Physio Lect 8 - Electrocardiogram - Normal Rhythm Part Two
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a Q-Wave?
the first negative deflection before the R-wave
The heart is____. Meaning that what we learn may not hold true for what we see on all ECG recordings.
variable
Basic vector/graph rules:
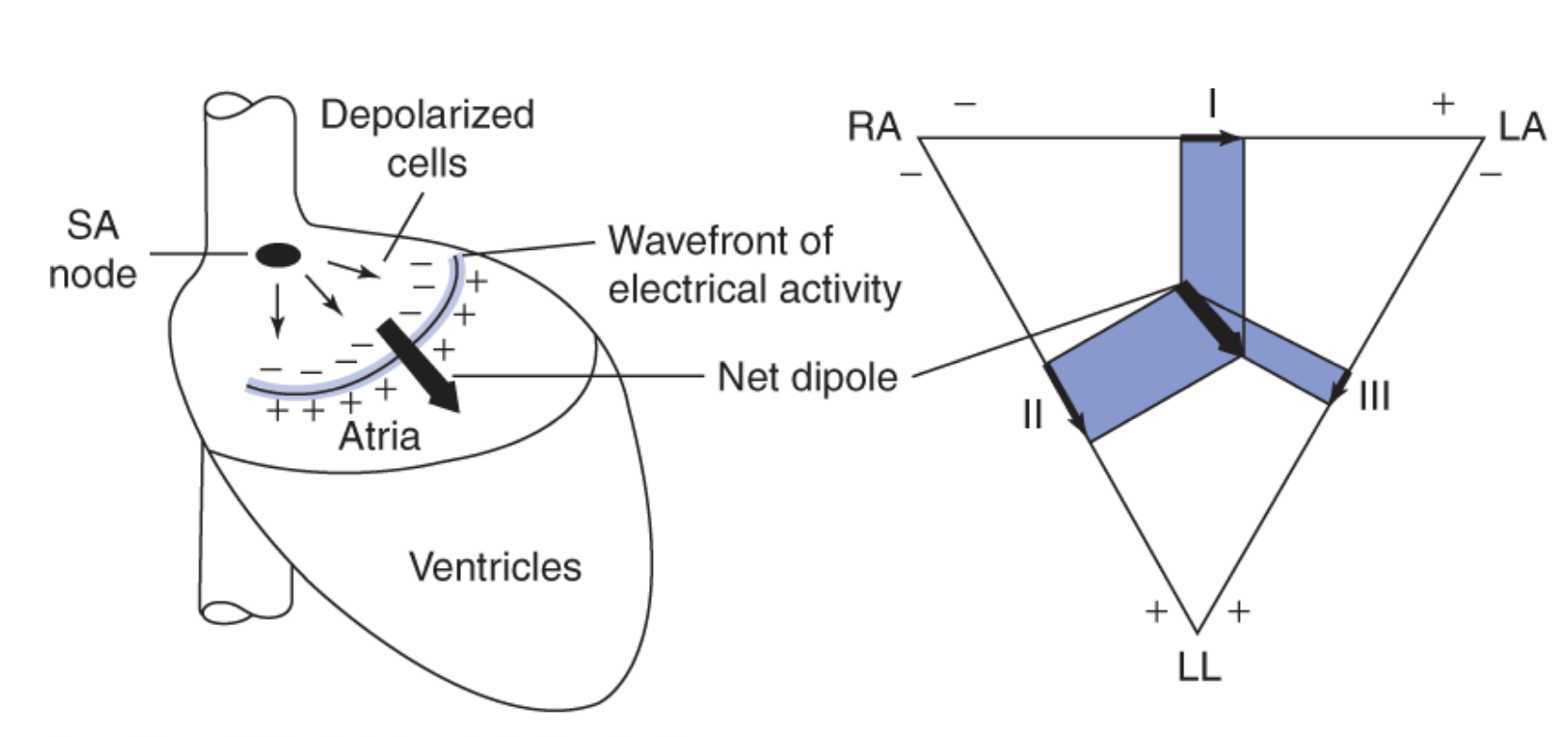
If the net dipole is more ____ to a bipolar lead, then the magnitude of voltage will be close to the magnitude of the net dipole
parallel
for example, in the figure below, the net dipole is mostly parallel to lead II compared to the other leads; therefore the magnitude of voltage on Lead II is very similar to the net dipole
Basic vector/graph rules:
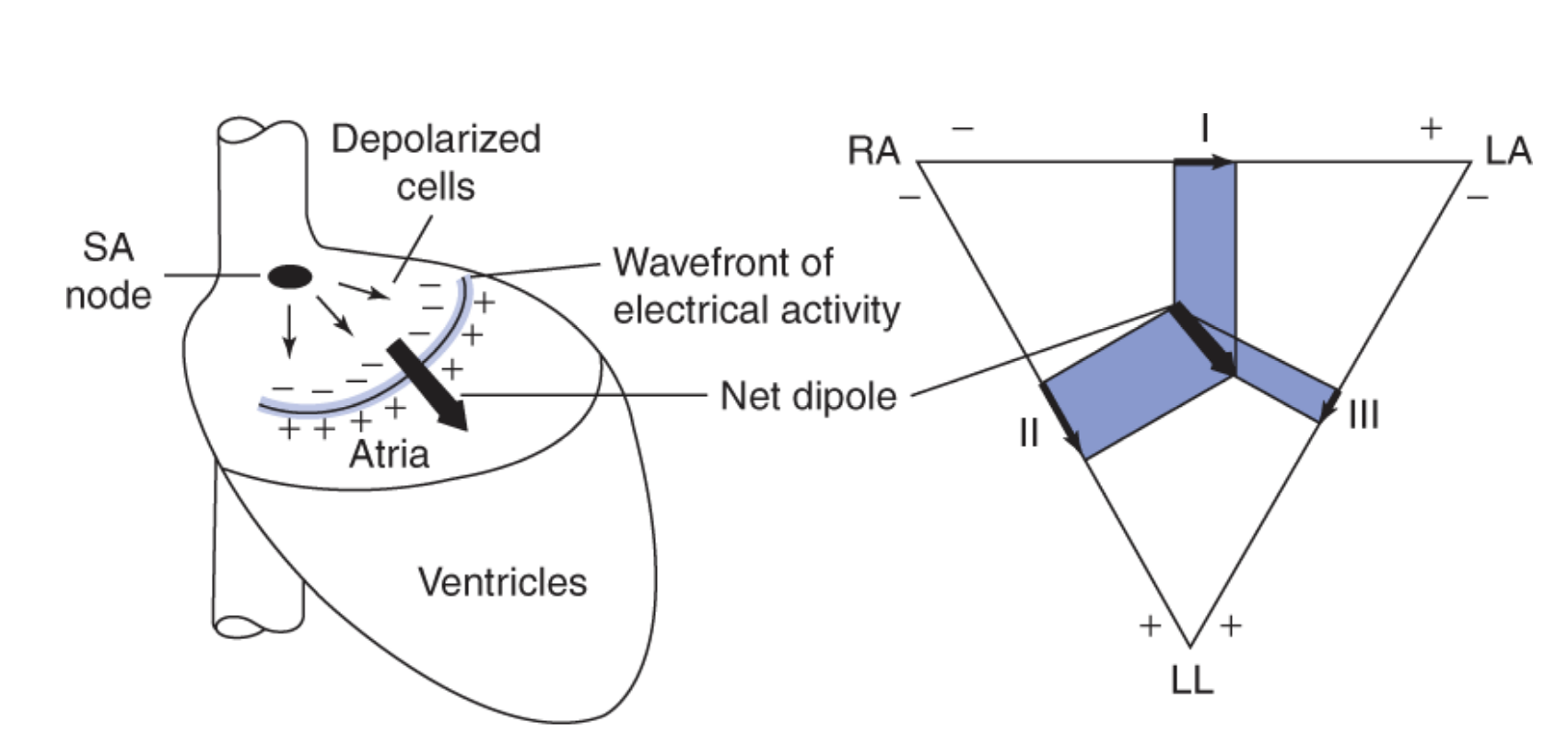
If the net dipole is more _____ to a lead, then the magnitude of voltage will be close to zero
perpendicular
for example, in the figure below, the net dipole is more perpendicular to Lead III compared to the other leads and the magnitude of voltage is the smallest in Lead III
Which part of the heart is termed the apex?
the pointy part (bottom area)

What is the last part of hte heart ot be depolarized?
the base of the left ventricle (near the separation between the atria and ventricle)
For the QRS wave, which wave is attributed to Panel 1?
Q-wave
What happens during the Q-wave/Panel 1 of the QRS-wave?
start of ventricular depolarization in the septum, net dipole to the right ventricle due to left side of septum depolarizing first
Where does the arrow point during the Q-wave panel?
