Something
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
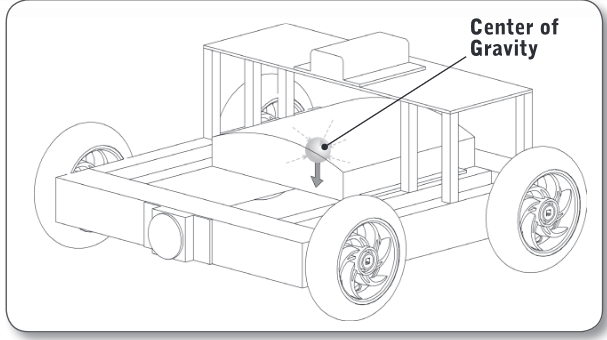
Center of Gravity
the “average position” of all the weight on the robot
\
heavier objects count more than lighter ones in determining where the (____) is, and pieces that are farther out count more than pieces that are near the middle
\
heavier objects count more than lighter ones in determining where the (____) is, and pieces that are farther out count more than pieces that are near the middle
2
New cards
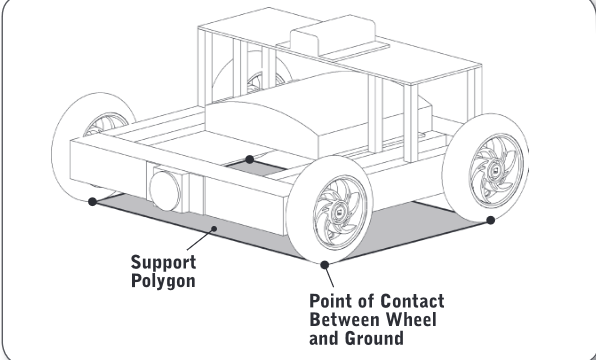
Support Polygon
the imaginary polygon formed by connecting the points where your robot touches the ground (usually the wheels)
\
usually has one per robot
\
usually has one per robot
3
New cards
Stability
the robot will be most (____) when the center of gravity is centered over the support polygon
4
New cards
Fasteners
allow for things to be put together
\
the most common problem with robots that fall apart or lose pieces easily is that groups of parts are not joined securely enough and separate from each other and move around
\
the most common problem with robots that fall apart or lose pieces easily is that groups of parts are not joined securely enough and separate from each other and move around
5
New cards
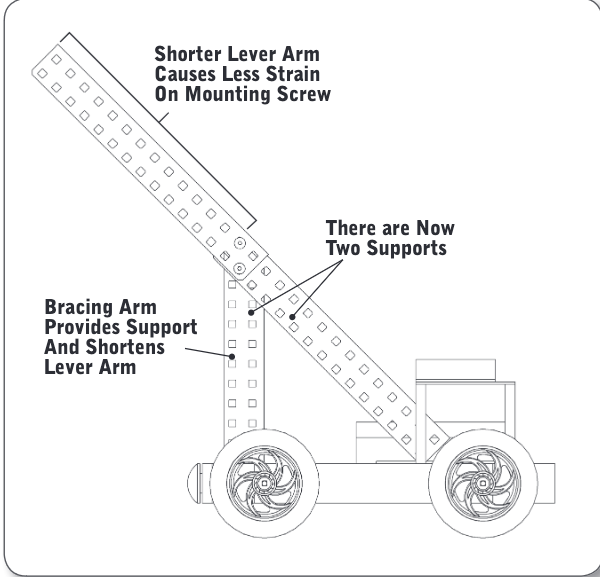
Bracing Arms
provides support and shortens the lever
6
New cards
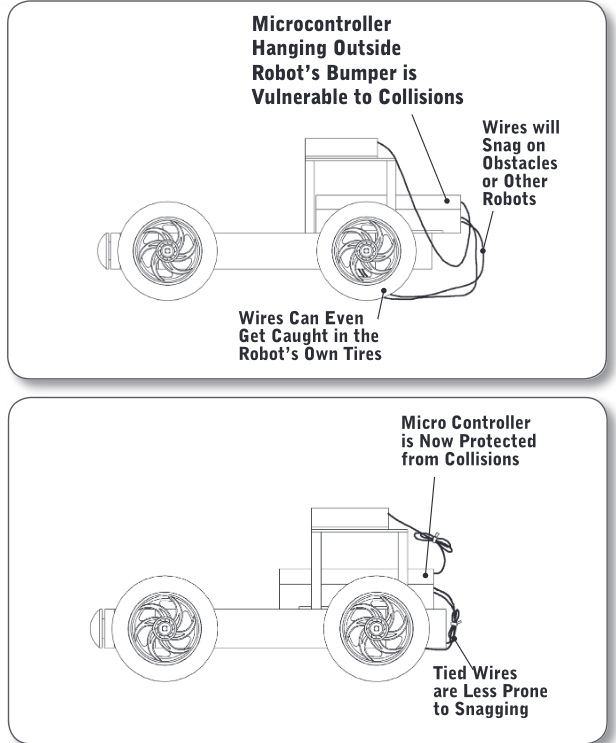
Exposure and Vulnerability
There are certain parts of a robot that are more fragile than others. Always plan the structural design to protect these parts from unwanted physical contact if possible
\
For the best protection ensure all robot components that can be damaged are well shielded and inside robot structure. Route wires inside the robot and away from all moving components.
