A&P Lab Exam 1
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
RUQ Organs
Liver
Gallbladder
Stomach
Pancreas
Ascending/Transcending Colon
Jejunum
Duodenum
RUQ Rule Outs
#1 Gallstones
#2 Hepatitis B&C
#3 Pancreatitis
Signs would include jaundice
Questions to ask: do they smoke, do they drink, do they eat nitrogenous foods
LUQ Organs
Stomach
Spleen
Pancreas
Liver
Jejunum
Ascending/Transcending Colon
LUQ Rule Outs
#1 Ruptured Spleen
Common in a motor Vehicle Accidents
RLQ ONLY Organs
Appendix
Cecum
Ileocecal Valve
Ascending Colon
RLQ AND LLQ Rule Outs
#1 for Women - Ectopic Pregnancy
Females ages 11-55 pain in either lower quadrant
#1 for Men (#2 for women) - Appendicitis
LLQ ONLY Organs
Sigmoid
Descending Colon
RLQ AND LLQ Organs
Bladder
Ureters
Anus
Fallopian Tubes
Ovaries
Uterus
Testicles
Scrotum
Penis
Rectum
Ilium
Jejunum
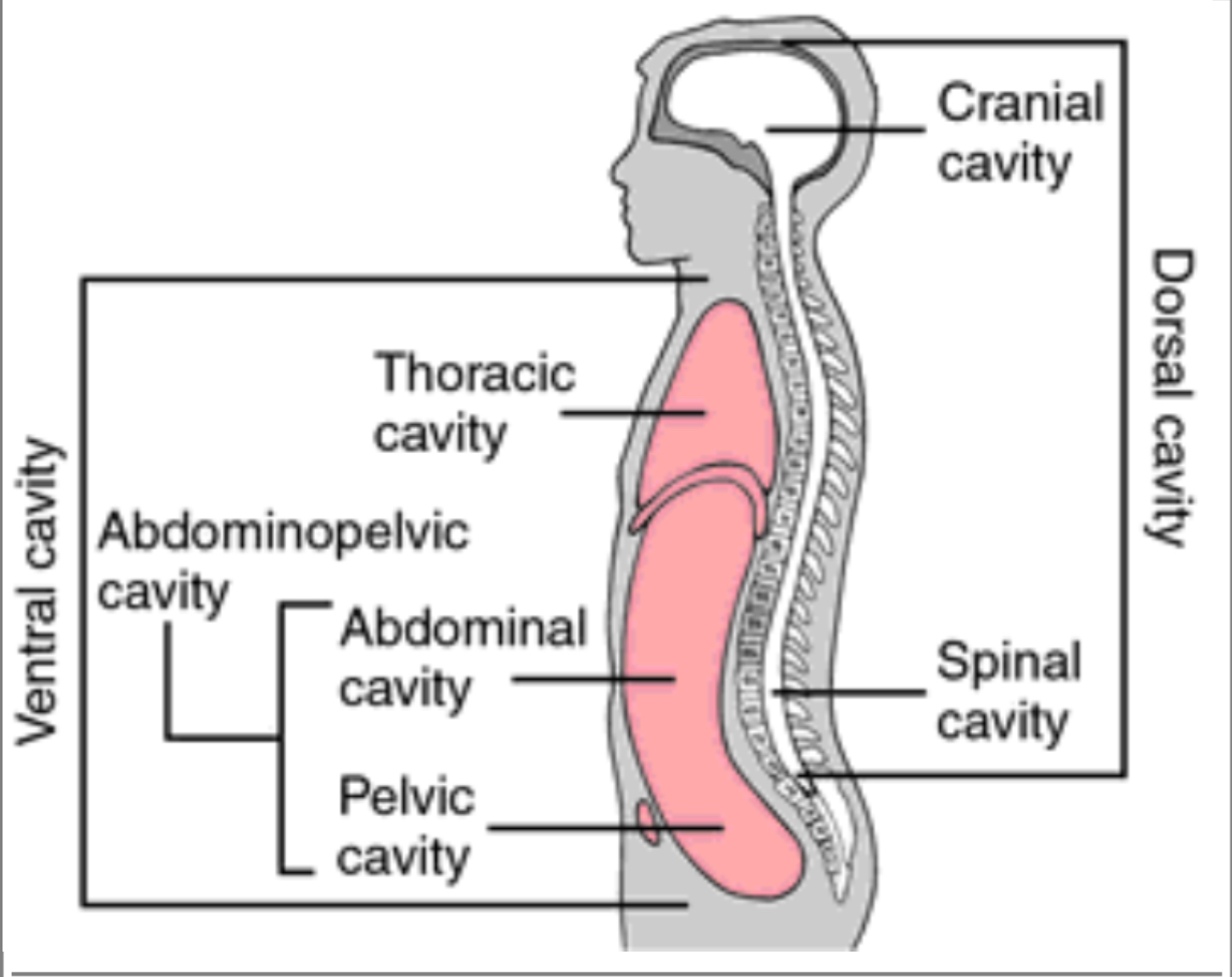
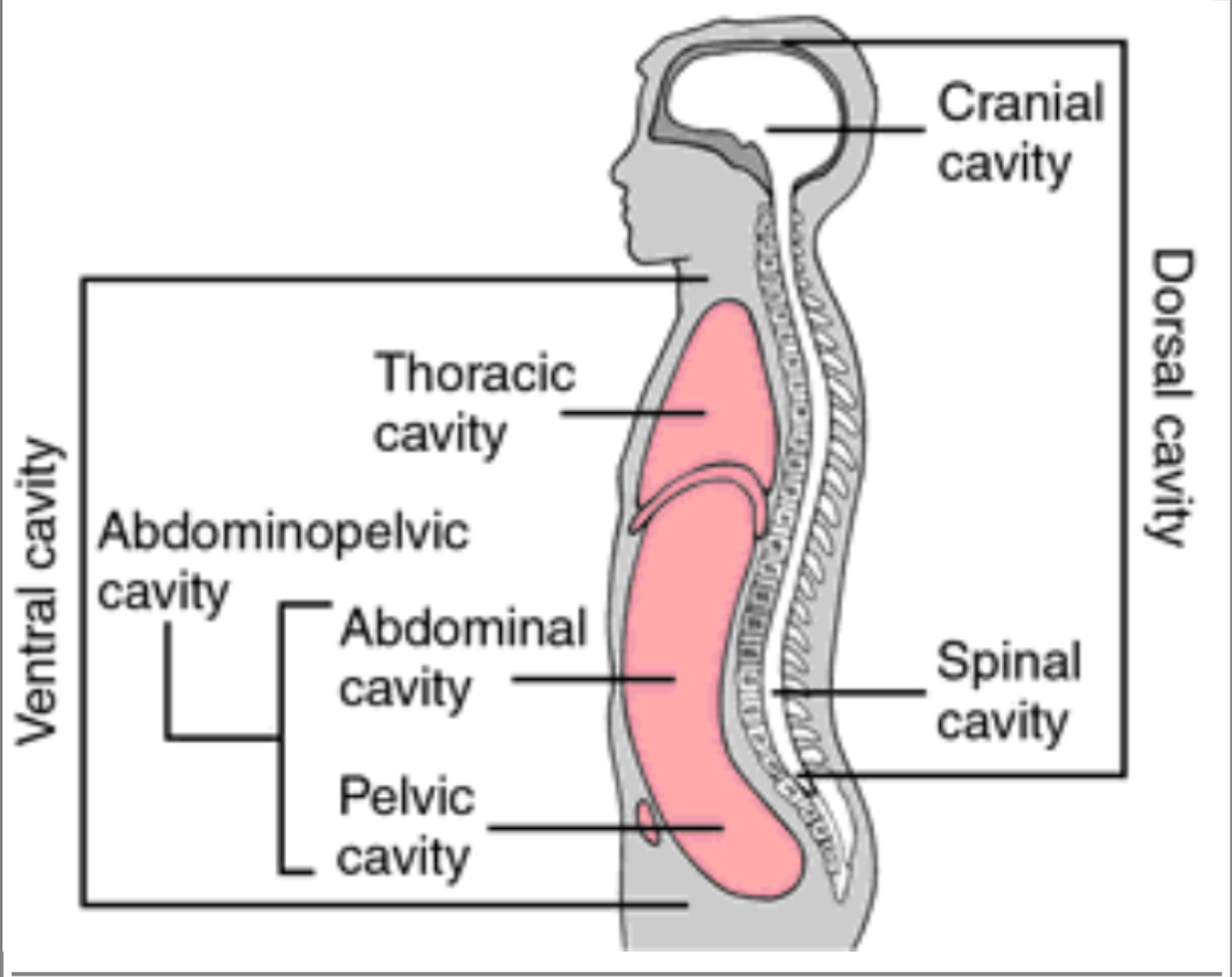
Dorsal Cavity (posterior aspect)
The WHOLE backside of the body (head to ass)
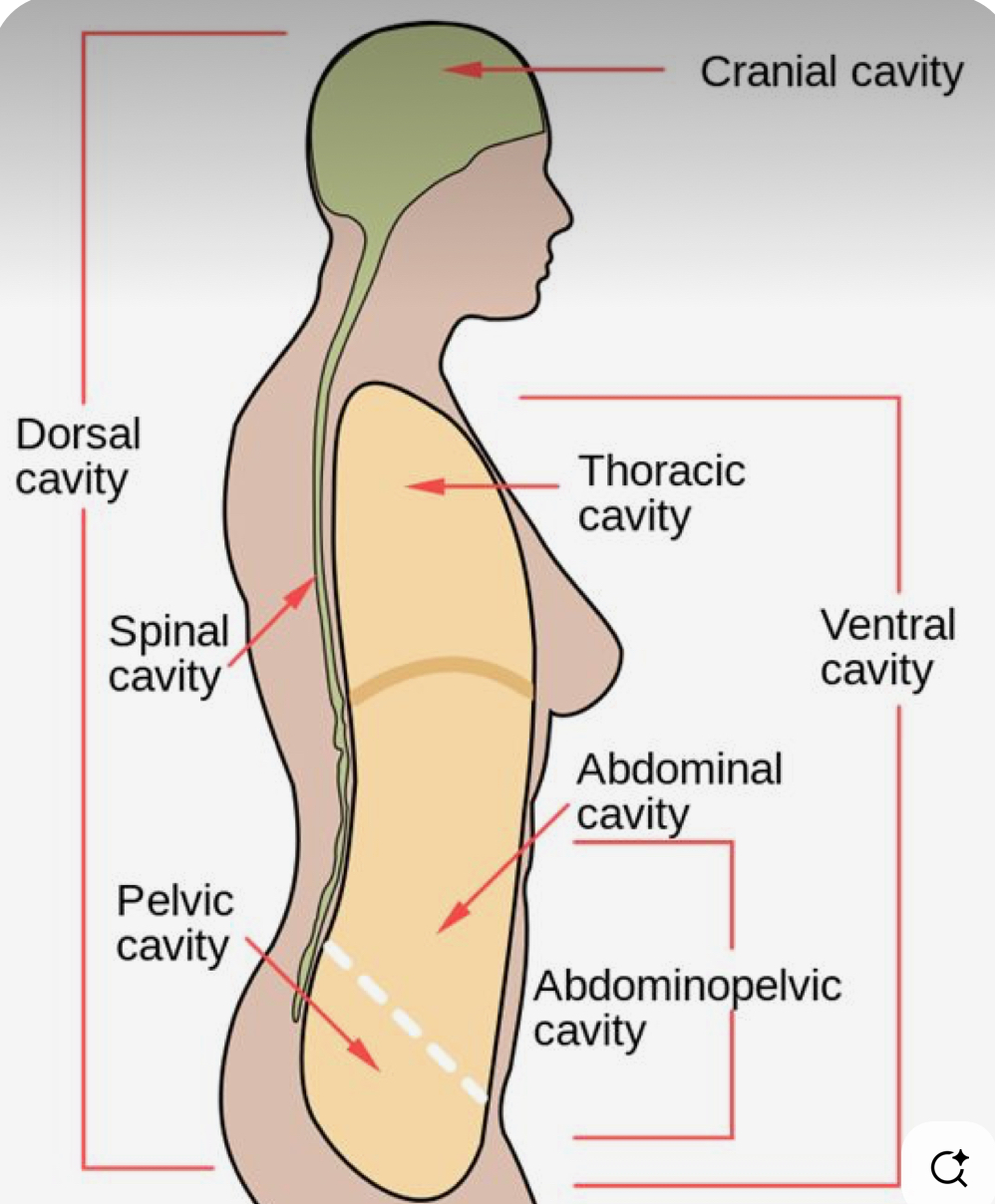
Peritoneal Cavity
The “chamber” of the abdominal pelvic cavity
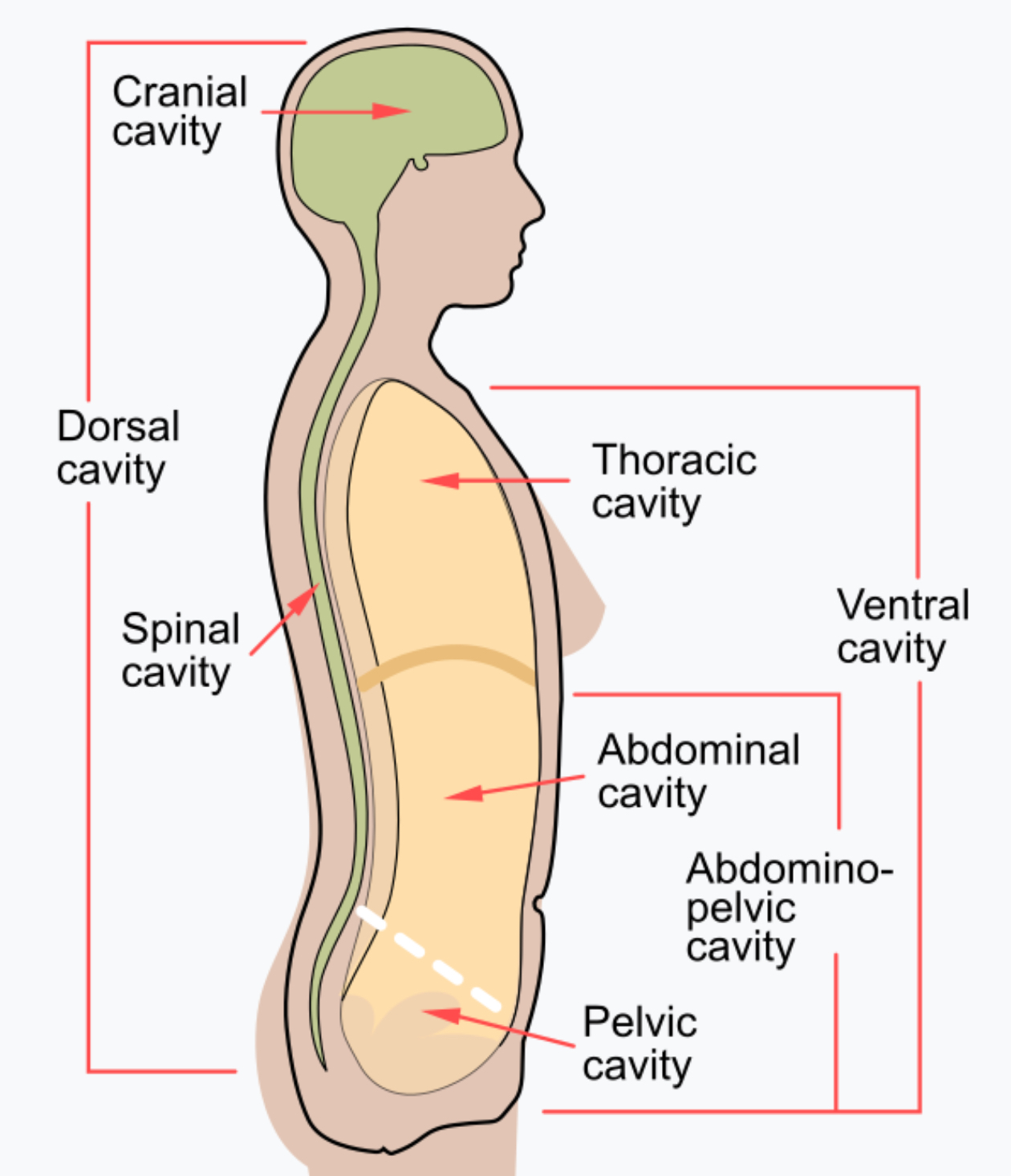
Cranial Cavity
Only referring to where the brain is housed, referring to the top ½ of skull (brackets from top of head to eyebrows)
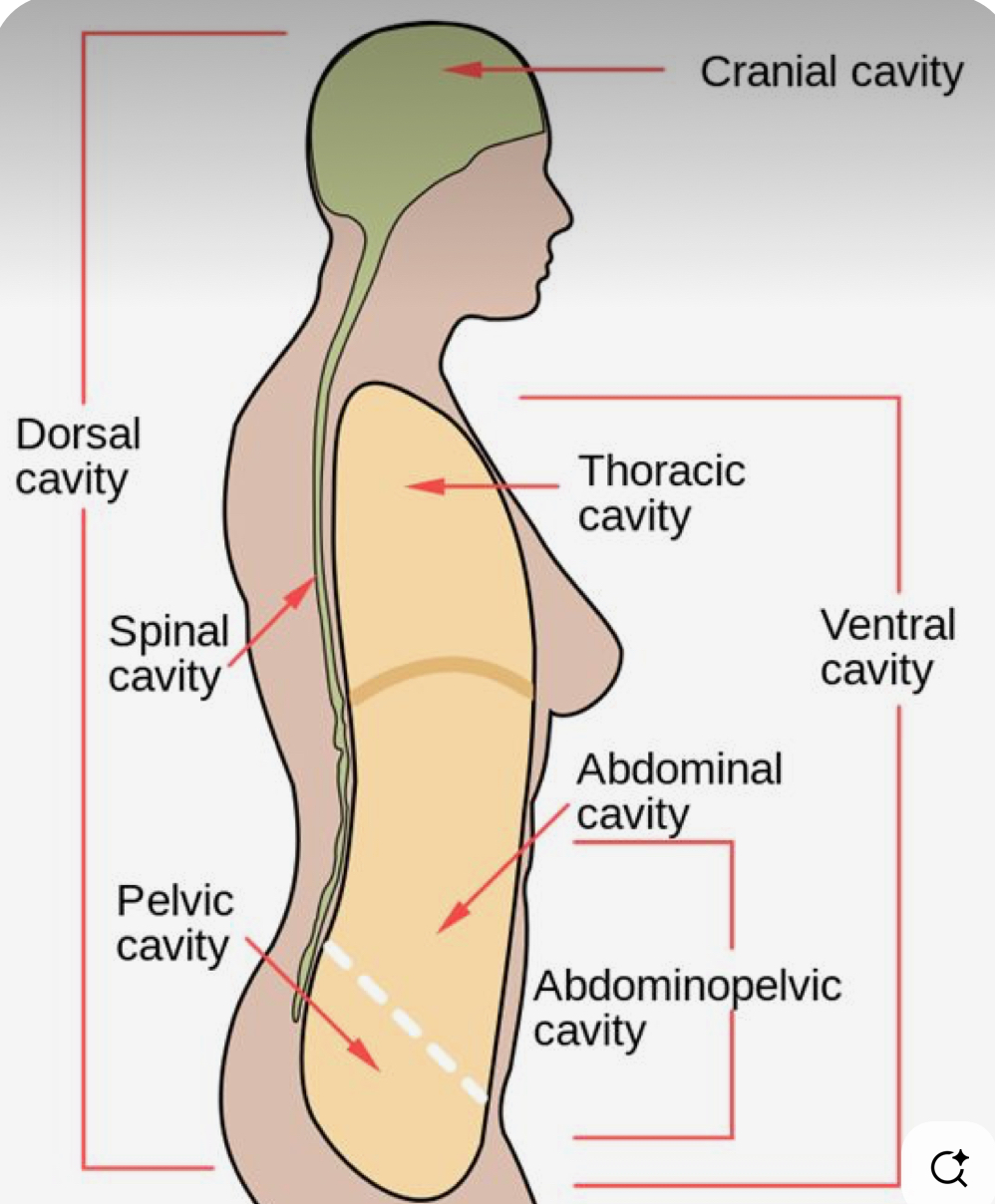
Spinal Cavity (Vertebral Canal)