more towards the negative of Lead I and II, hence negative deflection. no Q wave in lead 3
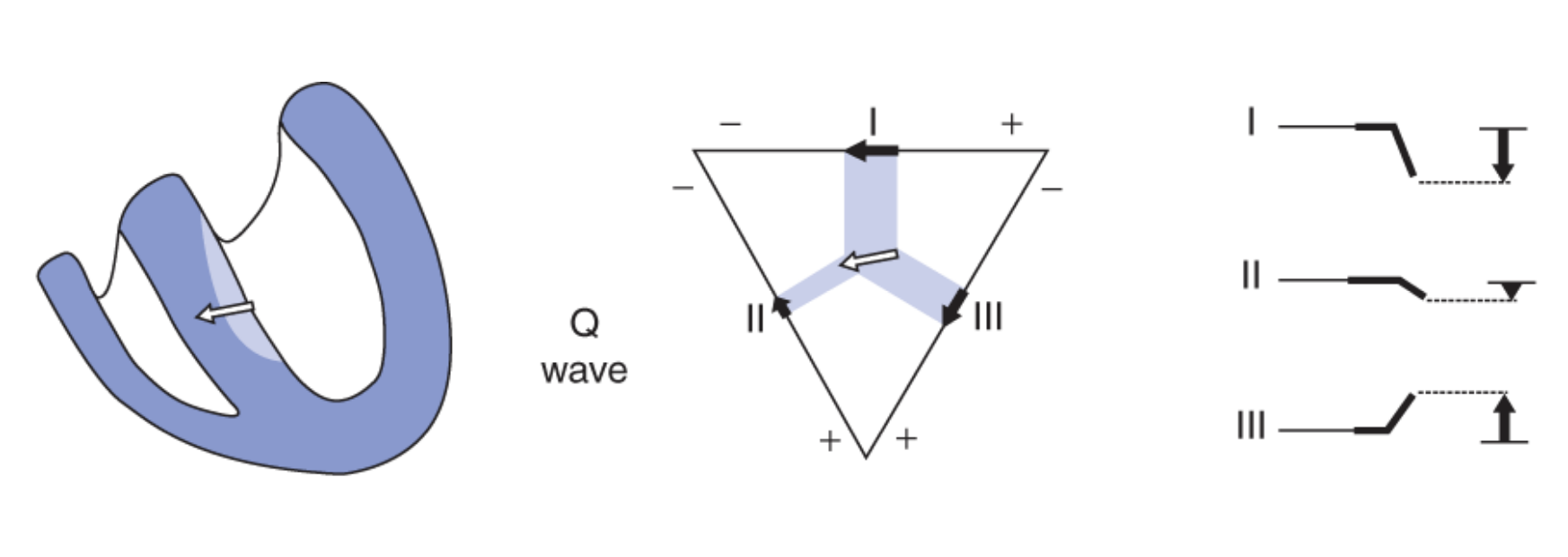
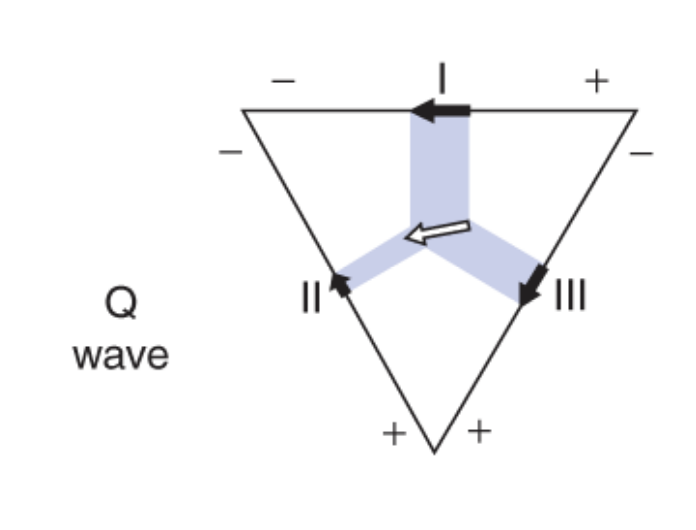
Why is there no Q-wave in lead 3?
the arrow points more towards the positive of lead III, no negative deflection means no Q-wave
Why is the Q-wave most times unnoticeable?
