TV4101 - MSAT - SP1
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms

What this?
Standard AI Pipette

What is this?
Who is it used for?
Any notable features?
How do we use it, why?
Another insemination catheter
Horses
Is flexible with a rounded end - can be used to be directed into a specific uterine horn tip (for when semen is frozen, low viability or low concentration)

What is this?
Used for who?
Why is it that shape?
How to manipulate it?
Ai catheter
Pigs
Cervix of pigs is elongated and spiralling
Push through cervix by pushing forward and turning (Eventually plugs the cervix and semen can be infused)

What is this?
Used for who?
How does it work?
Ai catheter (MAVIC catheter)
Dogs (smallies)
When in vagina and up against cervix can inject air to fill bulb that plugs the vagina b4 injecting semen

What is this?
Used in who?
How does it work? Features?
Artificial Vagina (Colarado)
Equines
Collecting semen from stallions - has a screw top lid to allow filling with warm water
Latex lining
Has a disposable sheath with a semen collection bottle (with filter to keep gel out) at the end
Removal of gel as gel can interfere with motility of sperm

For an AV for horses - the temp has to be btw?
40-50 degrees

What is that?
Purpose?
Muff
When in cold environs, put over equine AV to keep semen warm (and protect from light) while you are waiting for stallion to finish
What is considered to be the right tightness for an AV in equines?
What else do we do?
If you can pass your hand through with some resistance but aren’t stuck
Lubricate the entrance of AV
What is this?
Used for?
Disadvantages?
Advantages?
AV for Equines (Missouri)
Con - Less fluid so semen won’t be kept as warm for long
Pro - Much lighter than the Colarado

What is this?
Uses of the valve?
Ram AV
Can unscrew to fill with warm fluid (body temp roughly)
Can blow in the top and close valve to adjust the pressure of the lining

What is this?
Used why?
Positioning?
Ram electroejaculator
Used to collect semen from rams if not trained to use AI vagina
Probes must be faced down (see image)


What is this?
Use?
Duration and temp?
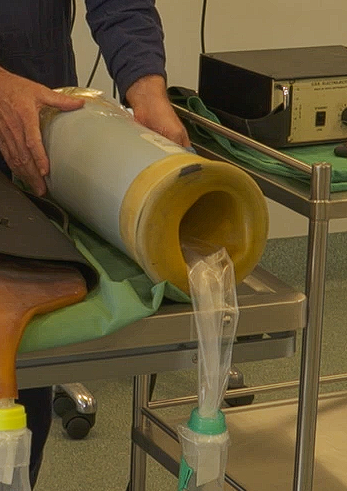
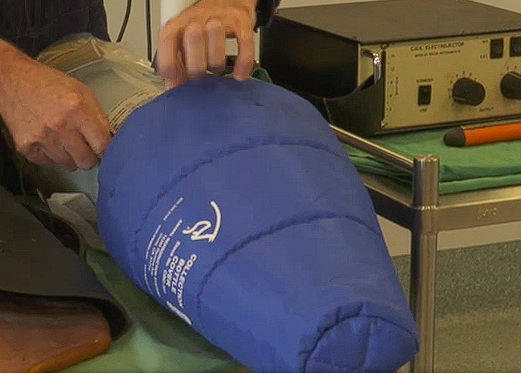
Styrofoam Transport box
Stores cooled (not frozen) semen at 5 degrees for 24 hrs

What is this?
Use?
Pros?
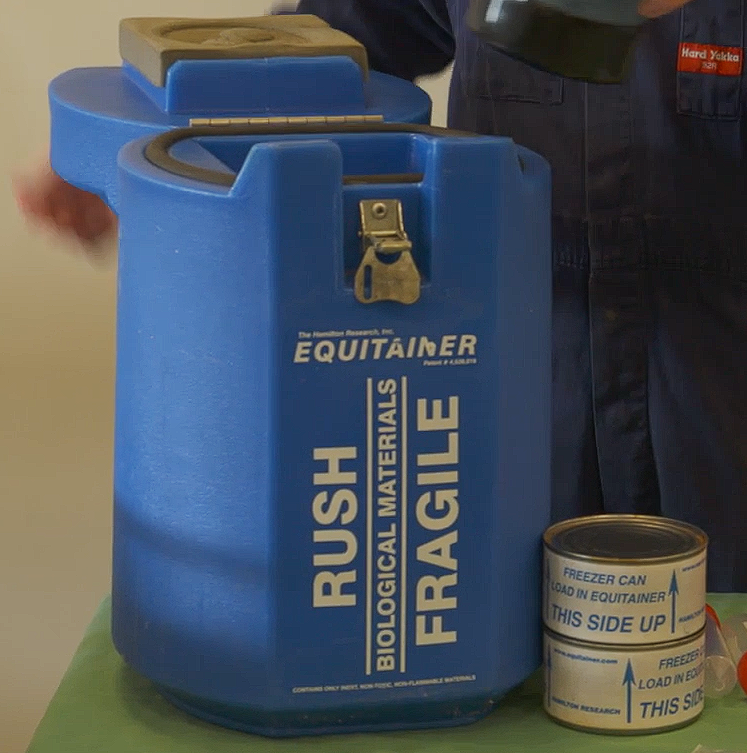
Equitaner - Cools semen slowly to 5 degrees (maintained for up to 72 hrs)
Pros
Can be transported by air or couriers)
Contains two cans that are frozen and placed under the semen containers
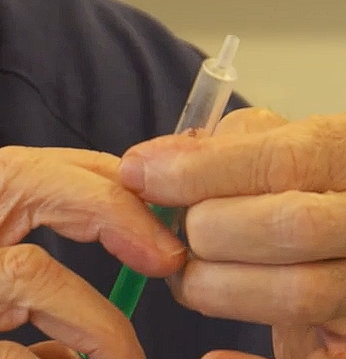
What is this?
Features?
Use?
Semen Safe Syringe
No rubber (believed to be harmful to semen)
Instead plunger is all plastic
Can be used with cats/dogs to transport semen by mail - just place a little cap on top and placed in styro storage box
The 3 parts of ejaculate in canines?
How does this affect collection?
Preejaculate - small amount and clear
Ejaculate - main part
Prostatic Ejaculate
When collectiing when the ejaculate in the collection receptible goes from cloudy to clear then use a new liner to collect the prostate ejaculate
OR
Have differen tubes with different coloured funnels
Liquid nitrogen safety
Respiratory aspect?
How to avoid?
Liquid nitrogen vapour into a poorly ventilated space can displace oxygen and cause asphyxia
Vapour is odourless gas and the seepage may not be detected
Ensure adequate ventilation and never dispose in confined area
Liquid nitrogen safety
PPE?
Why?
Protective clothing should be worn when handling liquid nitrogen. Eye protection (goggles or shields, not glasses) should be worn.
Wear trousers outside boots and pour liquid nitrogen slowly to reduce splashing
Liquid or even the cold nitrogen gas issuing from the liquid can cause burns, damage delicate tissues such as the eyes and if inhaled cause internal burns
Liquid nitrogen safety
Transport?
Secure liquid nitrogen flasks during transport and secure the lids.
Do not transport nitrogen tanks within the passenger compartment or a connecting boot of a vehicle.
In the event of an accident dangerous levels of nitrogen gas will be present in the car if the car windows are shut.
It is best to transport liquid nitrogen containers in the rear of a vehicle such as a ute that does not allow free liquid nitrogen to enter the passenger compartment during transport or in an accident
Liquid nitrogen safety
PLugs?
Never use a plug other than that supplied with the tank. Wrong plugs may interfere with the escape of gas and may cause the tank to burst
Liquid nitrogen safety
Embrittlement?
Liquid nitrogen can cause many common materials such as carbon steel, plastics and rubber to become brittle, or even fracture
Liquid nitrogen safety
Drains?
Liquid nitrogen must not be disposed of down the drain, as piping in laboratory sinks may not be able to withstand cryogenic temps
Liquid nitrogen safety
PSI?
How to rpevent?
Over pressurisation from boiling liquid N2 can inc after lid closure - opening lid can cause explosion of N2 over handler
Depressurise b4 remvoing lid
Liquid nitrogen safety
Checking?
Check the tank regularly for evidence of frost on the outside and for excessive loss of liquid.
Either state could indicate a breakdown of the insulation. The amount of liquid nitrogen in the tank can be checked by the frosting on a dip-stick.
Beware of using a hollow tube as a dip-stick as the liquid nitrogen will spray up through the centre.
Care and maintenance of a liquid nitrogen storage tank
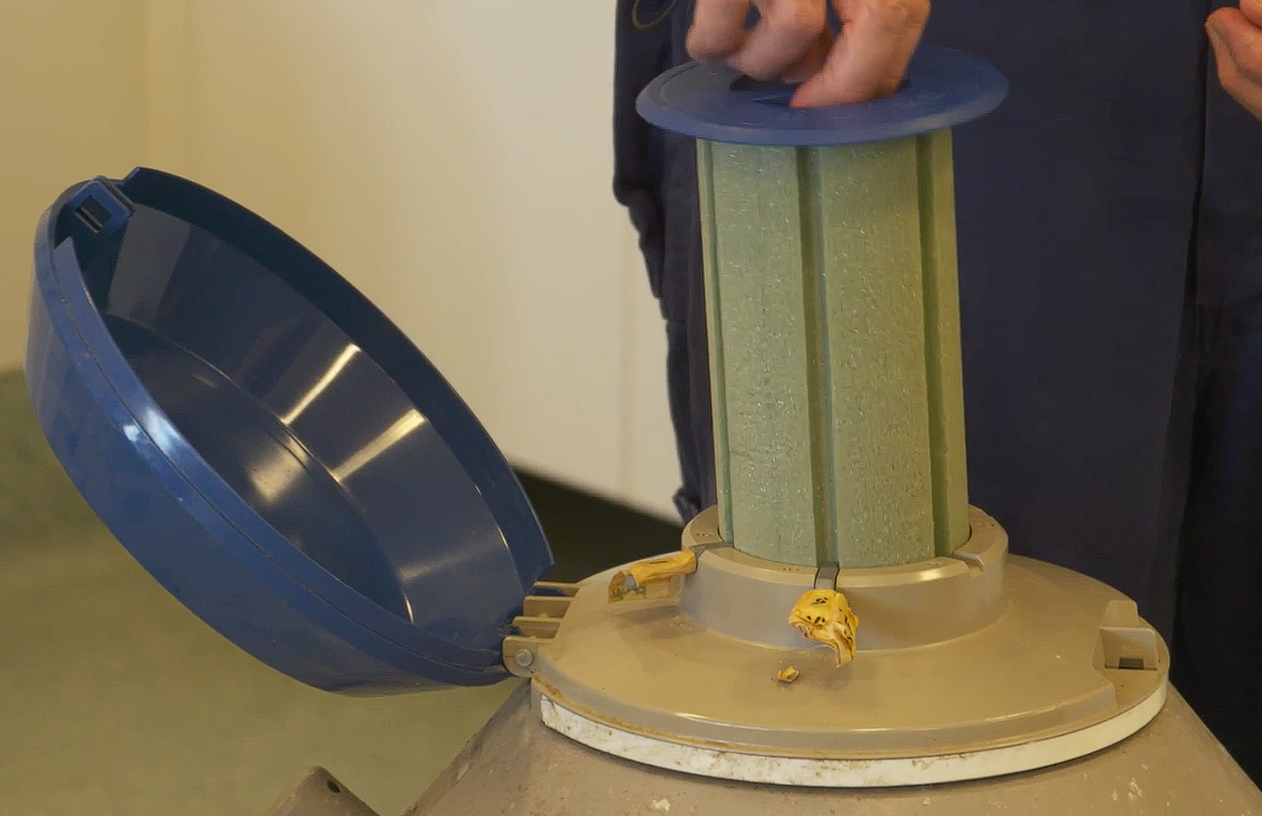