Houses the vertebrae, Directly in the middle of the back going up and down
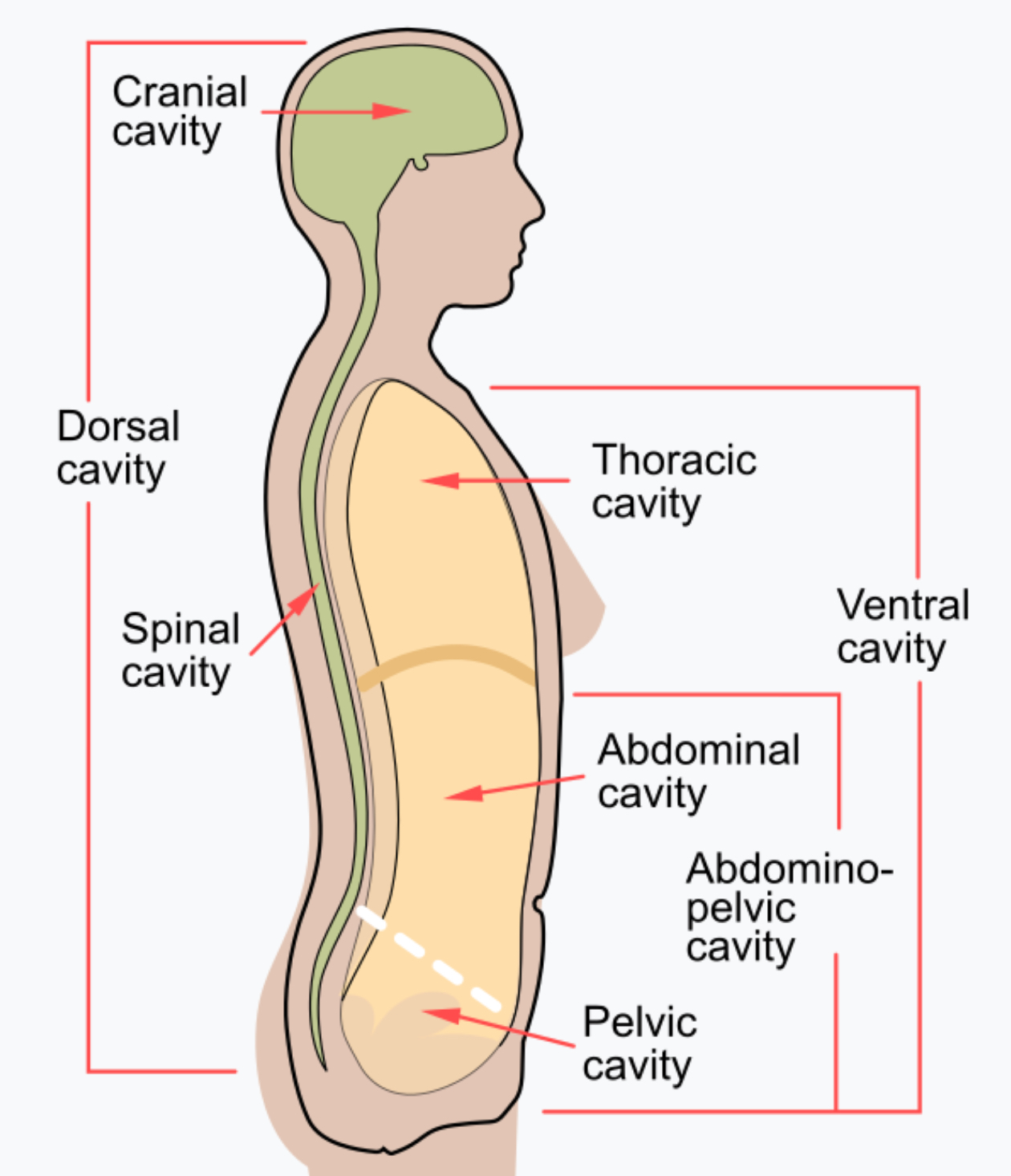
Ventral Cavity (=coelom)
ENTIRE front of the body
Diaphragm
Separates the Abdominal Pelvic Cavity from the Thoracic Cavity
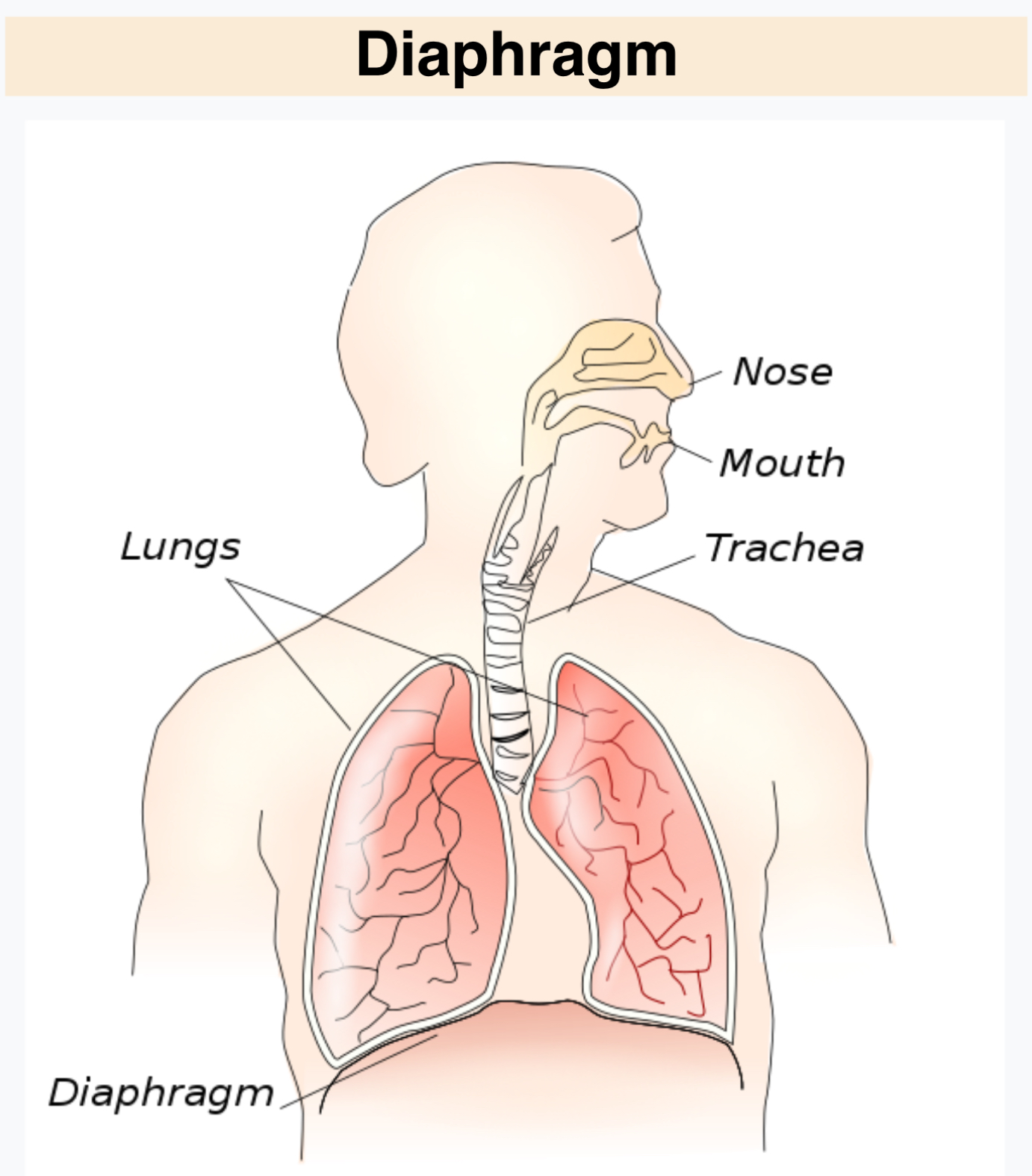
Thoracic Cavity
Everything above the diaphragm (chest area)
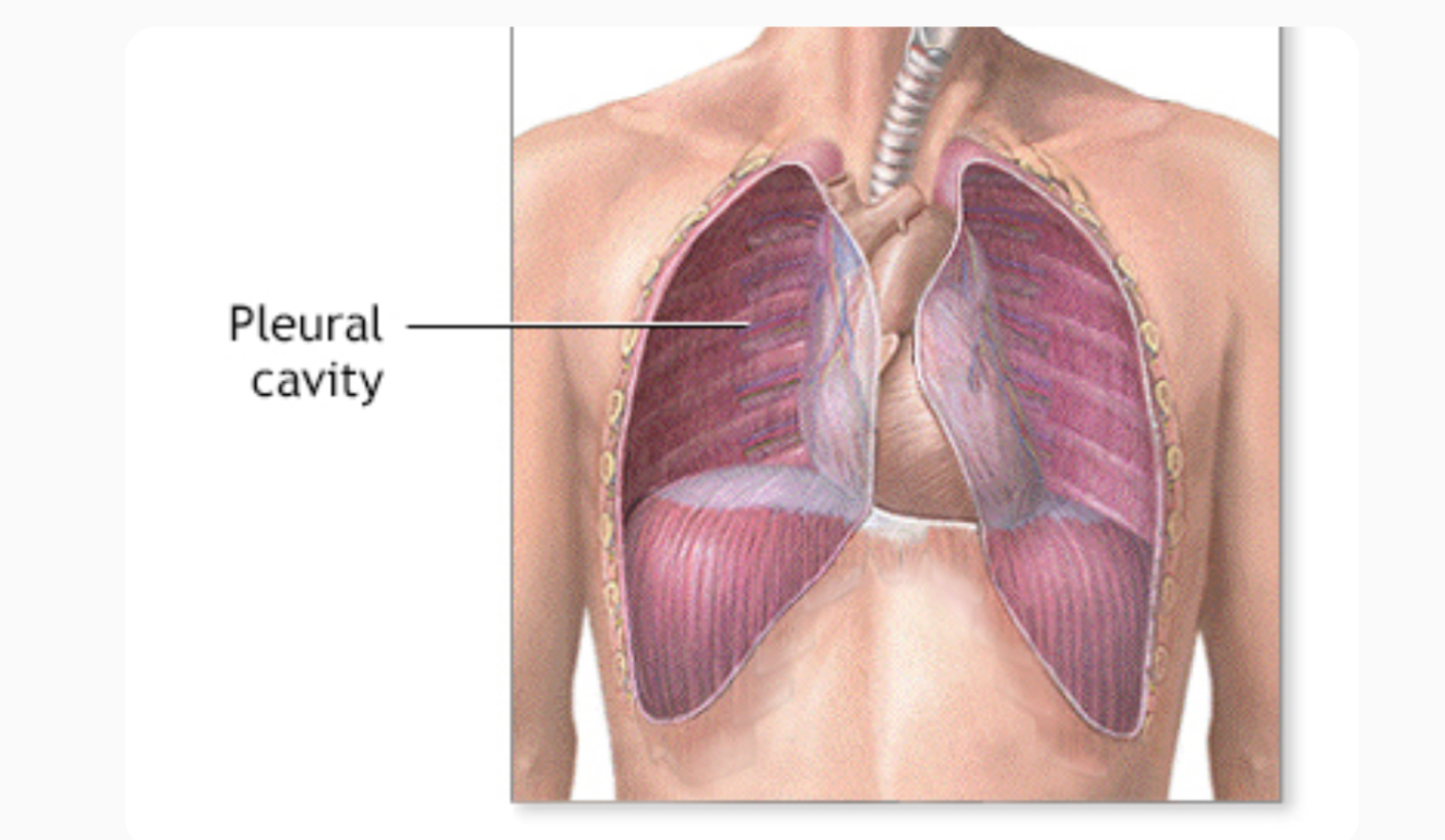
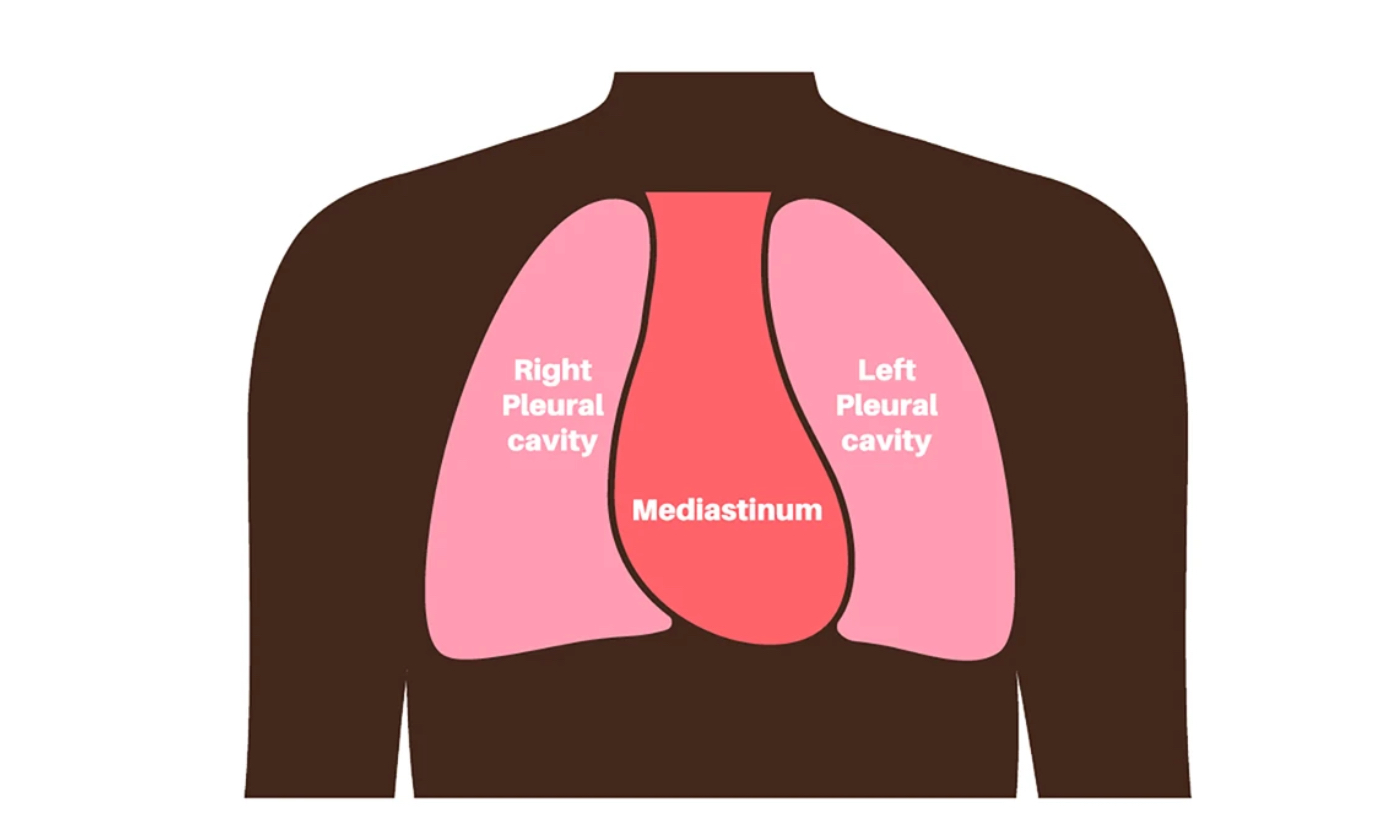
Pleural Cavity
Where the lungs are housed (2 of these) (in chest area)
Mediastinum
Middle of the thoracic cavity, between the lungs (houses the heart,thyroid, trachea, thymus, and esophagus)
Pericardial Cavity
Where the heart is housed
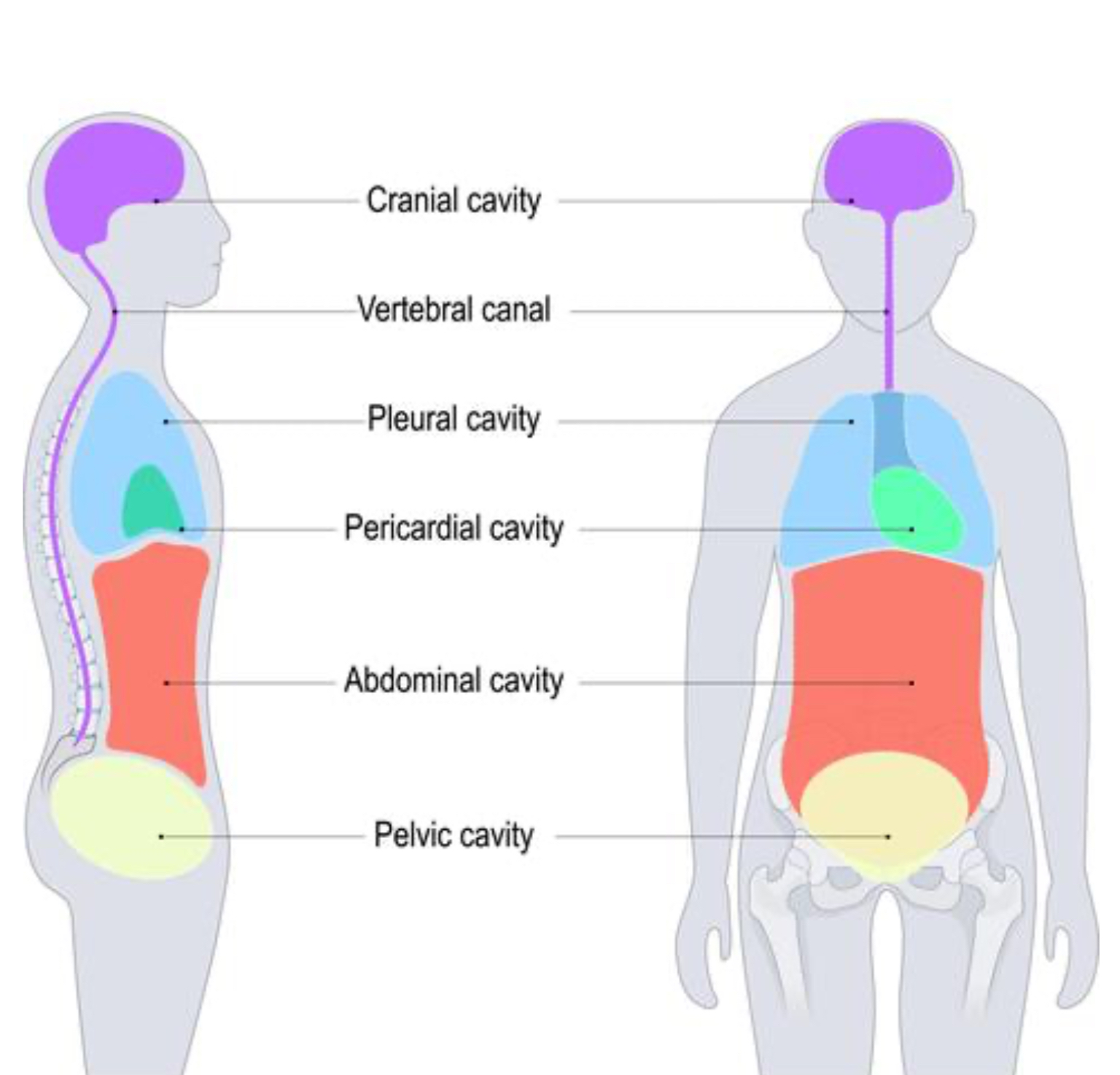
Abdominal Cavity