muscle mass in the septum is small
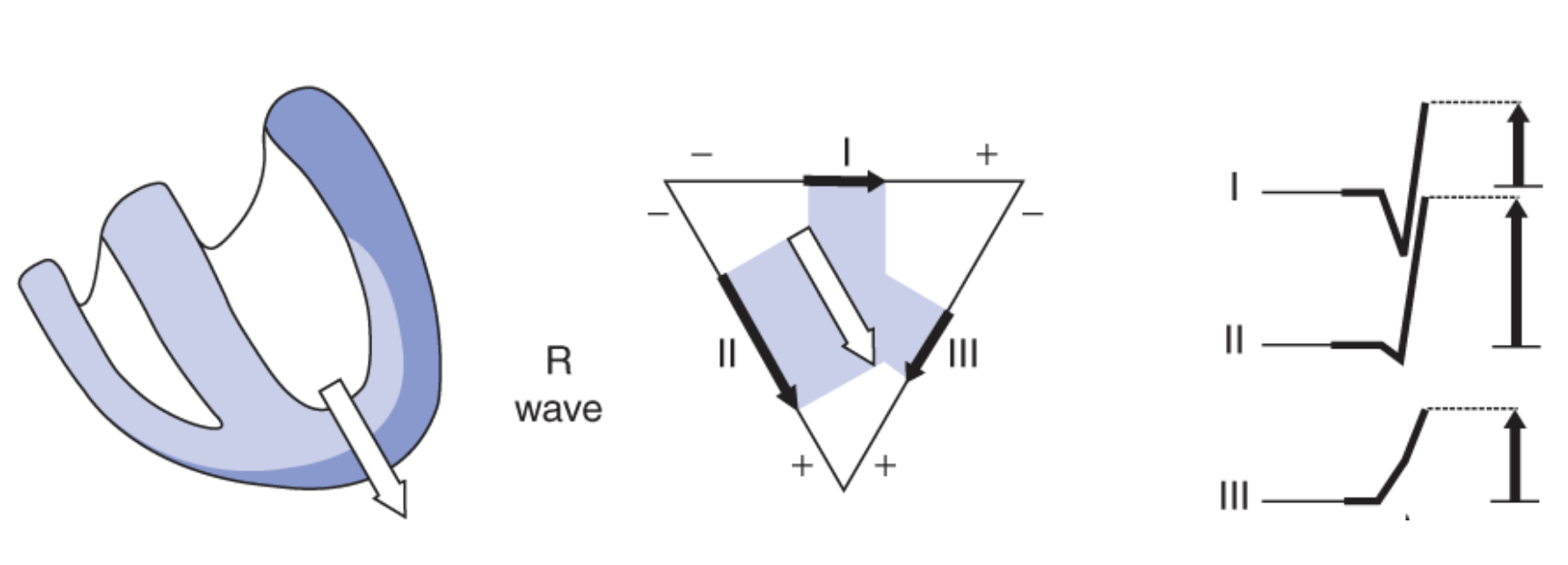
R-Wave/Panel 2: where is the net dipole? is it larger or smaller than panel 1? why?
toward the apex of the ventricle and larger due to increased muscle mass that the wave of depolarization travels through
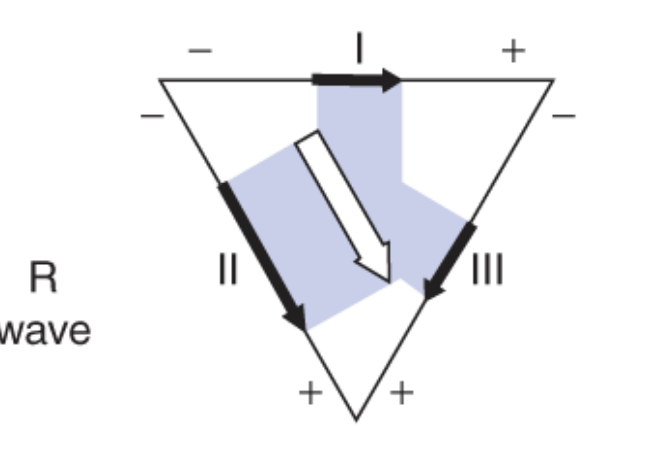
where is the net dipole pointed?
positive of Lead I, II, and III - positive deflection in large magnitude (R wave)
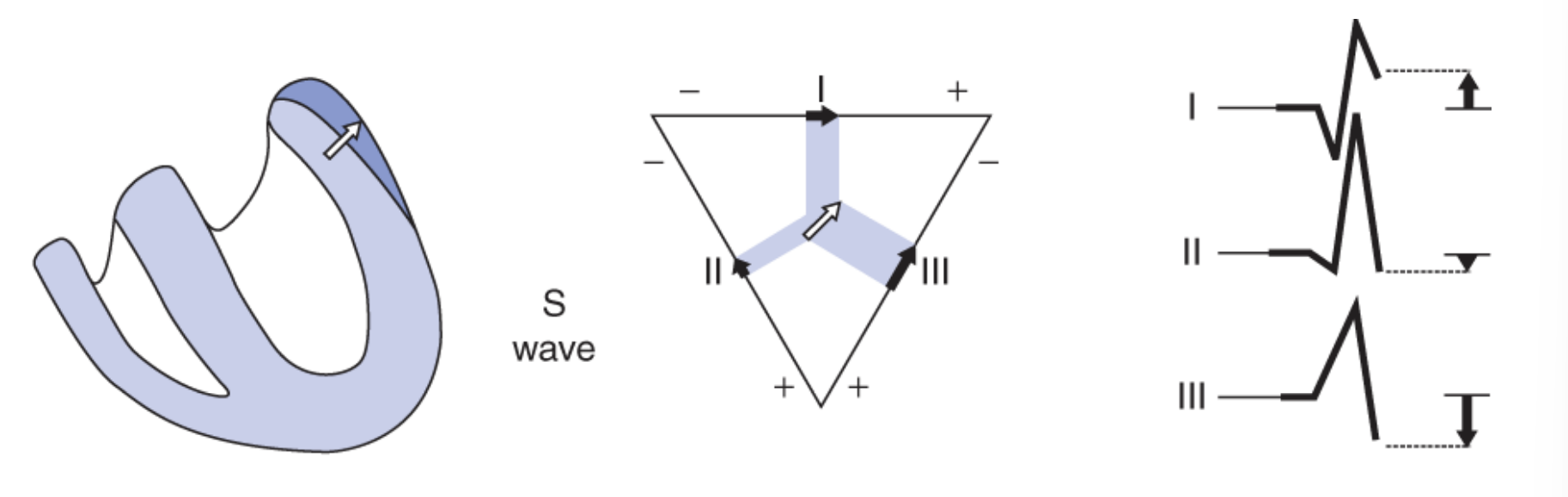
S-Wave/ Panel 3: where is the net dipole?
