Appendicular Skeleton
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
what is the elevating motion that lifts the front of the foot and the toes off the ground while the heel remains planted
dorsiflexion
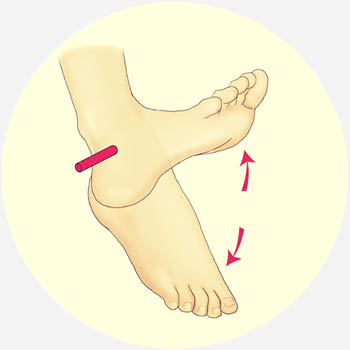
what is the motion that points the toes downward
plantarflexion
what is the twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole outward
eversion
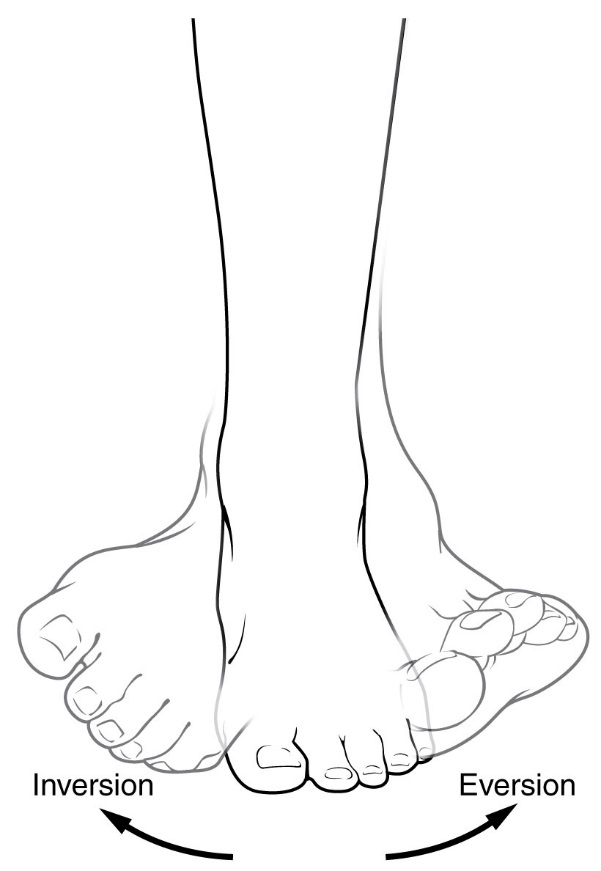
A twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole inward is (chapter question)
inversion
Almost all football knee injuries occur when the player has the foot “planted” and extended rather than flexed. What anatomical facts would account for that? (chapter question)
When the knee is flexed, it is able to move in response to a hit from the inside or outside (medial or lateral surfaces) However when the knee is planted the knee is in a locked position. In this position the medial and lateral collateral ligaments and the anterior cruciate ligaments are taunt, thereby increasing their chance of injury
What common mechanism holds together immovable joints such as skull sutures and the gomphoses, holding teeth in their alveoli? (chapter question)
The common mechanism that holds together immovable joints is dense fibrous connective tissue. For the skull has the sutural ligament. The teeth have a periodontal ligament.
The function of a bursa is to (chapter question)
reduce friction between a bone and a tendon and absorb shock
Which of the following is not a function of synovial fluid? (chapter question)
increase osmotic pressure within joint
how does synovial fluid provide nutrients in the synovial joint
Synovial fluid circulates throughout the joint when the joint moves. This nourishes the tissues, distributes dissolved gasses, and removes wastes.