Below the diaphragm and before the reproductive organs
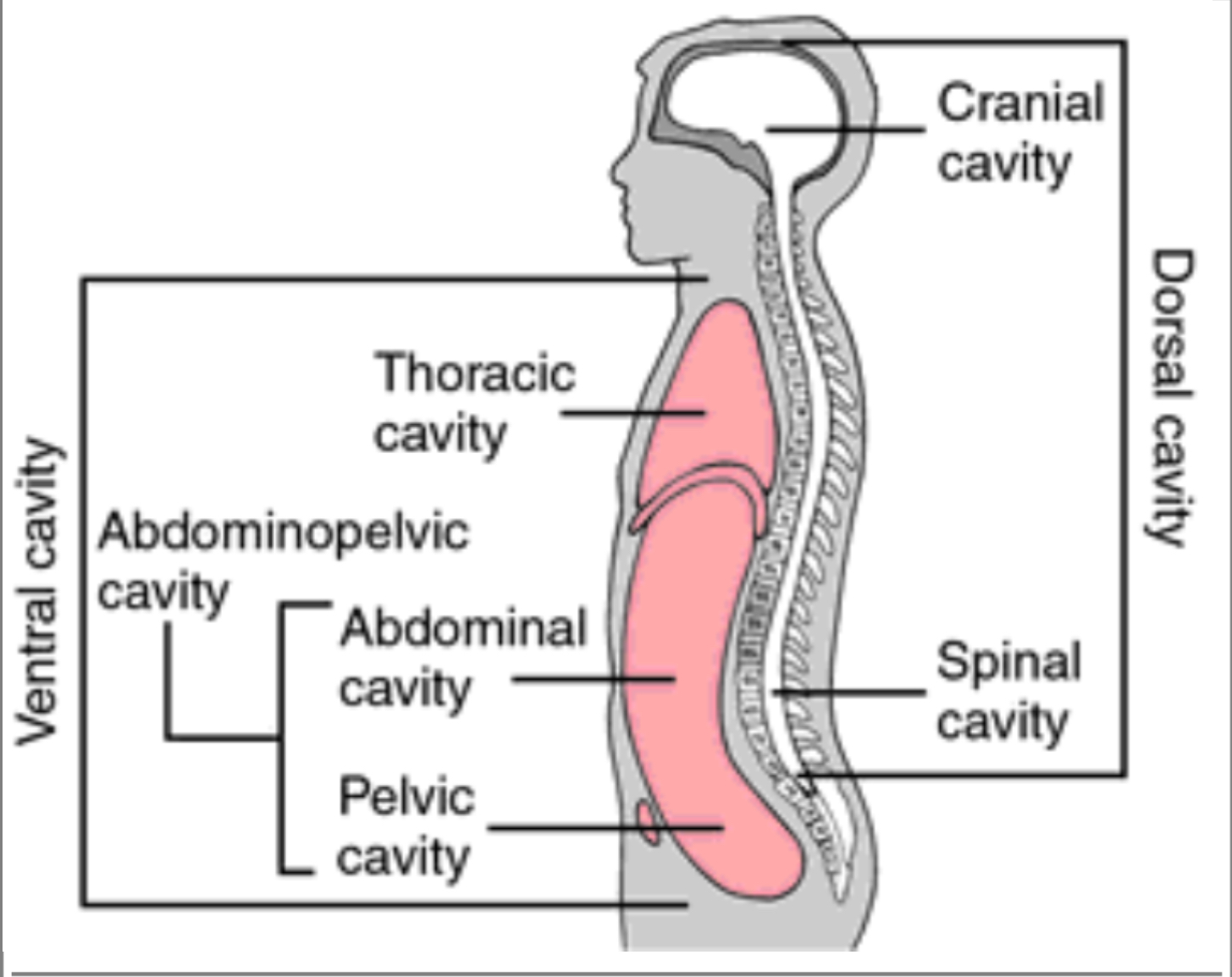
Pelvic Cavity
House the reproductive system, “in between” the pelvis
Parietal Pleural Membrane (=pleura)
Lining of the pleural cavity (membrane lining of where the lungs are housed)
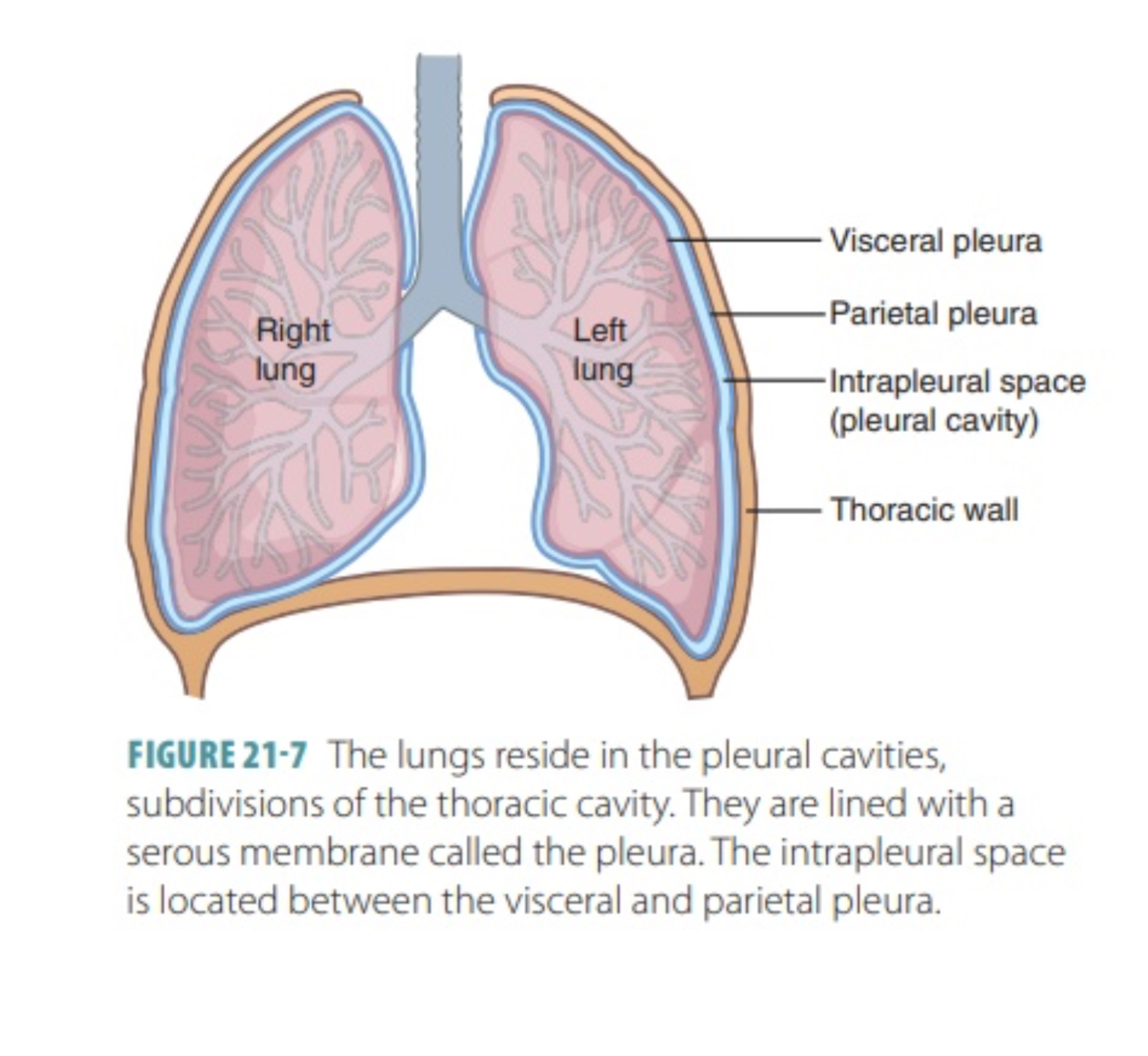
Visceral Pleural Membrane
Lining of (on) the lung
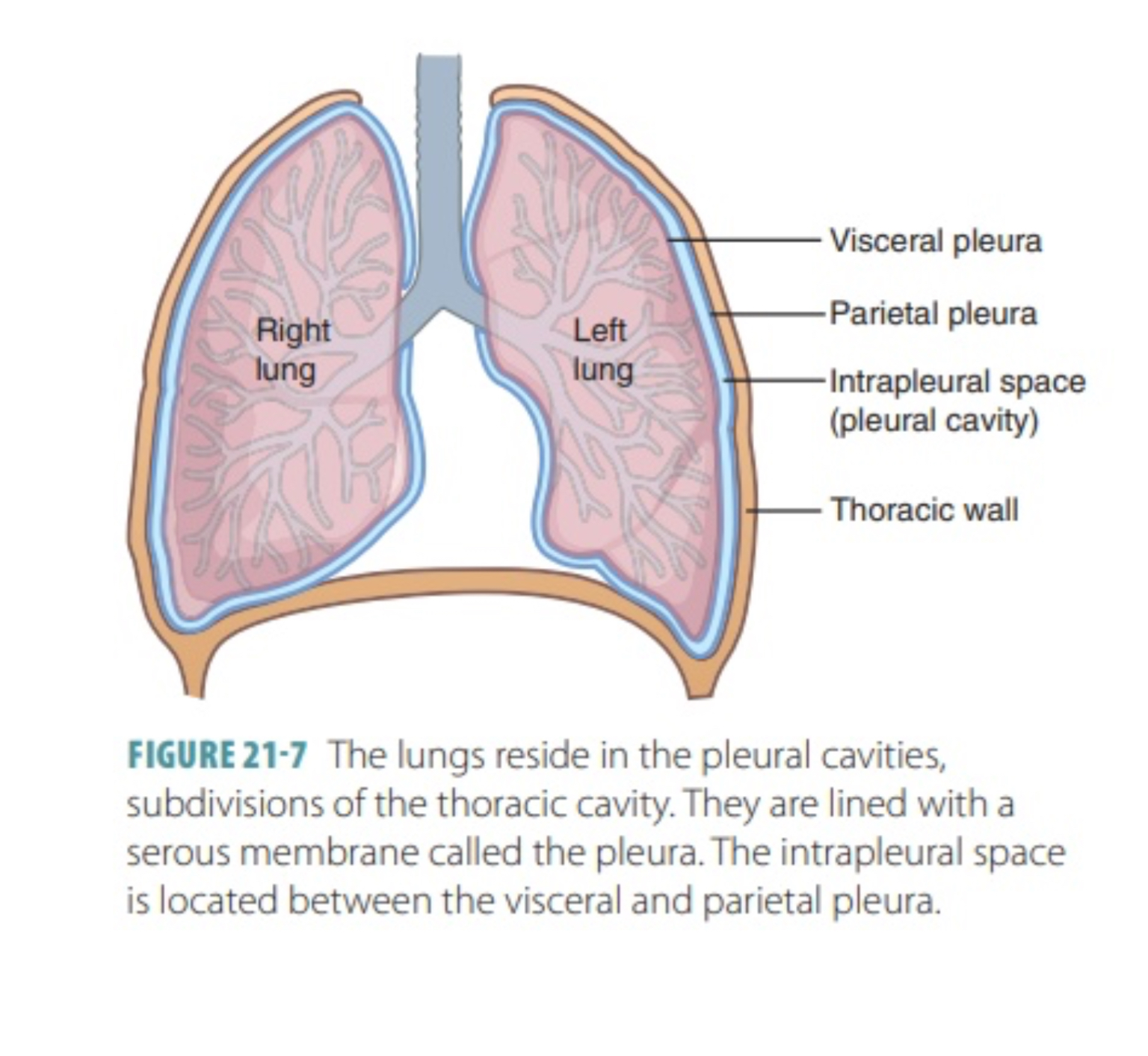
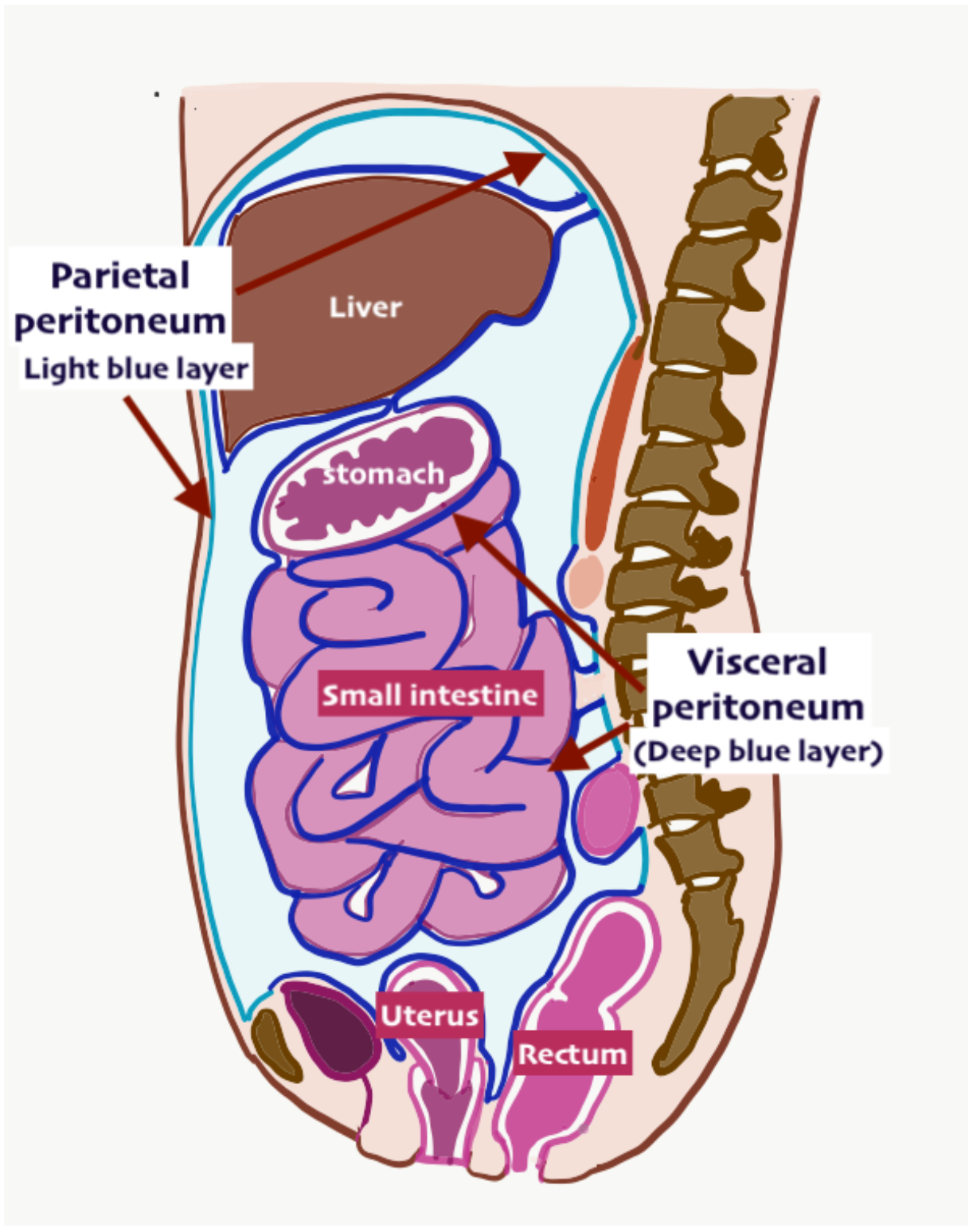
Parietal Peritoneal Membrane (=peritoneum)
Membrane Lining of the Abdominal Pelvic Cavity
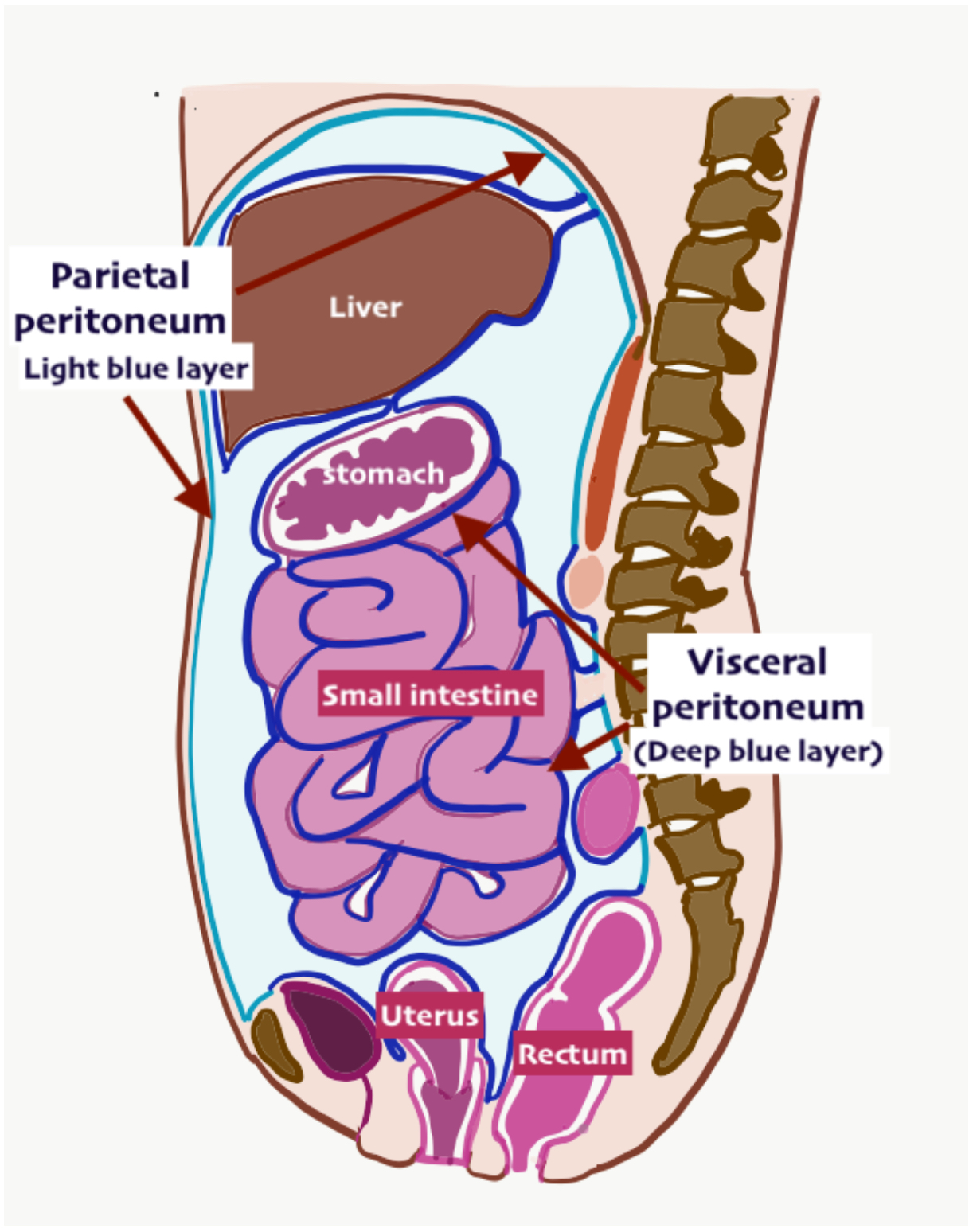
Parietal Pericardial Membrane (=pericardium)
Membrane layer of the pericardial cavity
Visceral peritoneal cavity
