Cell Test
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
3 parts of cell theory
All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells
The cell is the basic unit of structure of organization in organisms
All cells come from preexisting cells
Golgi Apparatus
receives, modifies & sorts proteins for transport (made up of flat vesicles that package things to be transported around or leave the cell)
Ribosomes
little grains floating around inside the cell where proteins are synthesized
In all cells (pro&eukaryotes)
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Series of membranes involved in protein synthesis
ER works with ribosomes to produce proteins for secretion (series of folded membrane pathways spotted by ribosomes)
Smooth ER stores CA++ & detoxifies
Chloroplasts
membrane bound organelle found in plants & algae
uses sun’s energy to convert CO2 to glucose (photosynthesis)
Cell (plasma) Membrane
A selectively permeable/semipermeable membrane that determines what gets into/out of the cell
(boundary between internal & external)
Cilia & Flagella
Flagella: Single tail
Cillia: many tails (looks hairy)
Hairlike projections used for cell movement through liquid or moving the liquid itself around
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound packets of hydrolytic enzymes (vesicles with digestive enzymes) that break down waste, foreign invaders, old cell parts etc.
Nucleus
Contains the DNA (DNA codes for proteins) & all our genetic info
Cell Wall
provides structural support to plant cells (& fungi)
Mitochondria
have double membrane that folds in on itself forming little finger-like projections called cristae, break down sugars into ATP through chemical conversion which is used as cell energy
Solution
A liquid with one or more substances dissolved in it
Solvent
liquid that the solute is dissolved in
Solute
Substance dissolved in a solution
Concentration
how strong it is→the solute/volume (percentage)
more particles=higher concentration
For cell to survive
concentration solutes
Concentration gradient
Occurs when there is a difference in concentrations
Diffusion
particles move high→low concentration to reach an equal concentration (equilibrium on each side)
Passive Transport
Molecules move high→low (no energy)
with/along/down concentration gradient
Active Transport
Molecules low→high (with energy)
against/up concentration gradient
Equilibrium=no movement?
No, molecules are constantly moving but net movement=zero
Which direction do particles move in?
molecules move randomly but net movement high→low
1 Type of Transport: Simple diffusion
Transport protein used?
No
Direction of Movement?
with concentration gradient (high→low)
Requires energy input from cell?
No
Types of substances?
CO2, O2 (small molecules)
Classification of transport?
Passive
2 Type of Transport: Facilitated Diffusion
Transport protein used?
Yes: channel proteins/carrier proteins
Direction of movement?
With concentration gradient
Requires energy input from cell?
No
Types of substances?
Glucose, water, (large polar) or ions (NA+)
Classification of Transport?
Passive
3 Type of Transport: Active Transport
Transport proteins used?
Yes: Pumps
Direction of Movement?
Against concentration gradient (low→high)
Requires energy input from cell?
Yes (ATP)
Types of Substances?
