Greek Theatre
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Why were plays held
Performed in religious festivals
Associated with the worship of Dionysus
(He was only featured in 4% of the plays)
Polis
A city-state in ancient Greece.
Lenaea
A drama festival (contest) held in Athens
Late January
Comedy took precedence (some tragedy)
Attica
Area around Athens
Delian League
military alliance led by Athens
Rural Dionysia
Drama festival held in the rural communities of Attica
In midwinter
Deme
Village or district of Attica
City Dionysia (purpose)
-Most important dramatic festival in late March
-Organised by eponymous archon:
Prep began a year in advance, trag writers present 4 synopsis and com present 1 > 3 trag were selected 5 com
Selected choregos (from elite)
-Entry was a days wage for an unskilled worker (2 obols) > excluded > state established a Theoric fund to pay for the poorest (democratic contest)
-Front row seats reserved for 500ish state officials
-4th cen divided to allow tribes to sit together (there are 13 sections but 10 tribes, women slaves foreigners?)
-Unclear if women were allowed
PURPOSE
-Marks coming of spring (D associated with regrowth + theatre)
-Reopening of sea lanes > chance to show off city to foreigners
Choregos
-Backer of a playwright
-Responsible for financing the production
(records of spending 3,000 in 410 and 1,600 drachmas in 401)
-Gained prestige
-Had to select members for the chorus, feed them, find rehearsal accomodations
-If the playwright wasn't skilled he would hire a trainer
-If the playwright won his choregos would finance a victory monument (his name would be inscribed too!)
Proagon
Preview event where plays were announced and synopses delivered
Dithyramb
Choral dance in honor of Dionysus
Tribe
Political division in Athens
All citizens were members
There were ten
Kômos
Loosely organized revel through the streets with song and dance
Theorie Fund
Established by the Athenian state
Paid for the poorest citizens to attend the theatre
Pompé
Grand religious procession
Eponymous archon
Leading politician of Athens
Responsible for running the City Dionysia
Would select 5 comics and 3 tragic writers (who wrote 3 tragedies and a satyr)
City Dionysia summary
BEFORE- Proagon (previews in Odeian), torchlight processions with wooden D statue from shrine on Elutherean mysteries (would stay in theatre to symbolise his presence)
1- Pompe, bull sacrifice, dithyrambic contests, komos
2-Opening ceremony (piglet sacrifice, parade of tributes and orphans, proclamation of honours), 5 comedies
3 + 4-3 tragedies and 1 satyr play
5-3 tragedies, 1 satyr-play,
Judging and prize-giving
AFTER- The reviews
-Athenian assembly would meet
-Citizens could pose a complaint > eponymous archon could by fined
-If it was voted a success he could be voted to receive a crown
JUDGING THE CITY DIONYSIA
Judging the plays was democratic
They would have sat in one of the 10 tribal areas in the theatre
1. Before the festival each tribe put 10 names of citizens into a sealed urn
2. At the beginning of the festival one name was chosen from each of the 10 urns at random and they were the judges
3. On the 5th day each judge wrote down the name of the playwrights in order or merit and the 10 tablets were put in an urn
4. the Archon drew out 5 of the tablets and the playwright with the most votes was declared winner.
Chorus
A group of characters in Greek tragedy (and in later forms of drama), who comment on the action of a play without participation in it
Initially 12 but became 15 possibly divided into formations of five or three
Ordinary citizens
Choregos would audition them and reuse them for all their performances
Would be spared from military service (highly esteemed) displayed democratic spirit
Each chorus had a leader who would directly interact with other actors
Highly stylised
ROLES
Actors (townsfolk's, elderly citizens) COMMUNAL PERSPECTIVE, voice of the people (rep a democratic commentary, it is more than gods and heroes)
Commentator (provide moral opinions and shape audience reaction)
Scene setting
Wider context (link it to myth)
Set the mood
Provide a scene break (like a curtain)
FUN trying to get the audience invested,
Theatre of Dionysus (short)
Main theatre in Athens
Situated on the south-east side of the Acropolis
Near a Dionysus sanctuary initially built in 320s and called the Lycurgus theatre
Remodelled by Romans
Why are we unsure of what theatres were used in 5th?
The surviving theatres are made of stone and date to 4 BC Before they were made of wood
We are unsure what they were like later
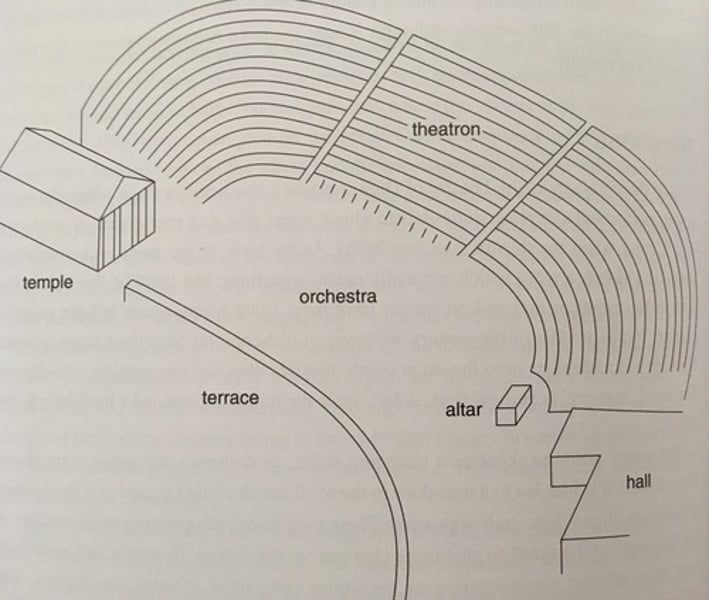
Theatron
The seating area in a Greek theatre
Often built by a hill to be steeped
Divided into 13 sections (10 tribes and possibly foreigners, women, slaves)
Low estimate pf 6,000 capacity
Wooden benches
prohedria
The front row seating in the theatron
Reserved for officials and dignitaries
Orchestra
Means 'dancing area'
The area at the front of the theatron where the chorus performed
An alter for D was there or near it
Used to be circular, scholars argue it was either rectangular or trapezial in the 5th
eisodos
The entryway into the orchestra from each side of the stage.
skene
The building at the back of the stage
A backdrop
(eg 431 Euripides Medea royal palace)
Where actors changed.
ekkyklema
A wheel platform used to portray indoor scenes or present dead bodies
Explained in a scholia to Aristophanes
crane
A device used to lift actors above the stage
First used in Euripides' Medea
Used to show divinity (deus ex machina)
Liturgy
(n.) a religious service or rite; the form of a ritual or other act of public worship
Black figure
a style in Greek pottery decoration composed of black figures against a red background
Red figure
Classical era (5th 4th)
Greek pottery in which the decoration is red on a black background.
Slip applied to background + with brush for details
Preferred > smooth flow, greater control of curves (toes)
Black figure
Common 7th 5th
Greek pottery in which the decoration is black on a red background
Slip painted on areas to be black
Details etched
Good for sharp + distinctive features]
But for details and curves
alabastron:
holding oil, especially perfume or massage oils.
narrow body with a rounded end, a narrow neck and a broad, splayed mouth.