\
For the best protection ensure all robot components that can be damaged are well shielded and inside robot structure. Route wires inside the robot and away from all moving components.
7
New cards
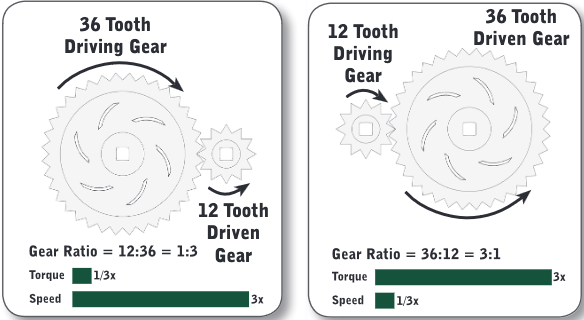
Gear Ratio
a “multiplier” on torque and a “divider” on speed
(3:1) multiplies troque
(1:3) divides torque
\
Driven/Driving
Out/In
(3:1) multiplies troque
(1:3) divides torque
\
Driven/Driving
Out/In
8
New cards
Mechanical Advantage
The ratio of the force a machine can exert to the amount of force that is put in. It can also be thought of as the “force multiplier” factor that a mechanical system provides
9
New cards

Idler Gears
inserted between the driving and driven gears
\
have no effect on the robot’s gear ratio
\
used to change the direction of spin and fill space between gears
\
have no effect on the robot’s gear ratio
\
used to change the direction of spin and fill space between gears
10
New cards
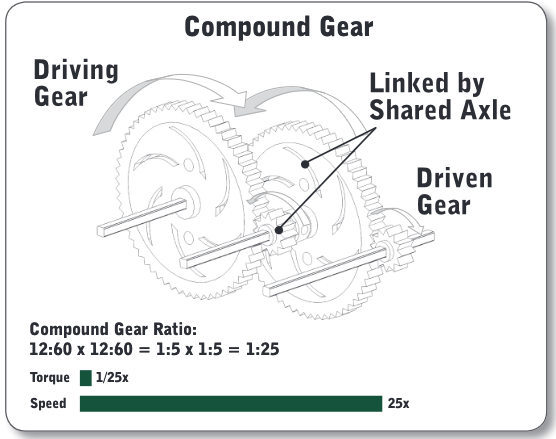
Compound Gear Ratio
formed when you have more than one gear on the same axle
\
Each pair has its own gear ratio, but the pairs are connected to each other by a shared axle
\
calculated by multiplying the gear ratios of each of the individual gear pairs
\
Each pair has its own gear ratio, but the pairs are connected to each other by a shared axle
\
calculated by multiplying the gear ratios of each of the individual gear pairs
11
New cards
Gear ratio with non-gear systems
(belt-and-pulley drives & chain-and-sprocket drives)
(belt-and-pulley drives & chain-and-sprocket drives)
Belt or chain drives are often preferred over gears when torque is needed to be transferred over long distances.
\
Unlike spur gear reductions, (____) reductions do NOT reverse rotation
\
Unlike spur gear reductions, (____) reductions do NOT reverse rotation
12
New cards
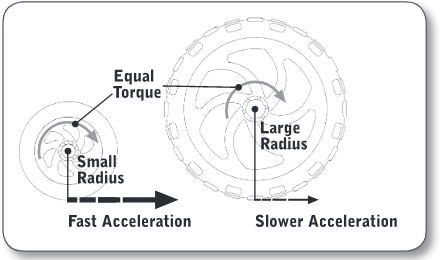
Wheel Sizes and Acceleration
bigger tires give you slower (____), while smaller tires give you faster (___).
