event) = 1 - P(Complement event)
Drawing at random means that a collection of objects have equal chances being picked.
Conditional probaility
chance that a certain event occurs given, another event has occurred
Multiplication principle
The probability that 2 events occur is the chance of the 1st event multiplied by the chance of 2nd event, given 1st has occurred.
Independence
2 events are independent if the chance of the 2nd given the 1st is the same as the 2nd.
How do you ensure independence
drawing randomly with replacement ensures independence
how does the multiplication principle apply to cases were two events are independent
the chance of both occurring is the product of their unconditional probabilities.
dependence
two events are dependent if the chance of the 2nd given the 1st is not the same as the chance of the 2nd as it depends on the result of the 1st event
how do you ensure dependence?
drawing without replacement
mutually exclusive
two things are mutually exclusive when the occurrence of one event prevents the other
event 1 occurs p(event 2) = 0
difference between mutually exclusive and independence
if something is mutually exclusive, then the chance of event 1 happening, prevents event 2, however, independence does not chance the chance of event 2 .
addition rule
if two things are mutually exclusive, then the chance of at least 1 occurring is the sum of the individual chances
P (at least 1 of 2 events occurs) = p(Event 1) + p(event 2)
Binomial coefficients
the number of ways of rearranging the n objects is given by the binomial coefficient —>
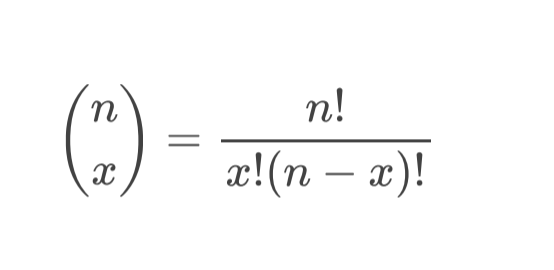
what is a binary trial?
where only two things can occur so P(event)= p p(not event) = 1 - p