NA+ ions & K+ ions
Classification of transport
Active
Endocytosis
Process of taking material into the cell by folding in pockets of the cell membrane into pouches called vesicles by forming a vacuole around it
Phagocytosis
endocytosis involving large solid particles
Pinocytosis
endocytosis involving liquid
Exocytosis
the process of removing material out of the cell where vesicles merge with the cell membrane to release contents, expelling waste from a vacuole
Osmosis
The diffusion of water
through aquaporin proteins
with concentration gradient (high→low) of water
no additional cell energy required
passive transport
Water vs. Salt
Water goes towards salt (salt sucks)
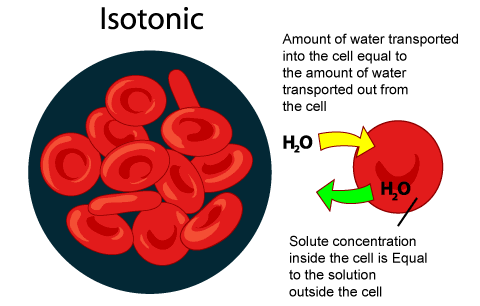
Concentration strength: isotonic
the solution & the cell have the same solute concentration strength-no osmosis
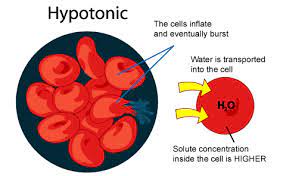
Concentration strength: Hypotonic
the solution with lower solute concentration (out→in)-causes osmosis
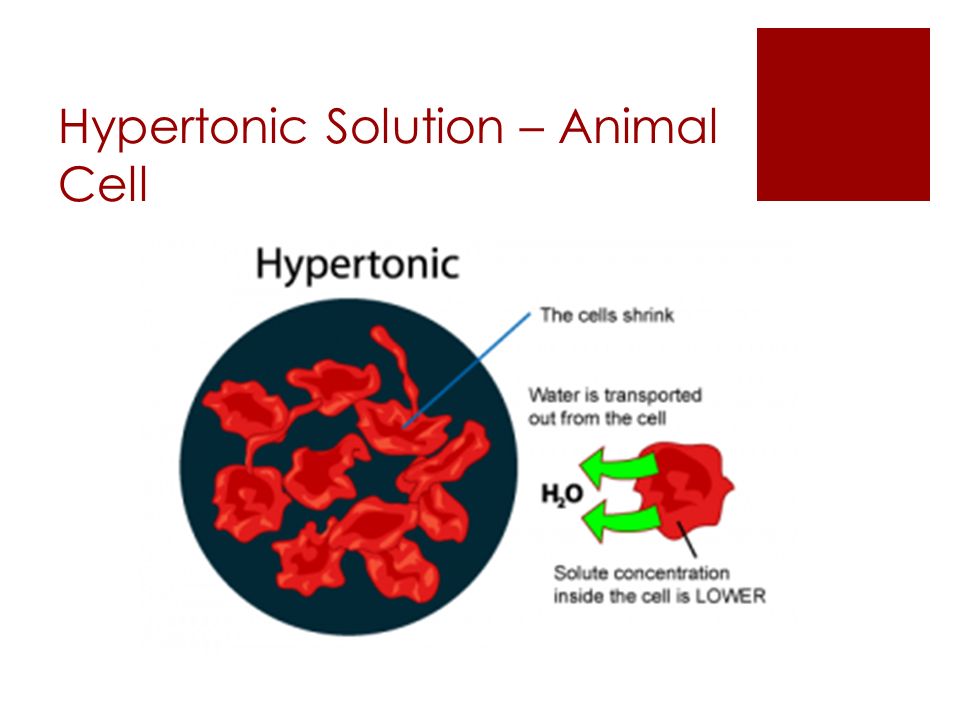
Concentration strength: hypertonic
the solution with the higher solute concentration (salt=solute) (in→out)-causes osmosis
Homeostasis (water balance)
maintaining internal environment water & solute concentrations
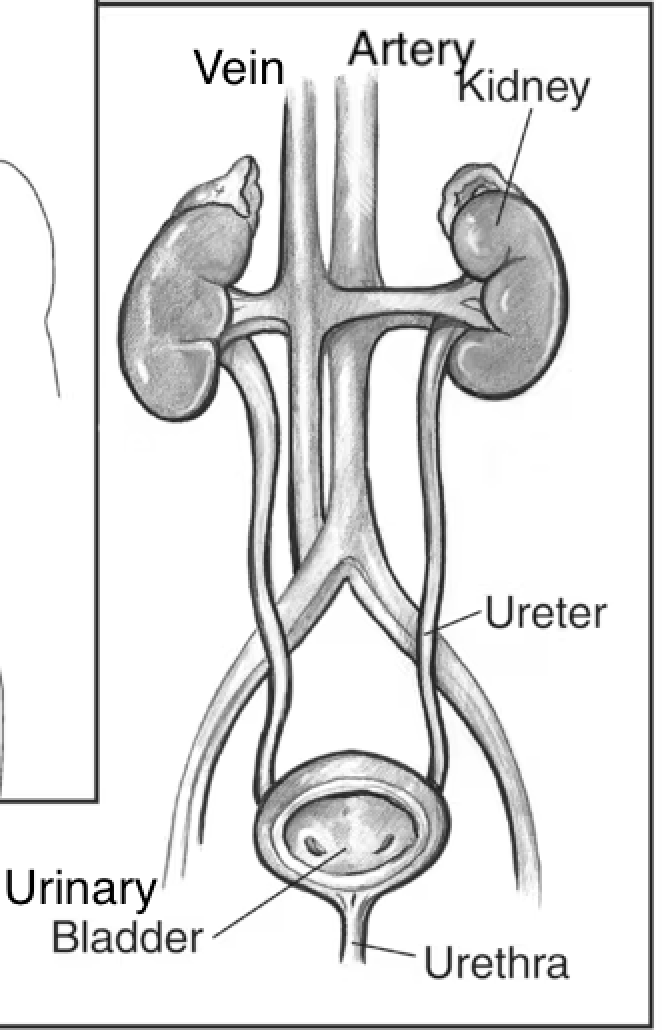
Excretory system
accomplishes both water balance & waste removal (several organs are important in removing waste from the body)
Liver: converts excess protein into urea→ Kidneys: remove unwanted substances such as urea, excess water & salt
Urea
Excess amino acids in body are broken down by liver→ammonia→urea
process is important because it converts toxic ammonia→urea (less toxic)
Once formed urea is transported by the circulatory system to the kidneys
The kidneys filter the blood, removing urea & excess water & salt, which forms urine
Urine is stored in the bladder before being excreted from the body
Path of Nitrogenous Waste
Cells break down proteins→Ammonia→Liver→Urea→Kidneys→Urine
Nuclear membrane
Membrane surrounding the nucleus that determines what goes in and out of it
Cytoplasm
watery medium in which all organelles float
vacuoles