amphora:
two handles and a long neck narrower than the body
They were used to transport and store various products, both liquid and dry.

krater:
A large vase used to mix wine and water.
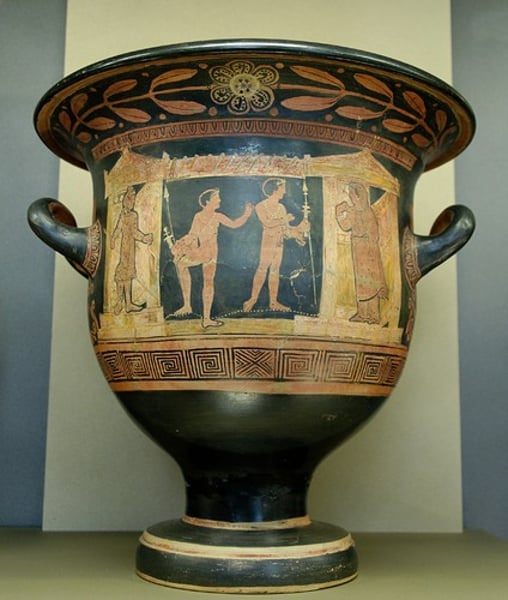

hydria:
A water jar with 2 horizontal handles attached to the shoulder for lifting, and one on the back for pouring, or carrying when empty.

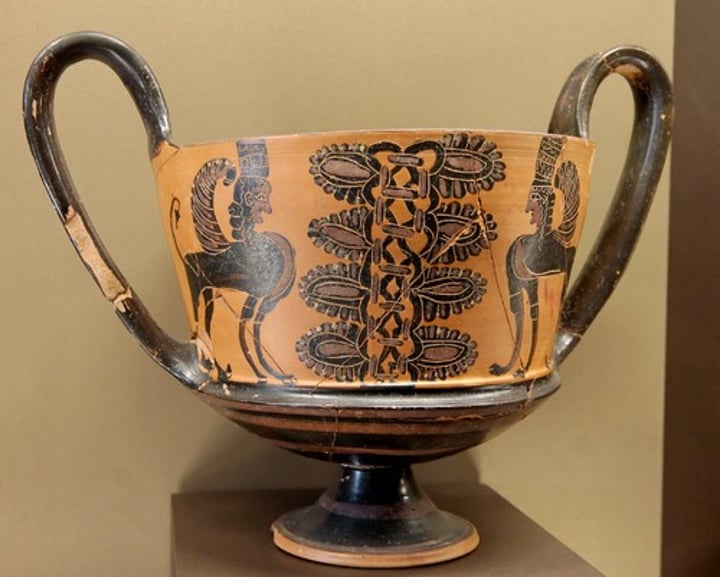
cantharos:
high swung handles which extend above the lip of the pot
drinking cup