Components of a Liquid Nitrogen Tank
What are these things? Purposes?
Left - Main lid: is cable tied down
Right - Polystyrene lid
Semen Evaluation
Density - Descriptions and Values?
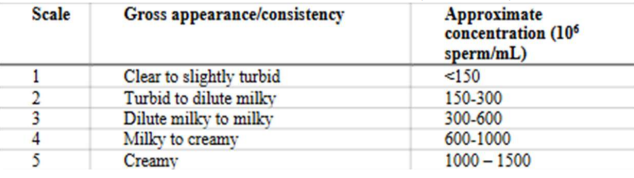
Semen Eval
Mass Activity
What is our setup?
What is it assessing?
How to observe?
Scale and description?

Semen Eval
Progressive Motility
How to eval?

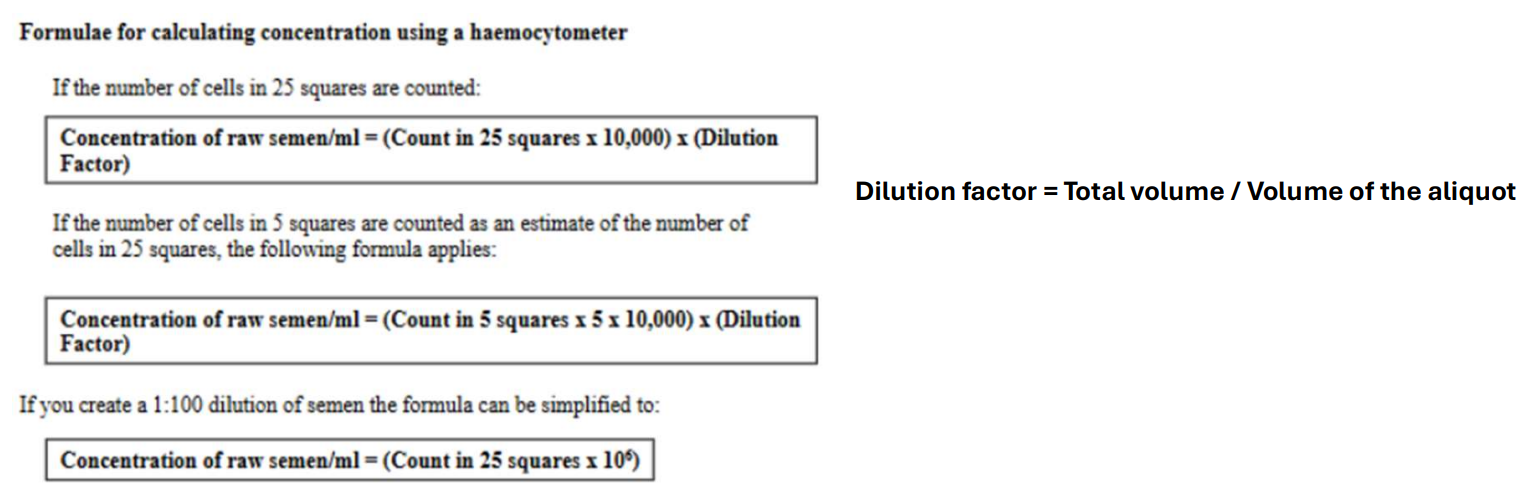
Semen Eval - Concentration Formulae?
Semen Eval - Morphology
What is a pass?
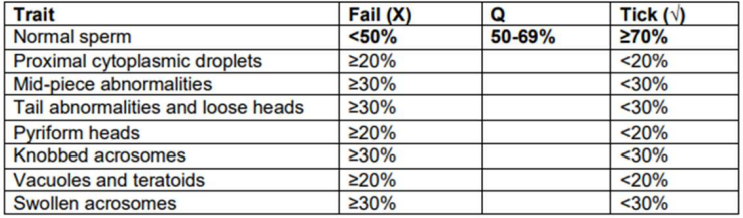
Crush Side Semen Examination
What is a fail, qualified and pass respectively?
Obstetrics - Decribe Presentation, position and posture

Obstetrics - Abnormalities of Posture inc?

