BBL Midterm NYU COD 25'
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
All amino acids with the exception of ______ exhibit chirality
glycine
Amino acids are derived from which cycles?
Glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and TCA
How is selenocysteine formed?
It is formed on a cysteinyl-tRNA where the seleno group is substituted for a sulfur group
Proteins only contain amino acids in what configuration?
L-config
L and D amino acids are ______
enantiomers
Buffer equation
pH=pKa + log [base]/[acid]
Why is proline a unique amino acid?
Proline contains a secondary amine, making it very rigid in structure, meaning it cannot be a hydrogen donor, only a hydrogen bond acceptor
All amino acids are formed by the amination of?
Keto acids
The major metabolic source of amino acid precursors is
TCA
All amino acids have an R group. What is the significance of the R?
Each of the 21 amino acids has a unique R group
At neutral pH, amino acids are dominantly
zwitterions
Branched chain amino acids
Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
nonpolar aliphatic amino acids
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Proline
*hydrophobic
hint: GLAMP VIPT
polar uncharged amino acids
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Tyrosine, Asparagine, Glutamine
* hydrophilic
Hint: STACT G
Acidic amino acids
Aspartate, glutamate (negatively charged)
*salt bridges and electrostatic interactions
basic amino acids
lysine, arginine, histidine (positively charged)
*salt bridges and electrostatic interactions
Abbreviation for: glycine, alanine, valine
Gly
Ala
Val
Abbreviation for: Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine
Leu
Ile
Met
Abbreviation for: Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, proline
Phe
Trp
Pro
Abbreviation for: Serine, Threonine, Cysteine
Ser
Thr
Cys
Abbreviation for Asparagine, Glutamine, Aspartate, Glutamate
Asn
Gln
Asp
Glu
Abbreviation for Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
Lys
Arg
His
Aromatic amino acids
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Tyrosine
What is body pH?
7
Which amino acid is the start signal for translation of mRNA to protein?
Methionine
The use of methionine in methylation is through
Adenylylation of methionine by enzyme to form S'adenosylmethionine
The unique amino acid found in the elastin protein is
Desmosine
The uncommon amino acid ornithine
Is the starting substrate of the Urea Cycle
The carboxylic acid group gets ____ while the amine group gets _____ at physiological pH
deprotonated
protonated
What does pI mean? What does it indicate?
