Lecture #6: Neutrophils
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Granulocyte/macrophage progenitor
gives rise to monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils and mast cells
Common myeloid progenitor
Originates from the pluripotent stem cell and gives rise to the granulocyte/macrophage progenitor
Pluripotent stem cell
The origin of every white blood cell; it gives rise to the common myeloid progenitor
Neutrophil location (and %)
Peripheral blood, in about 60-75%
Life-span of neutrophils
short lived, only being in circulation for about 6-12 hours
Neutrophil average diameter
10-20 micrometers
Main function of neutrophils
phagocytose and kill pathogens
Equine neutrophils
white or slightly pink cytoplasm with no visible granules; their nuclei is long, thin and knobby with clumps of condensed chromatin.
Feline neutrophils
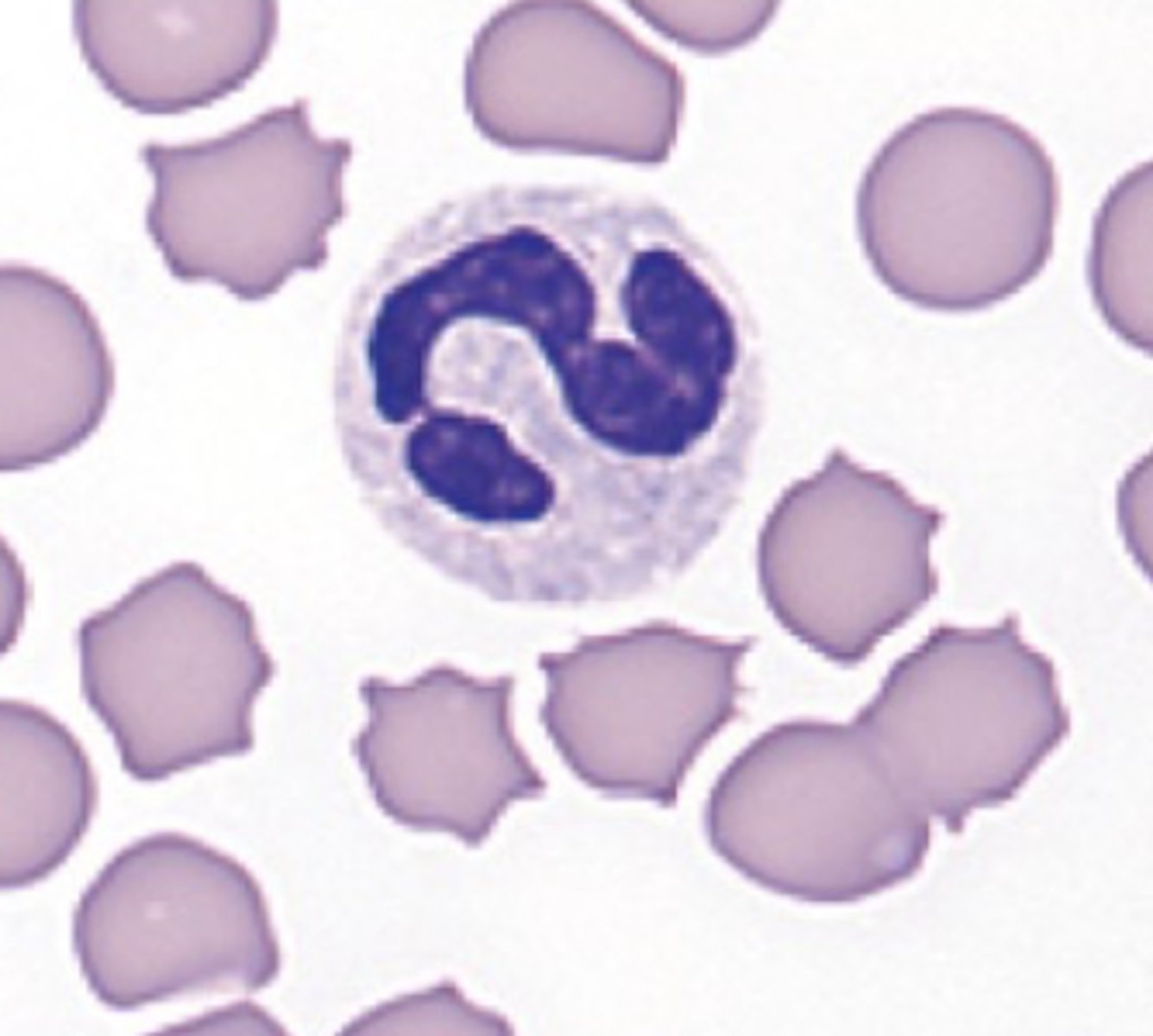
cytoplasm that is white and lacks visible granules
Canine neutrophils
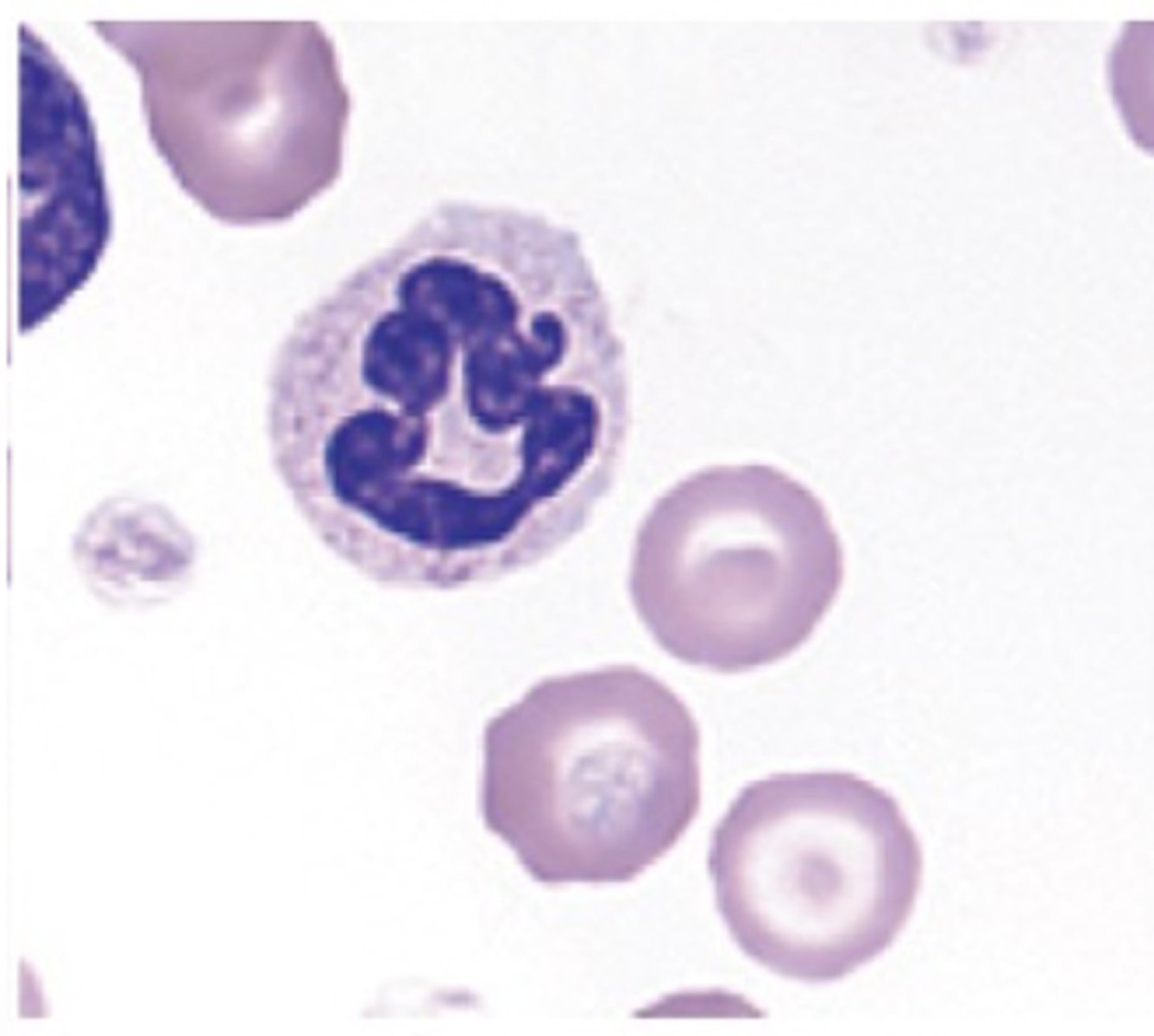
cytoplasm that contains small pink specific or secondary granules
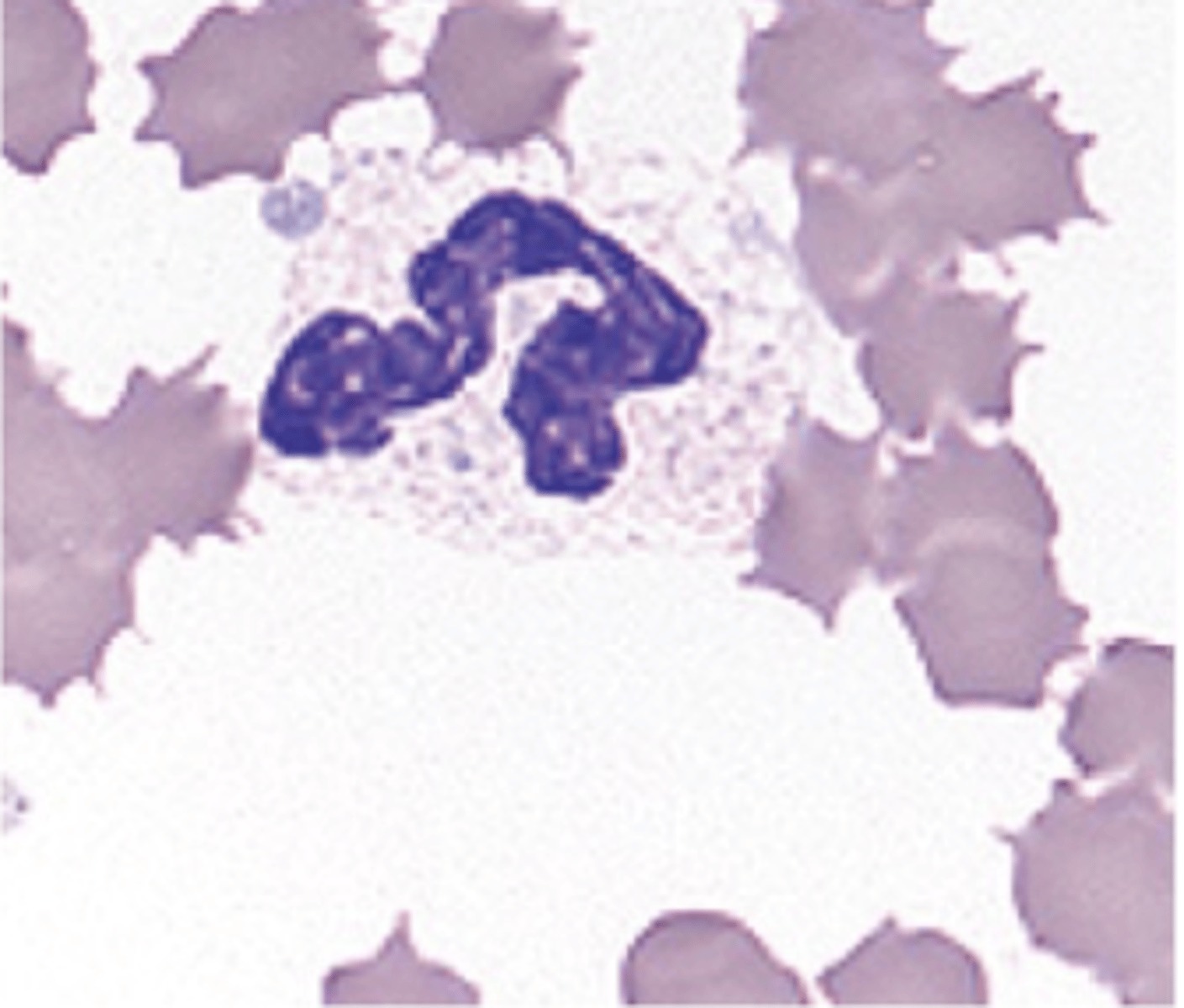
Equine neutrophils (photo)