\
motor generate a spinning force which wheels convert into a pushing force
\
Force = Torque/Wheel Radius
\
motor generate a spinning force which wheels convert into a pushing force
\
Force = Torque/Wheel Radius
13
New cards
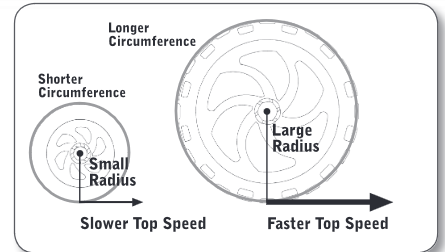
Wheel Sizes and Top Speed
rolling father per rotation allows for faster (___)
\
Speed = Circumference \* (turns/secs)
\
Speed = Circumference \* (turns/secs)
14
New cards
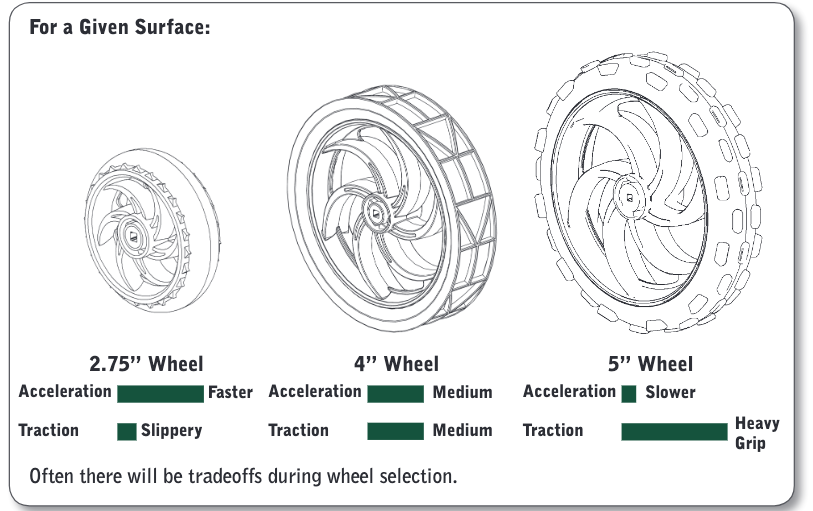
Friction
occurs everywhere two surfaces are in contact with each other
\
Wheel (___) has both positive and negative consequences for your robot. On the one hand, (___) between the wheel and the ground is absolutely essential in getting the robot to accelerate
\
Wheel (___) has both positive and negative consequences for your robot. On the one hand, (___) between the wheel and the ground is absolutely essential in getting the robot to accelerate
15
New cards
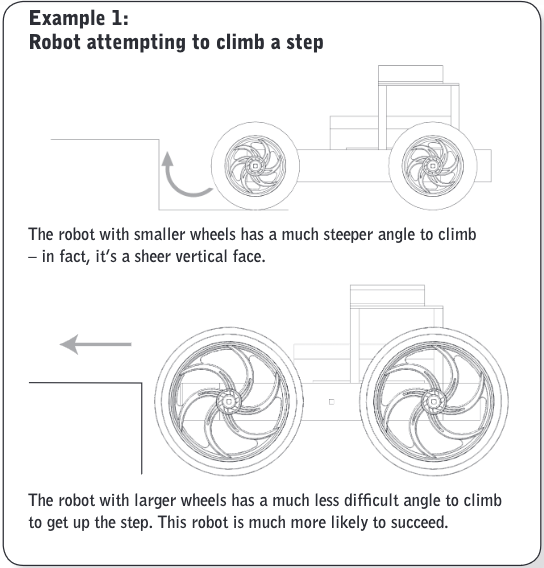
Terrain
Both the size of a tire and the amount of friction it generates will be very important in ensuring that you can successfully navigate over them.
16
New cards
Clutches
are designed to protect the gears internal to the motor from “shock-loads”.
\
once it pops for the first time, it is easier for it to pop every time after that; for some robotics applications it may be necessary to regularly replace it in key areas.
\
ALWAYS recommended
\
When it pops, it is doing its job.
When it pops, it is a sign that there is something wrong with the robot design.
\
once it pops for the first time, it is easier for it to pop every time after that; for some robotics applications it may be necessary to regularly replace it in key areas.
\
ALWAYS recommended
\
When it pops, it is doing its job.
When it pops, it is a sign that there is something wrong with the robot design.
17
New cards
First Use of a Battery
remember to let them charge fully before you use them the first time because they are usually shipped uncharged
18
New cards
Memory Effect
refers to a mistaken belief that total battery capacity diminishes PERMANENTLY by a failure to drain the battery to ZERO voltage and then recharge it to full
\
does not exist in consumer devices, only in very specific laboratory conditions.