what is the role of the menisci
They are pads of fibrocartilage that subdivide the synovial cavity, help keep the bones in the right position
what is the definition of bony fusion
the joint forms where two bones fuse into one
what is the definition of fibrous joint
the joint is held by fibrous tissue
what is the definition of cartilaginous joint
the joint is held by cartilage
what is the definition of synovial joint
contains synovial membranes and fluid
where are gomphosis joints found
they bind the teeth to the bony sockets in the maxilla and mandible
what are the different classifications of joints based off of the type of tissue that binds them together
bony fusion, fibrous joint, cartilaginous joint, synovial joint
what is the name of the joints that are diarthrosis
synovial joints
where are synovial joints found
at the end of long bones
what is a joint that has no movement
synarthrosis
what are the types of joints that fall under the category of synarthrosis joints
synostosis, sutures, gomphosis, synchondrosis
what category of joint are synostosis joints
bony fusion
what is an example of a synostosis joint
metopic suture
what is the classification of suture joints
fibrous joint
what is an example of suture joint
sutures in the skull
what is the classification of the gomposis joint
fibrous joint
what is the classification of the synchondrosis joint
cartilaginous joint
what is an example of the synchondrosis joint
epiphyseal plate and where the ribs connect to the costal cartilage
what is the name of a freely movable joint
diarthrosis
what is the name of a slightly moveable joint
amphiarthrosis
what types of joints fall under the category amphiarthrosis joints
syndesmosis and symphysis
what is an example of a syndesmosis joint
joint between the fibula and tibia
what category of joint does the syndesmosis joint fall under
fibrous joint
what is an example of a symphysis joint
intervertebral disk, disk between the pubic bones
what category of joint does the symphysis joint fall under
cartilaginous joint
The ____ of the radius assists in stabilizing the wrist joint
styloid process
what does the olecranon process form
the superior lip of the trochlear notch
on which bone is the olecranon process located
ulna
on what bone is the coronoid process located
ulna
Why are fractures of the clavicle so common? (chapter question)
Fractures of the medial portion of the clavicle are common because a fall on the palm of an outstretched hand produces compressive forces that are conducted to the clavicle and its articulation with the manubrium. The clavicle is a thin bone that can be broken easily.
Which of the following is not a carpal bone (chapter question)
-cuboid
-scaphoid
-hamate
-triquetrum
cuboid
Structural characteristics of the pelvic girdle that allow it to bear the body’s weight include (chapter question)
heavy bones.
stable joints.
limited range of movement.
all of the above at some joints.
all of the above at some joints
The protuberance that you can feel on the lateral side of the ankle is the (chapter question)
lateral malleolus
Why is the tibia, but not the fibula, involved in weight transfer to the ankle and foot? (chapter question)
The tibia is part of the knee joint and is involved in the transfer of weight to the ankle and foot.
The fibula is excluded from the knee joint and does not transfer way to the ankle and foot.
Why would a person who has osteoporosis be more likely to suffer a broken hip than a broken shoulder? (chapter question)
The hip helps support the body’s weight and weakening of it can result in it breaking under the weight of the body. The shoulder is not a load-bearing joint and is subject to the same stress as the hip.
How would a forensic scientist decide whether a partial skeleton found in the forest is that of a male or a female? (chapter question)
Many skull characteristics would reveal the sex of the individual, but there are also characteristics in other skeletal structures, such as the robustness of the bones, the angles at which the pubic bones meet, the width of the pelvis, and the angles of the femurs.