What is the presentation, position and posture?
Cranial Presentation
Dorso-sacral position
Left Sided Unilateral Elbow Lock
Elbow Lock
Describe it
What do we do?
Elbow of foetus gets stuck below the pelvic brim
Apply traction to limb to extend limb
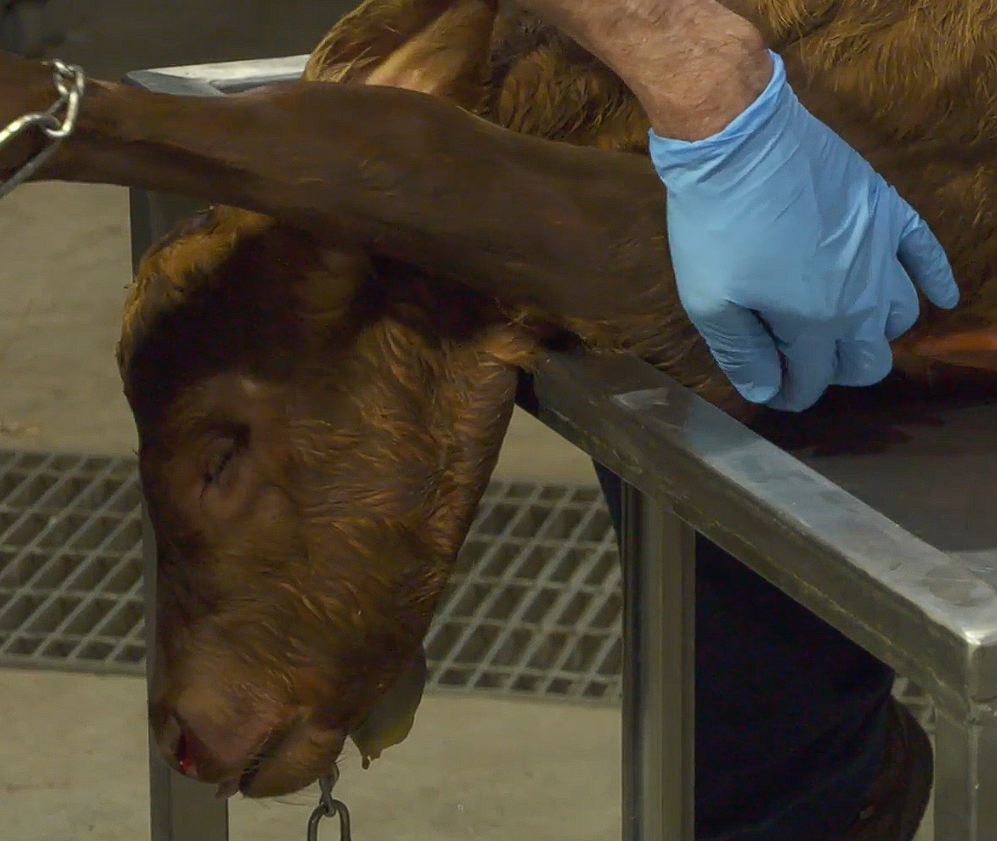

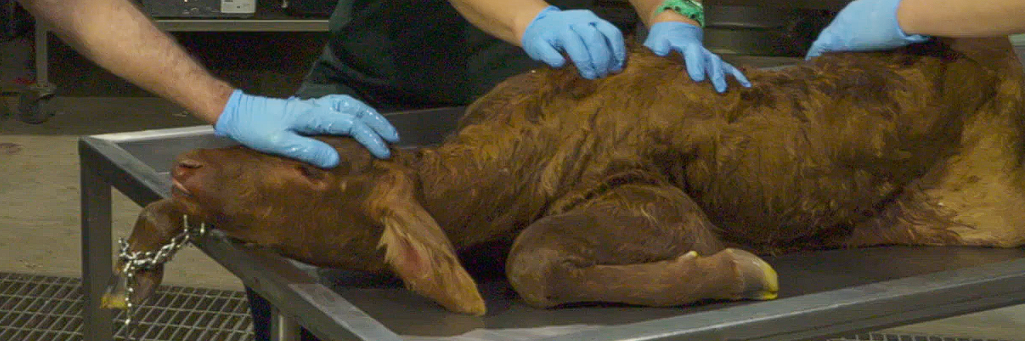
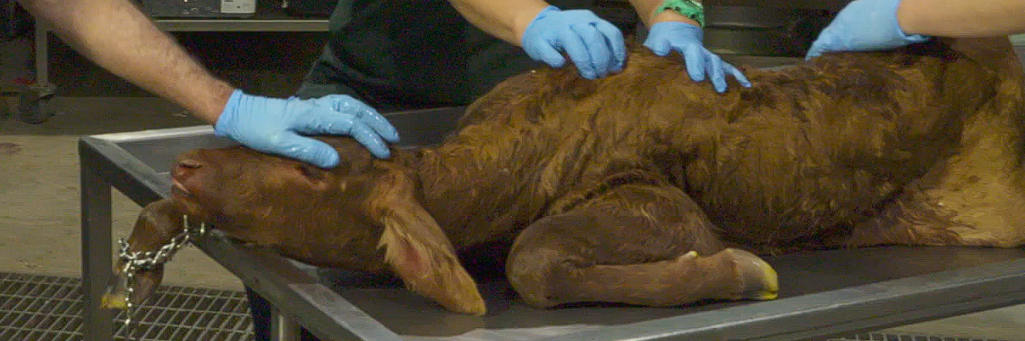
What is the presentation, position and posture?
Cranial Presentation
Dorsosacral position
Left Sided Carpal Flexion
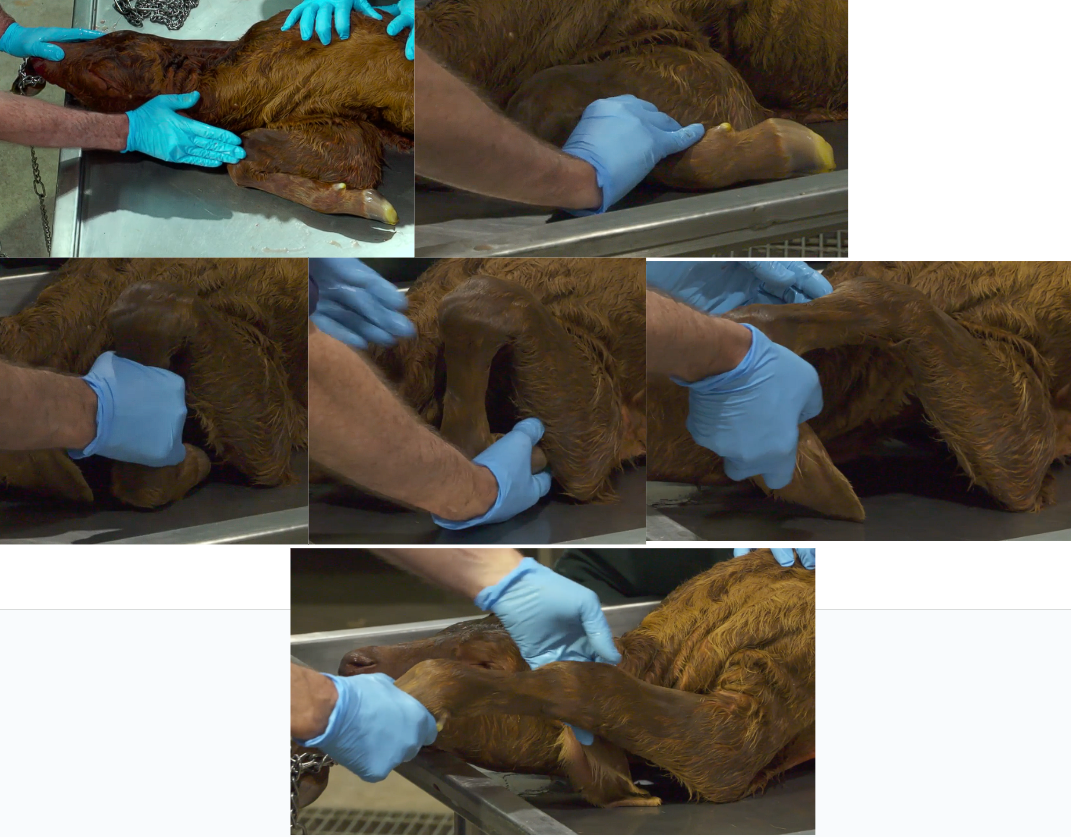
Carpal Flexion
How to correct?
Identify the carpus
Grab the metacarpus and elevate the carpus
Get hand to cover the claws and manipulate leg around up and over pelvic brim
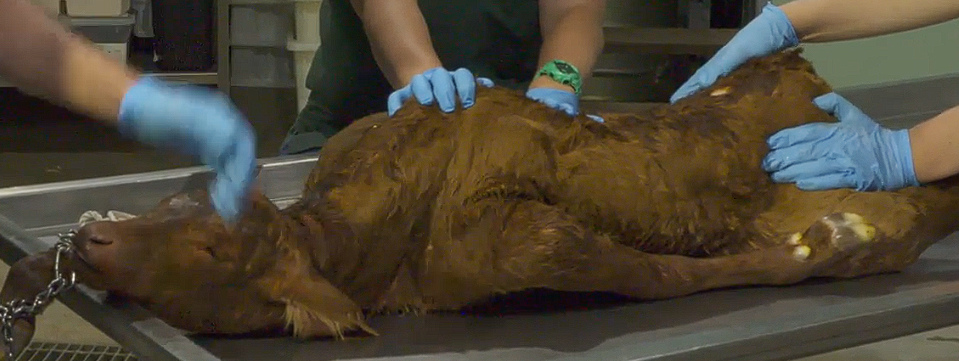
What is the presentation, position and posture?
Cranial presentation
Dorsosacral position
Left sided unilateral Shoulder flexion
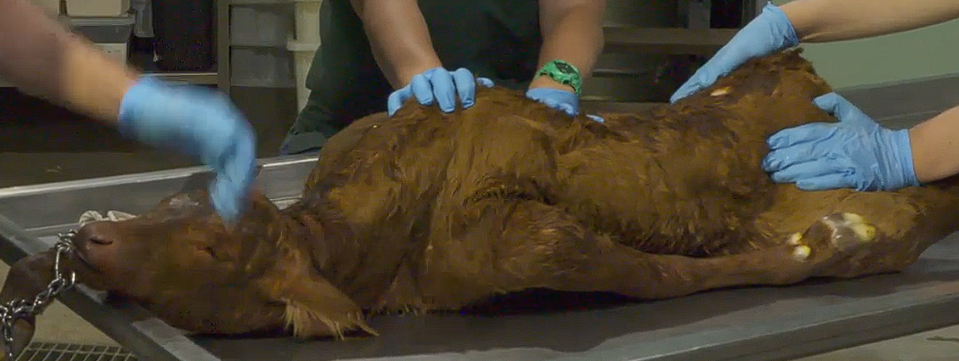
Shoulder flexion how to do?
Other method?
Aim to get into carpal flexion and correct from there
Find the radius and ulna → pull it forward
Then correct the now carpal flexion
Other method
Wrap rope around shoulder
Attach rope and move it down
Pull it forward
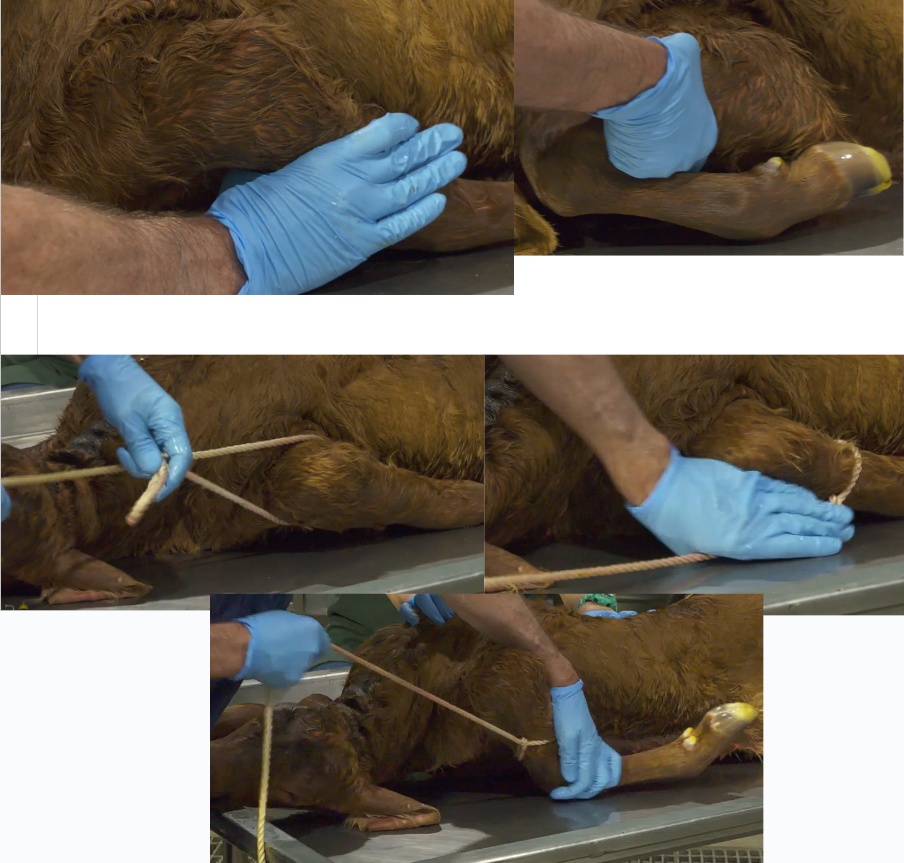