at the end of ventricular depolarization, net dipole is towards base of heart - epicardium of left ventricle
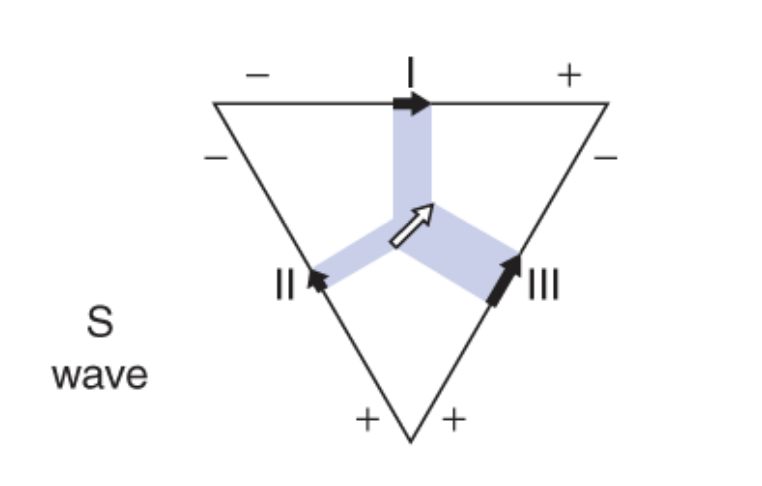
which leads have an S-wave?
Lead II, III
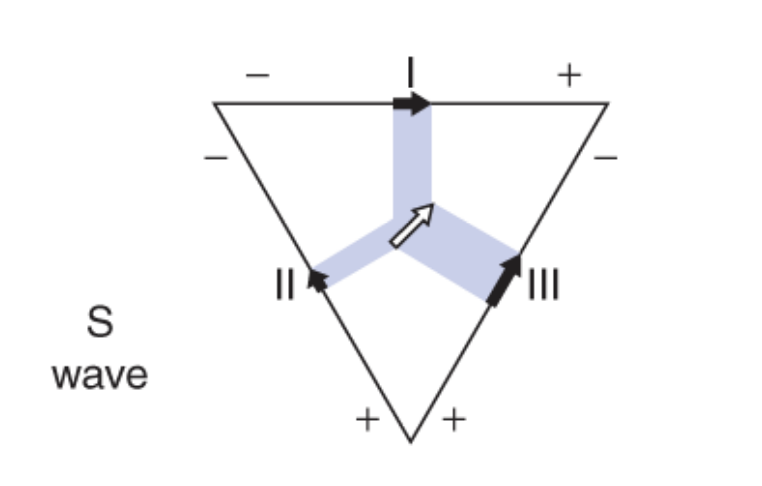
Of the two, which lead has a smaller S wave? Lead II or III?
