Oxidation of phenylmethanol to benzoic acid, and recrystallization of benzoic acid
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CALCULATIONS - Q2 2020, Q2 2015
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Explain why water is a suitable solvent for carrying out the recrystallisation of benzoic acid
Benzoic acid has a high solubility in hot water
Explain the purpose of the first (hot) filtration
[experiment to purify benzoic acid by recrystallisation]
To remove insoluble impurities
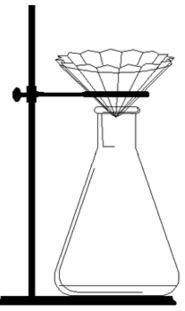
Fluted filter paper in a warm funnel, as shown in the diagram is used in the hot filtration.
Explain why this arrangement is suitable for hot filtration
Increased surface area / faster filtration / keeps solution warm / avoids benzoic acid coming out of solution
Explain why the second filtration is only carried out after a sufficient period of cooling
To maximise the yield / to allow crystallisation
What observation would the student make that shows that the recrystallised benzoic acid was pure?
Melting point
over a narrow range / sharp / close to correct value
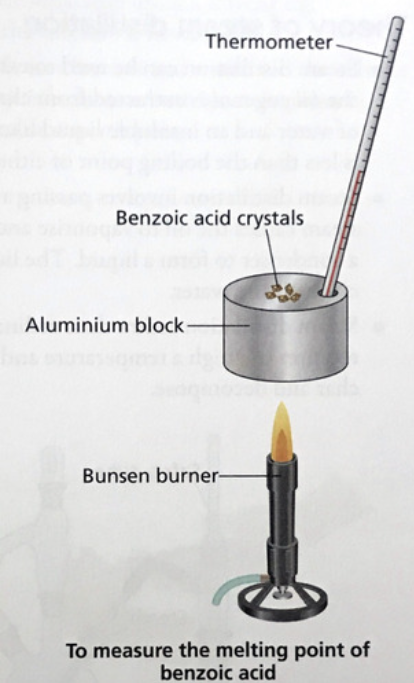
Describe with the aid of a labelled diagram, a method that could be used to measure the melting point range of a sample a benzoic acid
Sample (crystals) on aluminium block (shown in diagram) //
heat slowly (heat source shown in diagram) //
record the melting point temperature range
How could it have been verified that the recrystallised benzoic acid crystals were purer than the original sample?
Compare melting points
Impure (original) melting point lower, broader
purer (recrystallised) melting point higher, sharper
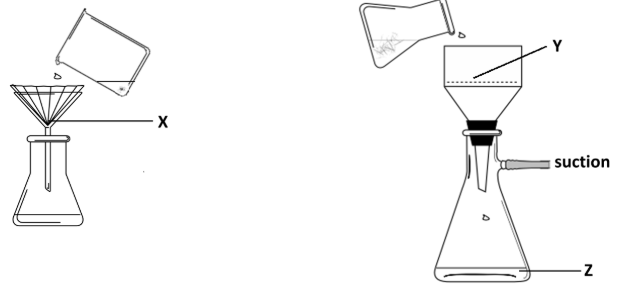
A student practiced the technique of recrystallisation of benzoic acid containing small quantities of two solid impurities: water-soluble potassium chloride (KCl) and black, insoluble charcoal (C).
Identify the substances collected at locations X, Y and Z
X: Charcoal / carbon / C //
Y: Benzoic acid //
Z: Potassium Chloride / Water
What steps are carried out to maximise the yield of pure benzoic acid,
i) between the first and second filtrations,
ii) after the second filtration?
i) Evaporate some water / heat filtrate / put flask in ice-water / cooling of flask / allow time for crystals to form
ii) Wash with cold water / dry crystals / recover more crystals from mother liquid / rinse flask into funnel
How would you expect the melting point value of a recrystallised sample of benzoic acid to differ from that of an impure sample?
Melting point higher / sharper range
or
Melting point impure crystals lower / broader range
Describe the appearance of phenylmethanol at room temperature
Colourless
Name a suitable piece of apparatus to measure accurately 1.5cm3 of phenylmethanol
Syringe / graduated dropper / graduated micropipette / burette
How does the appearance of the reaction mixture change when the phenylmethanol is heated along with potassium manganate(VII) solution to which sodium carbonate has been added?