Lines any/all of the organs in the abdominal pelvic cavity
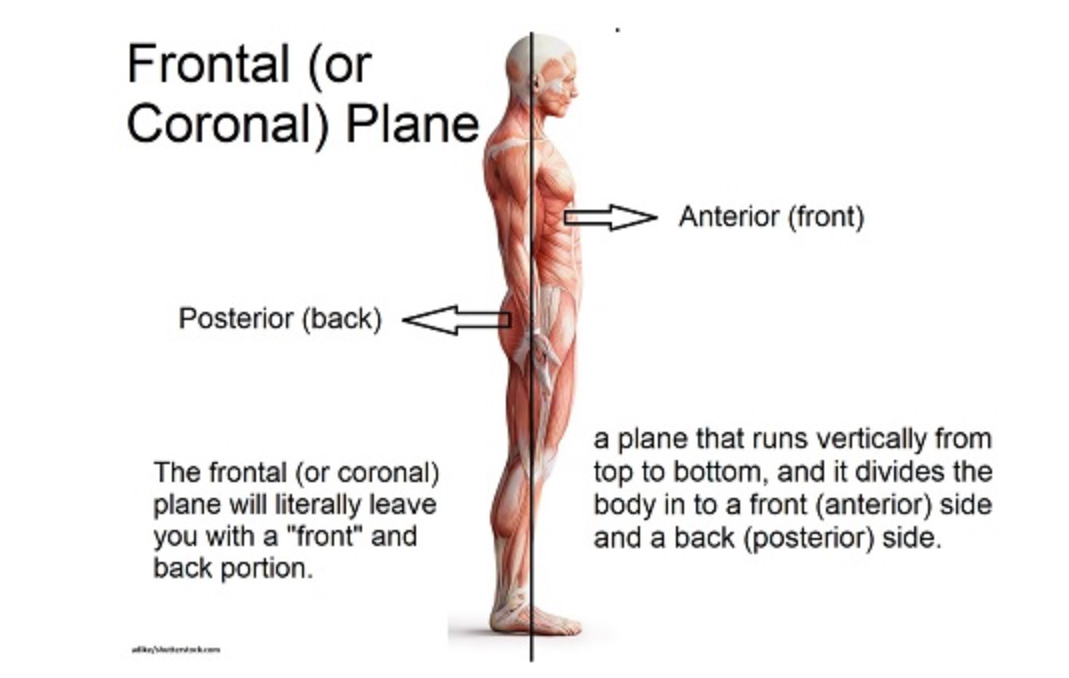
Coronal (=frontal)
Separates anterior (side with the face) from posterior (side with your ass)(can be equal or unequal parts)
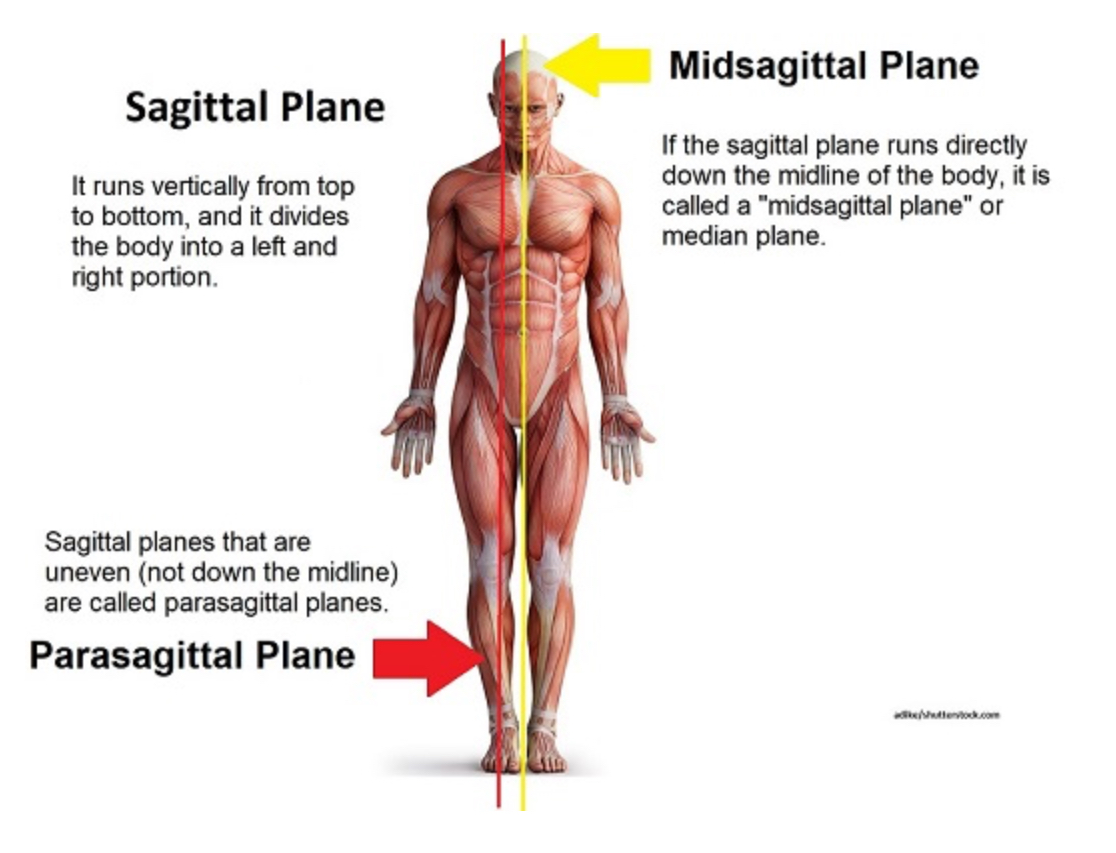
Midsaggital (=median)
Separates into right and left EQUAL parts
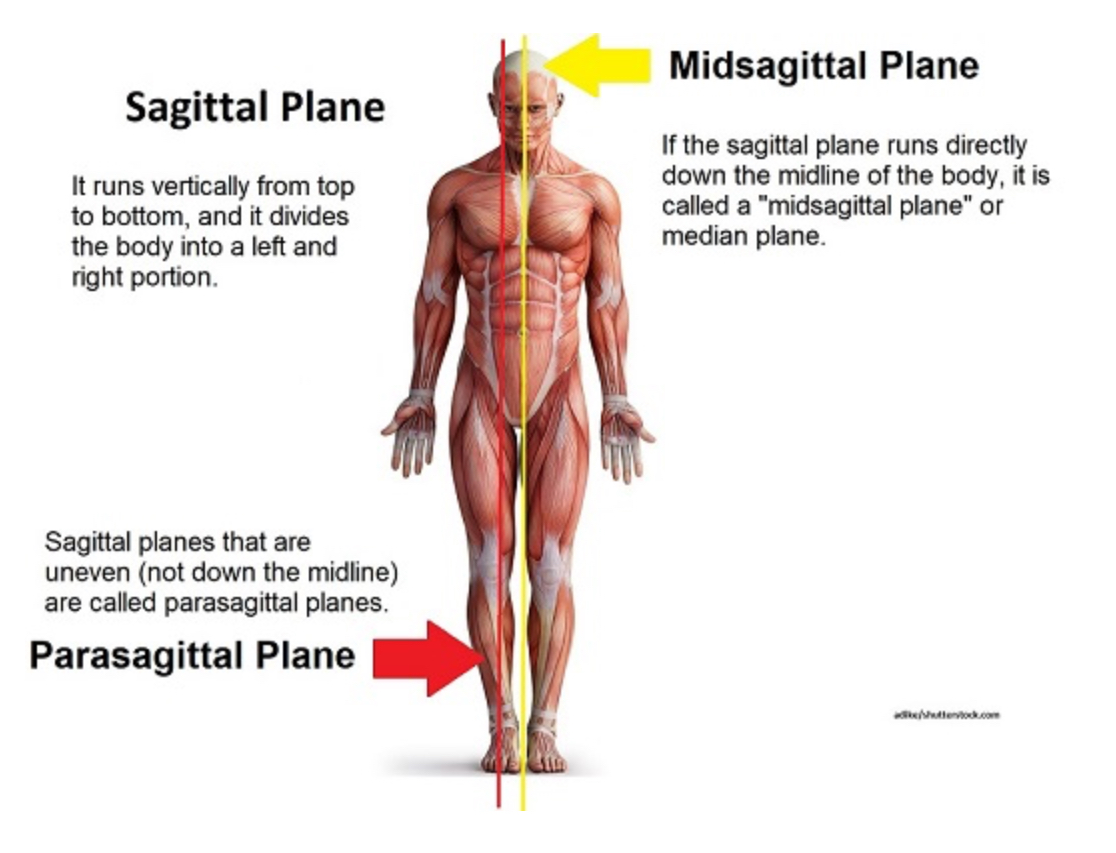
Parasaggital
Separates into right and left UNEQUAL parts
Oblique
A cut that starts in one plan and ends in different plane (I.e. starts in the coronal and ends in the transverse)
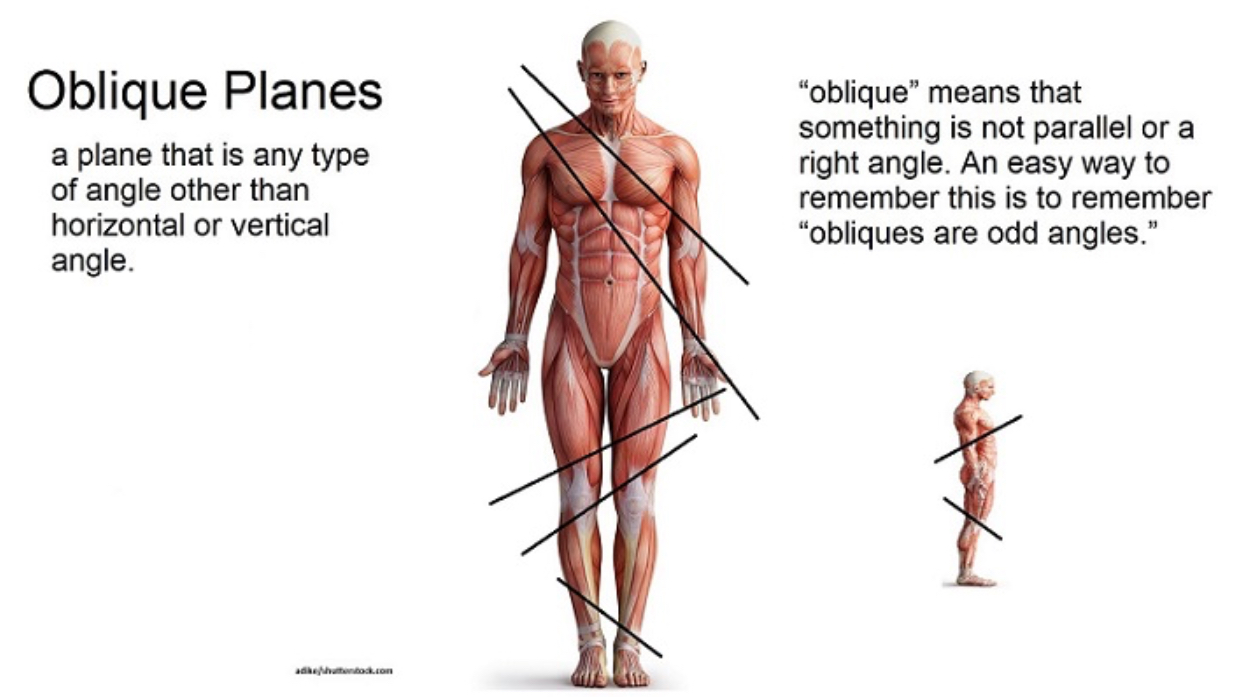
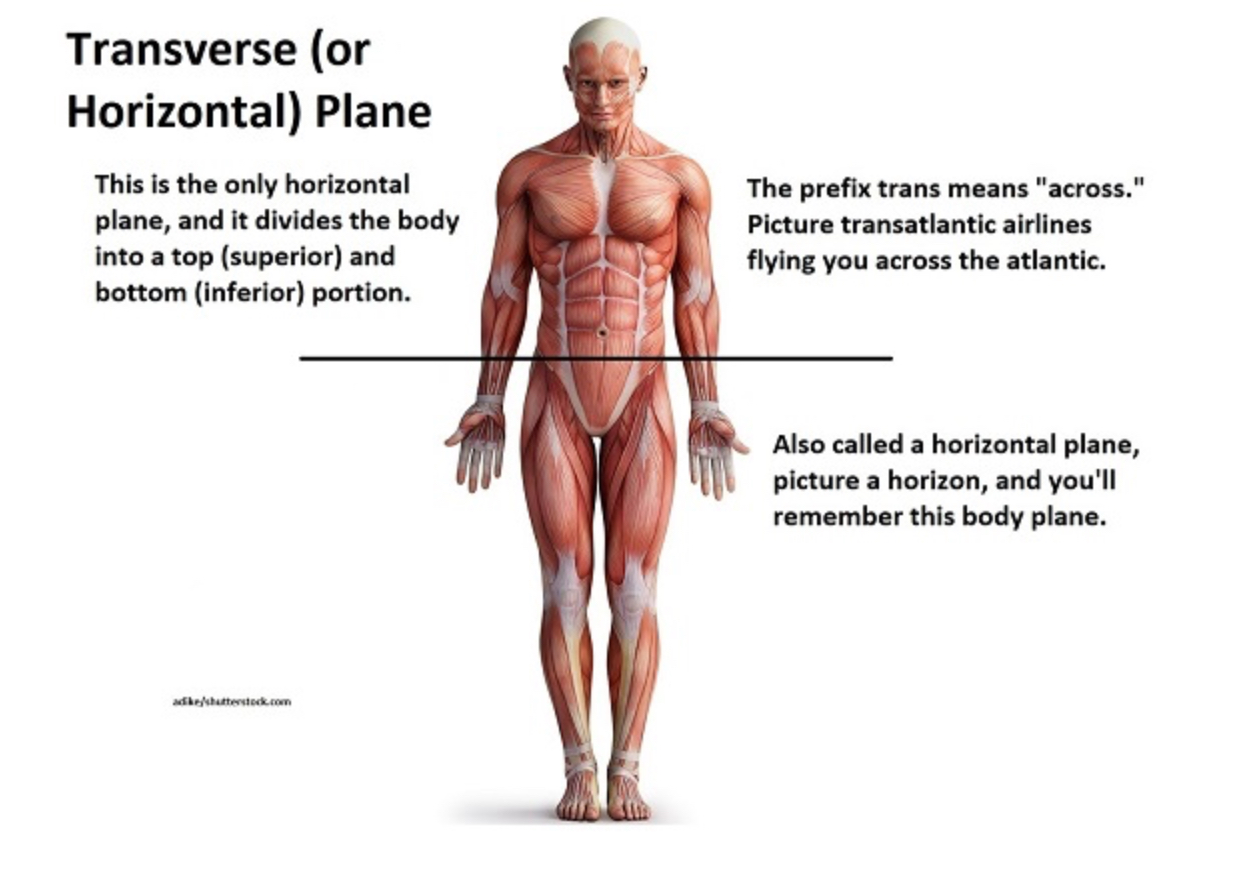
Transverse (horizontal or cross section)