Lead II
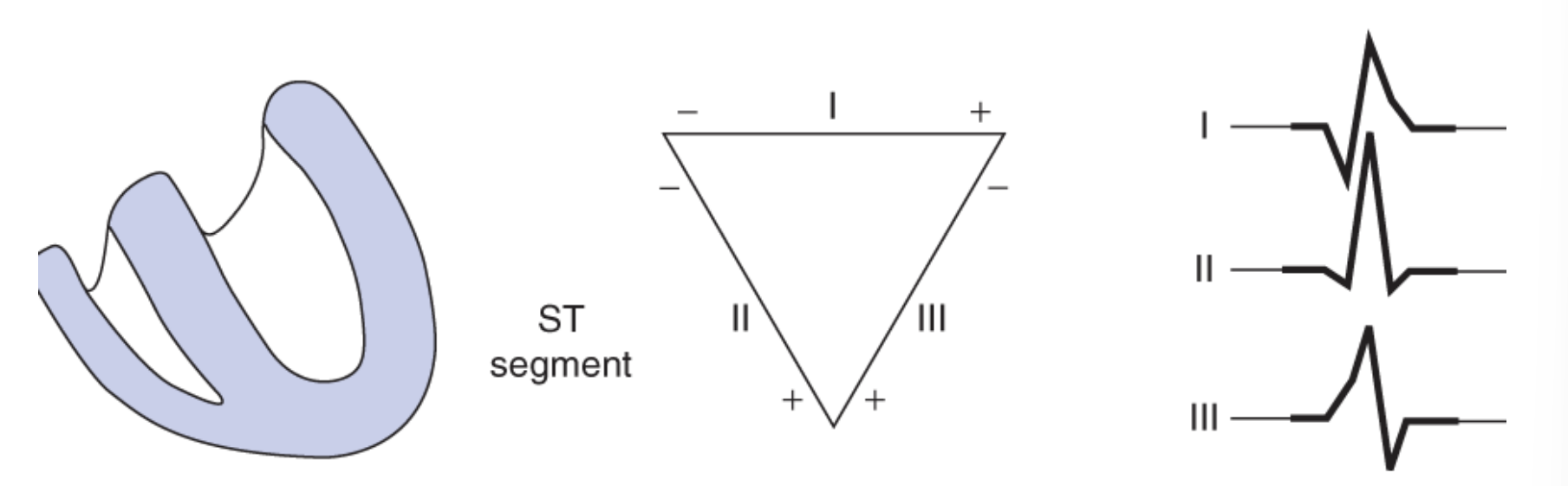
ST Segment/ Panel 4: where is the dipole? why?
there is no dipole - ventricular depolarization is complete - no voltage
When do we enter the isoelectric stage/ST segment?
phase 2 of muscle action potential
Does the T-wave have a positive or negative deflection in normal tissue?
positive

Determination of Mean Electrical Axis
Make sure you know and understand these rules
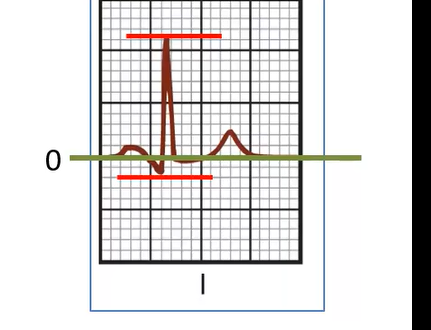
What is the net deflection in Lead I?
+9 mm
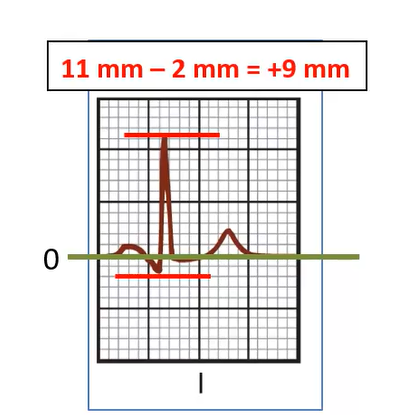
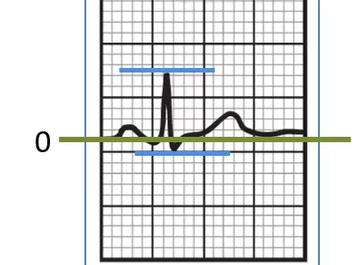
What is the net deflection in Lead II?
+5 mm
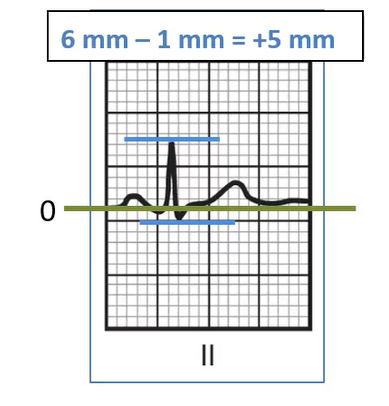
How would you plot the mean deflection if lead I was +9mm and lead II was +5mm?
plot the net deflection for both leads, then draw a perpendicular line from each of the arrow heads. where these perpendicular lines intersect is where the head of mean electrical axis is,draw a tail to the center of the plot to make the full line.