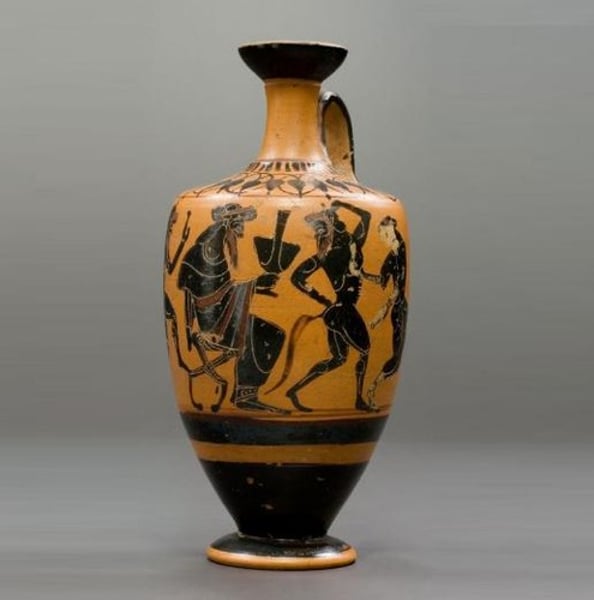
lekythos:
storing oil, especially olive oil used for anointing the bodies of the dead.
narrow body and one handle attached to the neck of the vessel.

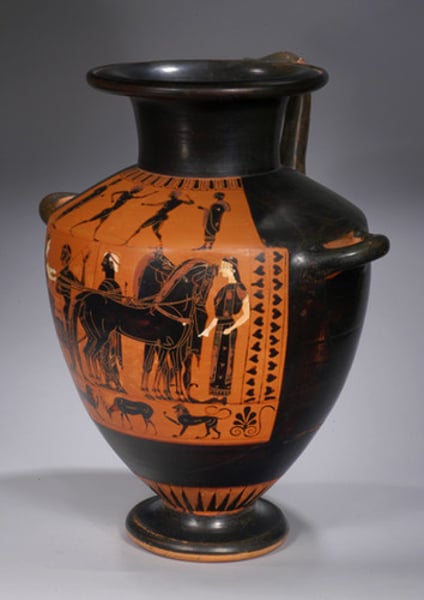
oinochoe:
A wine jug characterized by an S-shaped profile from head to foot.
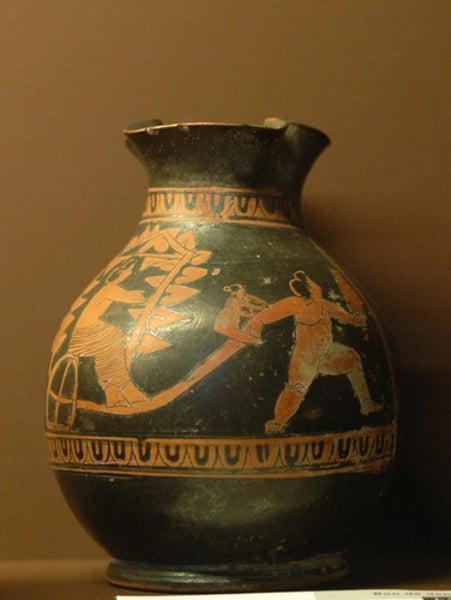

psycter:
wine cooler
broad bulbous body, a tall cylindrical stem, a short neck, sometimes with handles for carrying and a lid that fit over the mouth.
stood in a krater of ice or snow or cool water
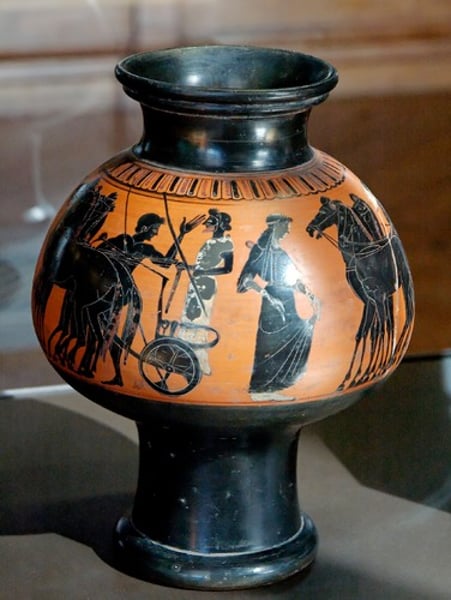

kylix:
wine-drinking cup
broad relatively shallow body raised on a stem with a foot and usually two horizontal handles.