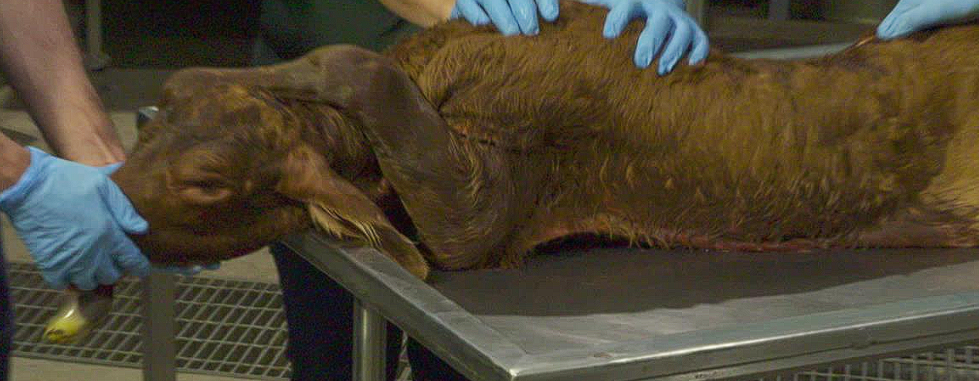
What is presentation, position and posture?
Cranial presentation
Dorsosacral position
Left Foot nape position
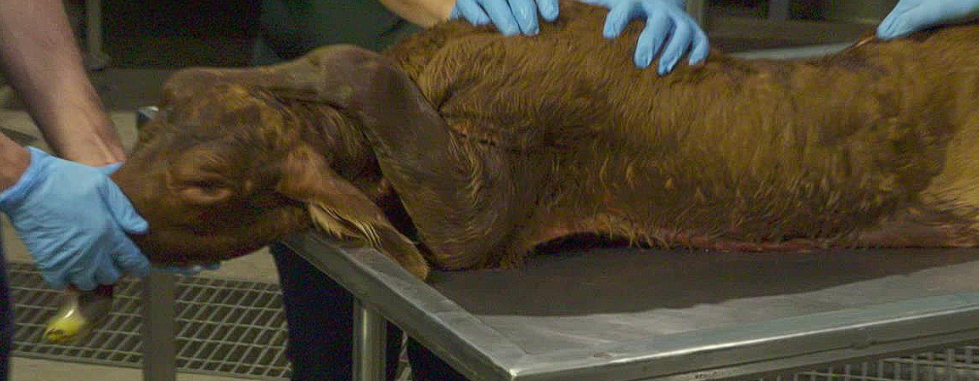
Foot nape position
How to correct?
Just take it off the head ffs


What is presentation, position and posture?
Cranial Presentation
Dorsosacral position
Left lateral deviation of the head (Left cephaloilial posture)

Lateral Deviation of Head
How to correct?
Follow neck to the head
Wedge finger into corner of mouth
Move the head to face you by moving it horizontally (or go up in an arc if you want)
If you can’t reach the mouth you can pull on an ear to be able to get to the mouth easier

Obstetrics - Using a Detorsion rod
When can detorsion be done?
For uterine torsion of <270 degrees
Also for dystocia in which calf is in dorsopubic position → dorsosacral
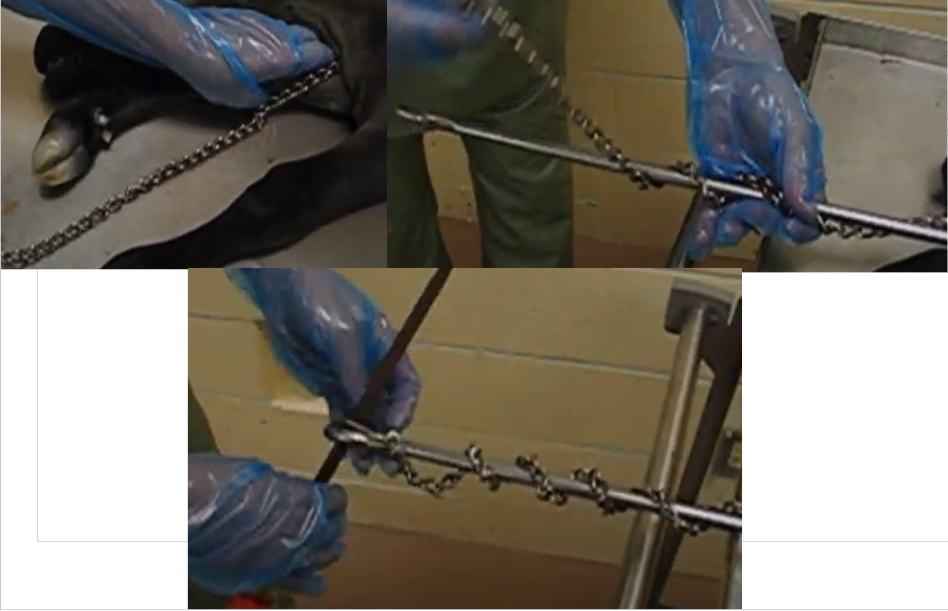
Obstetrics - Using a Detorsion rod
How to apply?
Put a chain on each limb as high up as possible (ideally over elbow on cranial and hock for caudal)
Wrap the chains around the detorsion bar in the direction you want the calf to go
Place a rod through the hole at the end of the detorsion bar and wrap the chain around that
Start turning - check to make sure the chain isn’t getting caught in the vagina frquently