Separates the superior (half including your head) from the inferior (half including your feet)(can be equal or unequal parts)
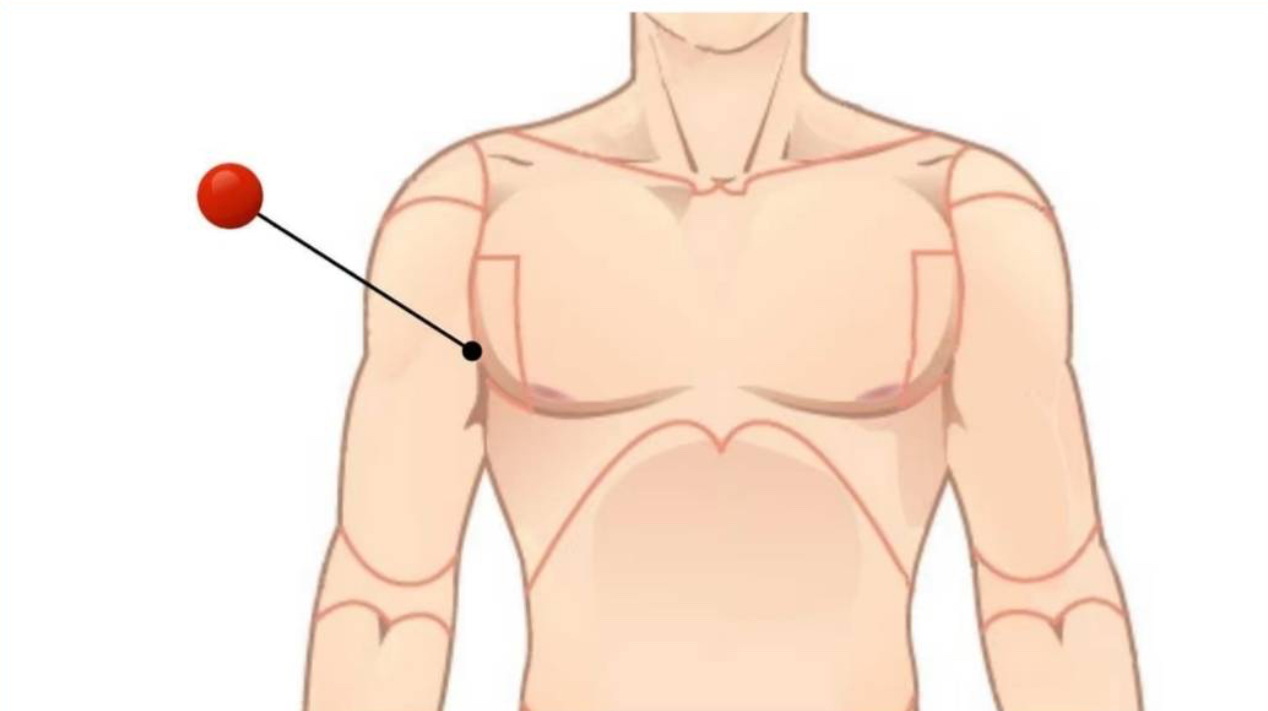
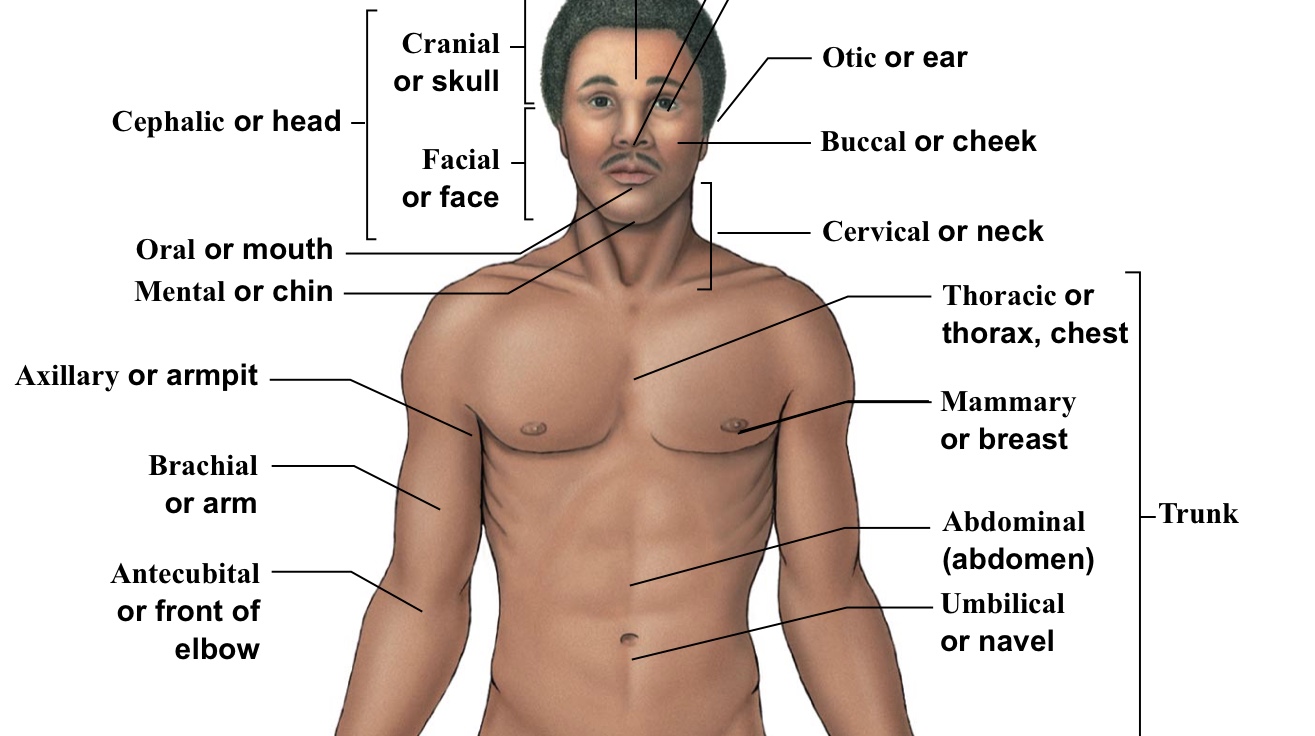
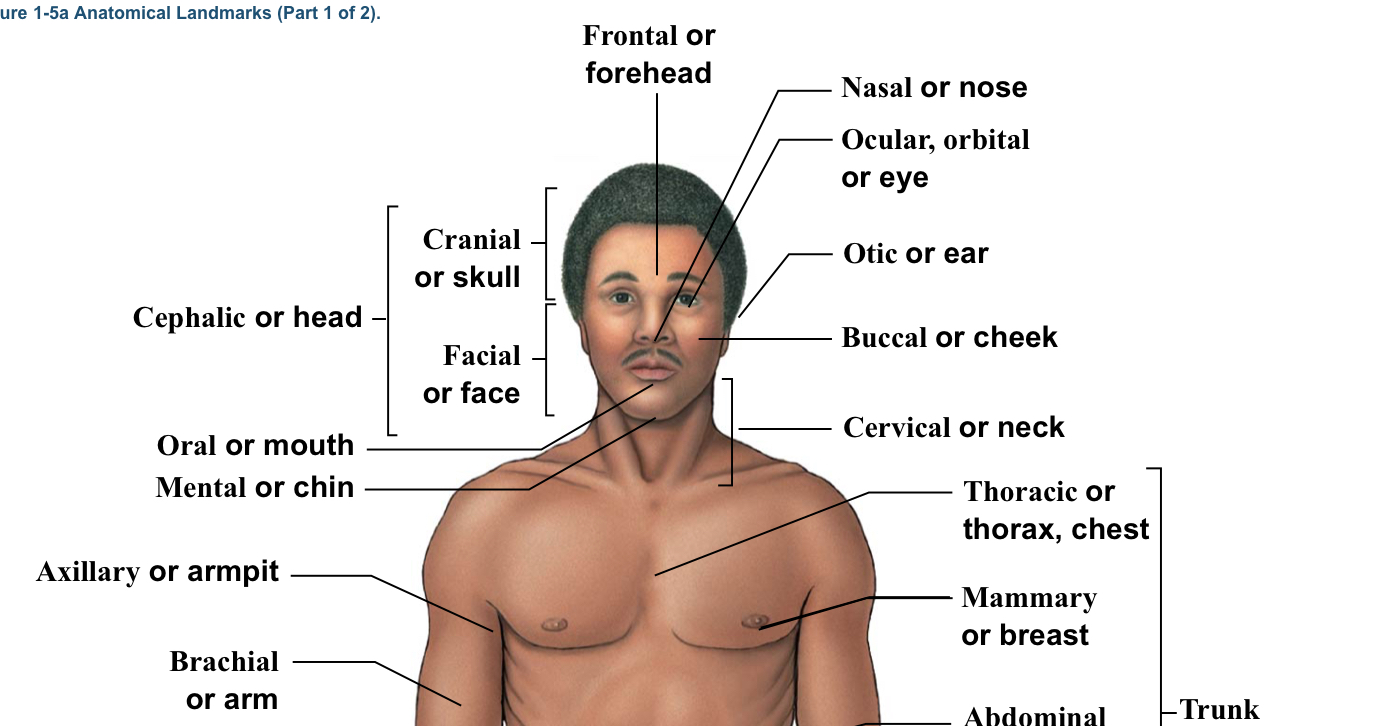
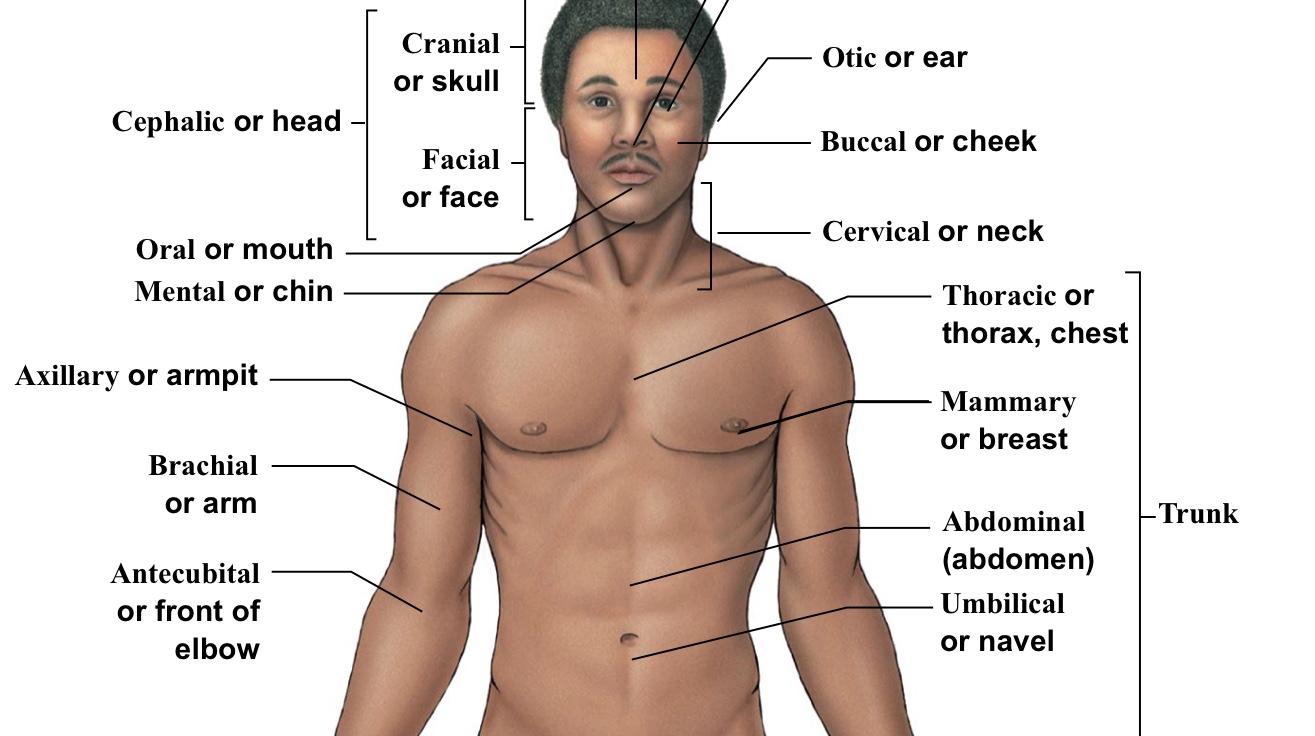
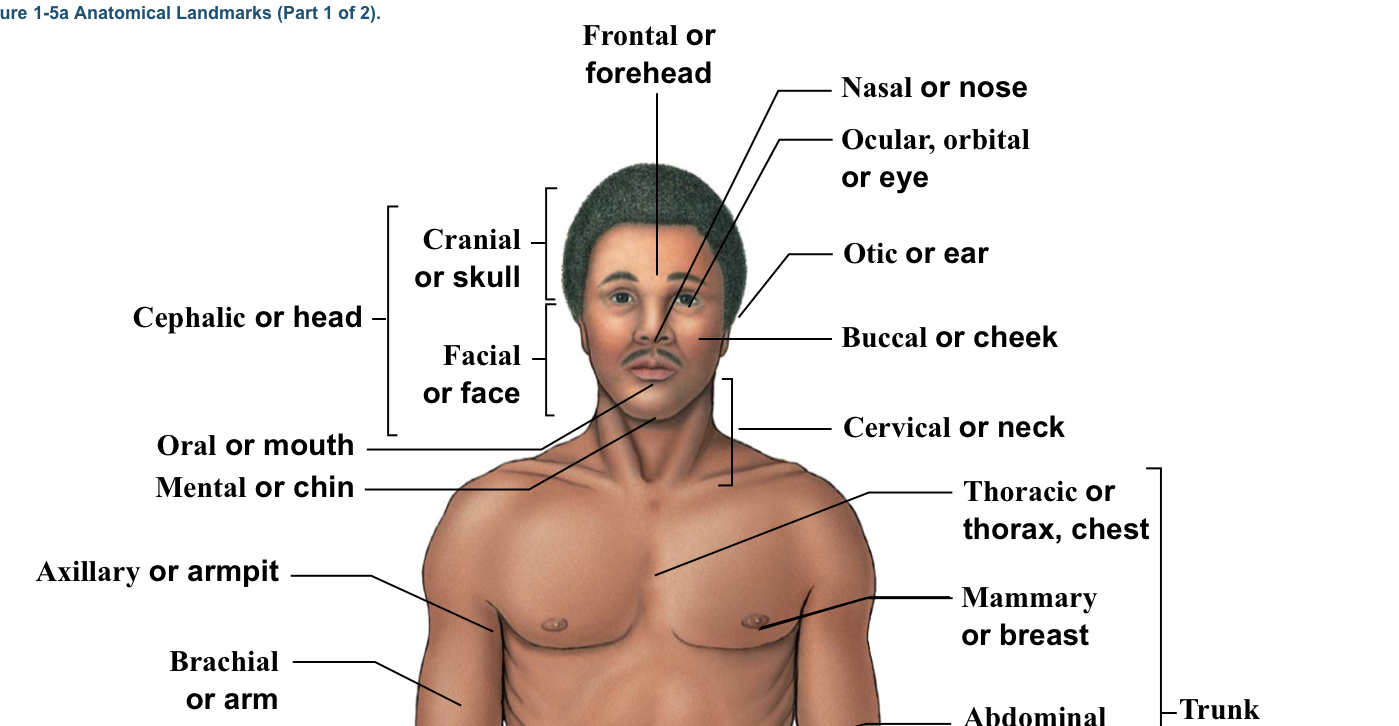
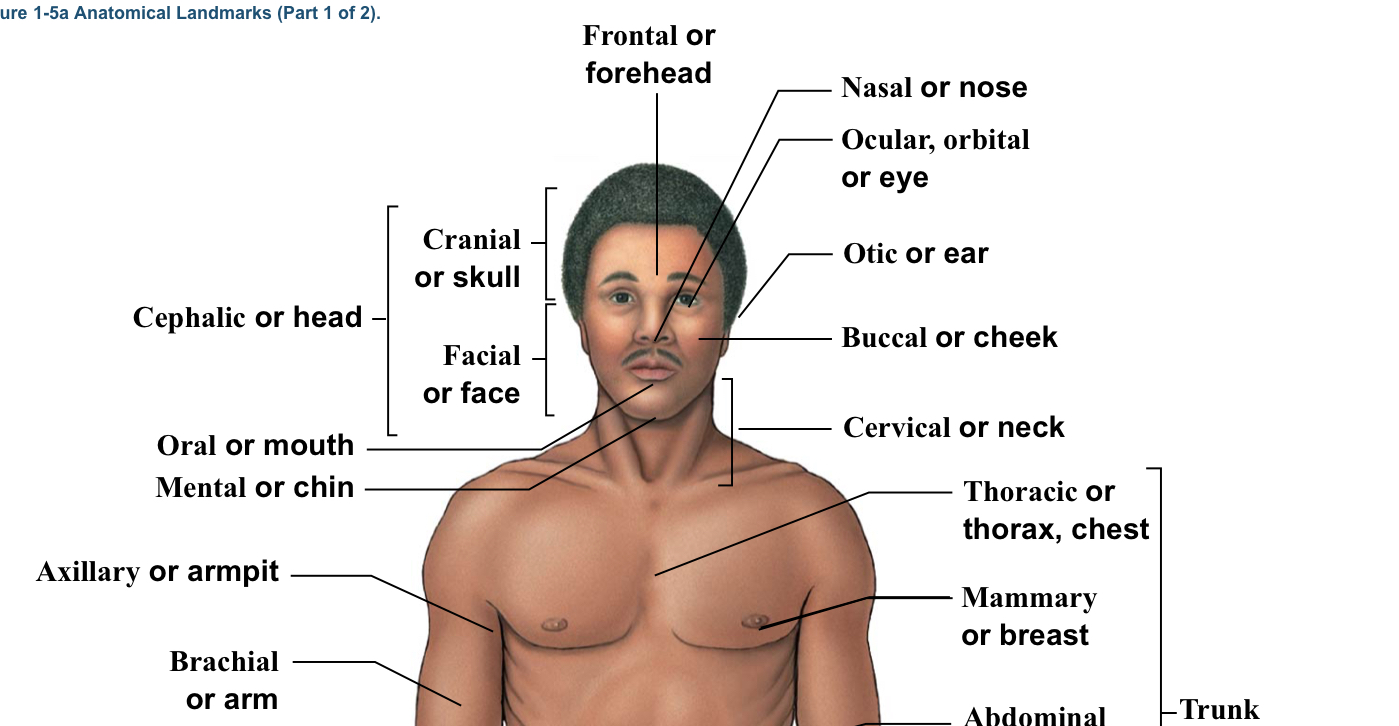
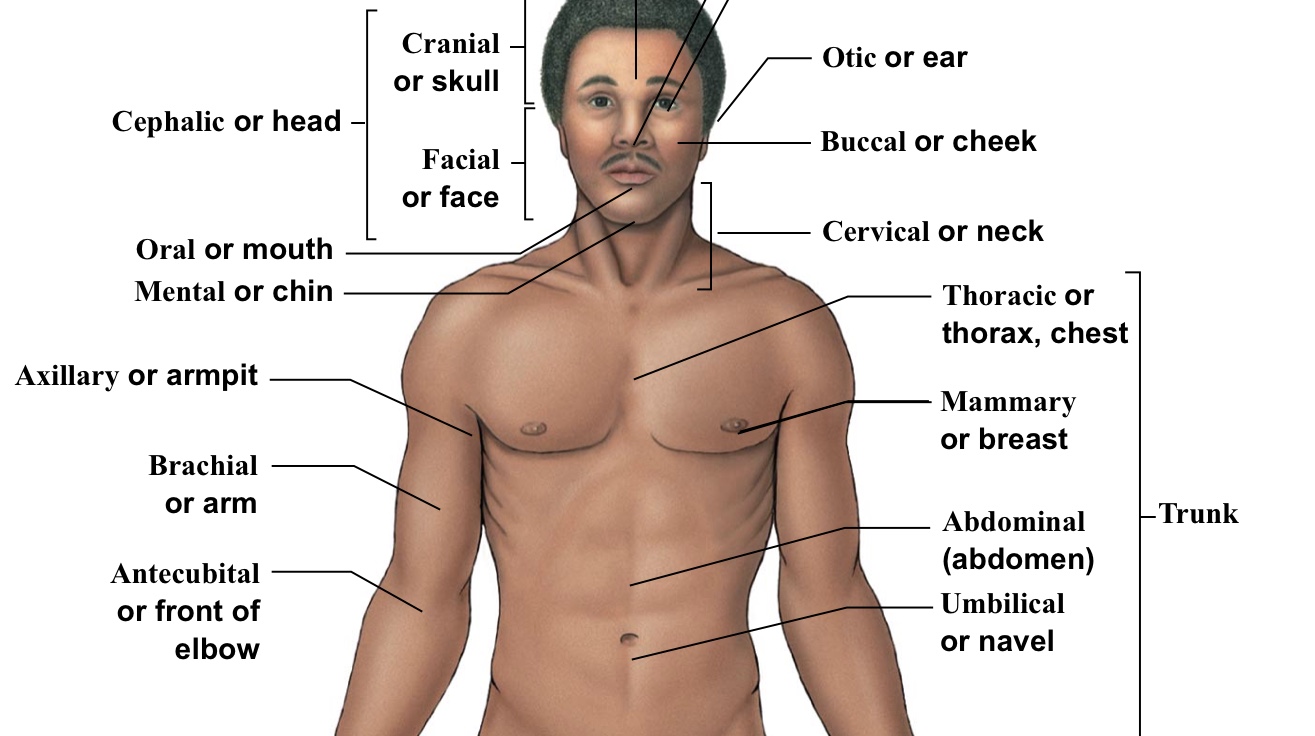
Axillary
Armpits
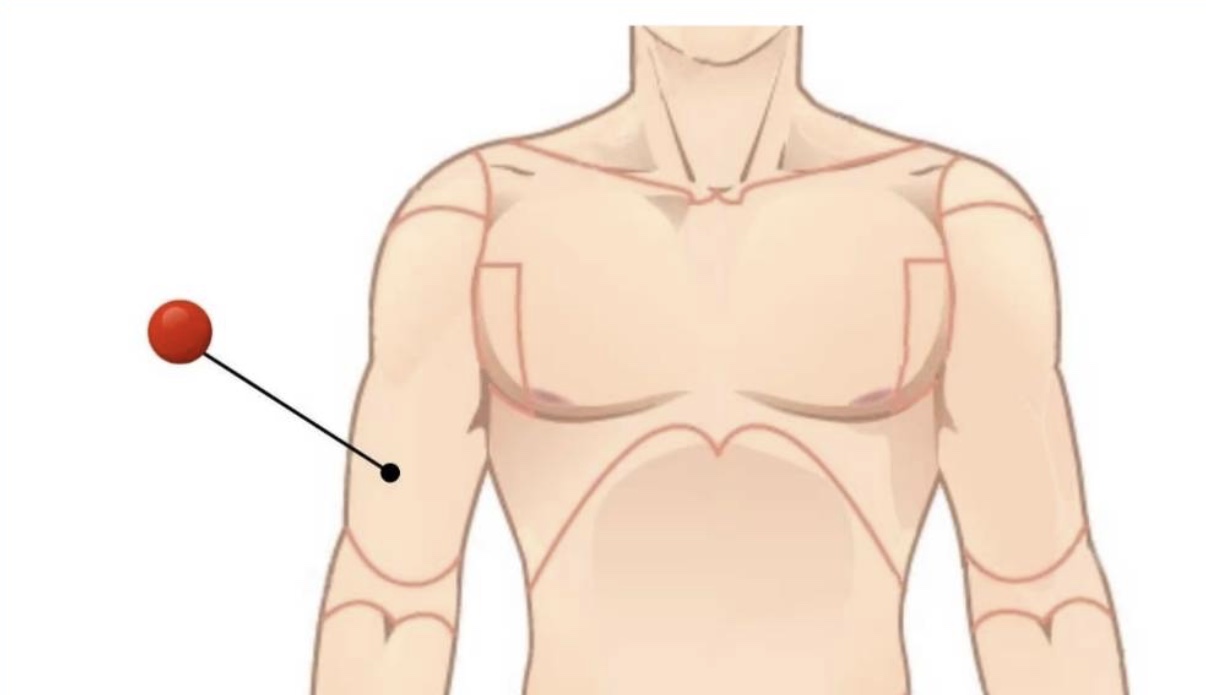
Brachial
Arm (arrow points to bicep section usually)
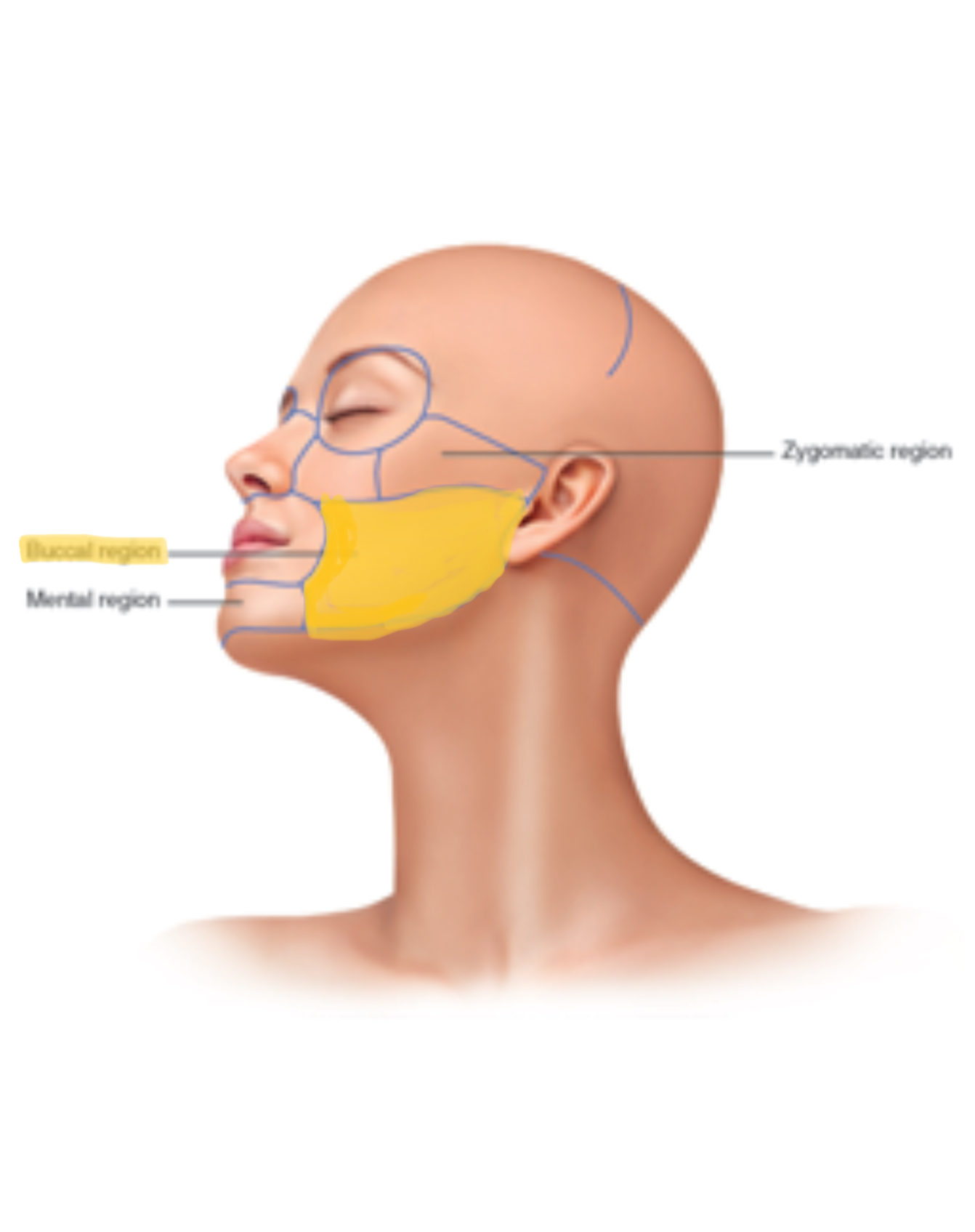
Buccal
Cheek
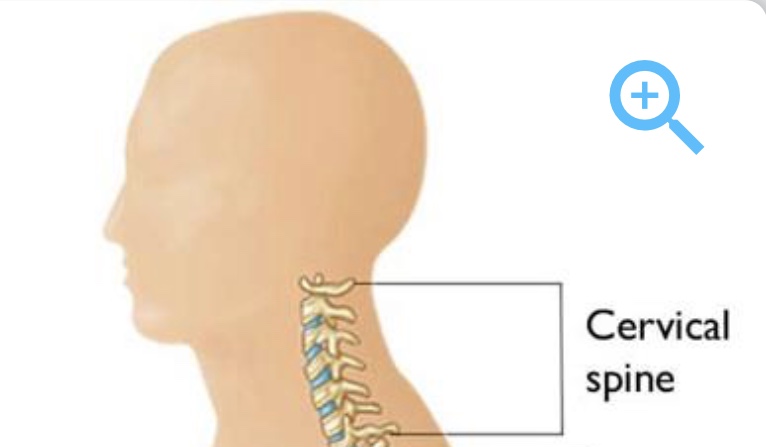
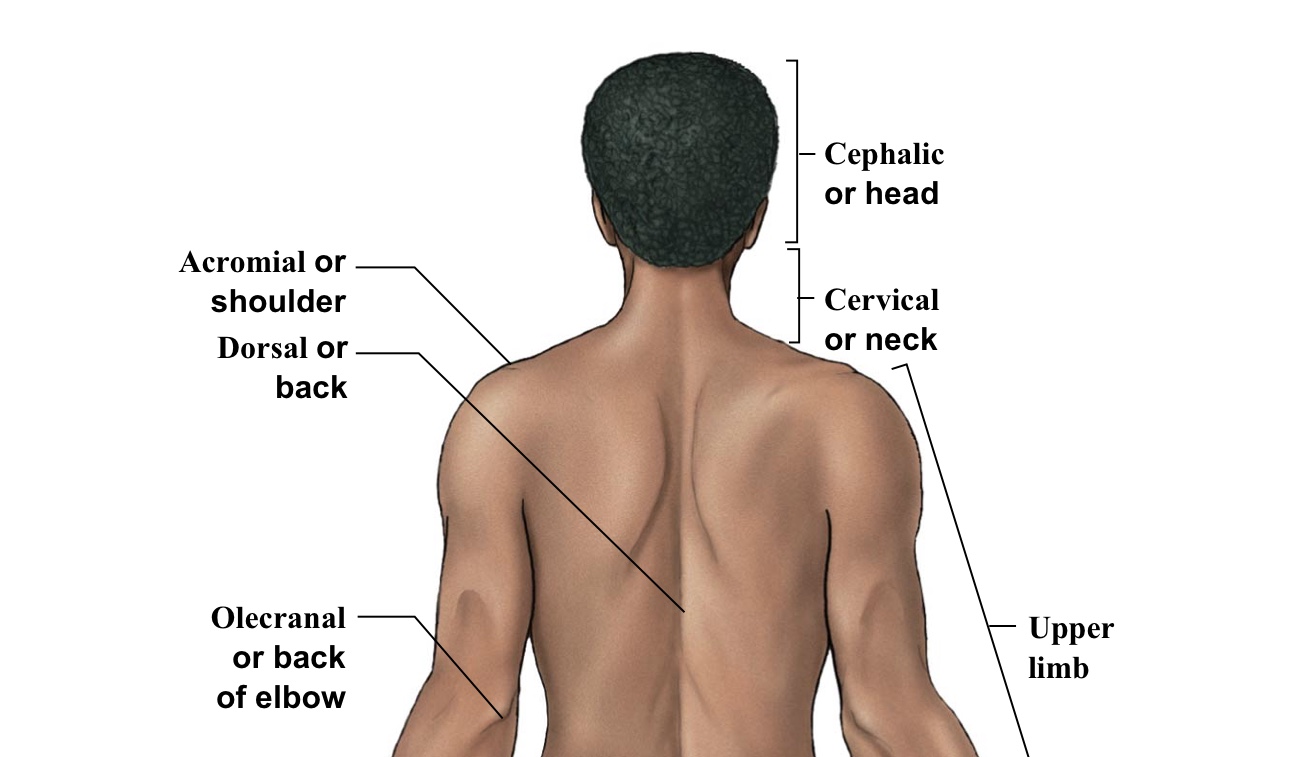
Cervical