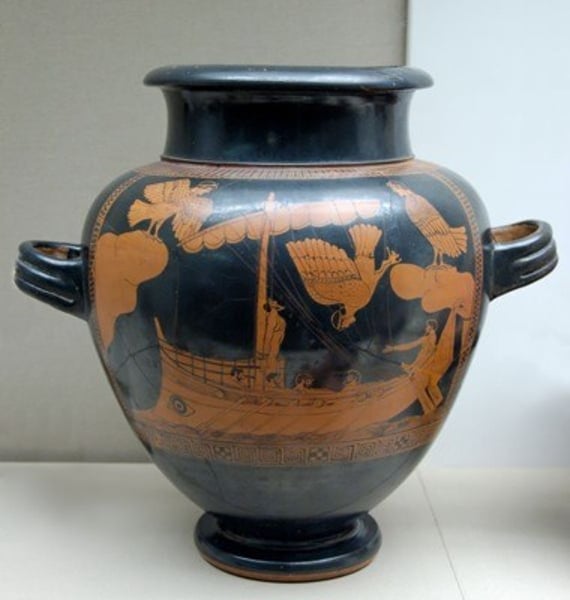
stamnos:
A lidded storage jar for liquids.
short, stout neck, a wide, flat rim, and a straight body that tapers to a base. Horizontal handles are attached to the widest part of the jar.

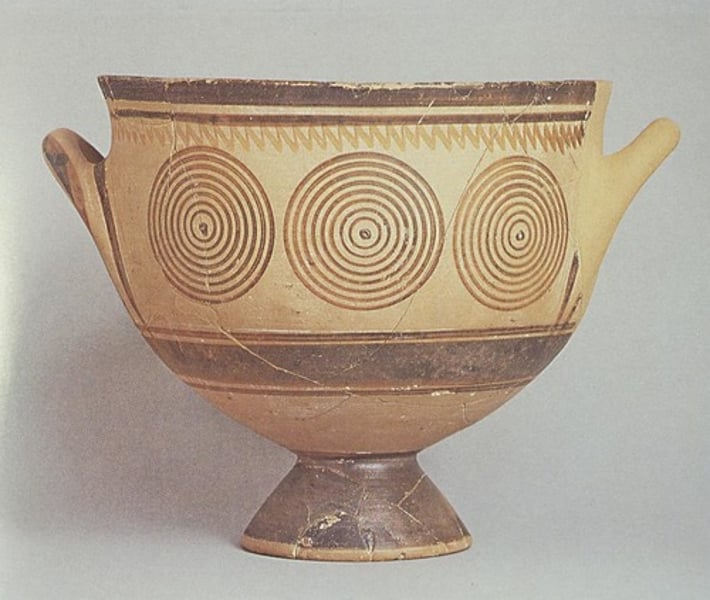
Skyphos:
drinking bowl

Theatre of Dionysus
Located in Athens- situated on the south-east side of the acropolis (protected from cold north wind) (above a sanctuary for D) (between religious heart if the city- Acropolis- and a sancturay)
Street led from theatre to agora- showed popularity (street of tripods because of monuments to festival victors)
Remains are dated to the 5th- first built in stone in 320s under supervision kf Lycurgus (lead Athenian statesman) but was remoddled over time and todays remains are thus in a Roman style
The largest ancient Greek theatre
It could seat as many as 17,000 people
In Lycurgus' theatre:
The theatron on was more circular than semi circular (for acoustics) split into 13 sections (10 tribes, slaves, foreigners, women)
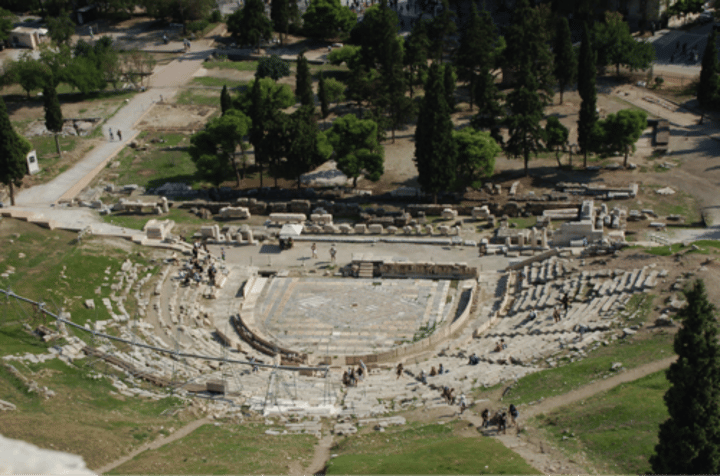