Feline neutrophils (photo)
Canine neutrophils (photo)
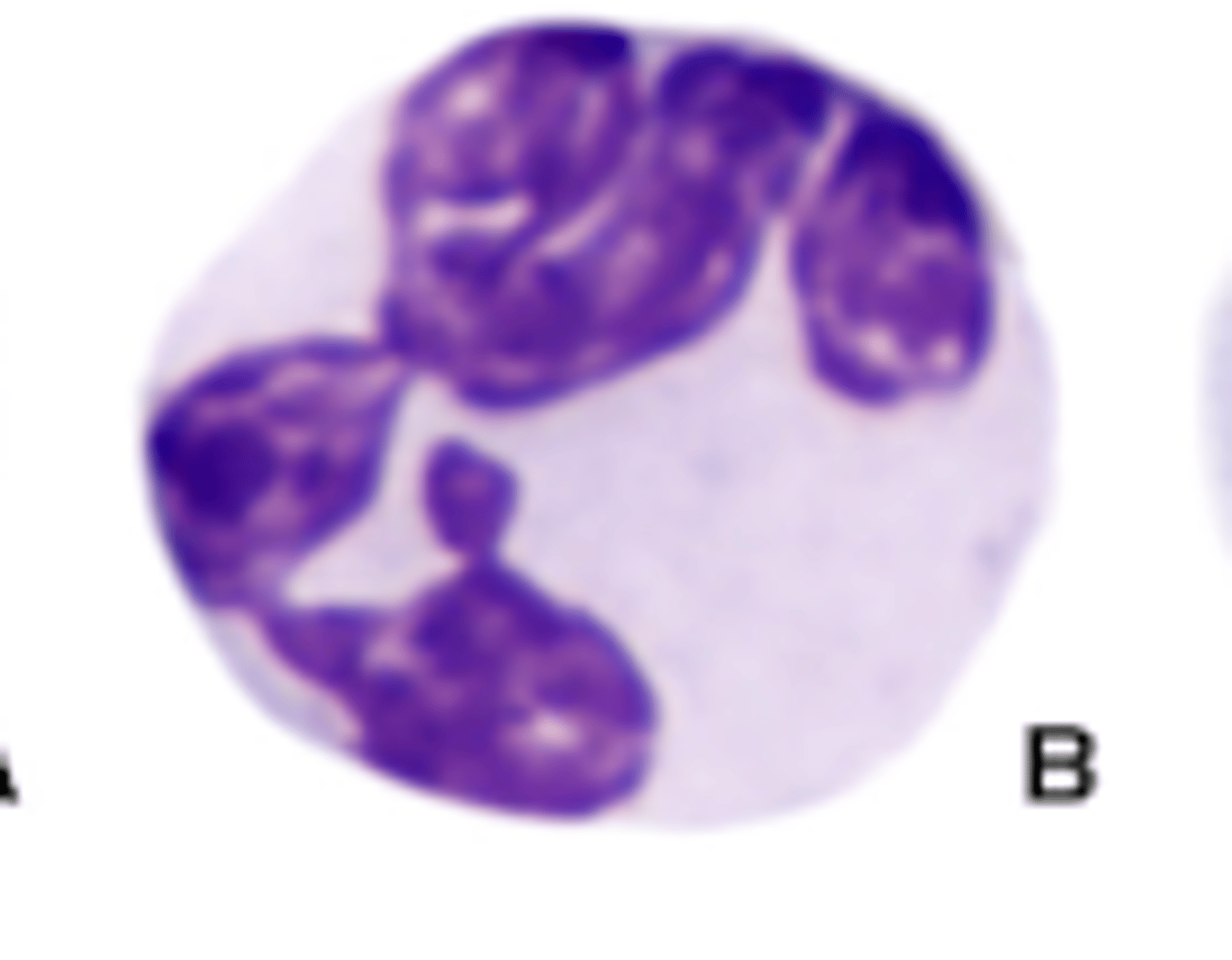
Panther neutrophils (photo)
Foal neutrophils (photo)
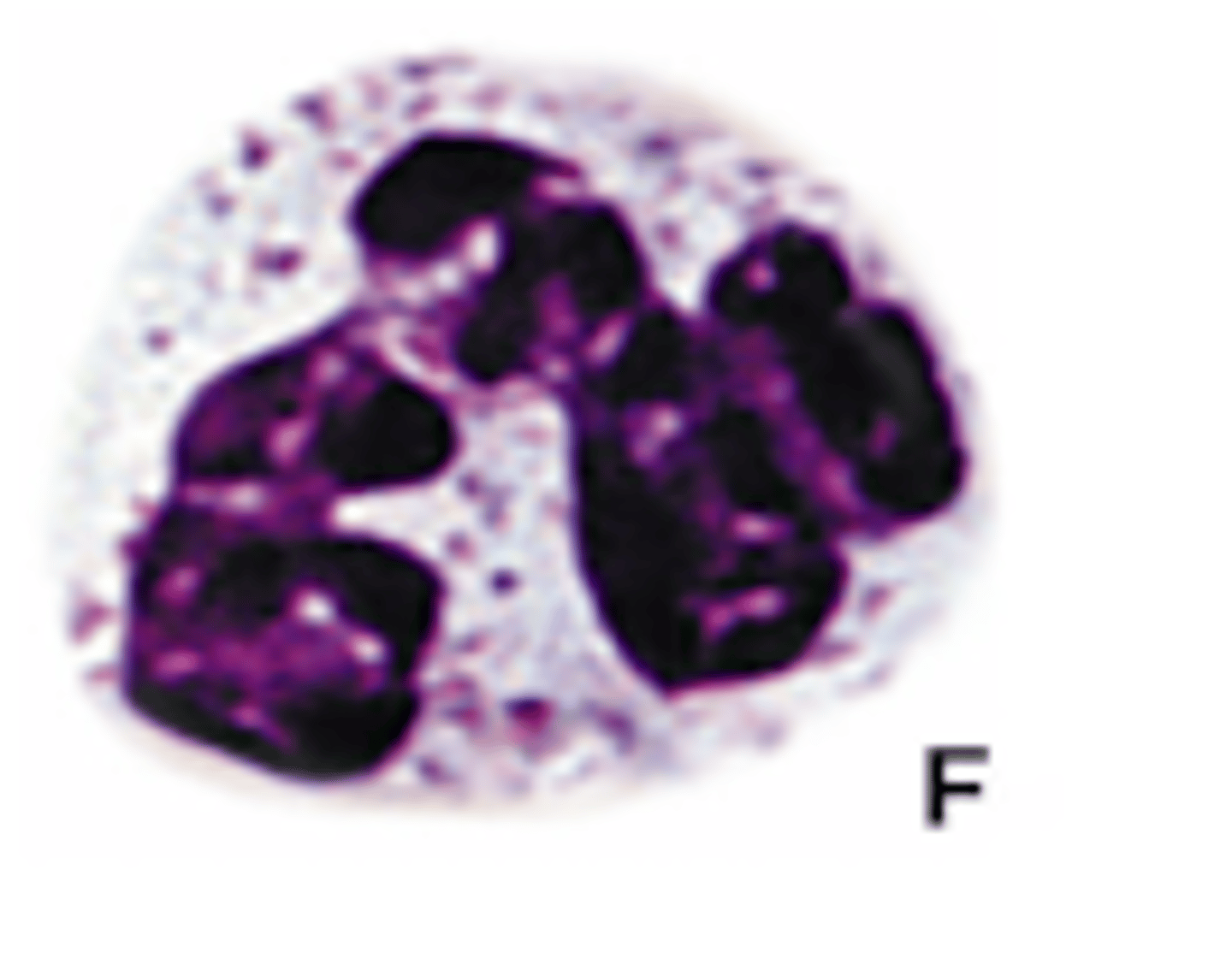
Shark neutrophils (photo)
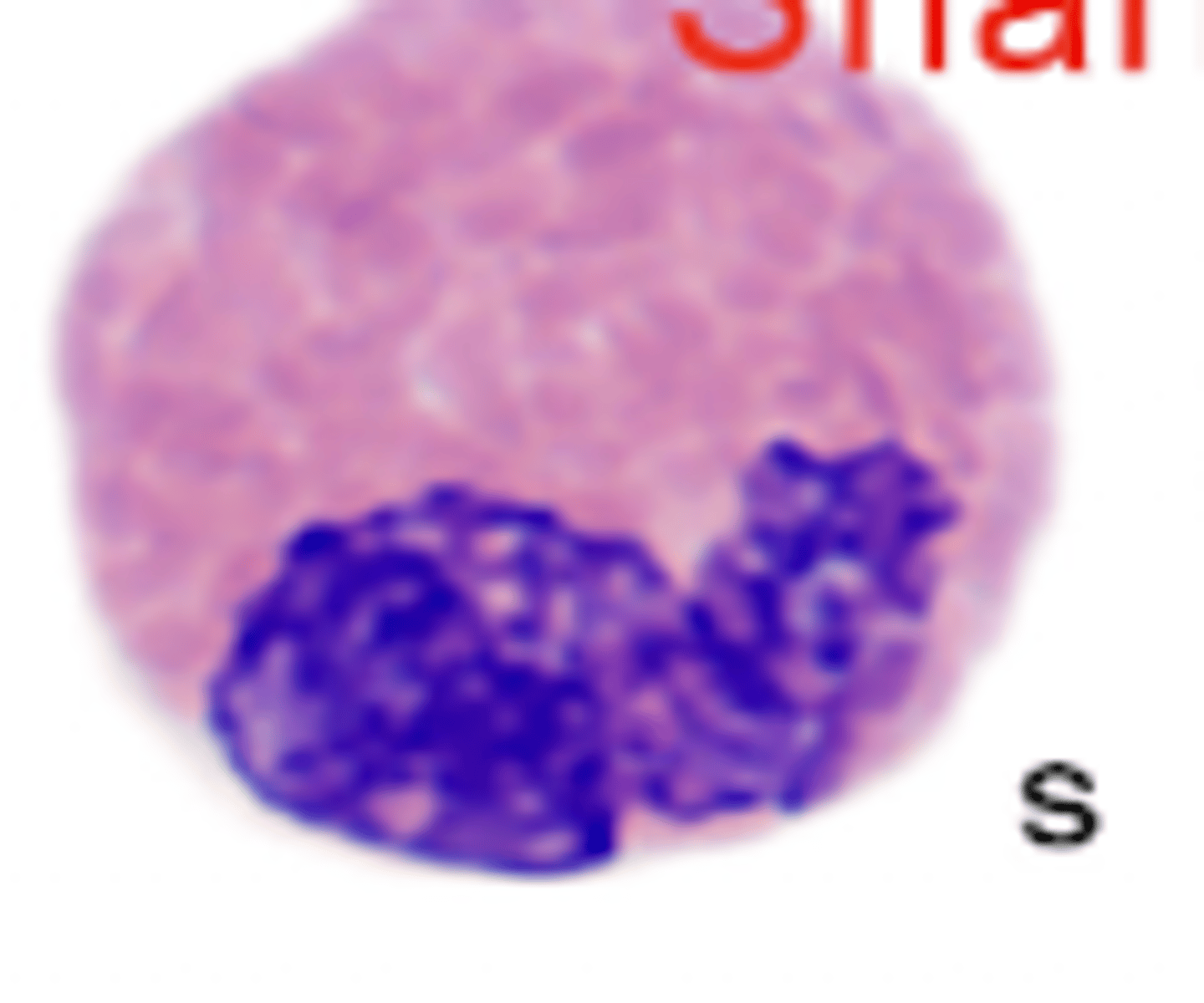
Iguana neutrophils (photo)
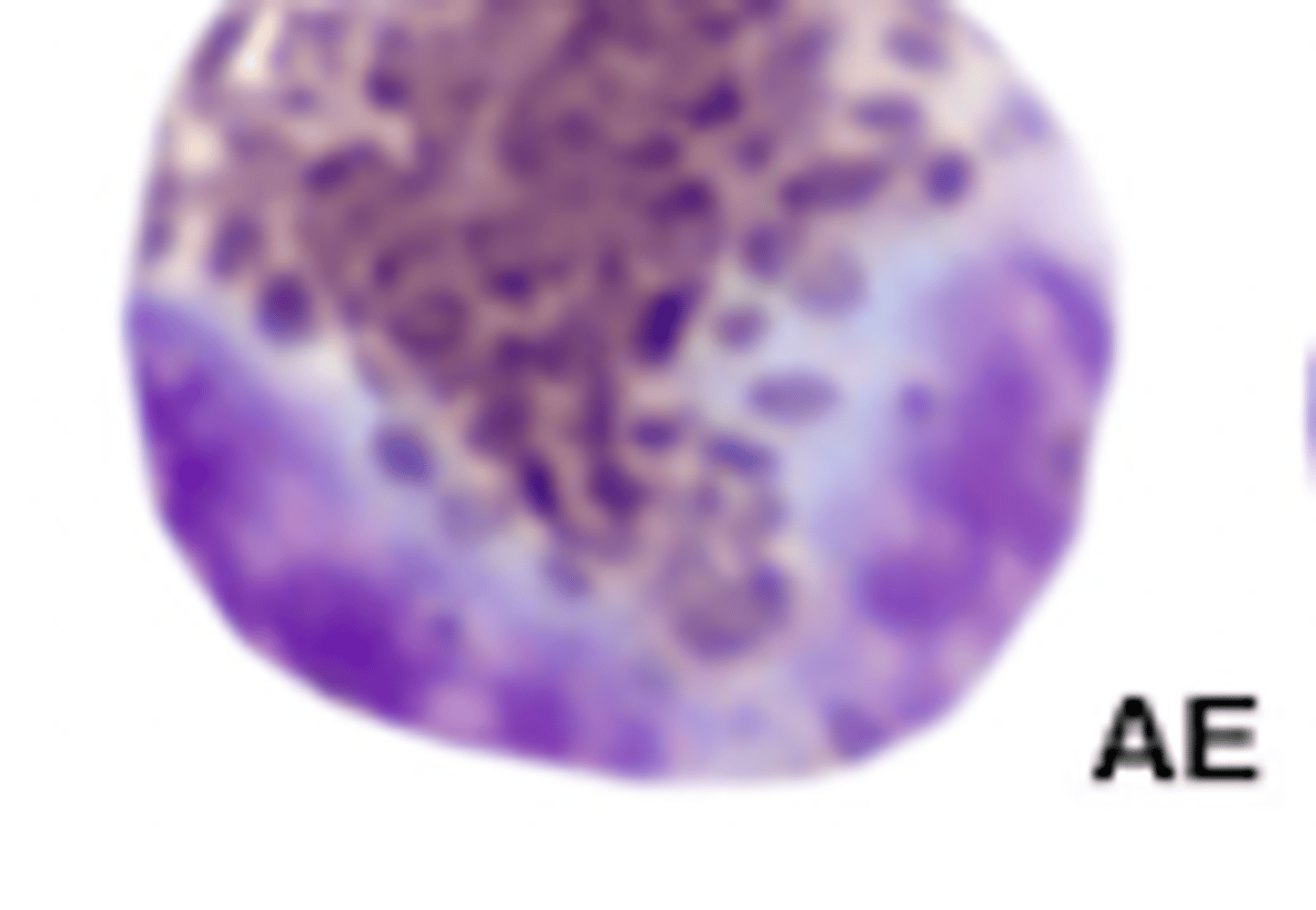
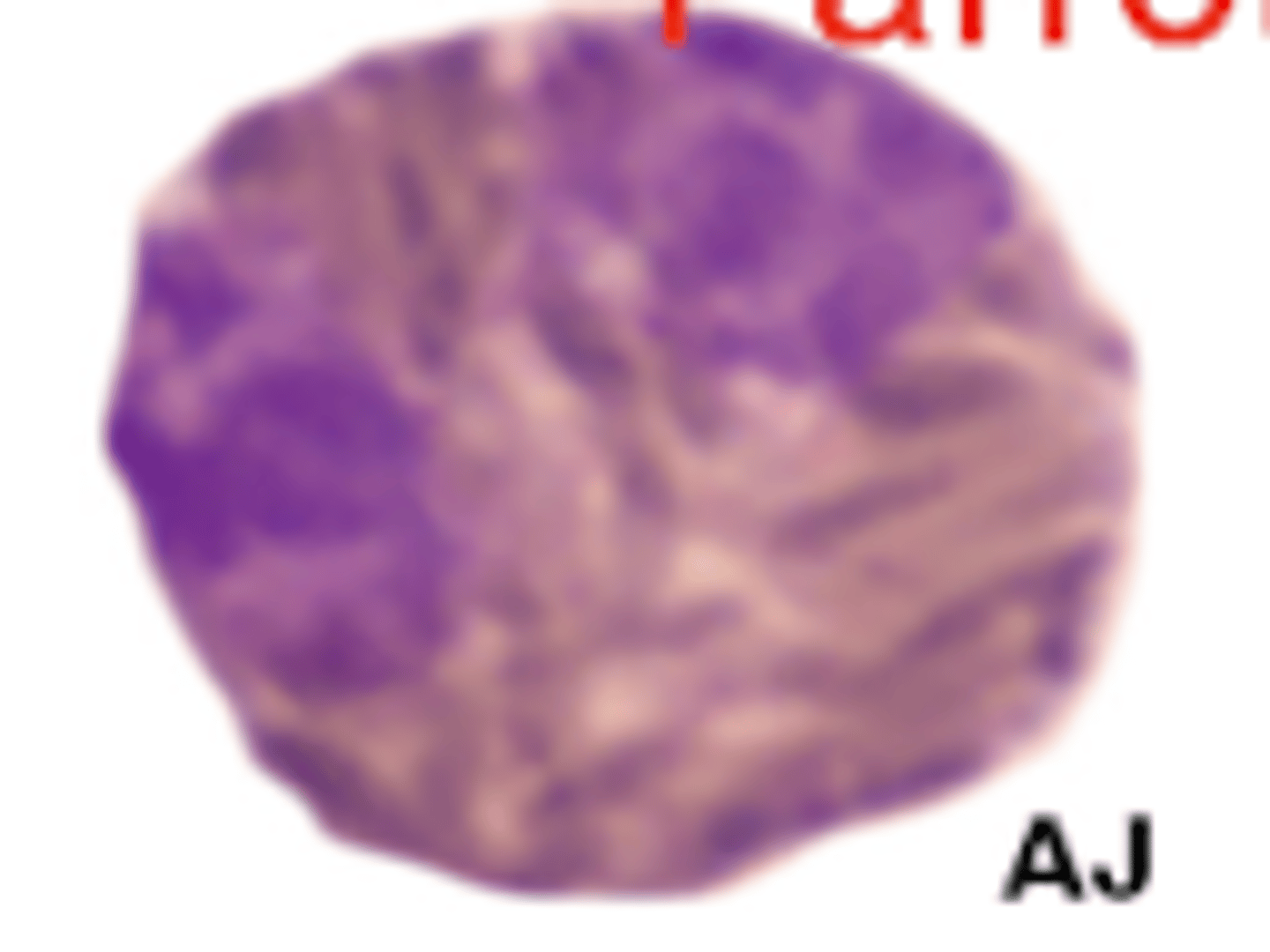
Parrot neutrophils (photo)
Difference of heterophil to neutrophil
granules are large and stained deep orange to red
Granulopoiesis (definition)
Process in which neutrophils are developed
Granulopoiesis (location)
Occurs in the bone marrow
Order of granulopoiesis
HSC --> MPP --> LMPP --> GMP --> Myeloblast --> Promyelocyte --> Myelocyte --> Metamyelocyte --> Band Cell --> Neutrophil
Primary granules include
• Myeloperoxidase
• Lysozyme
• Elastase
• Beta-glucuronidase
• Cathepsin Beta
Secondary granules include
• Lysozyme
• Collagenase
• Matrix metalloprotease-8
Tertiary granules include
• Gelatinase (MMP-9)
• Arginase I
• Cytochrome b558
Location where neutrophils are abundant
liver, spleen, lungs and bone marrow
Extravasation
Process where the neutrophils leave the circulation and migrate through the tissue
Extravasation requirements
requires a defined sequence of interactions between adhesion molecules, while also requiring chemokines to direct the cells to the site of the insult
Emigration from the blood stream requires changes in:
• Endothelial cells
• Neutrophils
• Integrins
• Emigration
What are selectins?