It means isoelectric point
it indicates the region of minimum buffering power
What is pH?
measure of hydrogen ion concentration
What is pKa? What is relevant about it in the context of amino acids?
dissociation constant
pK1 represents the pH where the COOH group is deproto/protonated.
pK2 represents the pH where the NH3 group is deproto/protonated.
pKR represents the pH where the R-group is deproto/protonated.
Which amino acids have R-groups that are ionizable? Around what pH does that happen for each?
Arg: 12.48
Lys: 10.53
Tyr: 10.07
Cys: 8.18
His: 6.00
Glu: 4.25
Asp: 3.25 **** hint: Aggravated Lions Try (CY)Silently Hunting Gluttonous Asps
What is the typical approximate pH that COOH groups are ionized
pH 2 to 2.8
What is the typical approximate pH that NH3 groups are ionized
pH 9 to 10.5
What is the approximate pI of non polar amino acids
5.5 to 6
What is the hydrophobic effect
release of water molecules on the structured salvation layer and around the molecule has the protein folds increasing net entropy
What are hydrogen bonds
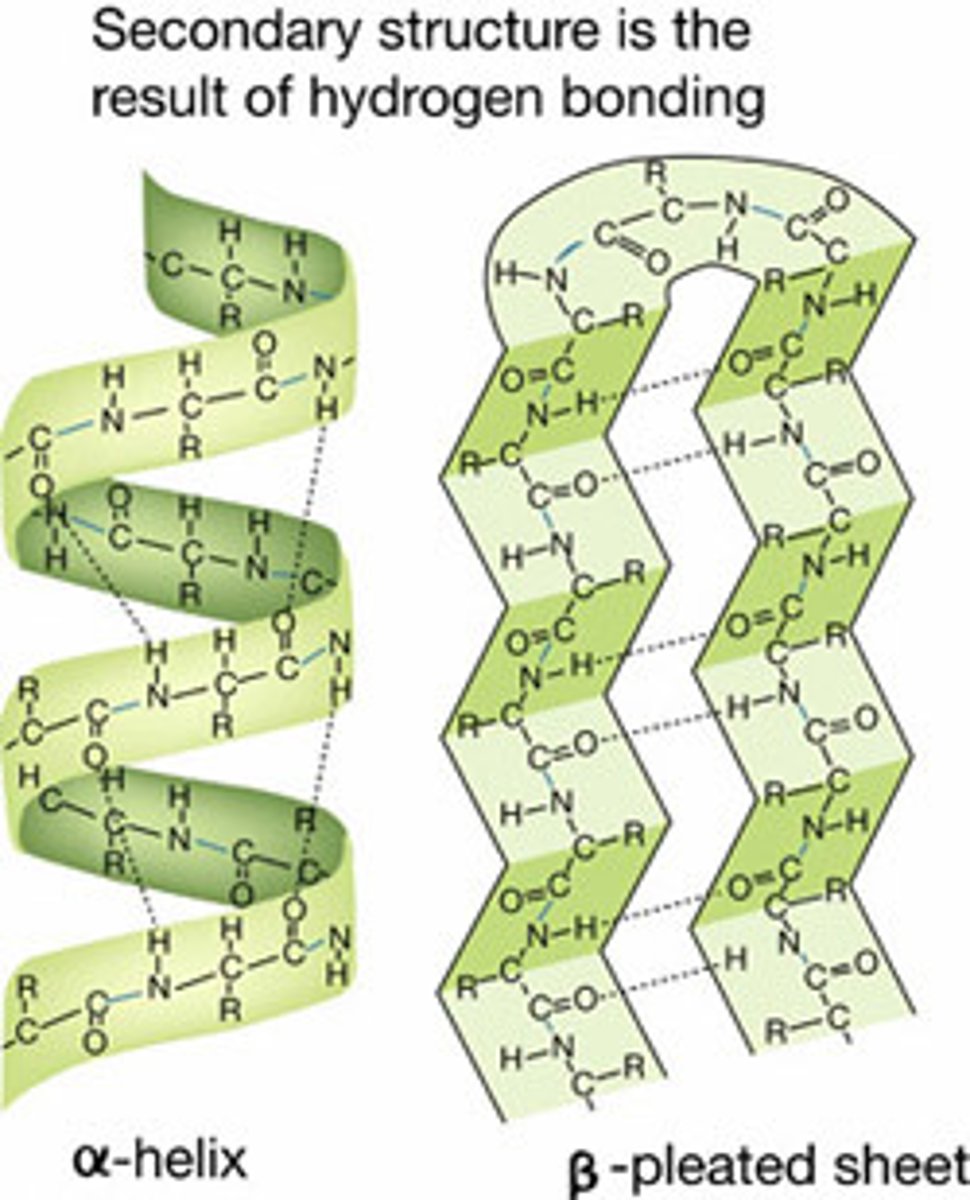
Interactions of the NH and CO of the peptide bond lead to regular structures, such as alpha helices and beta sheets.
What are London dispersion?
Medium range, weak attractions between all atoms contributes significantly to the stability in the interior of the protein.
What are electrostatic interactions
Long range, strong interactions between permanently charged groups. And salt bridges, buried in the hydrophobic environment, stabilize the protein in strong ways.
What is a salt bridge?
buried in the hydrophobic environment, stabilizing the protein in strong ways
What is a quaternary structure?
two or more polypeptides (called subunits) held together by noncovalent forces
How are peptide bonds formed? Where are they formed? What kinds of proteins are they found in?
formed between the terminal carboxylic acid of the first amino acid and the amine group of the second amino acid
primary and secondary
What kind of bonds do primary proteins use?
peptide and disulfide
What kind of bonds do secondary proteins use?
hydrogen, peptide, disulfide
What kind of bonds do tertiary proteins use?
hydrophobic, hydrogen, ionic, van der waals, disulfide
What kind of bonds do quaternary proteins use?
hydrophobic, hydrogen, ionic, van der waals, disulfide
What is a homomeric quaternary structure? What about heteromeric?
identical protein sub-units bonded together
different polypeptides bonded together
The three-dimensional structure of a protein depends on
Specific gene codes
What is a motif?