Theatre of Thorikos
a regional theatre of Attica which has a different layout from the circular acting area of the Theatre of Dionysus
Built 525-480 (classical age)
Used late 6th early 5th
Rural D held here
Holds 3000 people
Trapezoidal orchestra
Three sections (different social divisions)
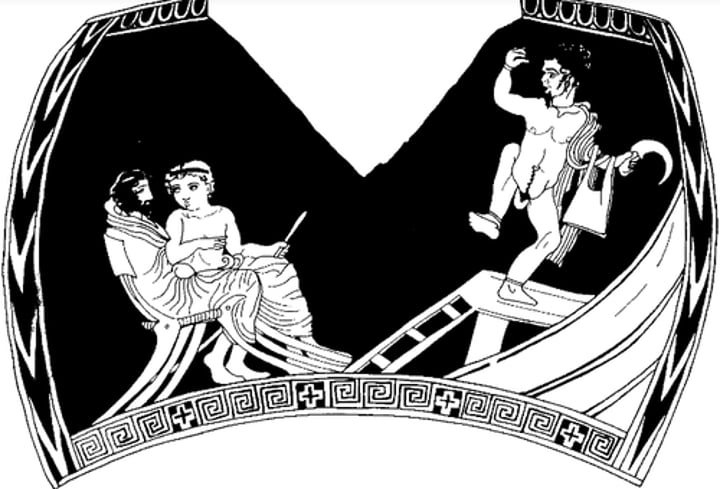
The Perseus Dance Vase
Damaged attic red figure chous (jug)
Dates to 420 BC (when the plays were happening PRIMARY SOURCE)
It depicts Perseus (made to seem naked with a phallic suit, indicated in the art by marking the end of the costume > comedy) holds a scythe and a bag (holding Medusa's head, very thin to comedically indicate no head)
Only attic vase to depict a stage (wooden stage evidence) AND only Greek painting to depict an audience
Audience a man and a boy (sex worker, lover?), the seats have backs > prohedria > high status fellows, rest of the audience is absent
No orchestra? What is on the other side? No chorus, theatron or skene

Wurzburg Telephs Vase
Mixing bowl
Red figure
Dates 318-70 BC
Produced in Apulia (411)
Shows a seven from Aristophanes' comedy 'Women at the Thesmophoria'
Doesn't show the the storm, the stage, the other actors
The relative is clean shaven (the masks are usually bearded)
Used alter as a part of staging
Comedy comes from baby being repped by a wine bag (ha ha women drunk)
Is this accurate? Not made in Athens. Probably based on a rerun
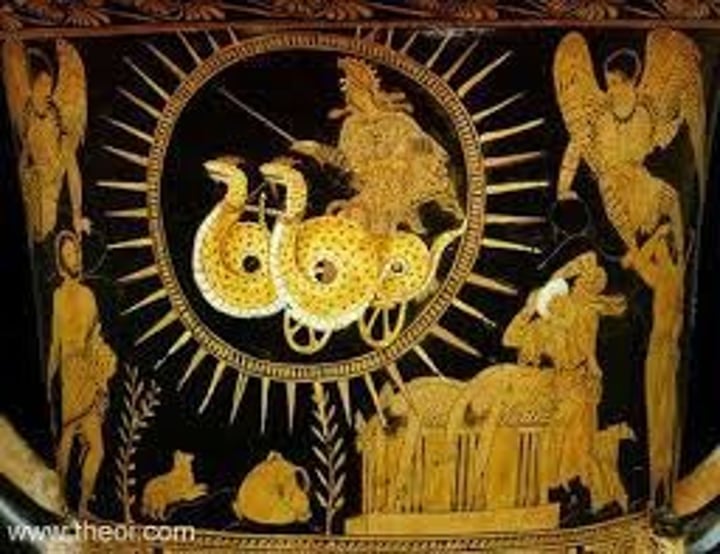
Medea's Escape (the vase)
Red figure crater (mix wine) can tell by low handles
Dates a few decades after Medea's performance (431)
The children are on the wheeled platform and her floating is evidence of the mechane
In the play she takes her sons with her and doesn't fly with dragons (just elevates) (inaccurate)