Cornual Nerve Block
Indications?
What nerve are we blocking?
Dehorning, disbudding calves and other surgiers around the horn base
Cornual branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Cornual Nerve Block
Where does it run?
Emerge from orbit → runs along and just below frontal crest to the base of the horn
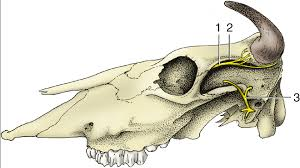
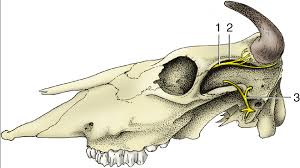
What is 1?
What is 2?
1 - Corneal Nerve
2 - Frontal crest
Corneal Nerve Block
Needle size?
Syringe size?
Volume of drug?
18-20 G × 1’’ needle;
10-20 mL syringe;
5-10 mL 2% lignocaine
Corneal Nerve Block
Finding the injection site?
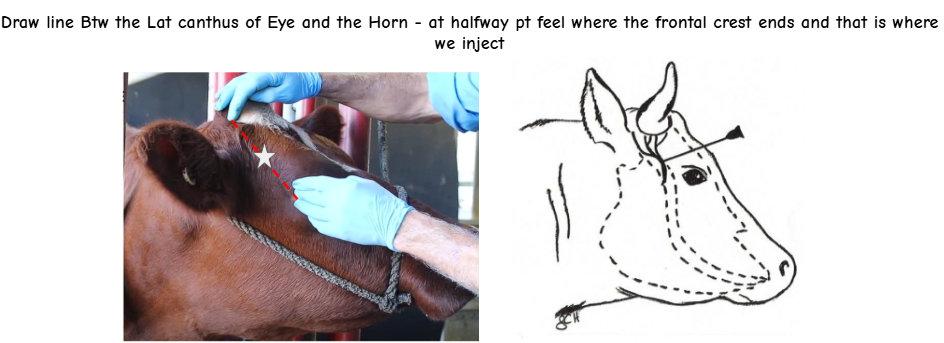
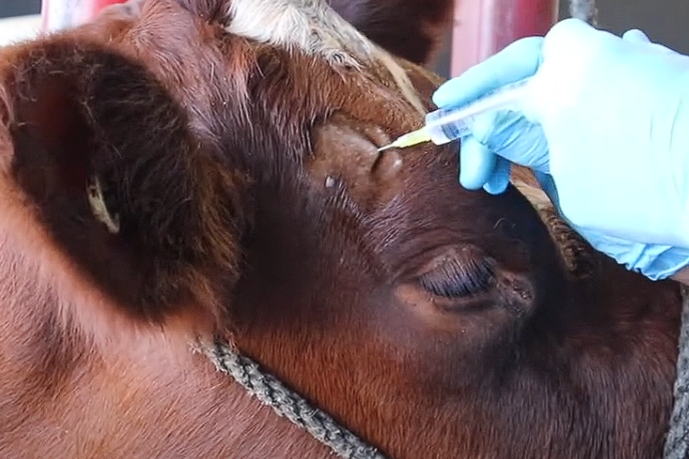
Corneal Nerve Block
Injection aspects?
Direct the needle at a 30° angle through the skin towards the base of the horn.
Draw back to ensure that the needle is not inadvertently intravascular (i.e. Corneal vein and artery are nearby)
Disperse drug in arc just below frontal bone then massage firmly
Corneal Nerve Block
When should its effects work?
Results?
5-10 minuntes
Removed sensation around horn (Lasts for an hour)
Corneal Nerve Block
Fat aspect?
In excessively fat animals, the nerve may be displaced and more anaesthetic solution may be required
Auriculopalpebral Block
Uses?

Auriculopalpebral Block
Advantages?
Facilitates the examination of the eye by abolishing the strong tone in the eyelids
Auriculopalpebral Block
Disadvantages?
- Analgesia of the eye or the eyelids is not produced by this block (it only blocks the motor function).
- It only effectively blocks the lower eyelid; therefore, a line block of the upper eyelid may need to be performed as well
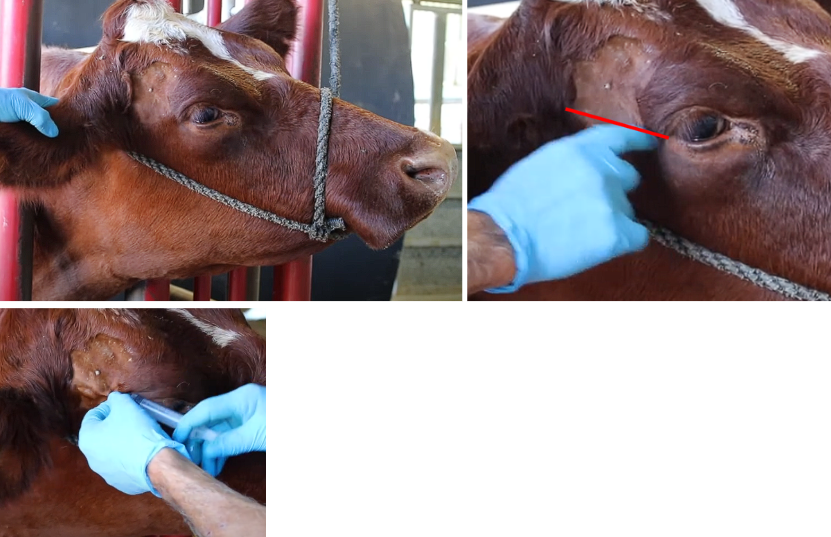
Auriculopalpebral Block
Where does it run?
Where is our injection site?
Dorsal border of the zygomatic arch then below the eye
Halfway btw lat canthus of eye and the ear along dorsal zygo arch (go superficial with it)
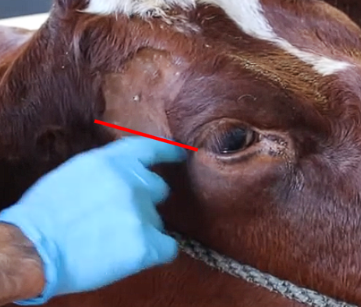
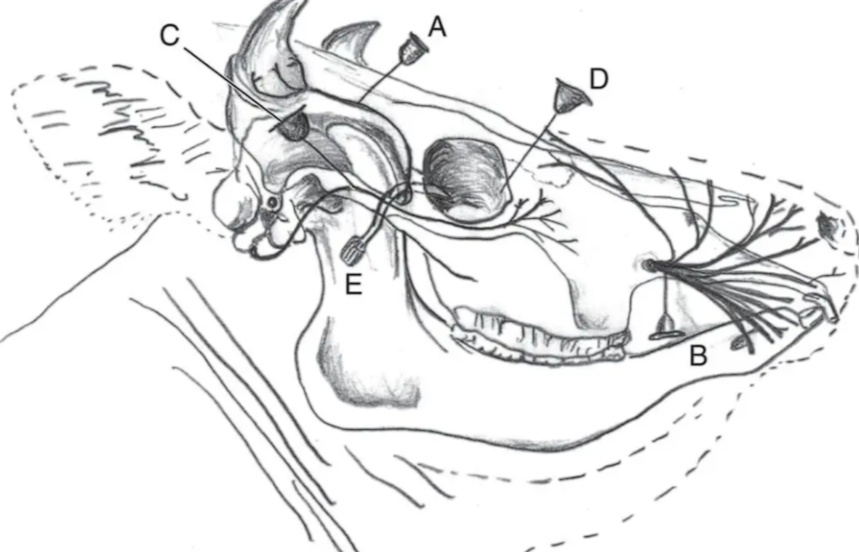
Which is Auriculopalpebral?
C
Auriculopalpebral Block
Injection aspects?
Inject superficially along the top of the zygomatic arch
Auriculopalpebral Block
Needke?
Syringe?
Drug volume?
18-19 G × 1.5” needle;
10-20 mL syringe;
10-15 mL 2% lignocaine
Auriculopalpebral Block
Onset of analgesia? Lasts for how long?
How do we know it worked?
In 10-15 minutes, and last for about one hour
Minimal blink reflex when touching the medial canthus of the eye
Peterson Eye Block
Blocks 4 cranial nerves, which ones?
What does the combined effort of these nerves do?
Oculomotor (CN 3)
Trigeminal (CN5)
Trochlear (CN 4)
Abducens (CN 6)
Responsible for the sensory and motor function of all structures of the eye except the eyelids
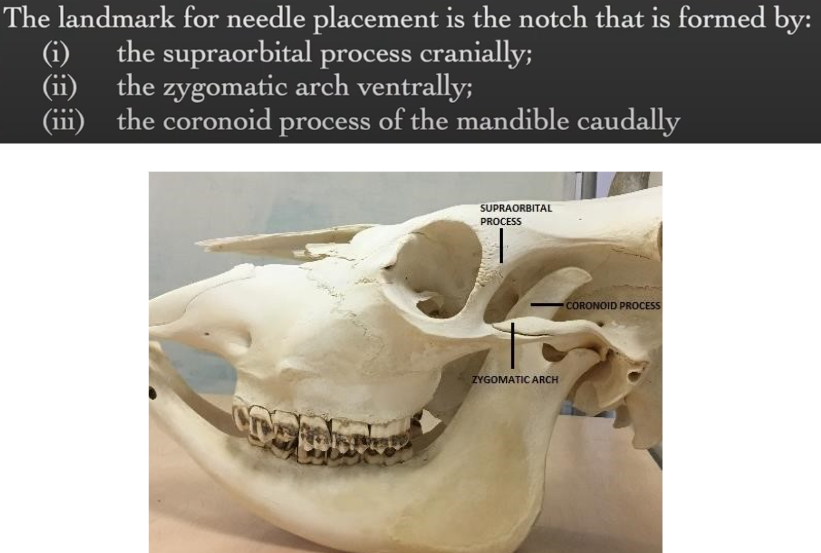
Peterson Eye Block
Landmark for needle placement?
Peterson Eye Block
Before doing the spinal needle one what do we normally do?
Perform Auriculopalpebral nerve block first (kinda)