Purple (violet) to //
brown
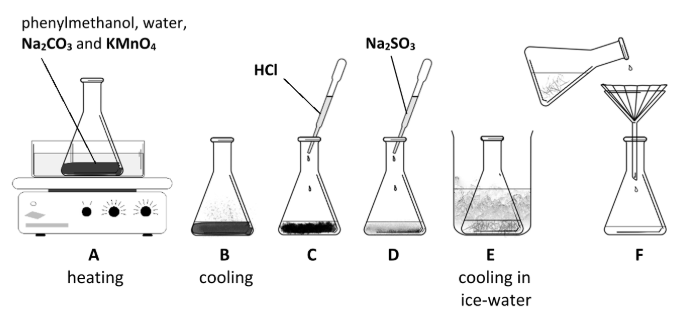
Describe what is observed during stages D and E.
Explain these observations
Brown solid disappears //
white benzoic acid crystals form / white solid appears
MnO2 reduced / soluble (colourless) Mn2+ formed //
crystallisation of benzoic acid
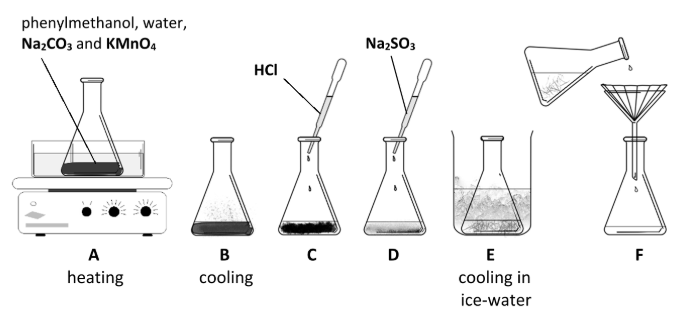
Name a suitable technique to purify the benzoic acid crystals collected at stage F.
Recrystallisation
A sample of benzoic acid, containing a small quantity of sodium chloride as the only impurity, was purified by recrystallisation. The impure crystals were dissolved in the minimum amount of boiling water. This solution was cooled thoroughly and the crystals that formed were separated by suction filtration as shown in the diagram. The crystals were then dried.
i) Why was there no need, in this recrystallisation, to carry out a filtration of the hot solution?
No insoluble impurities /
hot filtration removes insoluble impurities /
only impurity soluble /
sodium chloride soluble
ii) State one advantage of suction filtration over gravity filtration
Faster / helps dry the crystals
iii) Explain how you could verify that the recrystallised benzoic acid was purer than the original sample
Compare melting points of both samples
Impure (original) melting point lower, broader
purer (recrystallised) melting point higher, sharper
The melting-point range of benzoic acid sample F is lower and broader than that of G.
Which is the purer benzoic acid sample?
G /
F is less pure
Describe the appearance of phenylmethanol at room temperature
Colourless
Identify A and B in the reaction scheme that were added to allow separation of the benzoic acid from the other substances after the oxidation was complete
A = HCl
B = Na2SO3
What changes were observed in the reaction vessel on addition of HCl and Na2SO3 and as cooling occurred?
Brown disappears / mixture becomes colourless //
white crystals precipitate (form / appear)
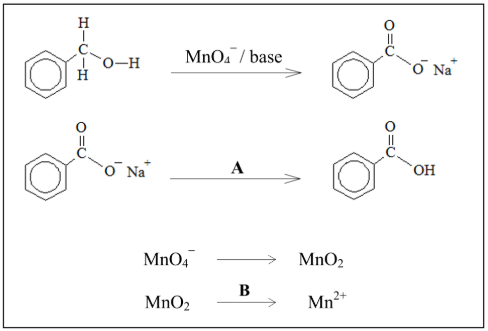
State the changes in the oxidation number of manganese during the experiment
7 to 4 / Mn7+ to Mn4+ //
4 to 2 / Mn4+ to Mn2+
State one way of maximising the yield of the recrystallisation process
Use minimum amount of boiling solvent (water) / cool fully / place in ice / use fluted filter paper
The melting points obtained by a student measuring the melting points of two benzoic acid samples were as follows:
A = 117 - 120oC
B = 120 - 121oC
Which was the purer sample? Justify your answer
B
higher melting point / narrower range
Students were required to recrystalize the impure benzoic acid. What solvent should they have used for the recrystallisation? Explain why this solvent is suitable
Water
Benzoic acid very soluble in hot water but less soluble in cold
Give one important use benzoic acid or its salts
Food preservative / disinfectant