Basal Dancers vase
Red figure column
Tragic chorus in action in front of a stepped altar
500-490 BC (early in tragedy)
The statue on top of the alter appears to be a ghost or a representation of Dionysus
3 pairs of two dancing in a choreographed rectangular formation
They are shown moving as one utilising their full body
Their same face suggests a mask
Costumes appear to be heavy armour
Bare foot
The Promos Vase
410 BC
Named after a famous aulosplayer pictured
They are costumed for a satyr
Depicts an ancient theatrical scene
Used as evidence for neutral masks
Costumes highly decorated
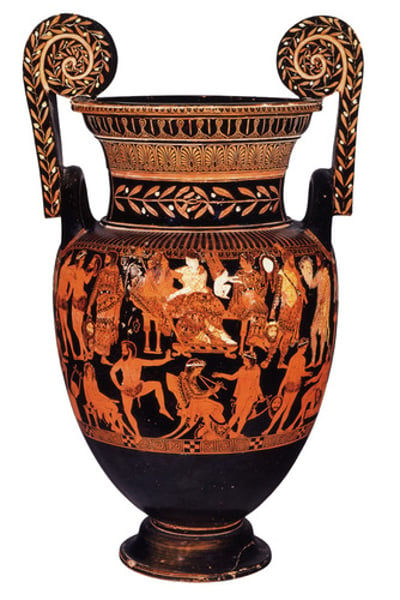

-Calyx Krater fragment by Capodarso
-Ft messenger, Jocasta (painted white to indicate woman), Oedipus, his two daughters
-Jocasta's moment of recognition
-Oedipus' ignorance is highlighted physically with him being surrounded by people in the know
-Evidence of the skene depicting a palace
-Evidence for a stage
-No masks > artistic choice but expressions are legible
-Jocasta is dabbing face to indicate sadness
Why is this moment depicted?
-It is a dramatic hinge moment
-Main characters are present
-Shows this was a recognisable image + play in The Canon
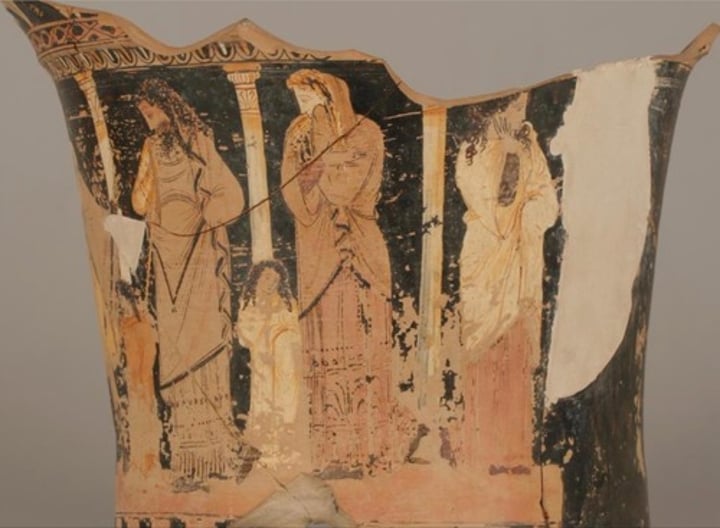

Red Figures 'maenad' stamnos
-Late 5th
-Maenad's (thyrsus, vine leaves, tamberine, dappled fawn skin, hair loose (signifies wildness))
-Dancing (movement, head flung back)
-Shrine to D, surrounded by wine stamnos on a stamnos (suggests user is partaking in Bacchic women)
-Gives us information on the connotations of Dionysian worship

Death of Pentheus
-480 BC- 70 years before, not helpful in displaying dramatic techniques, but shows it to be persistently well known
-Red figure kylix- used in symposiums>P is sexualised, beardless (youth) emphasis on physique
(idealised youthful male beauty, homoerotic, reveals male fear of women)
-Especially upsetting as it represents the destruction of Cadmus' family tree (which Athenians were paranoid about)
-They wear animal, panther skins (renound for hunting)
-The depiction of gore shows a cultural fascination for violence (not expected as violence occurs off stage- the same violent impulse shown in detailed messenger speeches)
Protruding bone, organs, dismembered foot
-Satyr astonished by D power
-Eyecontact + head patting suggests a relationship and the tenderness highlights the perverse cruelty
NOT A PLAY
-No boots, masks, stage or any evidence of dramatic techniques
-Women
507 BCE
Athenian leader Cleisthenes introduced democracy
490 BCE
Battle of Marathon (Athens defeats Persia)
481-79 BCE
Xerxes invades Greece
Athens is sacked by Persians
Eventual athenian victory
477 BCE
Delian League formed
(to defend against Persia)
461-46 BCE
First Pelopunesian war
440 BCE
Drama contest introduced to Lenea
430-29 BCE
Plague in Athens
Oedipus Rex Sophocles won 2nd prize at CD
406 BCE
Death of Euripides
405 BCE
Aristophanes' Frogs won 1st prize at Lenaea
Posthumous production of The Bacchae
404 BCE
Defeat of Athens by Sparta in Peloponnesian War
Athenian democracy replaced by oligarchy (Thirty Tyrants)
Hetairai
highly sophisticated courtesans in ancient Athens who offered intellectual and musical entertainment as well as sex.
Fancy prostitutes
Paideia
Education, culturalness
panegyric
elaborate praise
formal hymn of praise
Peripeteia
reversal of fortune
Aristotle notes it as an element of a tragedy
Anagnorisis
recognition or discovery
on the part of the hero
change from ignorance to knowledge