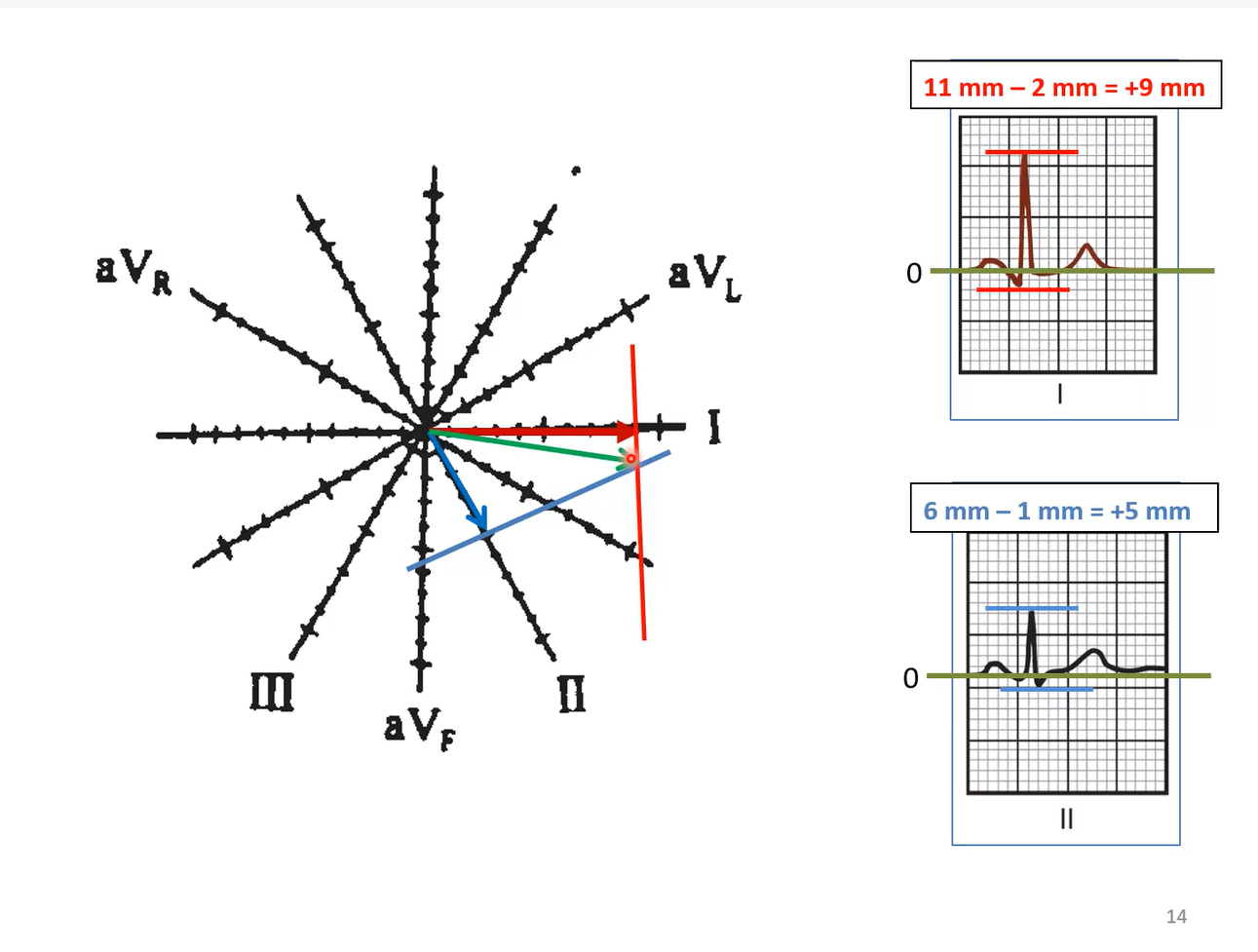
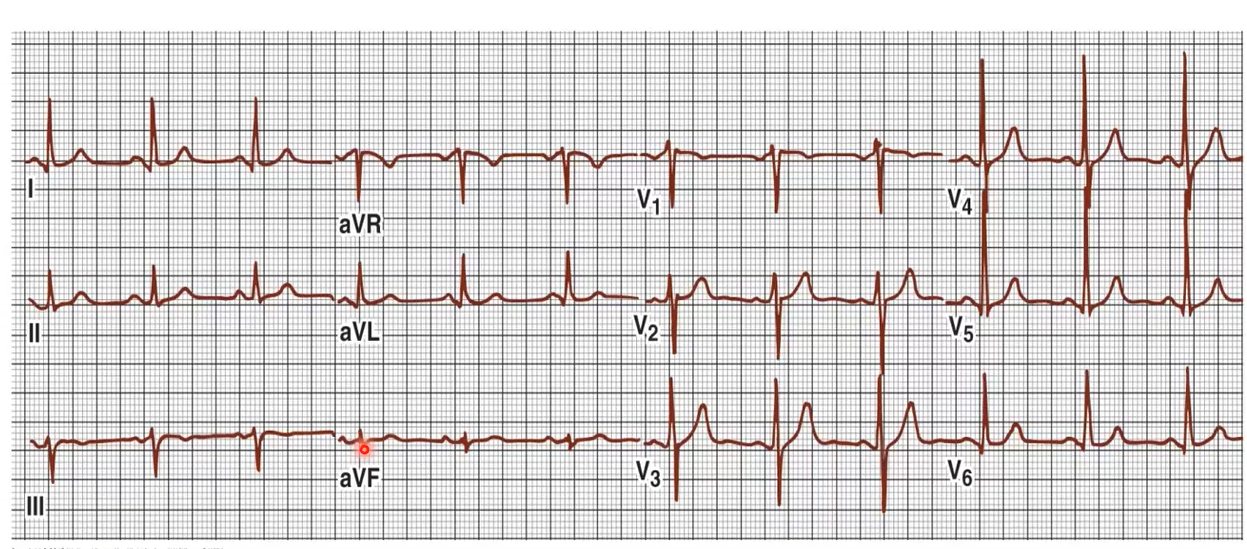
Determination of Mean Electrical Axis (Method II)