Adhesion molecules of importance during extravasation of white blood cells
Types of selectins
P-selectin and E-selectin, L-selectin
Where are P-selectin and E-selectin found?
Endothelial cells of blood vessels
Where are L-selectin found?
Neutrophils (in this particular case)
Steps of extravasation
• Tethering
• Slow Rolling
• Full arrest
• Firm adhesion
• Intraluminal crawling
• Transmigration
Neutrophils antimicrobial mechanisms
1. Phagocytosis
2. Degranulation
3. NETosis
Phases of phagocytosis
• Neutrophils become activated, which occurs upon
encountering activated endothelium and exposure to
cytokines
• Encounter/adhere to target
• Ingest/engulf target
• Destroy target
What does CD mean in neutrophils
Cluster of differentiation
Most relevant receptors for neutrophils
• Opsonins
• Leukotrienes
• Complement
• Cytokines
• Attaching neutrophils to blood vessel walls
Function of opsonins
coating the microbe, making it positively charged and therefore easier to grab
What charge do microbes and neutrophils both have?
Negative
Where does ingestion of a microbe occur
Within the neutrophil, which engulfs the bacteria
How is the membrane-bound vacuole that contains the bacteria called
Phagosome
Phagolysosome
Junction of phagosome and lysosome
Process by which the microbes inside the phagolysosome are destroyed
respiratory burst and the action of the granule-associated lytic enzymes and antimicrobial peptides
Respiratory burst
consists of using reactive oxygen species, such as O2-, H2O2 and OH-, to damage membranes.
Examples of granule-associated lytic enzymes and antimicrobial peptides
• Proteolytic enzymes: degrade bacteria and tissue
• Lactoferrin: binds iron (which bacteria require)
• Defensins: bactericidal, recruit and activate other WBC
Degranulation
represents a much faster mechanism to kill pathogens; it consists of the release of granules to the extracellular space
Secretory granules used during degranulation would include
proteases, myeloperoxidase, reactive oxygen species, lysozyme and cationic proteins
Secretory granules used during degranulation are characterized by being
some of the most toxic, readily releasable factors
What are NETs
extracellular webs of microbicidal cytosolic and granule proteins assembled on a scaffold of decondensed chromatin or mitochondrial DNA
NET formation is induced by
various pathogenic triggers
Steps of the NET formation pathway (1/2)
• Nuclear delobulation and the disassembly of the nuclear envelope
• Cellular depolarization and chromatin decondensation
• Plasma membrane rupture and release of NETs
Neutrophils fate
short lived with a high rate of spontaneous apoptosis, with most of them only surviving a few days
When does apoptosis of neutrophils occur?
presence of inflammatory stimuli
Which system is in charge of removing the apoptotic neutrophils
mononuclear phagocytic system (macrophages)
The ingestion of neutrophils by the mononuclear phagocytic system (macrophages) triggers and induces:
trigger the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-Beta) and the resolution of the inflammatory process
Benefits of neutrophils
Phagocytosis of pathogens and clearance of dead cells and debris, anti-microbial peptides, influence other cells (T cells) and aid in resolution of inflammation
Detrimental effects of neutrophils
Tissue damage via excessive MPO, NE, MMP production, oxidative burst and NETs, impaired function during co-infections and drivers of asthma exacerbation
Molecules involved in the extravasation process
Selectins, Integrins and Chemokines
Extravasation steps
Rolling, tethering, adhering and transmigration
Steps of phagocytosis
Activation, adherence, ingestion and destruction
Additional antimicrobial mechanisms of neutrophils
Degranulation, NET formation