Bird vase
480BC
It shows an old comedic chorus, costuming, vine branches represent Dionysus, depicts competition between tragedy and comedy
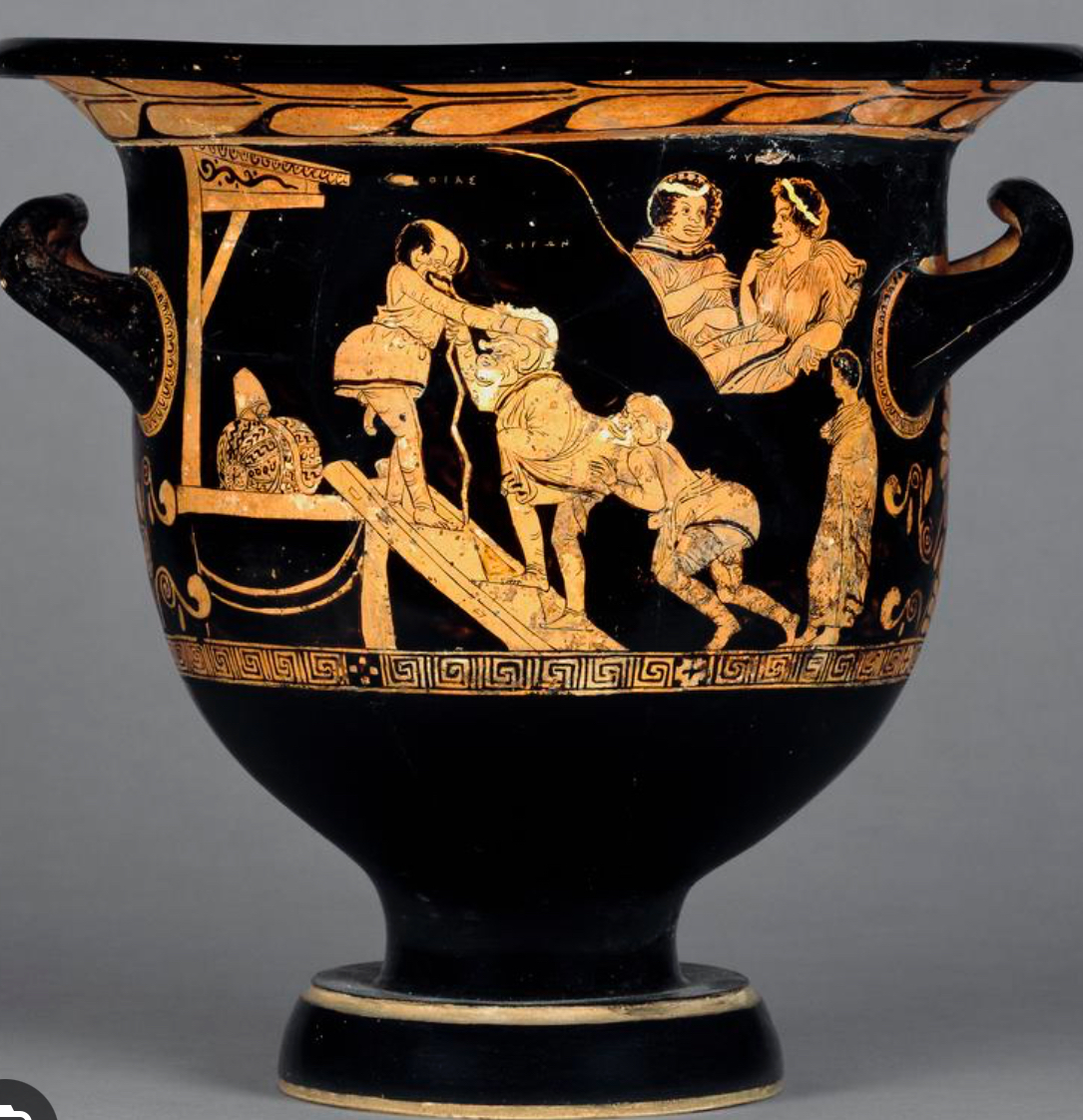