make sure to know these steps

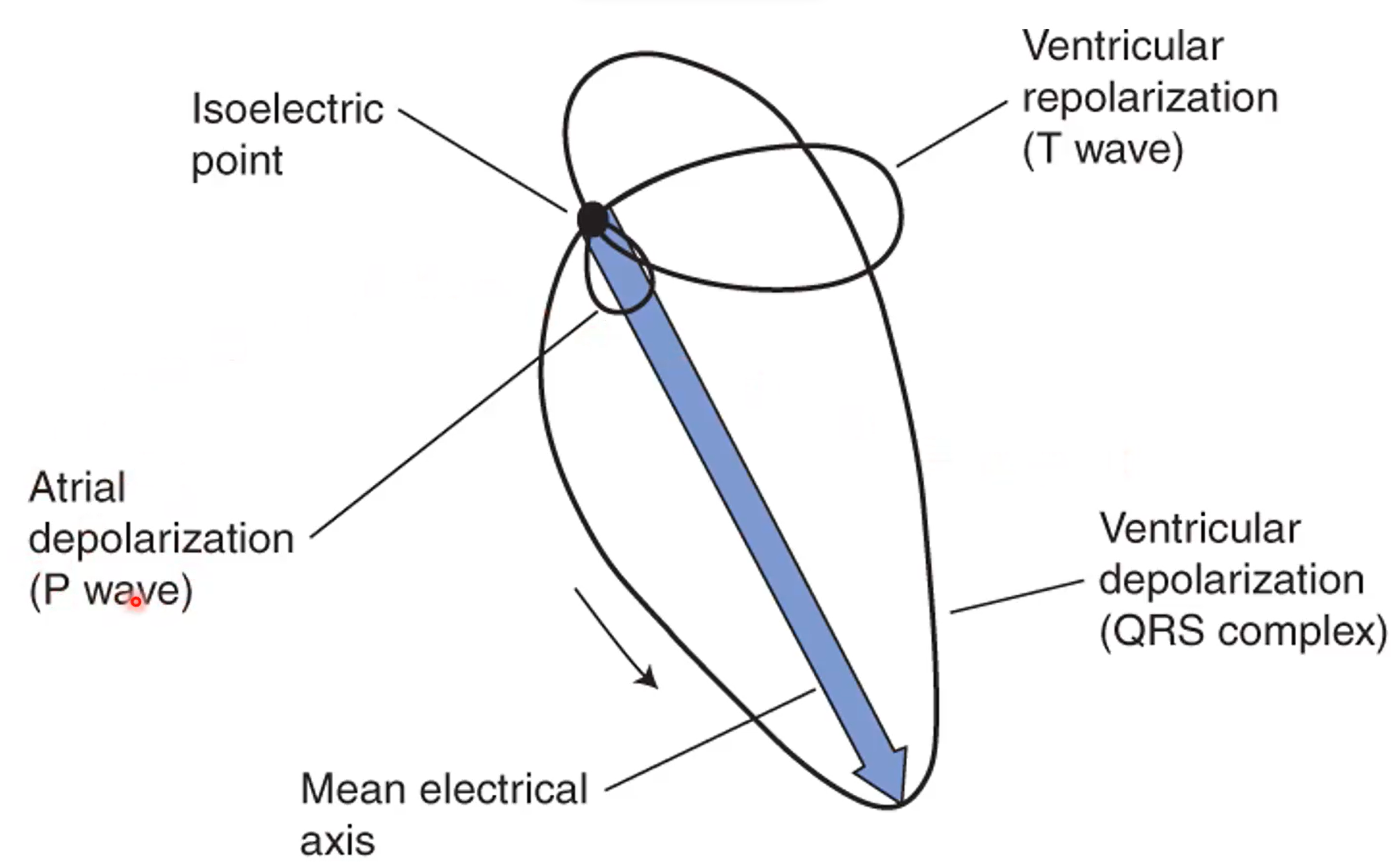
What an ECG where we follow the tracing would look like