The neck area (think c spine)(the bracket is around the whole neck area)
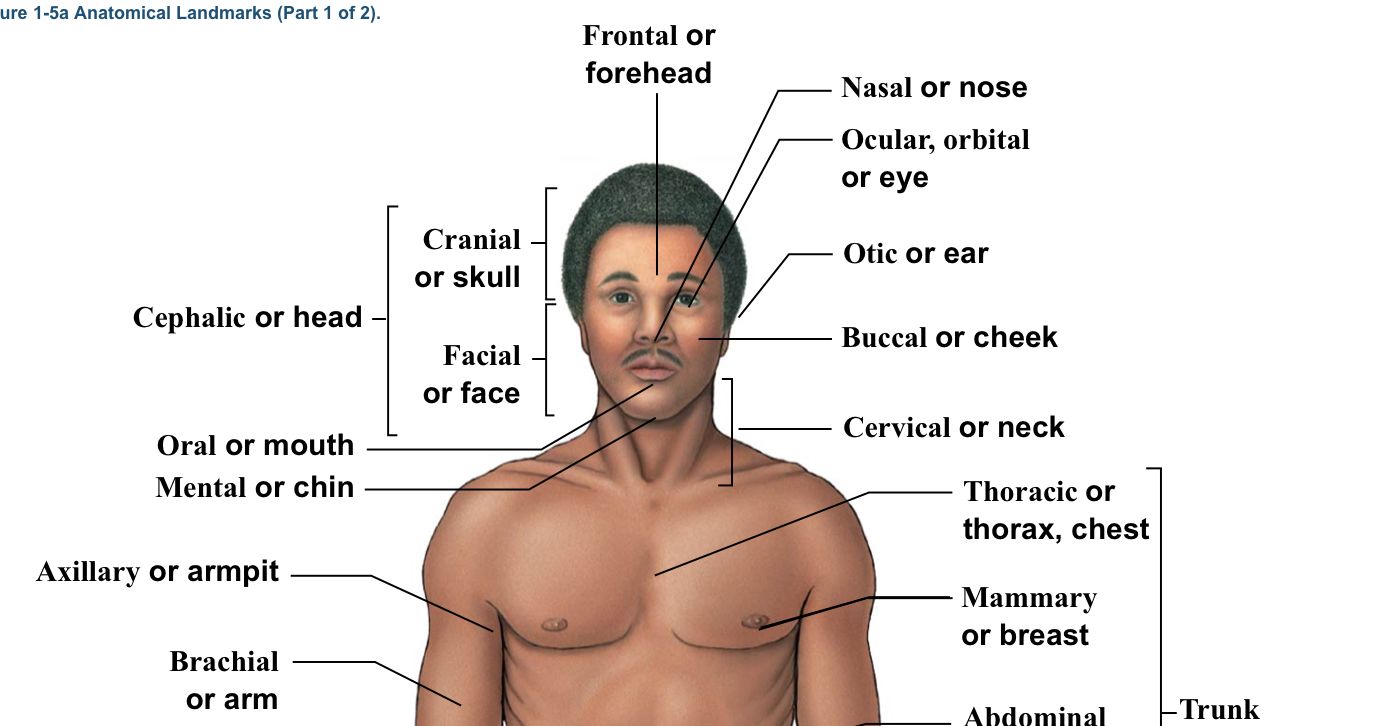
Facial
Bracket of head (the bracket is located from the eyebrows to the chin)
Mental
Chin
Nasal
Nose
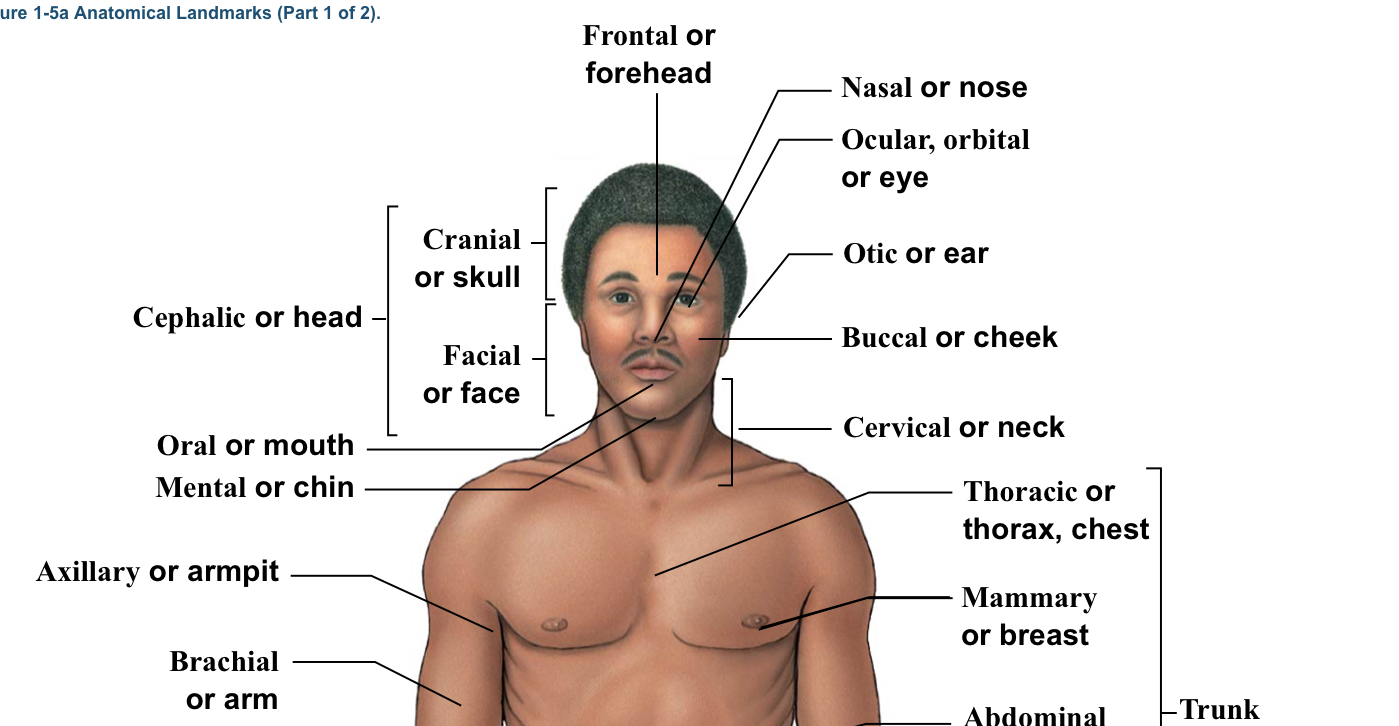
Oral
Mouth
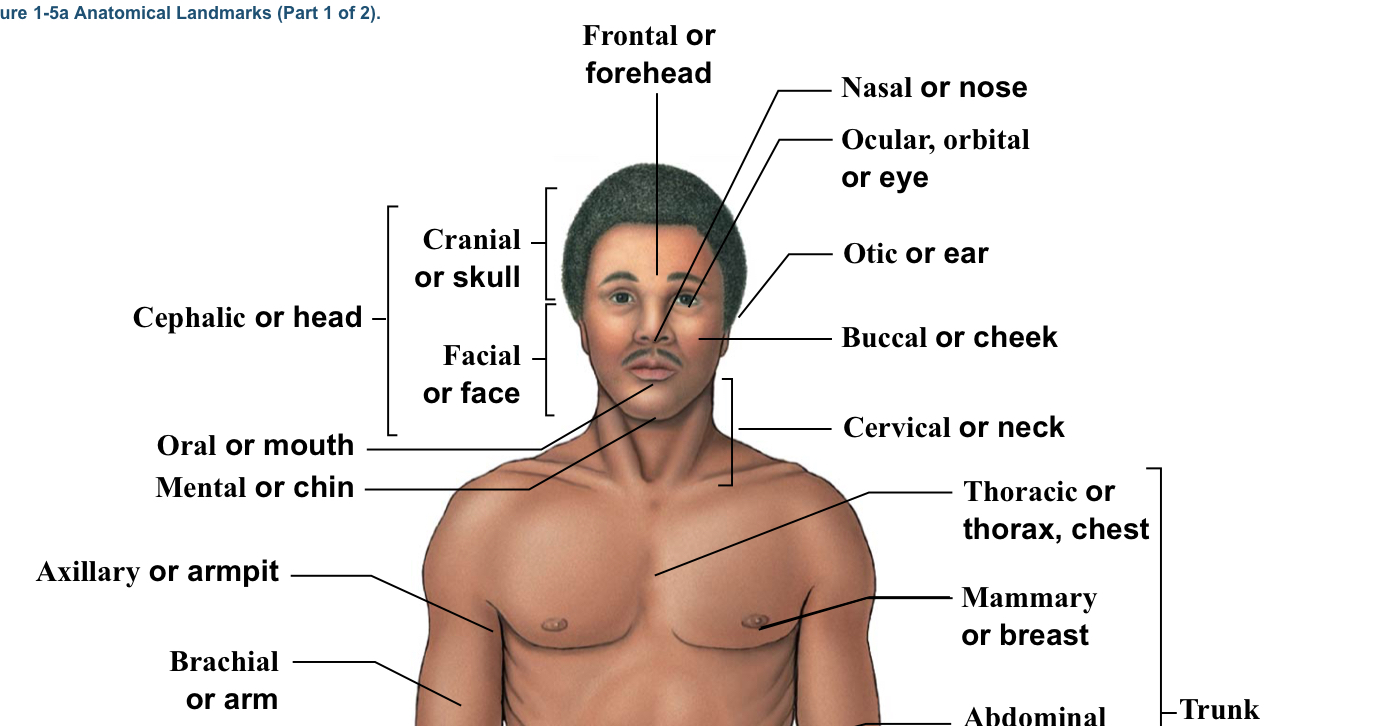
Acromial (deltoid)
Shoulder (Arrow points to the very top and center of shoulder area-refer to picture)
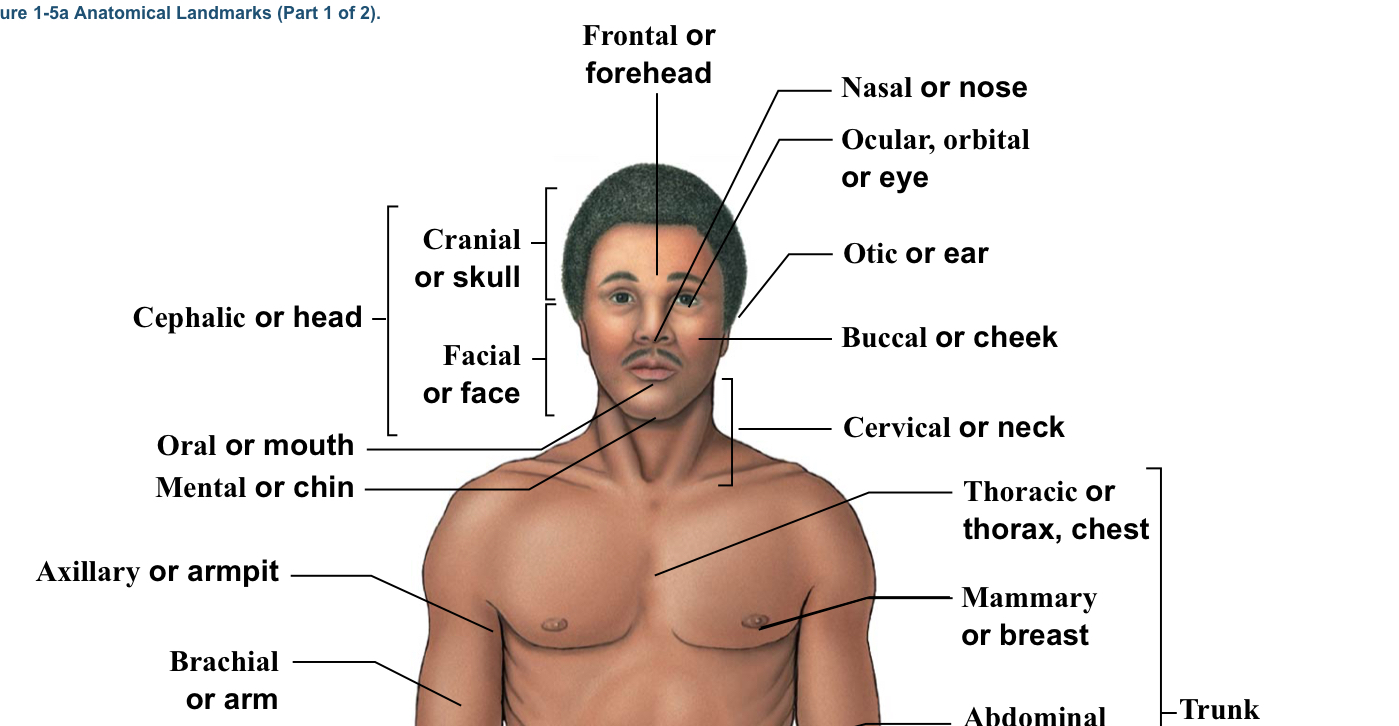
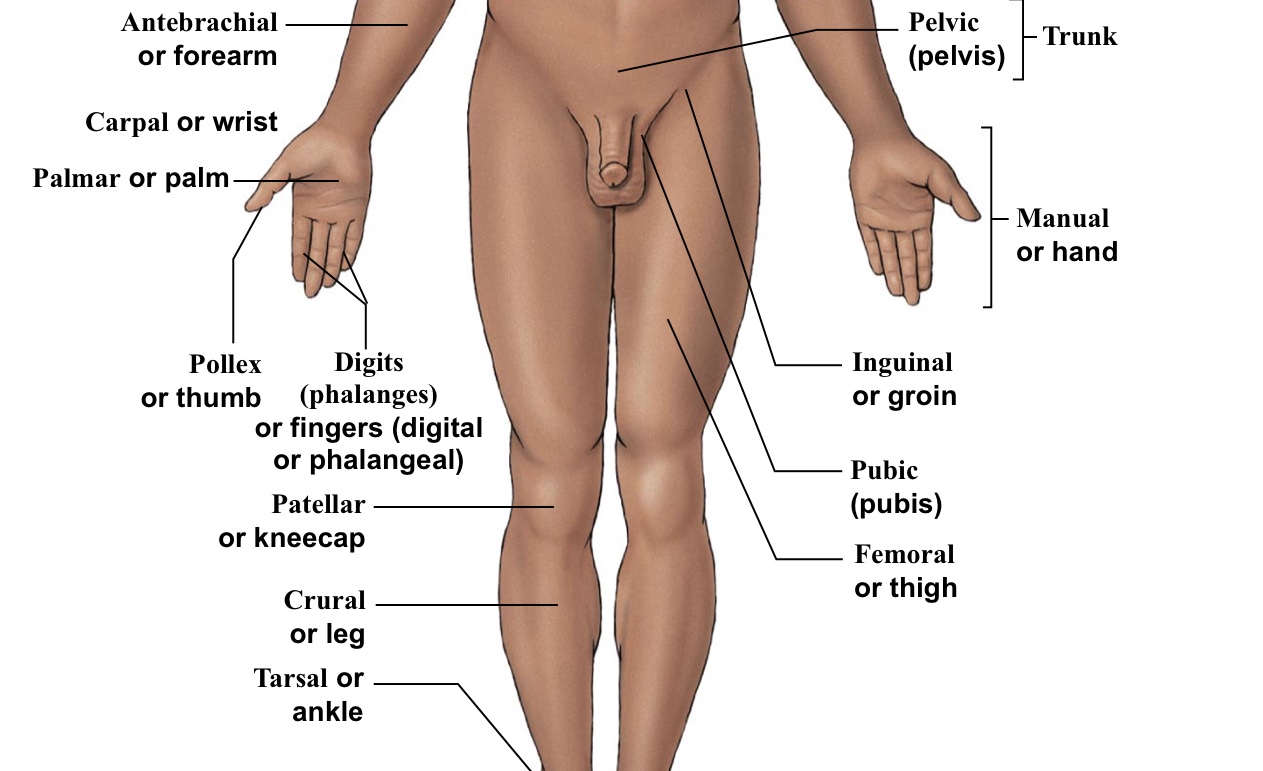
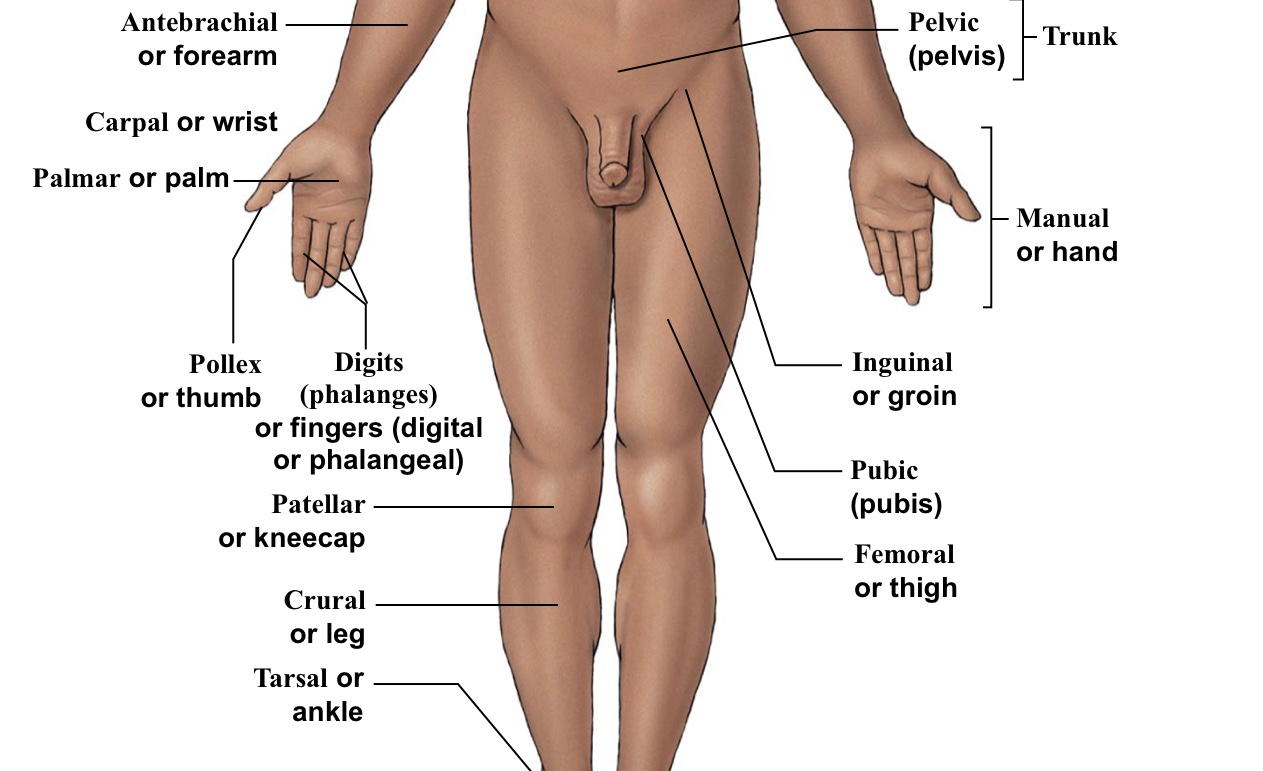
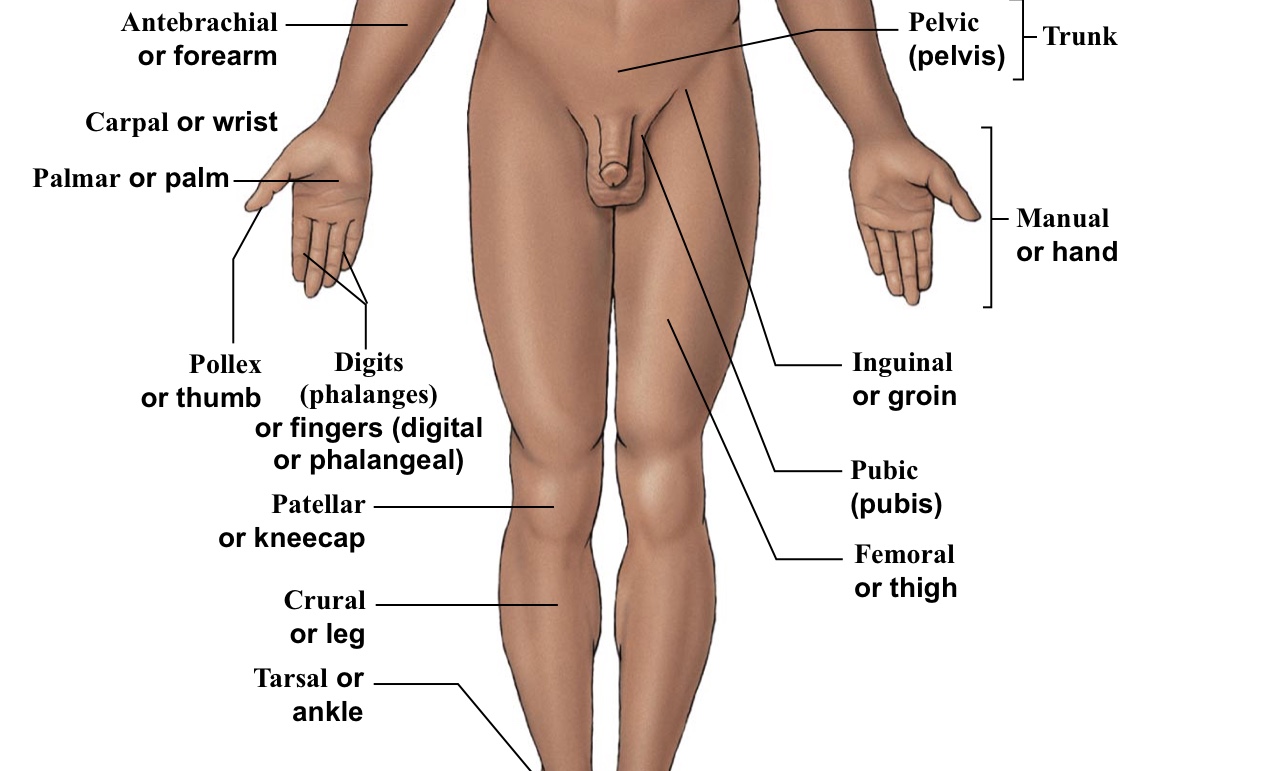
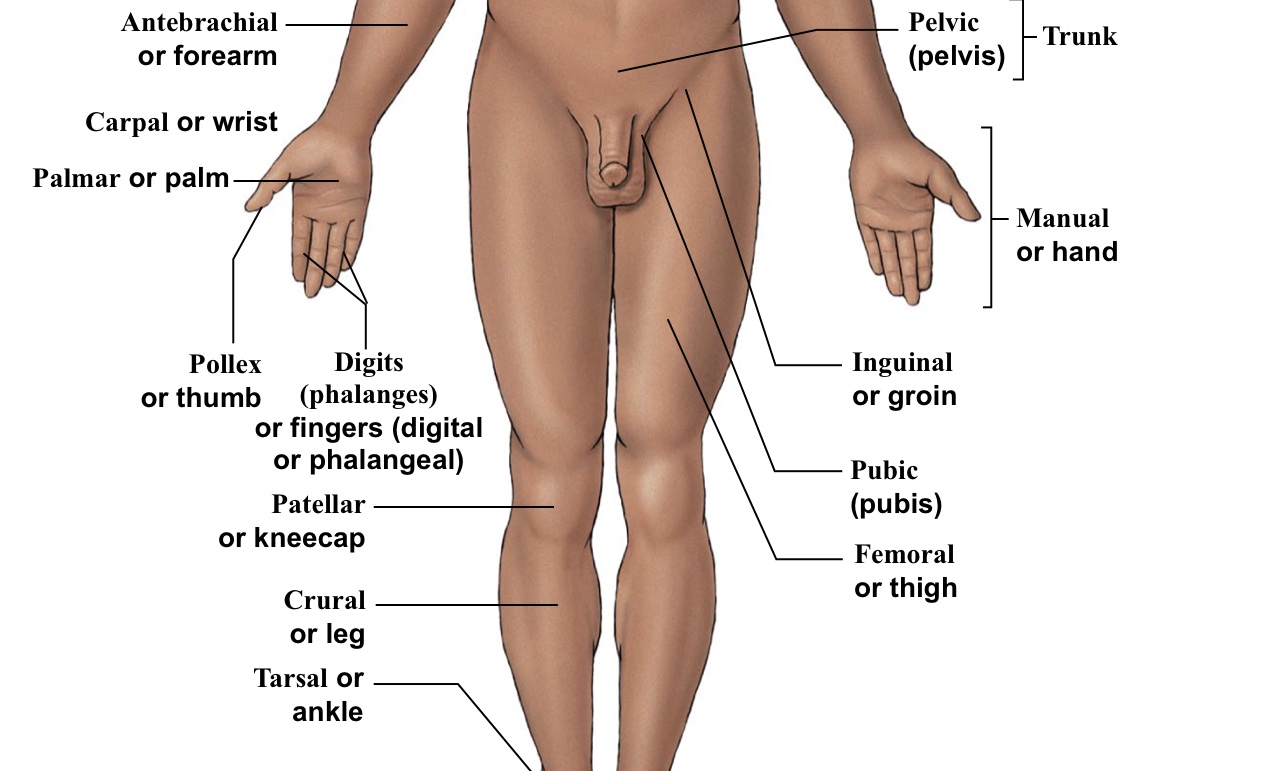
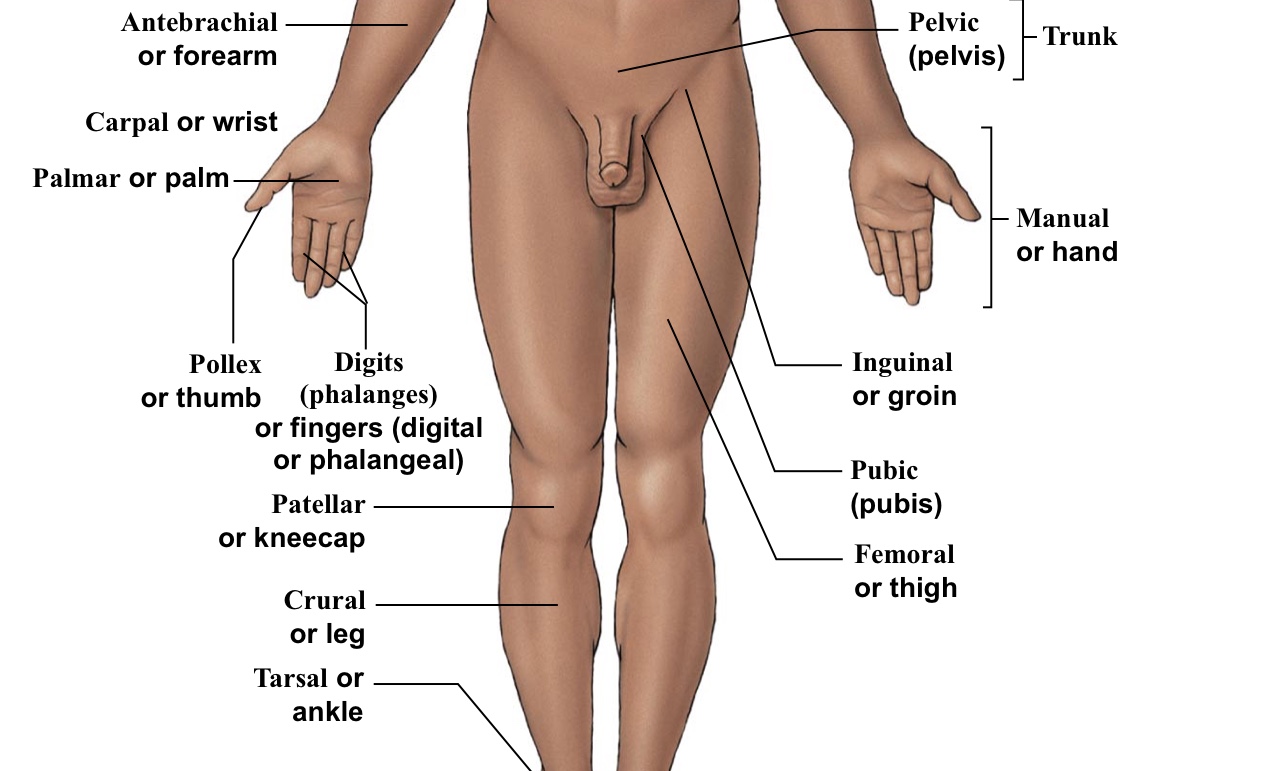
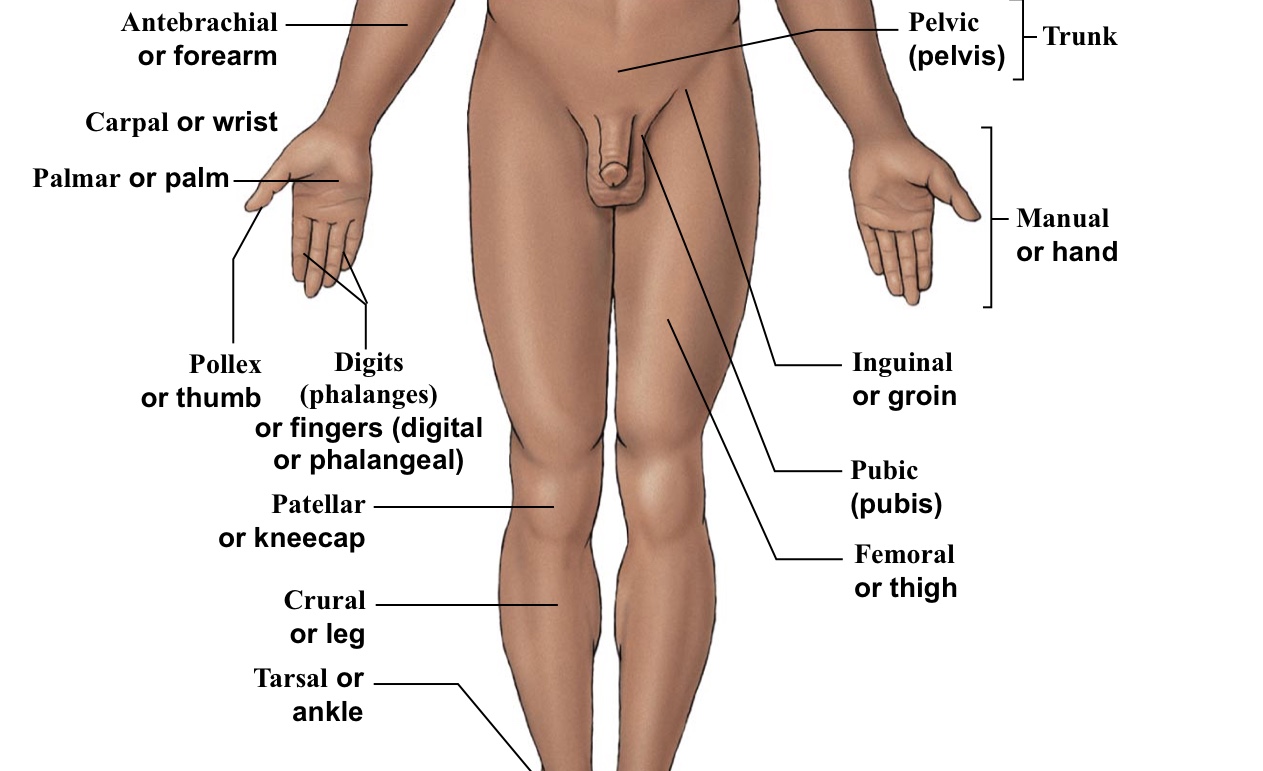
Antebrachial
Forearm