A short, recurring sequence or structural pattern in a protein.
What is a domain?
A larger, independently stable part of a protein that can fold and function on its own. Domains often correlate with specific functions, like binding DNA or catalyzing reactions.
What are the amino acids known as helix breakers?
Proline and glycine
they disrupt the regularity of the helix backbone
Examples of primary structure
amino acid polypeptide chain
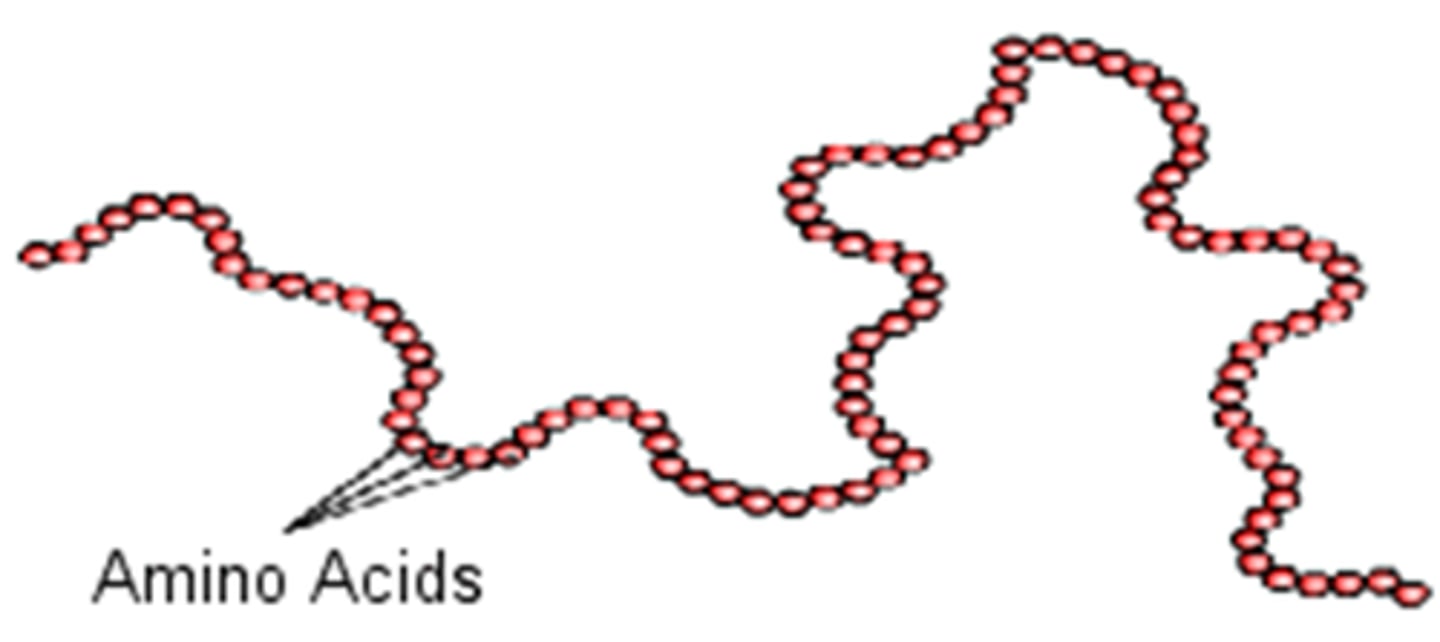

Examples of secondary structure
alpha helix: keratin (hair and nails)
beta sheet: silk fibroin (spider silk)
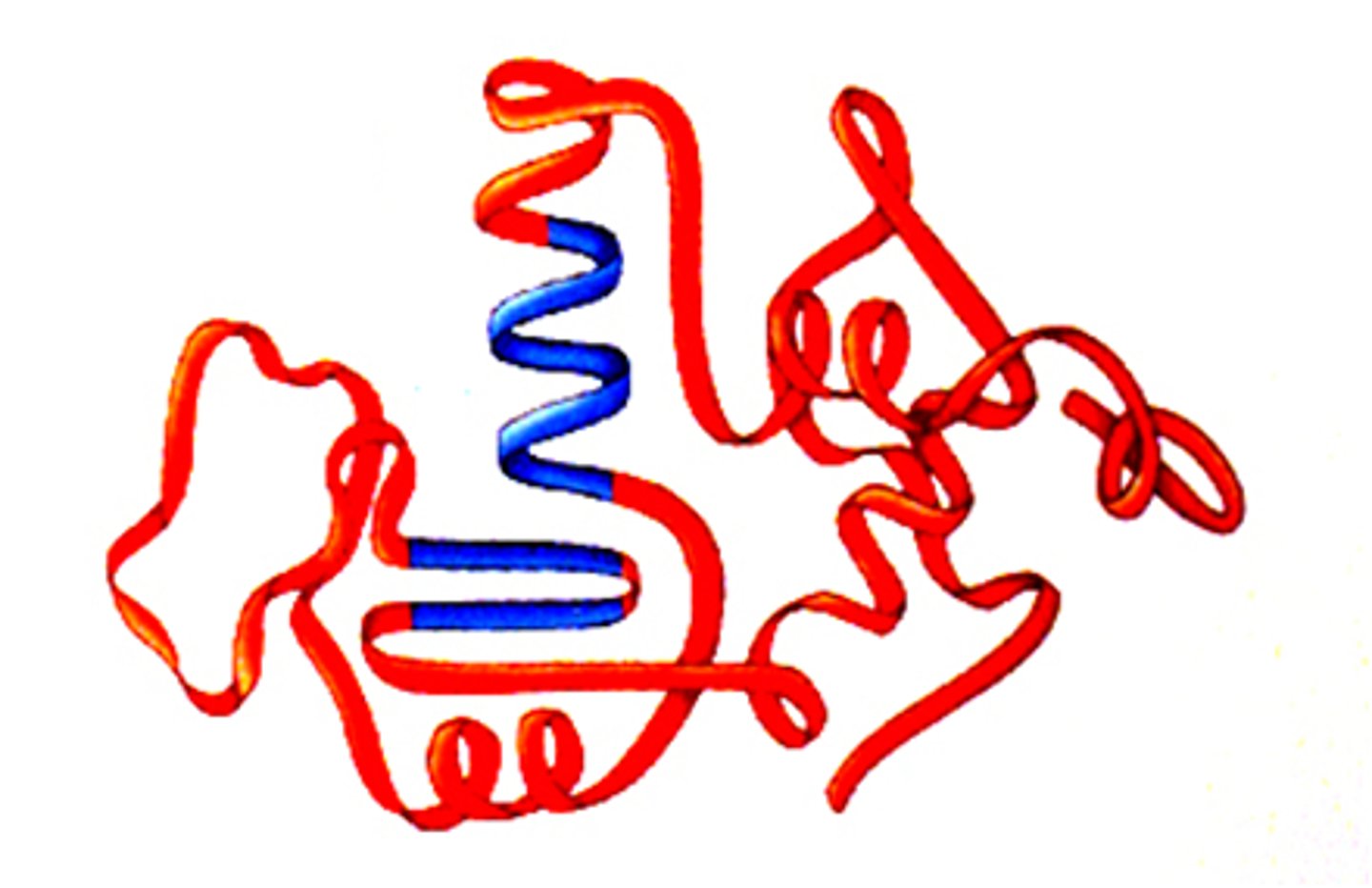
examples of tertiary structure