Peterson Eye Block
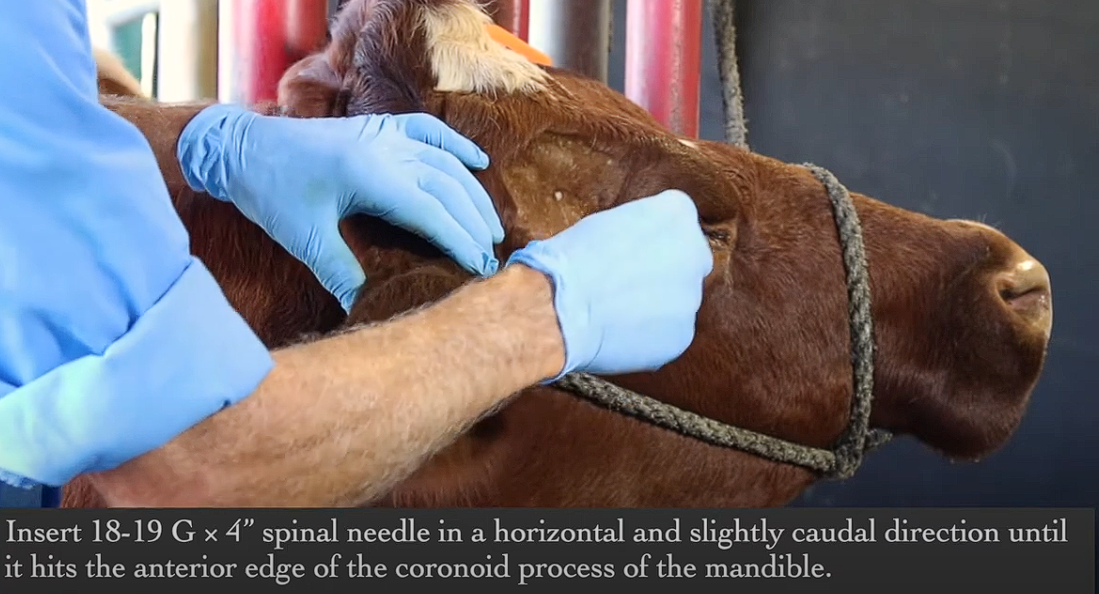
Spinal Needle part how to perform?
Angle spinal needle parallel to ground (also perpendicular to skin) and slightly angled back - go through the bleb that you just made
Peterson Eye Block
Spinal needle part - you’ve hit the coronoid process now what?
After you’ve walked off the anterior edge of coronoid keep moving needle further in until you hit bone again
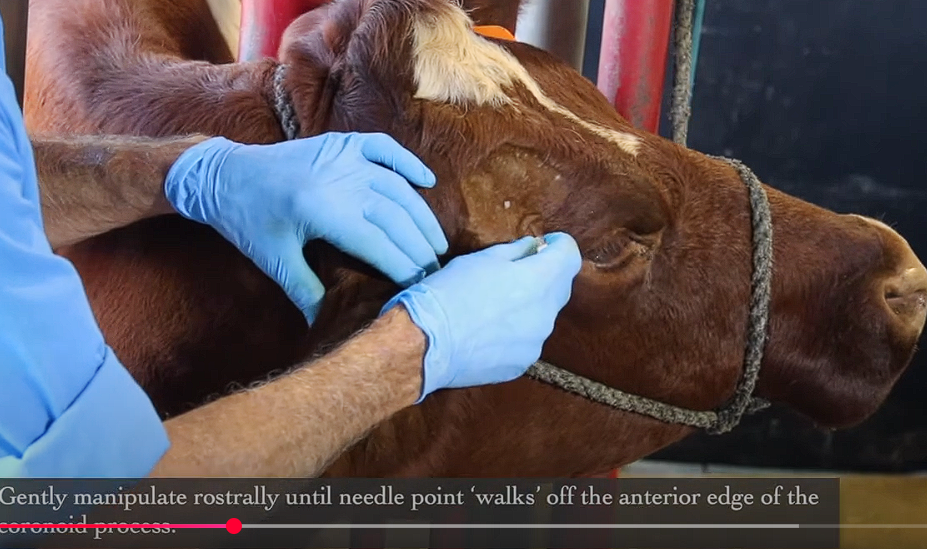
Peterson Eye Block
Administering the spinal needle part, what do?
Remove the stylet
Attach syringe - draw back so you aren’t hitting the ventral maxillary artery
Inject about 30-40mls in total at above below and cranially to the area around the orbital foramen
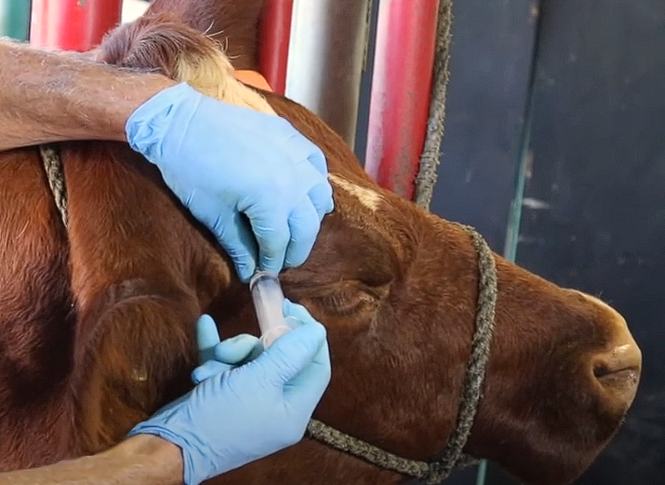
Peterson Eye Block - How do we know it worked?
Oculomotor - involved in pupil constrcition
Trigeminal involved in sensory
Trochlear - involved in eye movement