what are the basic features of the synovial joint
articular capsule, fibrous joint capsule, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, hyaline cartilage, joint cavity, and synovial fluid
what type of cartilage makes up the articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage
what is the role of articular cartilage in the synovial joint
it allows bones to artculate without friction
what is the joint cavity filled with
synovial fluid
what secretes synovial fluid
synovial membranes
what is the function of synovial fluid
it acts like a lubricant on the articulating cartilage
how are joints grouped together
by the range of movement possible at the junctions between bones
what are the accessory structures found in complex joints
menisci, fat pad, extracapsular ligament, intracapsular ligament, bursa
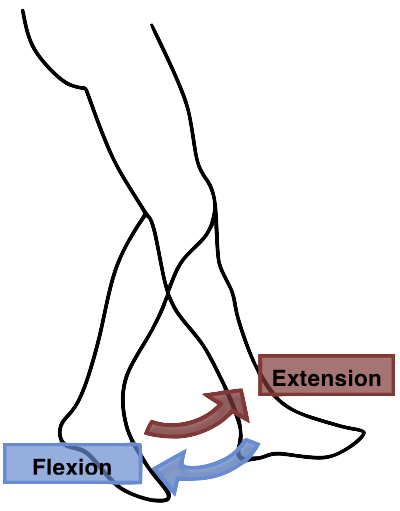
what is the motion that extends the leg out
extension
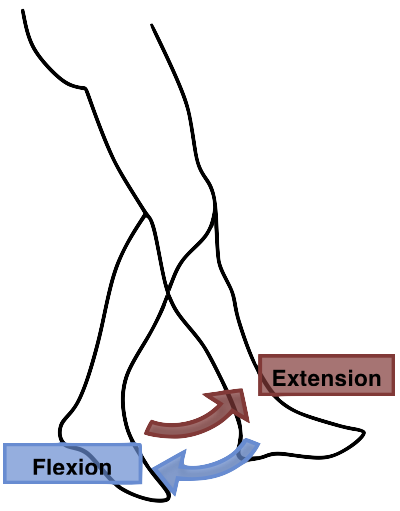
what is the motion that bends the leg back
flexion
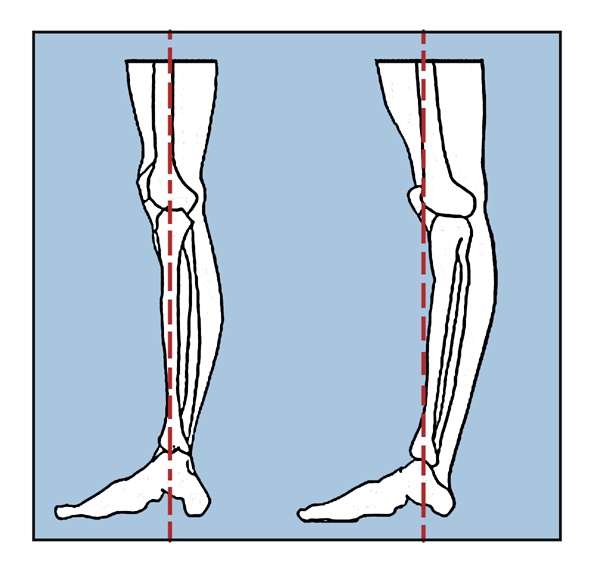
what motion is hyperextension
moving even further past the extension point
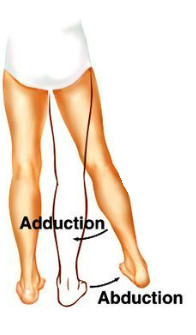
what motion brings the leg closer to the body
adduction
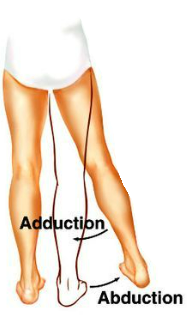
what motion brings the leg further from the body
abduction
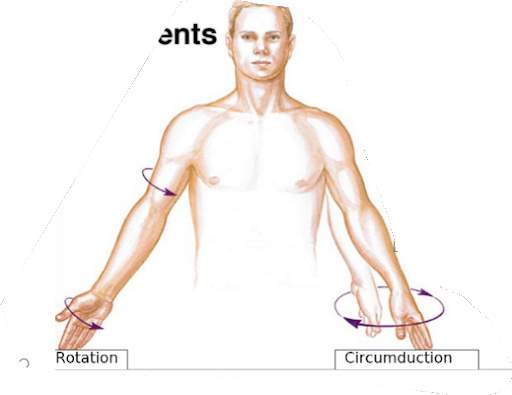
what motion are arm cicles
circumduction
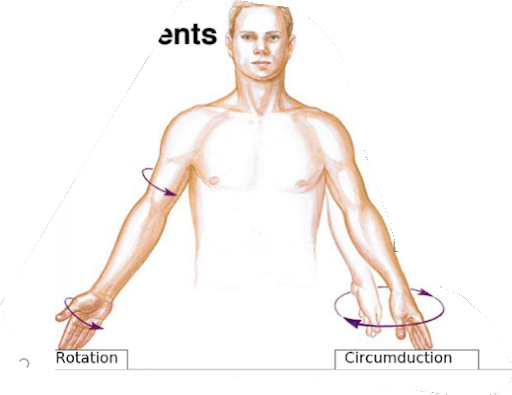