Myoglobin (single chain globular protein that stores oxygen in muscle)
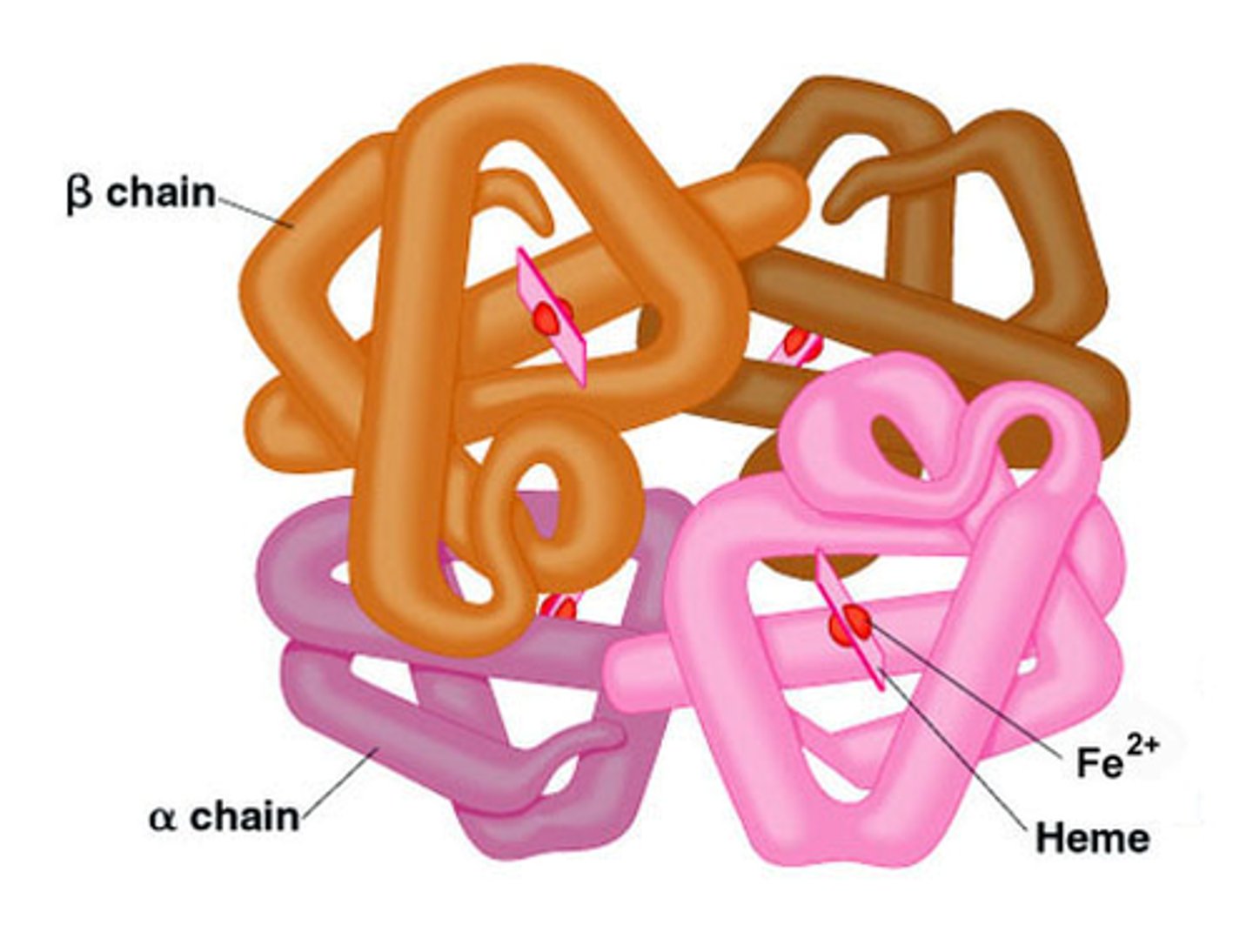
examples of quaternary structure
Hemoglobin (4 subunits (2a, 2B) that carry O2
DNA polymerase
Tell me about immunoglobin: bond type, structure type, function, key things
bond: disulfide
structure: quaternary
function: antibody that bind antigens
key: modular domain allow recognitions of many antigens
Tell me about myoglobin: bond type, structure type, function
bond: hydrophobic interactions
structure: tertiary
function: stores oxygen in muscle
Tell me about hemoglobin: bond type, structure type, function, key point
bond: salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic affect
structure: quaternary
function: transports oxygen in blood
key: shows cooperative binding
What causes sickle cell anemia? What effect does this have?
cause: mutation in hemoglobin beta chain (Glu to Val mutation at position 6)
effect: hydrophobic valine causes Hb to polymerize which equates to the sickle cell
primary structure change affects quaternary structure change which leads to disease
What type of reaction forms a peptide bond?
A condensation reaction (releases H₂O) between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another.
Which atoms are involved in a peptide bond?
The carbon of the carboxyl group and the nitrogen of the amino group (C-N bond).