Epidural Nerve Block
Used for?
Dystocia is a biggie

Epidural Nerve Block
Pros and Cons?
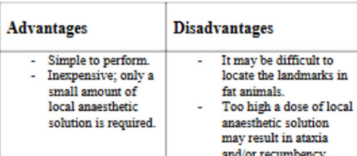
Epidural Nerve Block
A high caudal epidural block administered where? (We didn’t perform this one)
It blocks what?
into the sacrococcygeal space (the space btw the sacrum and the first caudal vertebrae) desensitizes S2, S3, S4, and S5
See B
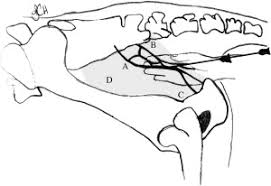
Epidural Nerve Block
A low caudal epidural block administered where?
It blocks what?
First two coccygeal vertebrae desensitizes S3, S4 and S5
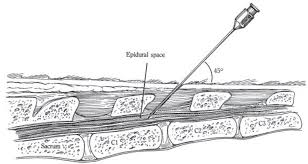
Epidural Nerve Block
How to locate the site for low caudal epidural block?
What should we see?
Pump the tail up and down - n. The most obvious articulation caudal to the sacrum is the first intercoccygeal space (Large space that moves a bit)
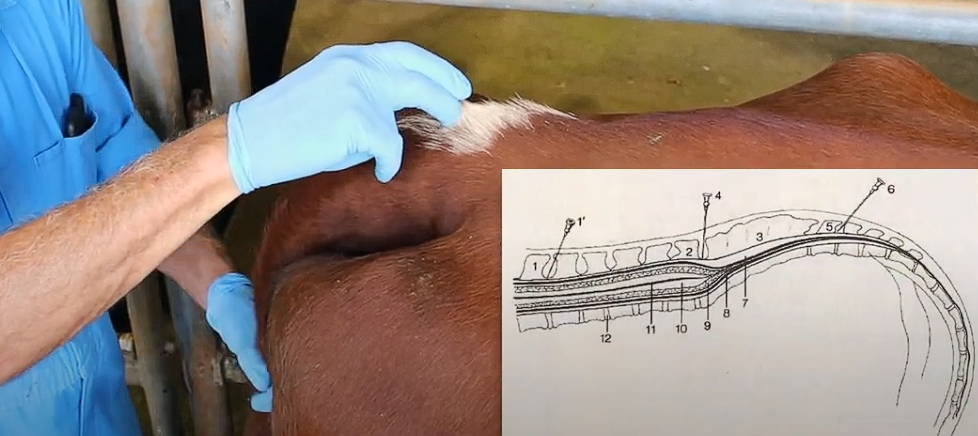
Epidural Nerve Block
Needle?
Syringe?
Volume of Drug?
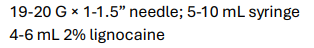
Epidural Nerve Block
Following clipping the top of the tail and scrubbing, what next?
Get unattached needle - inject perpendicular to skin and precisely in the midline (Be slightly cranial)
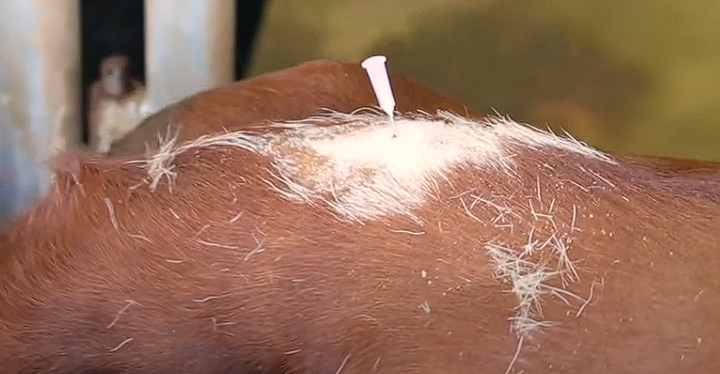
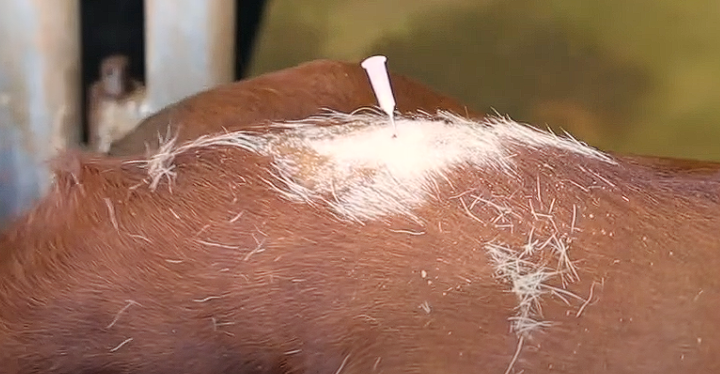
Epidural Nerve Block
We have the needle in the right location, what next?
Check if in right spot - hanging drop technique
Drop some local anaesthetic into the needle
If in the right space the drop should get sucked in via negative pressure
Other method - get som air into syringe with the drug and inject - should go in easily (don’t inject the air though)
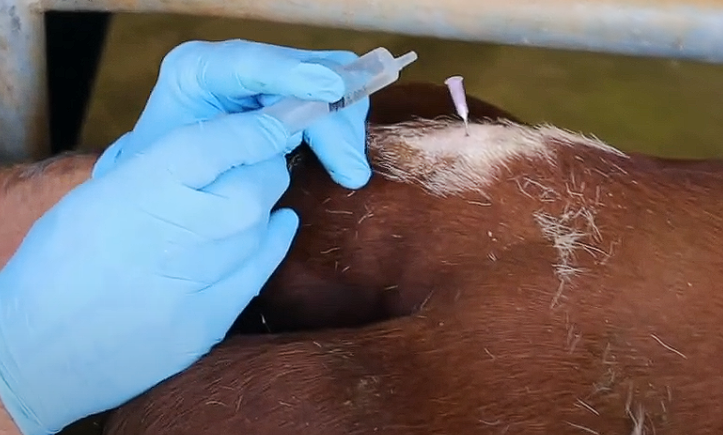
Epidural Nerve Block
How much do we inject?
How do we inject?
Why do it this way?

Epidural Nerve Block
How do I tell if its worked?
The tail is relaxed (‘floppy’).
Sensory innervation is lost from the anus, vulva, perineum and caudal aspects of the thighs.
The anal sphincter relaxes and the posterior part of the anus may balloon out somewhat.
Any tenesmus will be relieved, while obstetric straining may be prevented
Paravertebral Block
Indications?

Paravertebral Block
Pros and Cons?
Anesthetises all layers (skin, muscle and peritoneum) - good
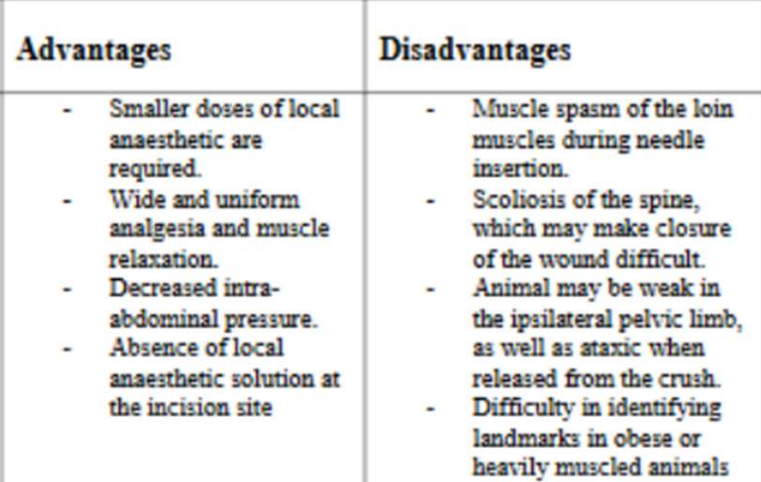
Paravertebral Block
Where are the points of injection? What do we block?
About 5-6 cm (matchbox sized) away from the dorsal midline
• to block T13 the injection point is the cranial edge of L1
• to block L1 the injection point is the caudal edge of L1
• to block L2 the injection point is the caudal edge of L2
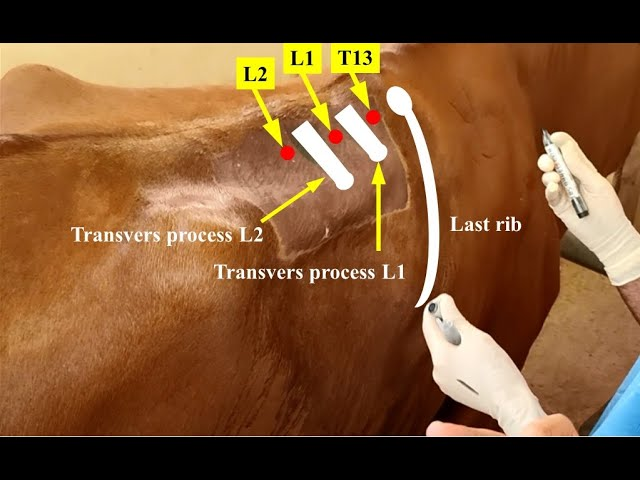
Paravertebral Block
Signs of success?