what motion is rotating your entire arm face-up and then face-down
rotation
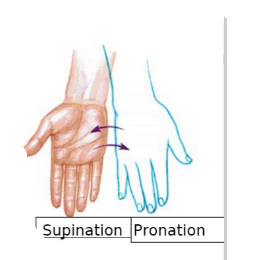
what motion is rotating your hand to be palm side up
supination
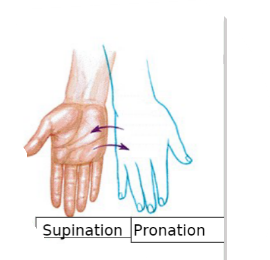
what motion rotates the hand palm-side down
pronation
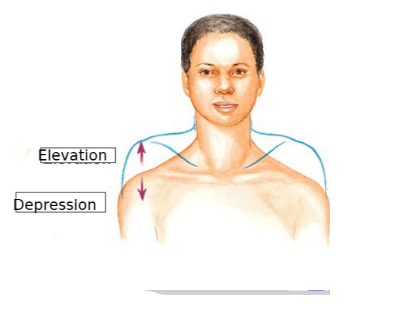
what motion raises the shoulders
elevation
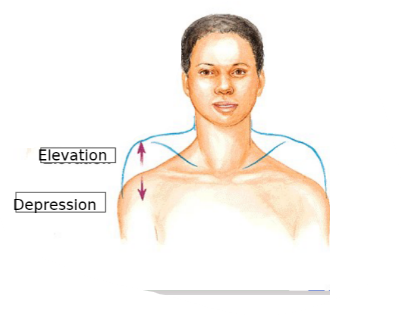
what motion lowers the shoulders
depression
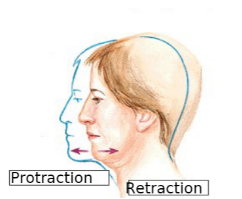
what motion pushes the head forward
protraction
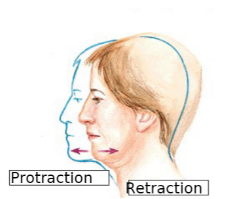
what motion pulls the head back
retraction
what is the function of the fat pad
keeps the ligament in place
where is the extracapsular ligament located
outside of the joint capsule
where are the intracapsular ligaments located
inside the joint capsule
what is the bursa
it a membrane sack filled with fluid that can slide and move
what is the purpose of the bursa
takes up space in the joint and helps keep the bones in the right position, allows the membranes to roll and slide past one another as the knee moves
how are synovial joints classified
according to their type and range of motion
what defines the motion in synovial joints
their structure
what are the types of synovial joints
ball and socket, ellipsoidal, gliding, hinge, pivot, and saddle
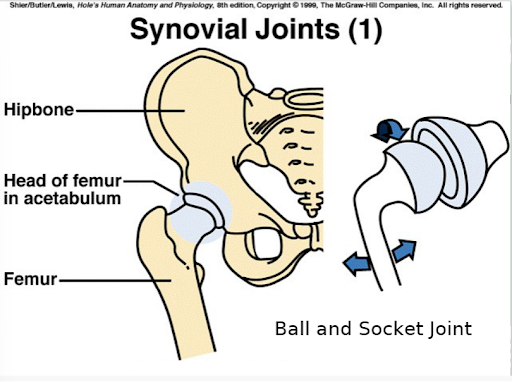
the head of the femur rotating in the acetabulum (located on the hipbone) is what type of joint
ball and socket joint