Why is rotation restricted around the peptide bond?
The peptide bond has partial double bond character due to resonance, which prevents free rotation.
What is the nature of the peptide bond?
It is planar, rigid, and usually in the trans configuration to reduce steric hindrance.
What is the overall result of peptide bond formation in a polypeptide chain?
Formation of a backbone with repeating N-Cα-C units that determines protein secondary structure.
What is the spatial orientation of amino acids in a peptide, with exception of proline?
Amino acids are trans of each other
What is the native state of a protein?
The properly folded, functional 3D structure of a protein under physiological conditions.
Name 4 common causes of protein denaturation.
Heat, pH changes, heavy metals, and SDS (detergents).
What happens to a protein during denaturation?
It loses its 3D structure and function, unfolding into a nonfunctional state.
What does the folding funnel model show?
Proteins fold stepwise from high-energy, high-entropy states to a low-energy, native state, sometimes passing through intermediate forms.
Interaction of N-H and C=O of the peptide bond leads to local regular structures such as
Alpha helix and beta sheets
Which pair of amino acids are strong alpha-helix formers?
Alanine and leucine
In beta pleated sheet peptide chains, H bonds between parallel strands are
Weaker, 1 Kcal/mol
What is the orientation of the R groups of amino acids in beta sheets?
Perpendicular to the axis and trans to each other
What amino acids are most commonly present in beta turns?
Proline and glycine
The beta turn is composed of four amino acid residues. Where does the H bond form in the beta turn?
Between the CO of the first amino acid residue hydrogen bonds with the NH group of n+3 residues from it
The native configuration of a protein is
The lowest entropy state and lowest energy state when folded
If two proteins share a secondary structural motif, then it can be assumed
Nothing in regards to their secondary structural similarities
What can be said about the enthalpy and entropy of a properly folded protein?
Both entropy and enthalpy decrease
Substrate binds to the active site through
Non-covalent interactions
The binding energy of the enzyme for the substrate
Lowers the energy requirement for the reaction to occur
Which kinetic value is experimentally determined?
Vmax
How many classes of enzymes catalyze reactions in the cell?
6
What determines the specificity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
The enzyme-substrate complex, including energy of activation, transition state, and whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
Define the active site of an enzyme.
The specific region of the enzyme where the substrate binds and the reaction occurs, formed by a unique arrangement of amino acid R groups.
What are binding and catalytic sites in an enzyme?
The binding site holds the substrate, while the catalytic site carries out the chemical reaction.
What is an allosteric site?
A site on the enzyme, distinct from the active site, where molecules can bind to regulate the enzyme's activity.
Explain competitive inhibition. What happens to Km and Vmax?
The inhibitor binds to the active site, competing with the substrate. Vmax remains unchanged, but Km increases.
Explain non-competitive inhibition. What happens to Km and Vmax?
The inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site, reducing Vmax but leaving Km unchanged.
What is Km (Michaelis constant)?
The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax.
What does a low Km indicate about enzyme-substrate affinity?
High affinity, as the enzyme requires less substrate to reach half of Vmax.
What role do coenzymes play in enzymatic reactions?
They act as carriers of intermediate products, often derived from vitamins.
What is the energy of activation (EA)?
The energy required to form the transition state in a reaction, lowered by enzymes.
How does an enzyme lower the energy of activation?
By stabilizing the transition state through binding energy released during substrate-enzyme interaction.
What is the transition state in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
The high-energy intermediate state during the conversion of substrate to product, stabilized by the enzyme.
What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions?
Endothermic absorbs energy (ΔH is positive); exothermic releases energy (ΔH is negative).
How are endothermic and exothermic reactions coupled in biological systems?
The energy released from an exothermic reaction drives an endothermic reaction.
What is the induced fit model of enzyme-substrate interaction?
The enzyme changes conformation upon substrate binding to better fit the substrate, as opposed to the rigid "lock and key" model.
What is the role of Mg²⁺ in substrate-level phosphorylation's?
It shepherds the negatively charged phosphate group during reactions like ATP hydrolysis.
What is the equilibrium constant (Keq)?
The ratio of product to substrate concentrations at equilibrium, unaffected by enzymes.