Paravertebral Block
Describe the lumbar vertebrae
Can’t feel the transverse process of the 6th lumbar as its hidden by tuber coxae
Count back from LT5 to LT1
Paravertebral Block - Step 1 in terms of drug admin?
Get assistant to apply a tail jack
Place 2ml (maybe use like 5-10mls) bleb of local at each of the injections sites (matchbox length away from midline)
Have needle perpendicular - put needle in first unattached
Attach syringe and the inject as drawing out
Paravertebral Block - Step 2 in terms of drug admin?
Spinal Needle Part
Describe how we do it for the LT2 injection site (should be similar for the other ones)
Put the spinal needle through where you put the blebs
Check that there is resistance when trying to draw back - if you suck in air you might be too deep i.e. abdomen deep
Caudal edge of LT2
Go through bleb and angle slightly forward as you want to hit the process
Walk off the process and keep moving down
Should feel a “pop” when you the ligament
Inject 15ml below the transverse process
Inject 10 ml above as you’re coming out
Technically its above and below the intertransverse ligament but yeah
Put a lil bit on top of the vertebrae as well
Single retrobulbar nerve block
Uses?
How does it work?
Used in cattle practice for enucleation of the eyeball
Blocks the nerves to the ocular muscles causing paralysis of the eyeball, as well as analgesia
Single retrobulbar nerve block
How to perform? (We didn’t do this one)
Insert the forefinger either into the medial or the lateral canthus, between the eyeball and the conjunctival sac
Alongside the finger pass a very bent (almost semicircle) an 18-19 G x 4’’ needle through fornix of conjunctiva
4-Point retrobulbar nerve block (Didn’t perform this one)
Use?
How does it work?
For enucleation of the eyeball
Local anaesthesia is achieved by infiltration of the orbital tissues
4-Point retrobulbar nerve block (Didn’t perform this one)
Injection points?
Needle used?
Volume?
The 4-point block is performed by injecting through the eyelids, both dorsally and ventrally, and at the medial and lateral canthi.
A slightly curved, 18-19 G × 4” spinal needle is directed towards the apex of the orbit
About 40 mL of anaesthetic solution is injected, divided in to 10 mL quantities per site
4-Point retrobulbar nerve block (Didn’t perform this one)
How to know it worked?
Exophthalmos, corneal anaesthesia and mydriasis
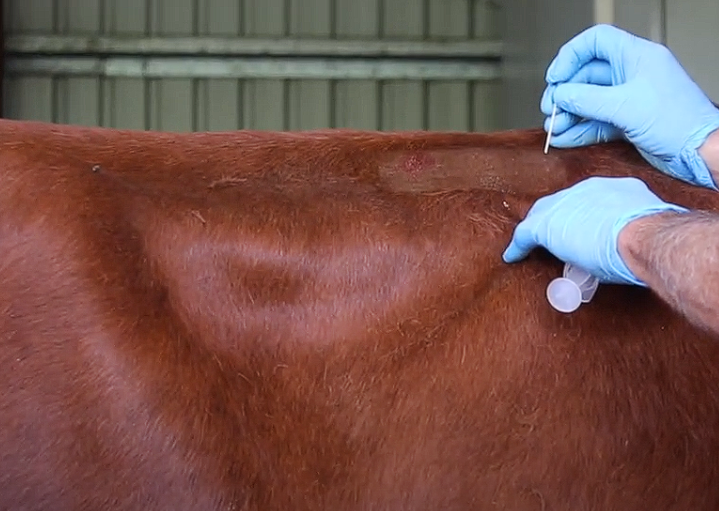
Retrograde Intravenous Nerve Block
Method?
Beedle Size?
Volume?
Place tourniquet above injection site (tuck the end under itself)
Need to find a venous plexus - look at the groove (Insert exactly in the midline and 2-3cm below fetlock jt) - Full depth needle
Move the needle around gently until we see blood coming out (venous plexus)
Don’t draw back - inject as fast as possible (Don’t risk getting kicked)
20ml
Retrograde Intravenous Nerve Block
The 2nd spot if needed?
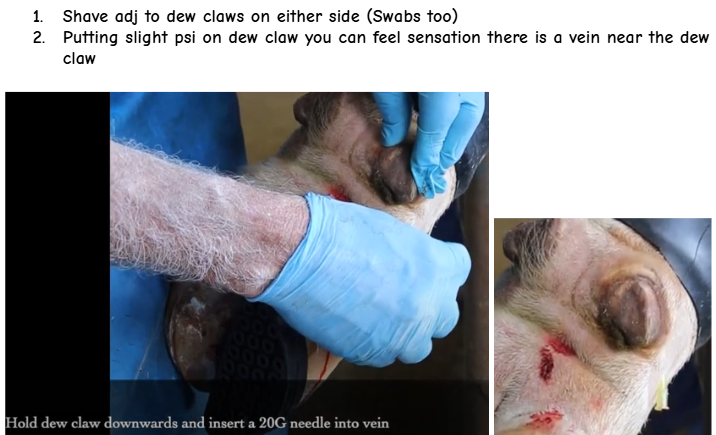
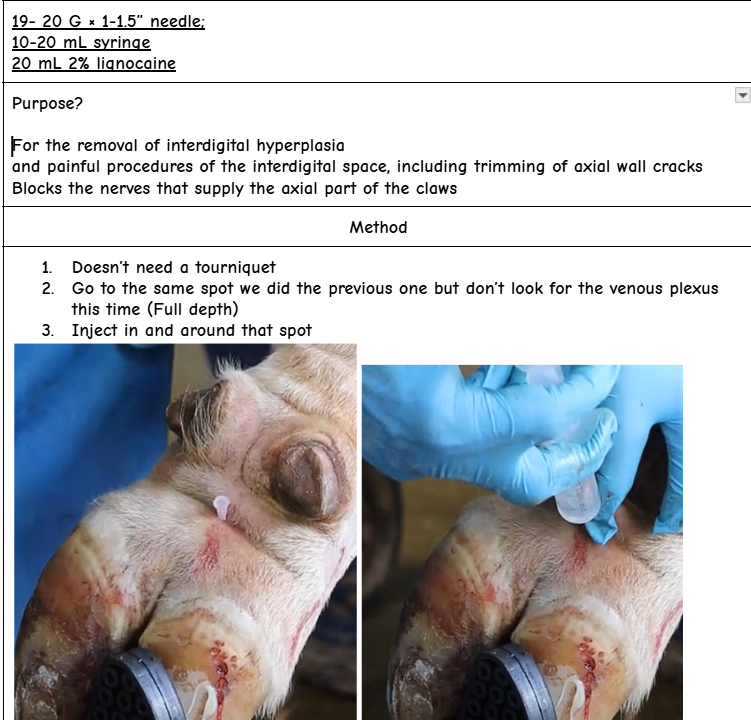
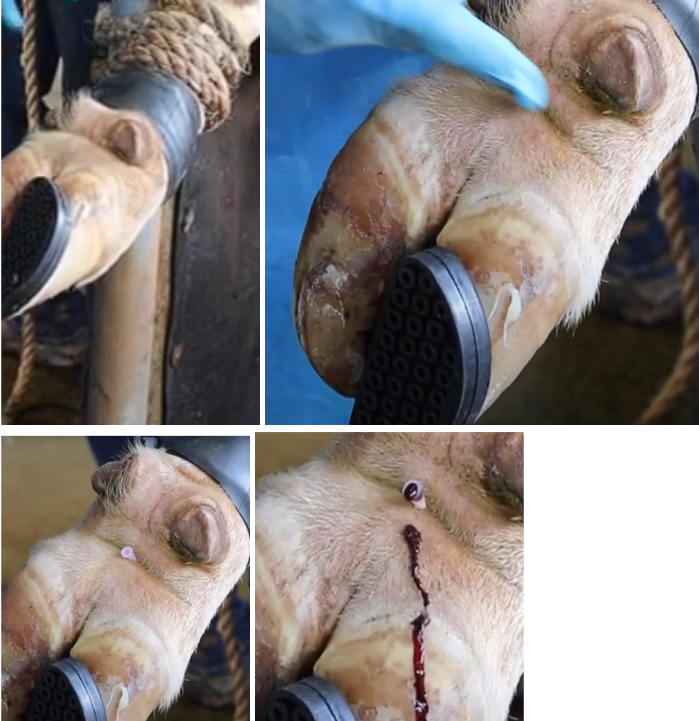
Interdigital Nerve Block
Volume?
Needle Size?
Syringe Size?
Purpose?
Blocks what?
Method?