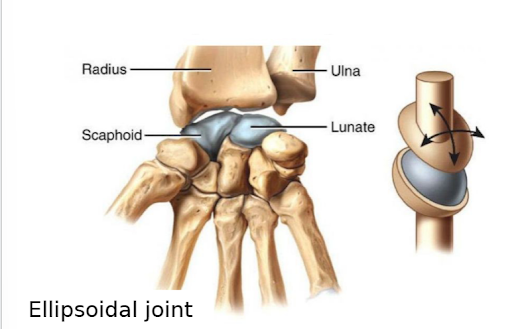
the radius and ulna rotating with the scaphoid and lunate is what type of joint
ellipsoidal joint
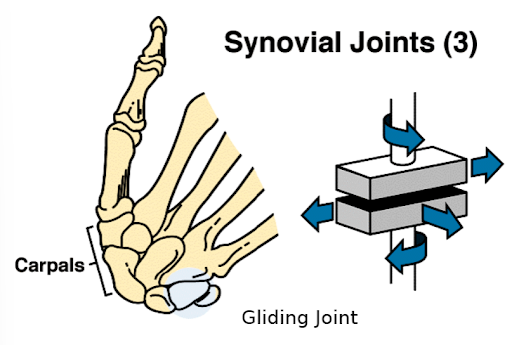
the carpal bones sliding aginst one another is what type of joint
gliding joint
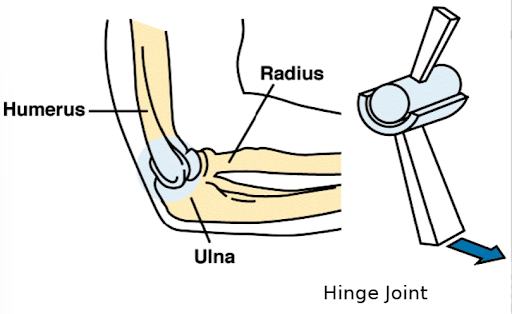
the ulna rotating with the humerus is an example of what type of joint
hinge joint
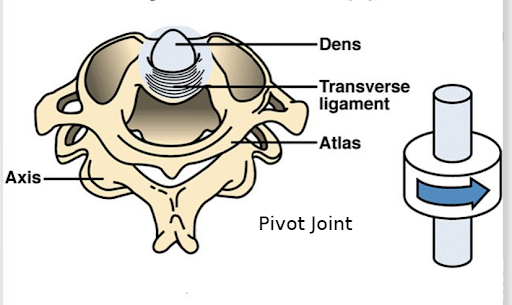
what type of joint is the dens of the axial vertebrae rotating with the atlas
pivot joint
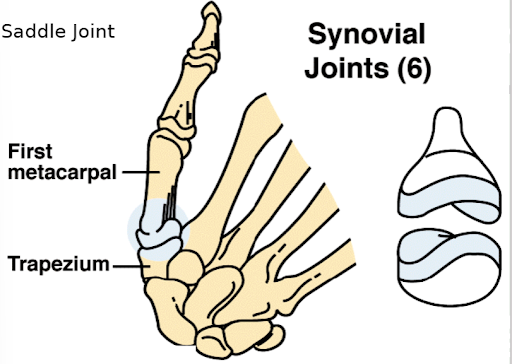
what type of joint is the thumb (the first metacarpal roating with the trapezium
saddle joint
____ enable a wide variety of body movements
joints
why is each muscle in your body an organ
becuase it is comprised of a different types of tissue
what can every skeletal muscle be subdivided into
fascicles
what surrounds and separates each fascicle
connective tissue
what can fascicles be further divided into
individual muscle fibers which are the muscle cells
what is another name for a muscle fiber
muscle cell
what binds the muscle together
layers of connective tissue
what is the epimysium
dense fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle
what is the epimysium connected to and surrounded by
the deep fascia
what type of tissue is the deep fascia
dense fibrous connective tissue
what does the perimysium surround
it surrounds each fascicle
what fibers does the perimysium contain
both collagen and elastic fibers