Krater Cheiron
380BC
Comedic evidence, door represents entry to the temple of Apollo at Delphi, masks, costuming, props
-It shows figures wearing costumes in a performance of comedy.
COSTUME
-The tunics are short.
-They are padded.
-It shows that the actors wore a phallus.
-figures wearing masks- faces have grotesque expressions.
>shows that the characters have different ages.
-Two of the figures have walking sticks. (props)
BUT
-It is not from Athens.
>It was made in Southern Italy.
-It is later than most of Aristophanes' plays.
>400 - 380 BC.
-There is no distinction between actors and Chorus.
>The two outside actors appear to be chorus members, while the one in the middle is a named character.
-The scene does not correspond to any known play. (A01)
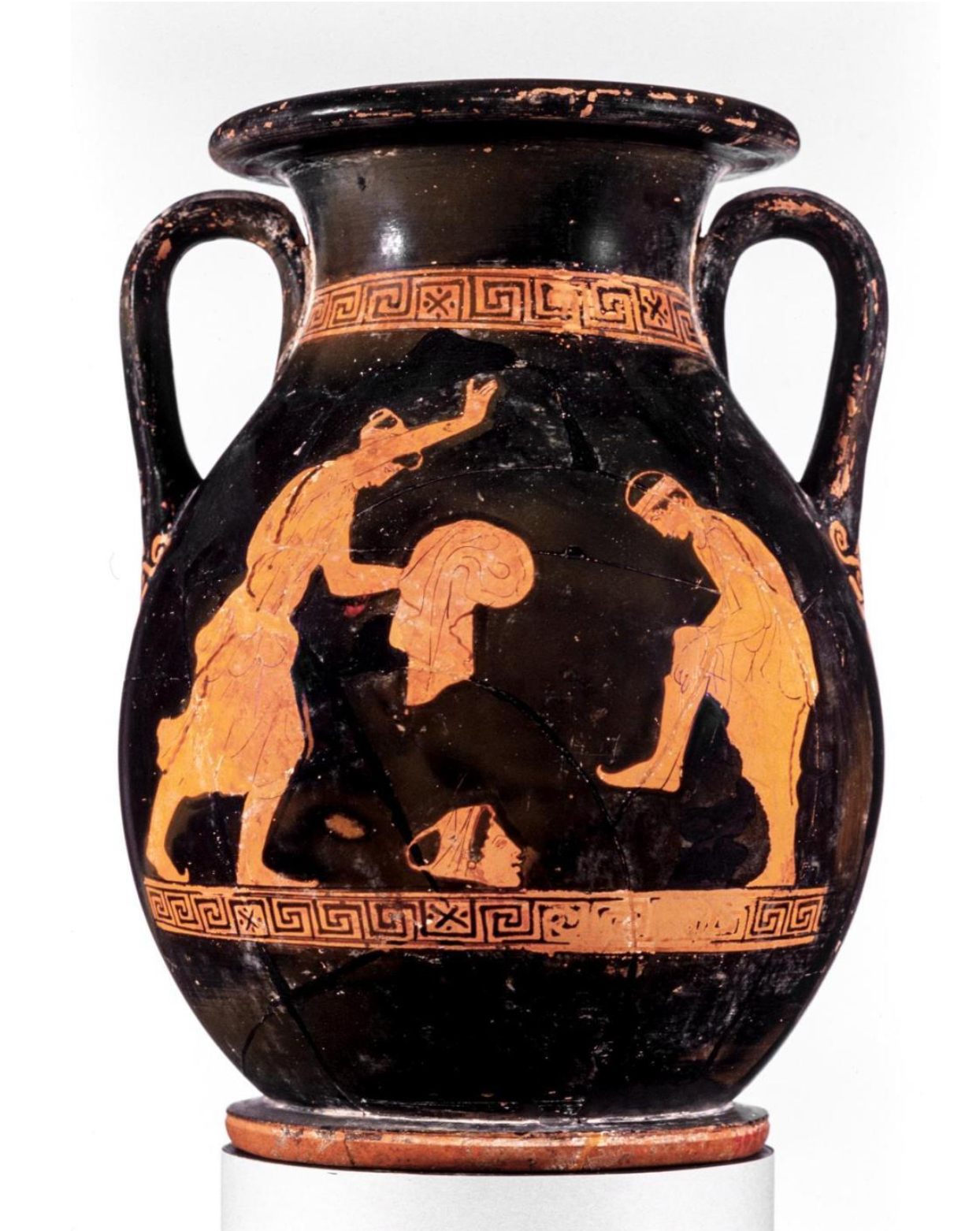

Redfigure by pelike