large membranous sacks for storing things
Channel protein
Transport protein that provides a tube-like opening in the plasma membrane through which particles can diffuse
Carrier protein
transport protein that changes shape when a particle binds it (sodium & potassium ions)
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney (millions)
concentrate/remove waste from the blood & reclaim liquid + important nutrients
Purpose of kidney
keep what’s beneficial
eliminate waste (urea)
balance water
Filtration 1st stage Kidney nephron
blood cells, platelets, other large components stay in blood vessels
Filtrate (stuff first collected): water, urea, uric acid, glucose, amino acids, salts etc. are forced into Bowman’s capsule (glomenular capsule)
cells stay in blood, liquid plasma w/dissolved solutes goes into glomerulus
Reabsorption 2nd stage Kidney
Reabsorption from the liquid filtrate to the blood can occur by passive or active transport
Filtrate descends down from the loop of Henie (loop of the nephron) & as it moves, important molecules & ions are reabsorbed into the blood
Active Secretion step 3 Kidney
Some substance are moved by active transport from the blood into the loop of the nephron to the eventual urine
How is osmoregulation achieved?
Filtrate moves through the nephron down the loop, water moves by osmosis from the nephron to the fluid & is taken up by the cappilaries)
outerpart less salty-kidneys
innter part very salty (hypertonic)-kidneys
As traveling down the kidney, solution becomes more concentrated, kidney also becomes more concentrated to utilize osmosis
salt gradient purpose: to pull/reclaim the water (produced by active transport & passive transport)
Water is pulled out of the filtrate & reclaimed by osmosis
Lower abdominal area
Phospholipid bilayer
two layered arrangement of phospholipid molecules forming cell membrane
Phospholipid’s composed of hydrophilic head & two hydrophobic fatty acid tails
Aquaporin
Several proteins found in cell membrane that selectively permit water to pass in and out of the cell
Glycoproteins
identify cells as familiar or foreign, help cells bind