\
does not exist in consumer devices, only in very specific laboratory conditions.
19
New cards
Voltage Drop
a measurable phenomenon where a battery that is repeatedly “shallow discharged” (used only part way before recharging) will start delivering lower and lower voltages, and will run out sooner
20
New cards
Discharge Cycles
to fix voltage drop drain/recharge and recharge the battery a few times
21
New cards
Overcharge
can cause permanent damage to the battery by (____)
important that you get a good NiCd charger that knows when to stop adding charge to the batteries.
important that you get a good NiCd charger that knows when to stop adding charge to the batteries.
22
New cards
Trickle Charge
a charger should switch over into (____) mode
a low current mode that can be safely applied over a long period of time to maintain a full charge, or shut off \n the charger
a low current mode that can be safely applied over a long period of time to maintain a full charge, or shut off \n the charger
23
New cards
Temperature
Charging or draining batteries quickly will result in them heating up
\
Excessive heat can cause permanent damage to the battery
\
Do not store batteries in high temperature conditions
\
If batteries are hot after charging or running, let them cool down before charging or running
\
Excessive heat can cause permanent damage to the battery
\
Do not store batteries in high temperature conditions
\
If batteries are hot after charging or running, let them cool down before charging or running
24
New cards
Age
Rechargeable NiCd batteries can be used over and over again for hundreds of battery cycles if properly maintained
\
HOWEVER all batteries will eventually wear out over time
\
HOWEVER all batteries will eventually wear out over time
25
New cards
Environmental Issues
The cadmium found in NiCd batteries is highly toxic, and should not be disposed of in the trash. It is illegal to do so in many countries and states.
26
New cards
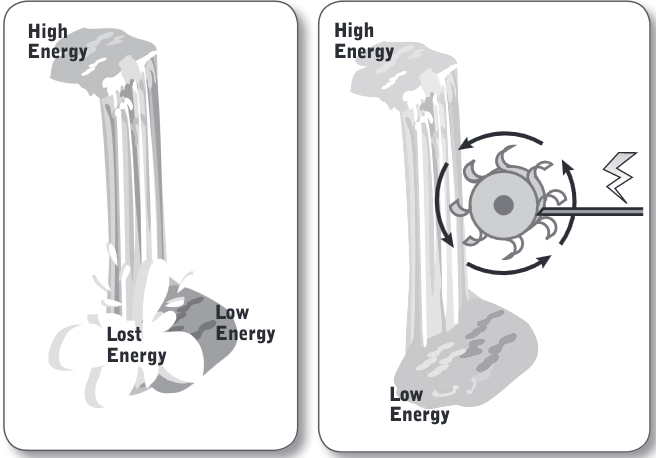
Gravitational Potential Energy
When the water was up on top of the cliff, it had a lot of (____), energy that was stored in the water because it was high up even though gravity wanted to pull it downwards
27
New cards
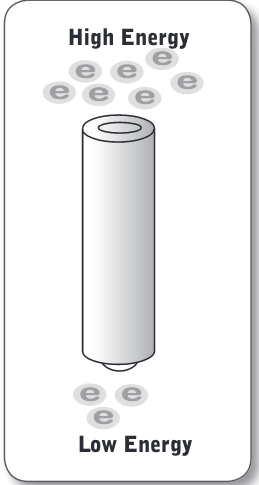
Electrons
have negative charges, and naturally move \n toward areas with positive charges because opposite charges attract
28
New cards
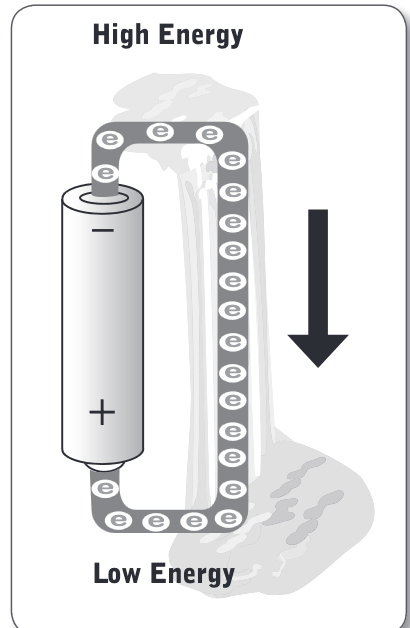
How Batteries Flow
Tne end (the “–“ side) holds electrons at an area where they have high potential energy, just like the top of the cliff. The other side (the “+” end) is like the bottom of the cliff, an area of low potential energy that the electrons would like to travel toward.
