Lecture 20 - Predation, Parasitism And Disease
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What does the lokta-volterra model predict for predator-prey interactions?
Coupled lagged population cycles
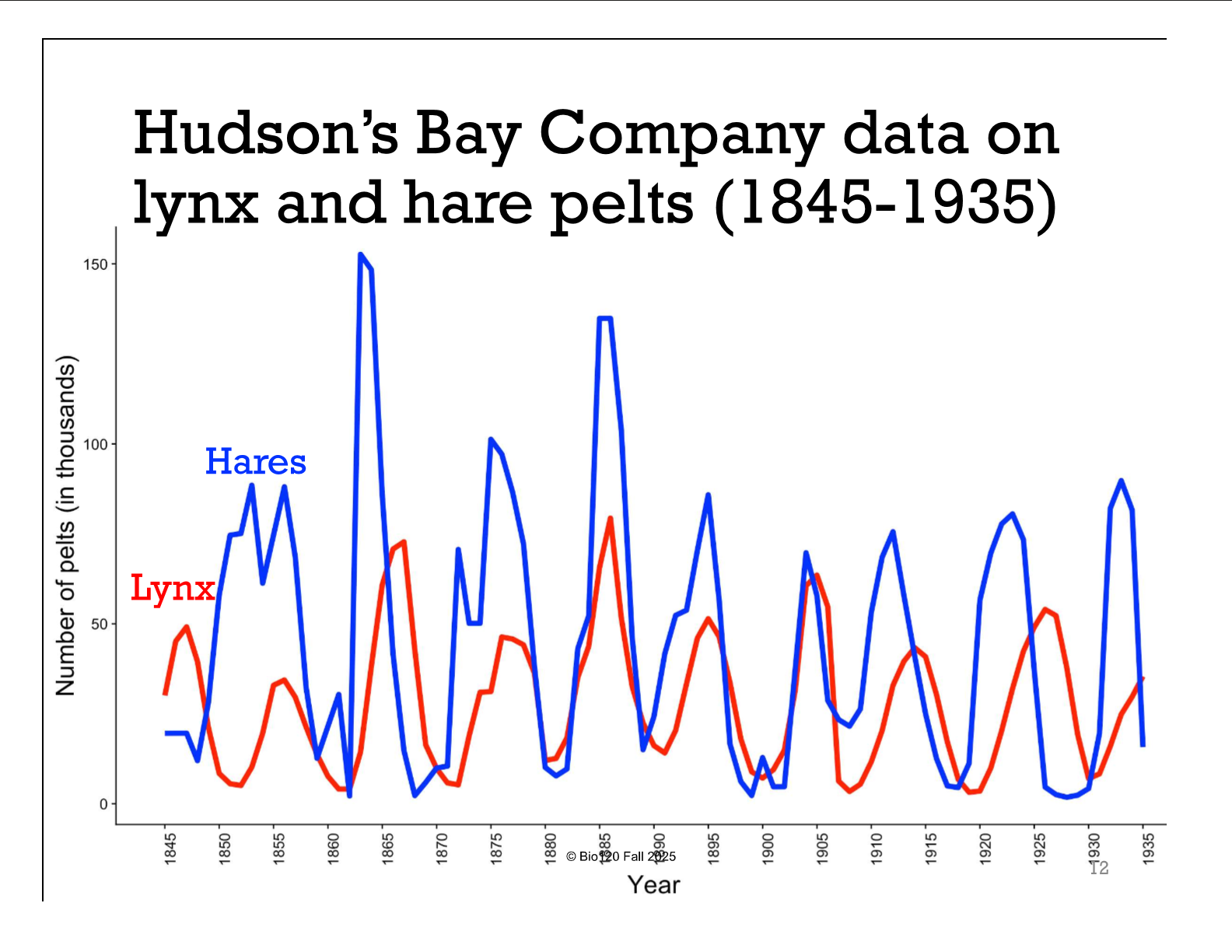
True Or False: lynx-hare cycles are complex in nature
True
What are 2 additional factors of lynx hare cycles?
Damage of plants due to heavy browsing (caused by hares/ herbivores)
social stresses in overcrowded hare populations
Prey are under stronger selection for ________
Defenses
True Or False: Predators have ________ selection for counter defenses
Weaker
True Or False: Prey are under stronger selection than predators
True
How does an imbalance in selection affect predators and preys
Predators: evolve slower
Prey: evolve faster
If competition tends to decrease biodiversity explain how the predator-prey relationship in Paine Piaster’s experiment increases biodiversity
Mussels are great predators and they often outcompete other invertebrates in their area. The predator-prey relationship between the starfish and mussels keeps the mussels population in check. This also means the the level of biodiversity is maintained when more mussels are eaten because it lowers the level of competition between those species.
What Is The Enemy Release Hypothesis?
(Ask’s why invader species are so much impactful (harmful/beneficial) when their not in their natural habitat)
Invaders have fewer natural enemies when they immigrate compared to their native area
True Or False: Parasites have simple life cycles
False, they’re very complex
Define: Direct Life Cycles
Parasites that only need a single host species to complete their life cycle
Define: Complex life cycles
Parasites require 2 or more host species in order to complete their life cycle
Define: Vectors
Hosts that transport parasites to their next host
Define: Reservoirs
Animals species that carry diseases and parasites in the long term (without getting very sick)
What Are The 2 Different Possible Outcomes Of How Disease Risk Affects Communities?
Dilution effect
Amplification Effect
Define: Dilution effect
When host diversity dilutes the disease risk from spreading
Define: Amplification effect
Risk increases when there are more host or vector species for diseases to infect
True Or False: There Are Less Diverse Pathogens In Temperate Places
False, there are more diverse pathogens
Ex. Malaria