\
The battery doesn’t just let the electrons travel freely from the high-energy end to the low-energy end. You need to provide a path for the electrons in order to let them get from one end to the other by connecting the battery to a circuit. The wire provides a path for electrons to get from the “–” side to the “+” side.
\
The battery doesn’t just let the electrons travel freely from the high-energy end to the low-energy end. You need to provide a path for the electrons in order to let them get from one end to the other by connecting the battery to a circuit. The wire provides a path for electrons to get from the “–” side to the “+” side.
29
New cards
Batteries in Series
add battery their voltages together
\
how multiple AA batteries (which are 1.2-1.5V each) produce a single larger “battery pack”
\
how multiple AA batteries (which are 1.2-1.5V each) produce a single larger “battery pack”
30
New cards
Battery Cells
Individual batteries (like a single AA) are often called (____), to distinguish them from the entire “battery” pack.
31
New cards
Analog Sensors
can detect and communicate any value in a range of numbers
(____) = Shades of Gray and Black and White
(____) = Shades of Gray and Black and White
32
New cards
Digital Sensor
can only detect two values, maximum and minimums
(____) = Black or White
(____) = Black or White
33
New cards
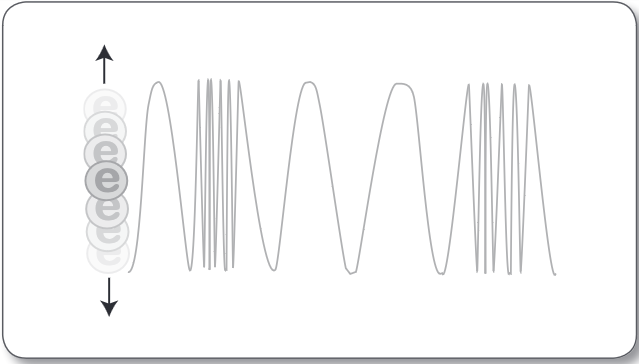
Electromagnetic Waves
When electrons accelerate, they radiate an electromagnetic signal that moves at the speed of light. By accelerating and decelerating electrons in a controlled pattern, a wave pattern can be generated in the radiated electromagnetic field. These are called (____)
\
Good at carrying information quickly from one place to another
\
Good at carrying information quickly from one place to another
34
New cards
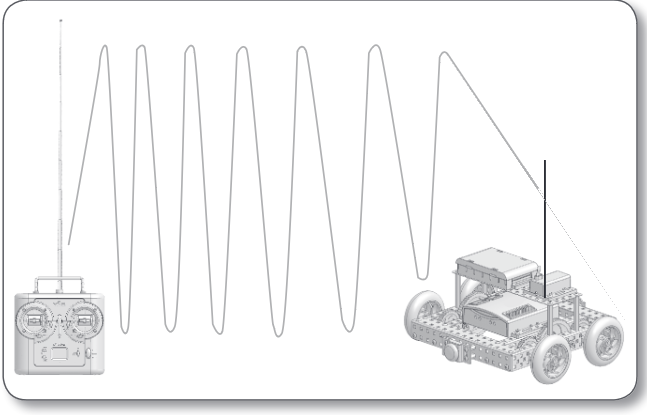
Frequency Modulation (FM)
The VEX Radio Transmitter uses an electromagnetic wave with a certain frequency to transmit data to the RF receiver module.
\
Is a way of encoding information in wave patterns such as these.
\
Is a way of encoding information in wave patterns such as these.
35
New cards
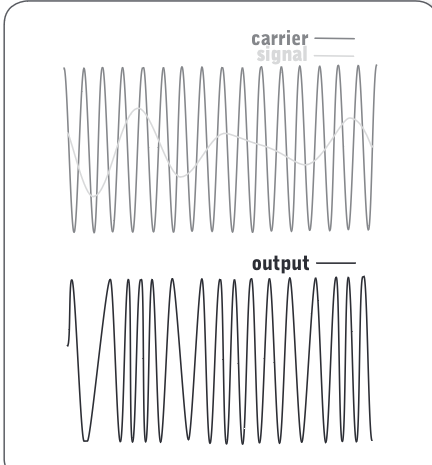
Frequency-Modulated Signals
The frequency of the basic wave, known as a carrier wave, is modified by combining it with another signal known as the modulating wave. This produces a final wave that looks irregular, but is really carrying the data from the signal wave on top of the carrier wave.
36
New cards
AM vs FM
(______) is less susceptible to interference than other radio transmission methods, such as amplitude modulation (______) or direct transmission of the signal wave.