Antecubital
FRONT of elbow (where IVs get placed)
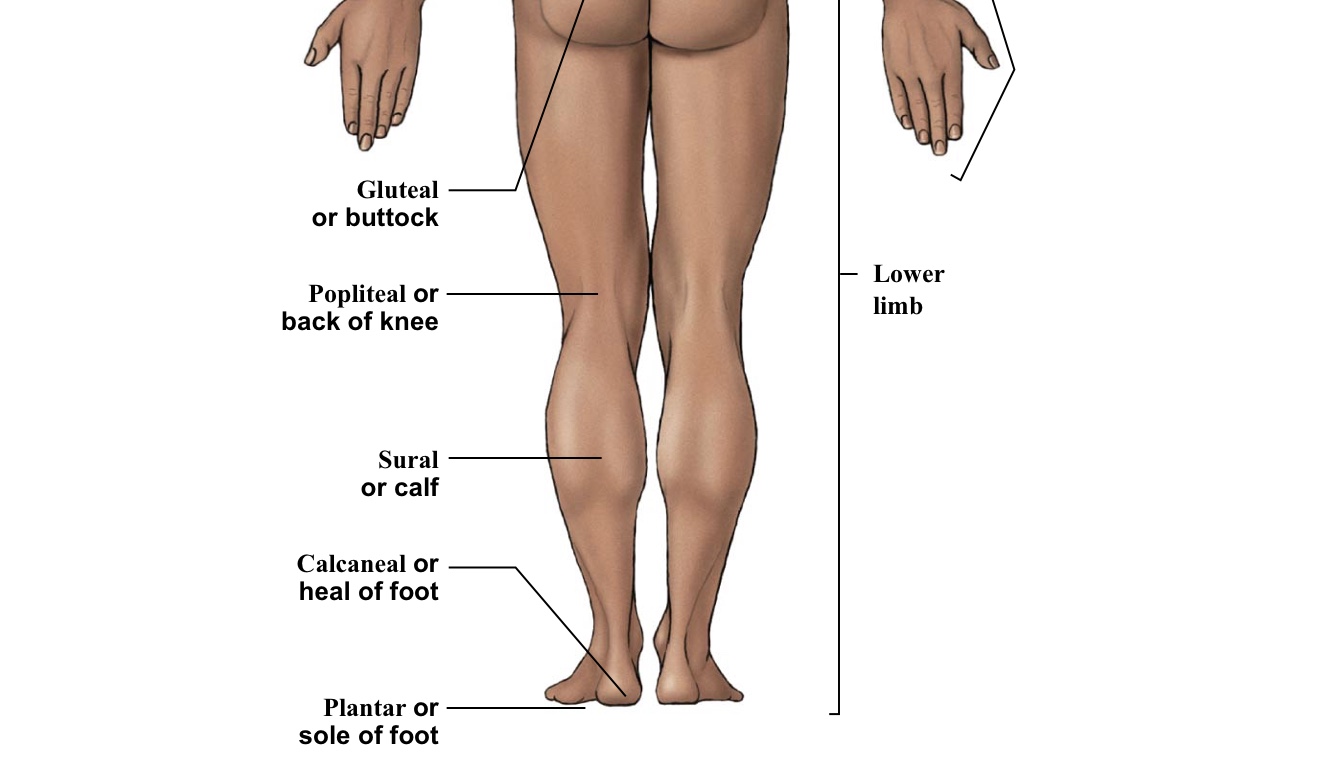
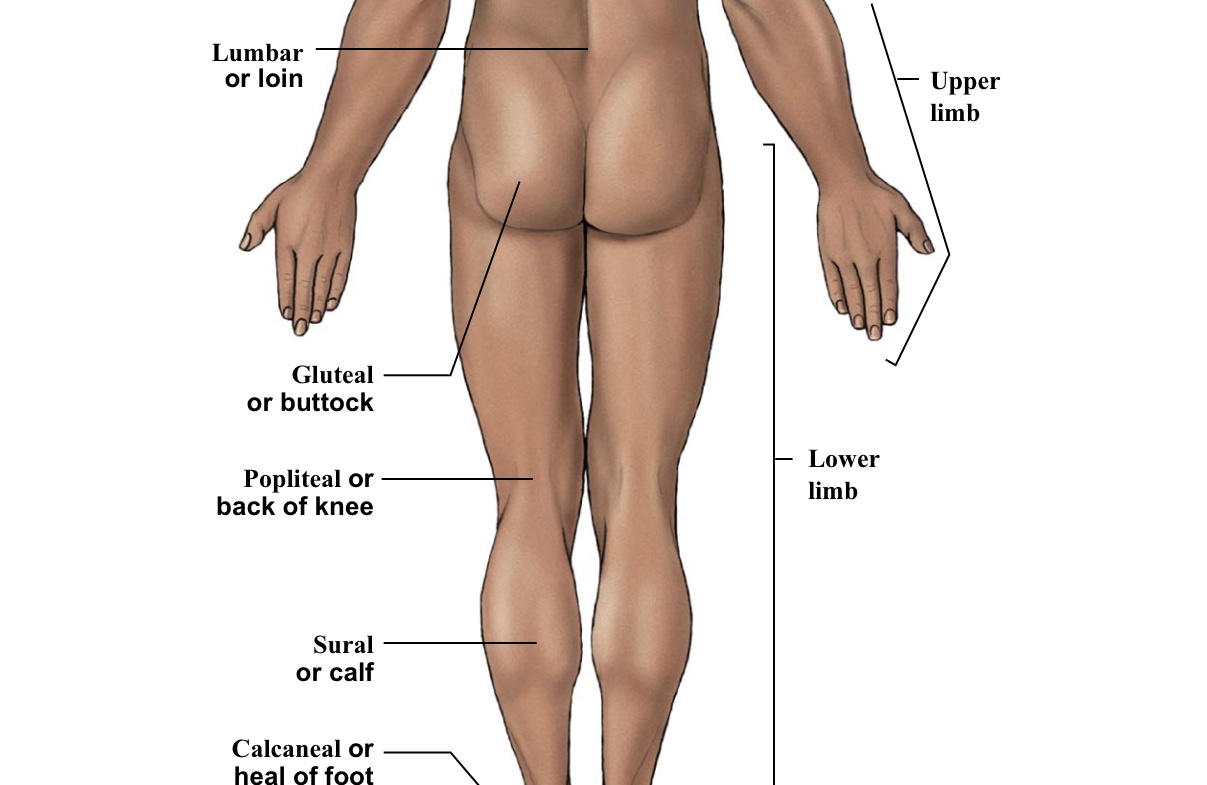
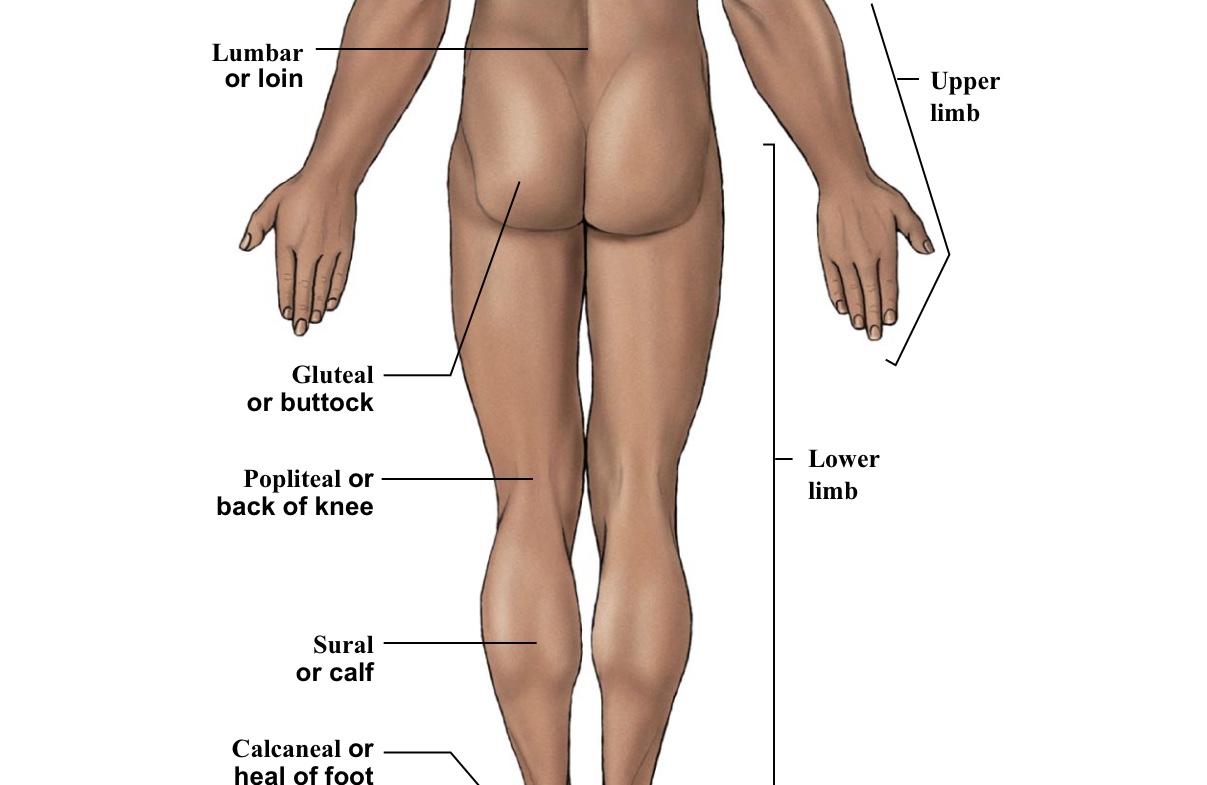
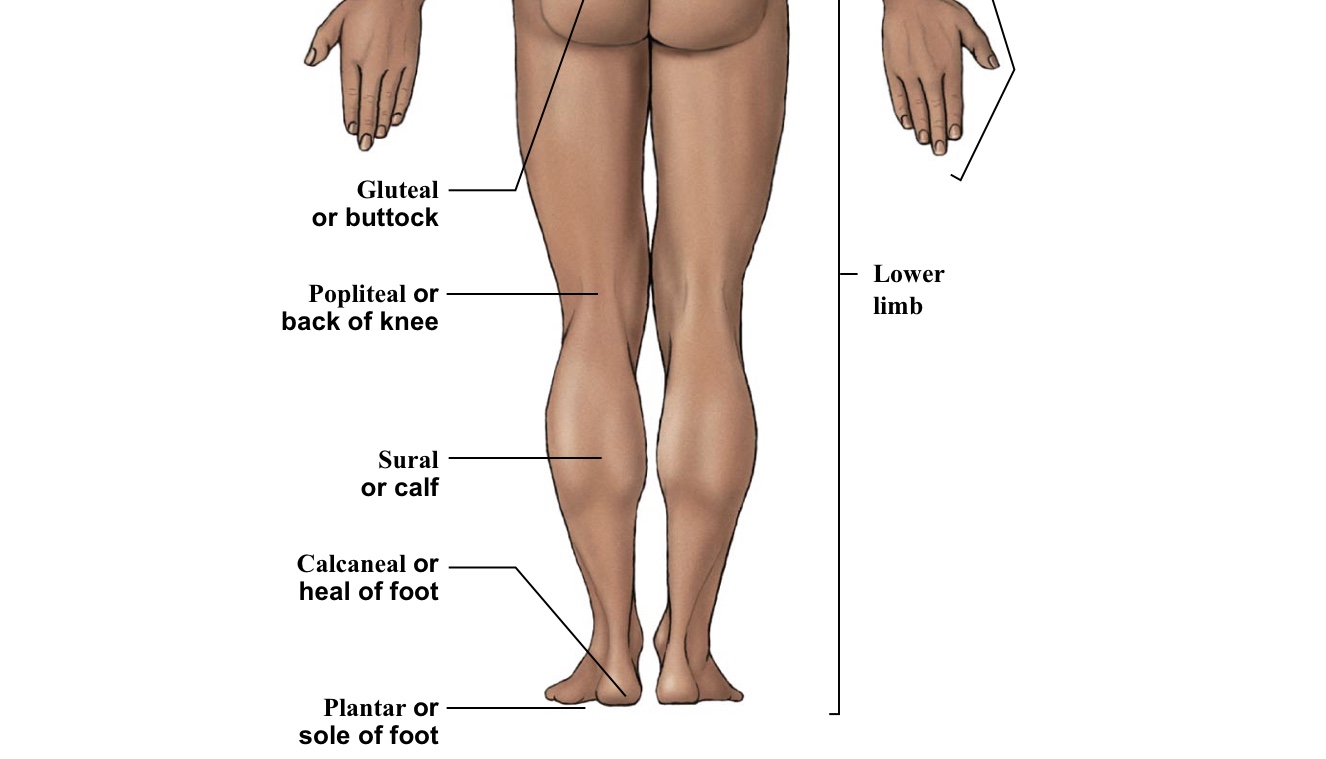
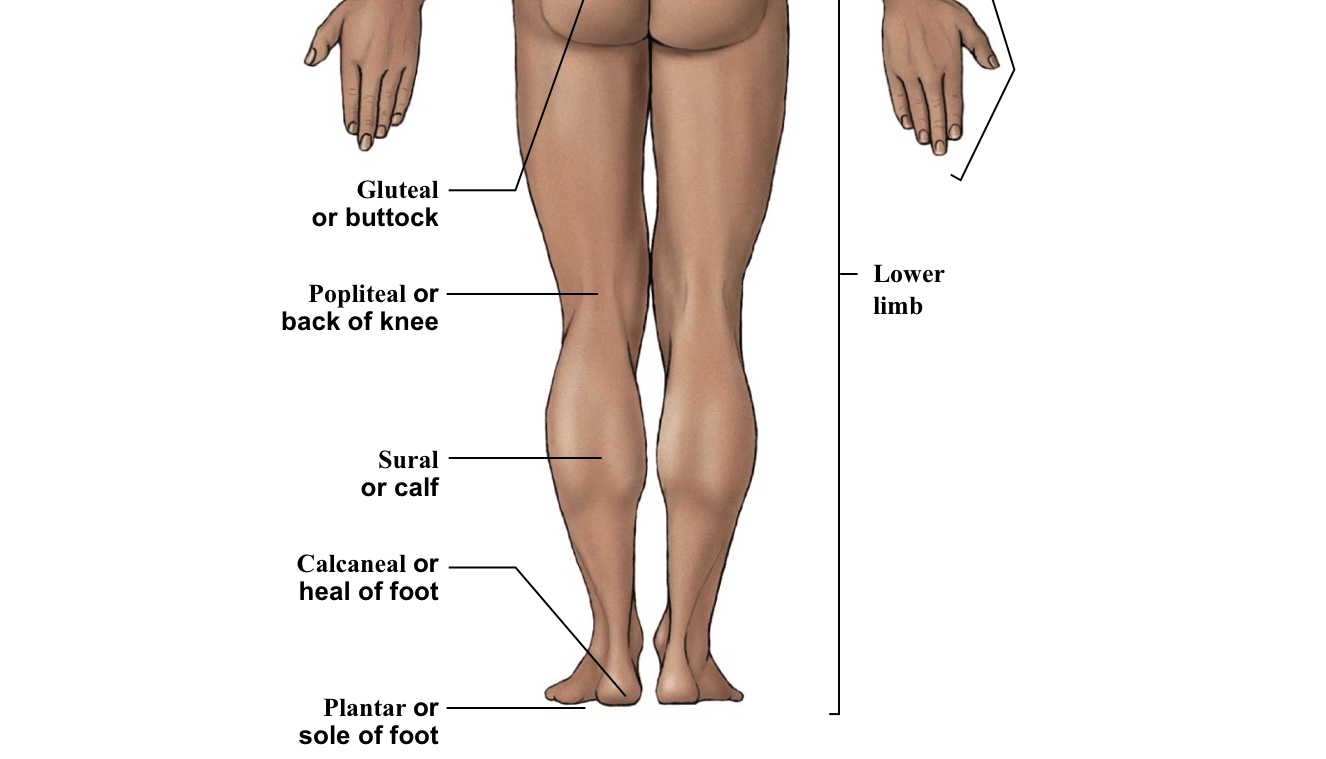
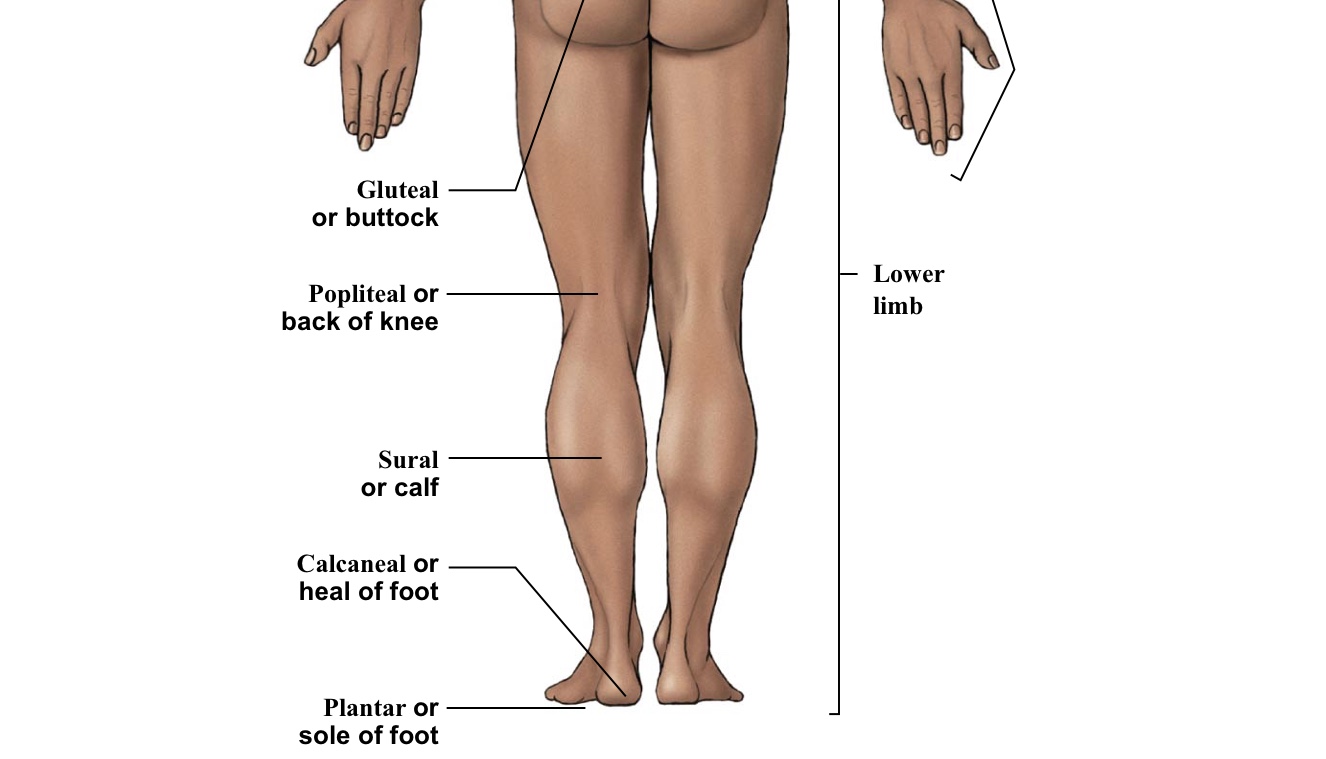
Calcaneal
Heel of foot
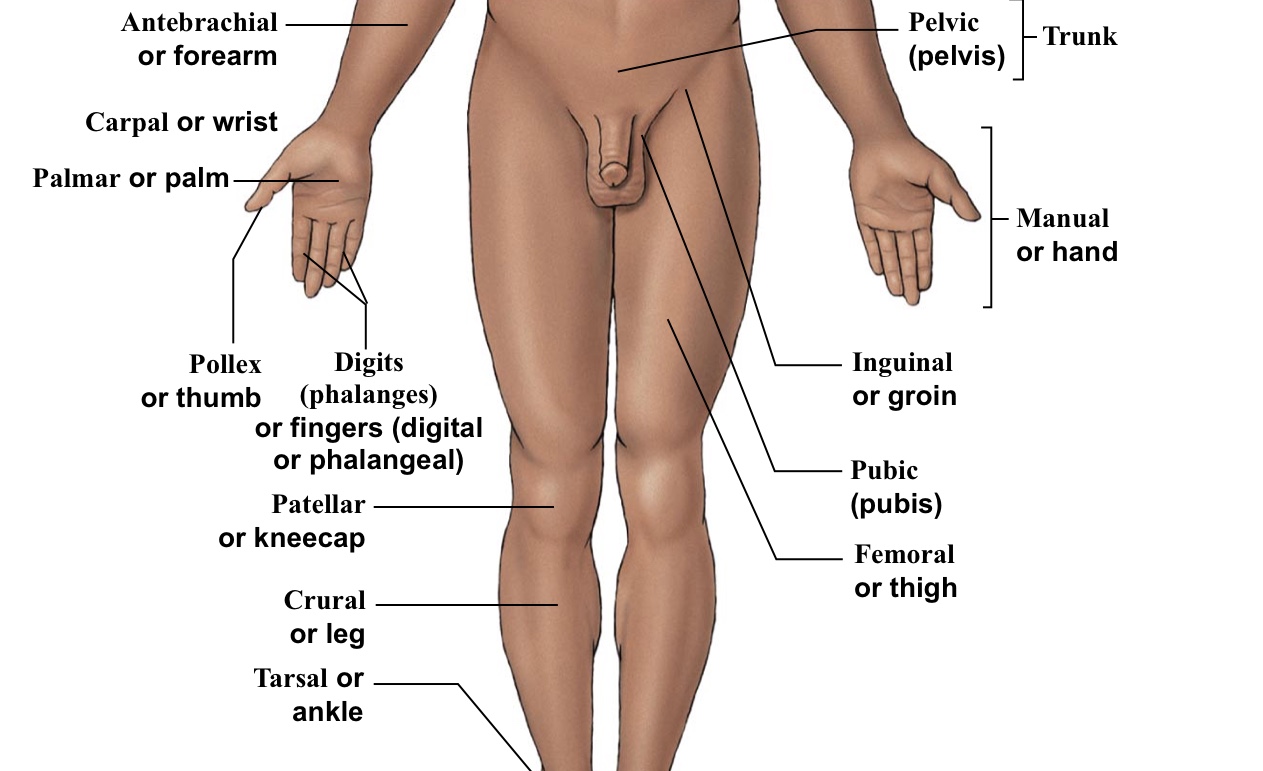
Carpal
Wrist
Cephalic
WHOLE head (bracket includes the top of the head to the chin)
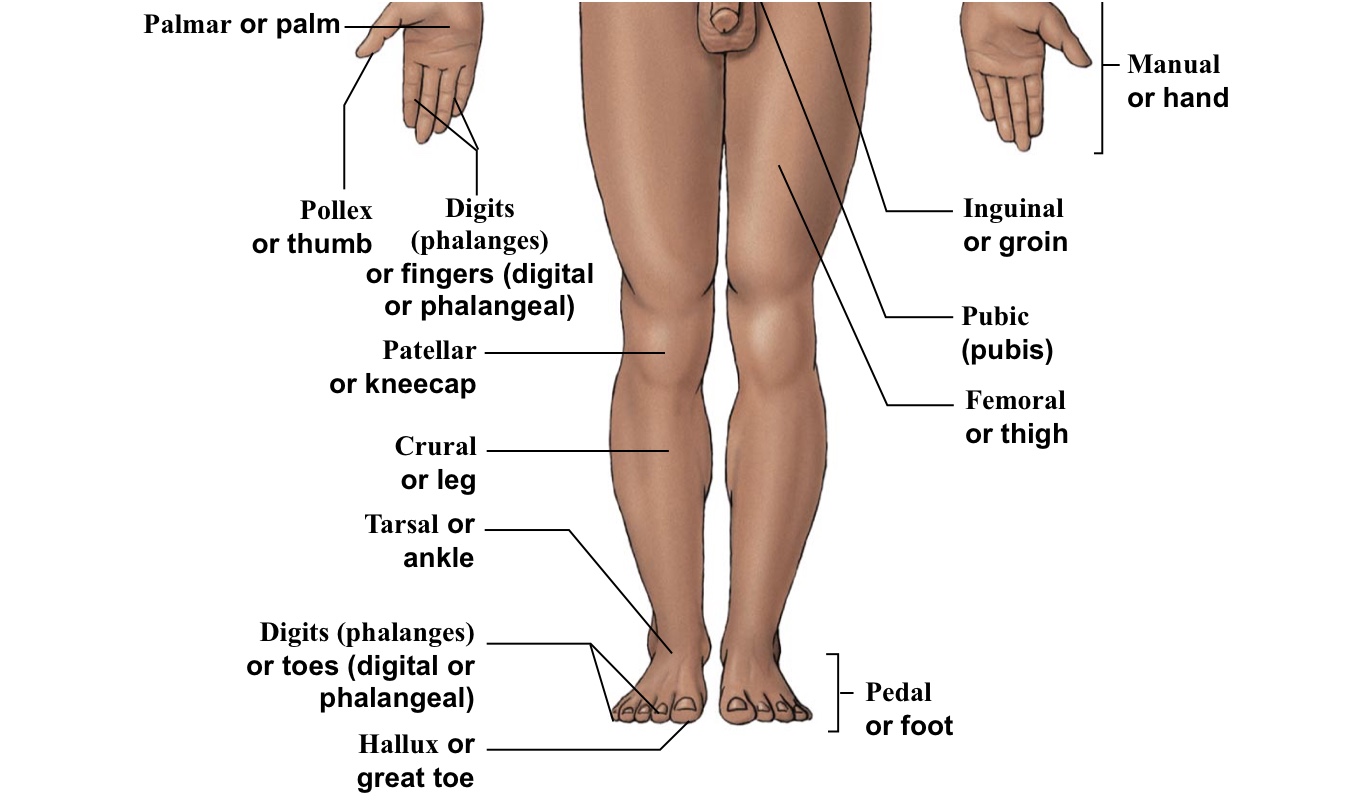
Crural
Shin (portion of leg under the kneecap on anterior half of the body)
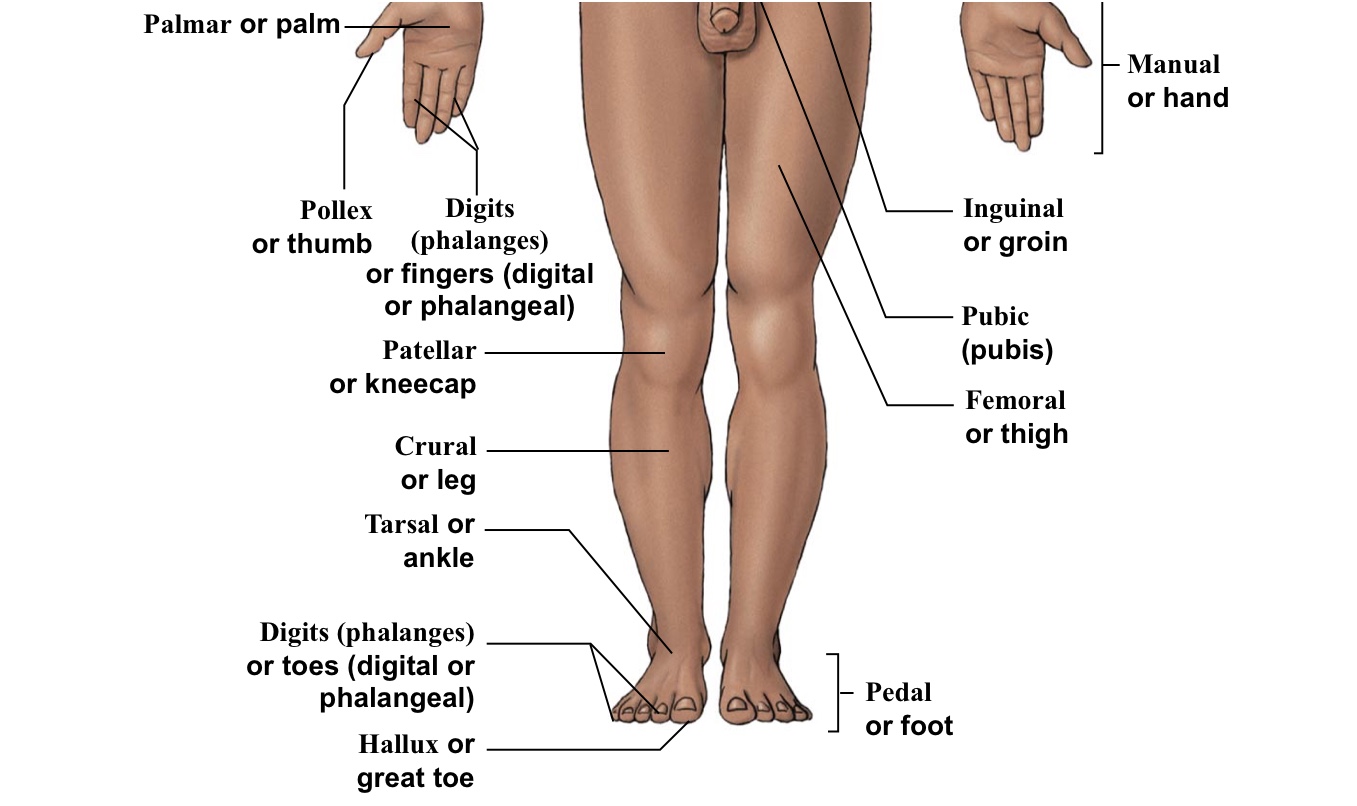
Digital (=phalangeal)
Fingers (but not the thumb)
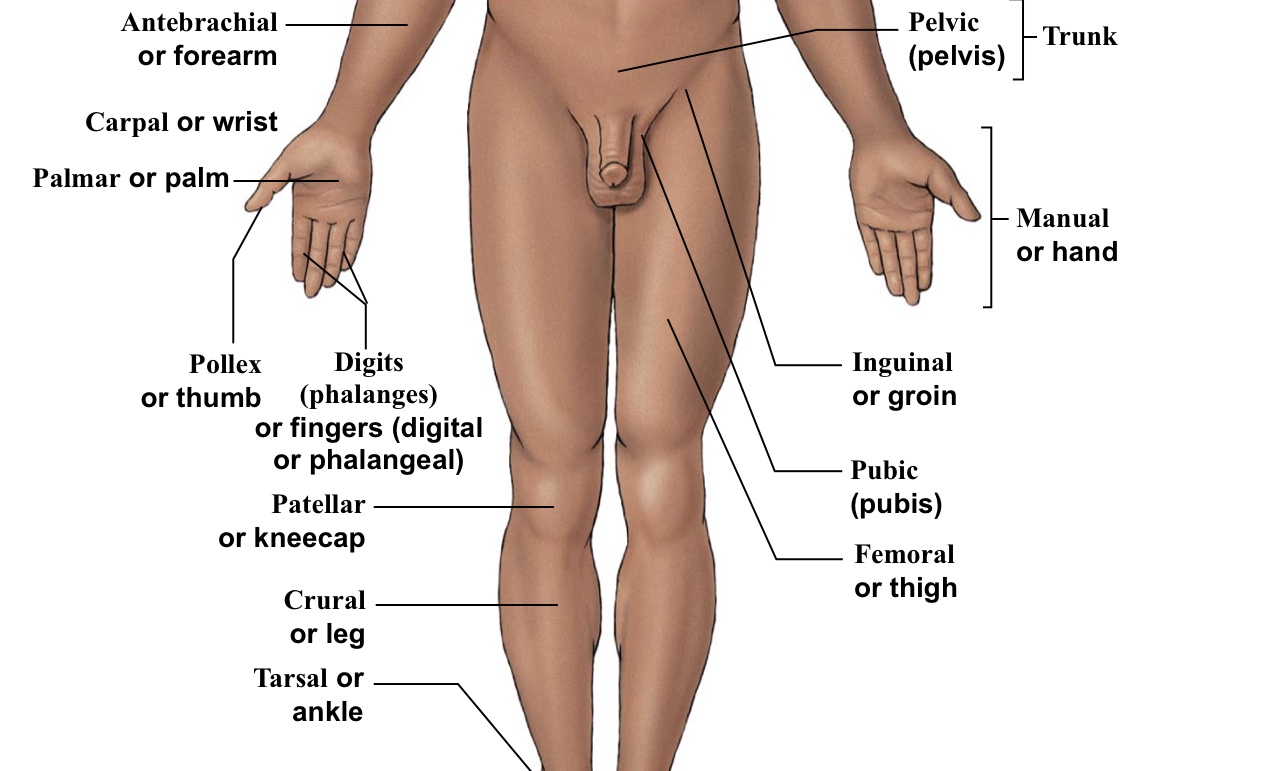
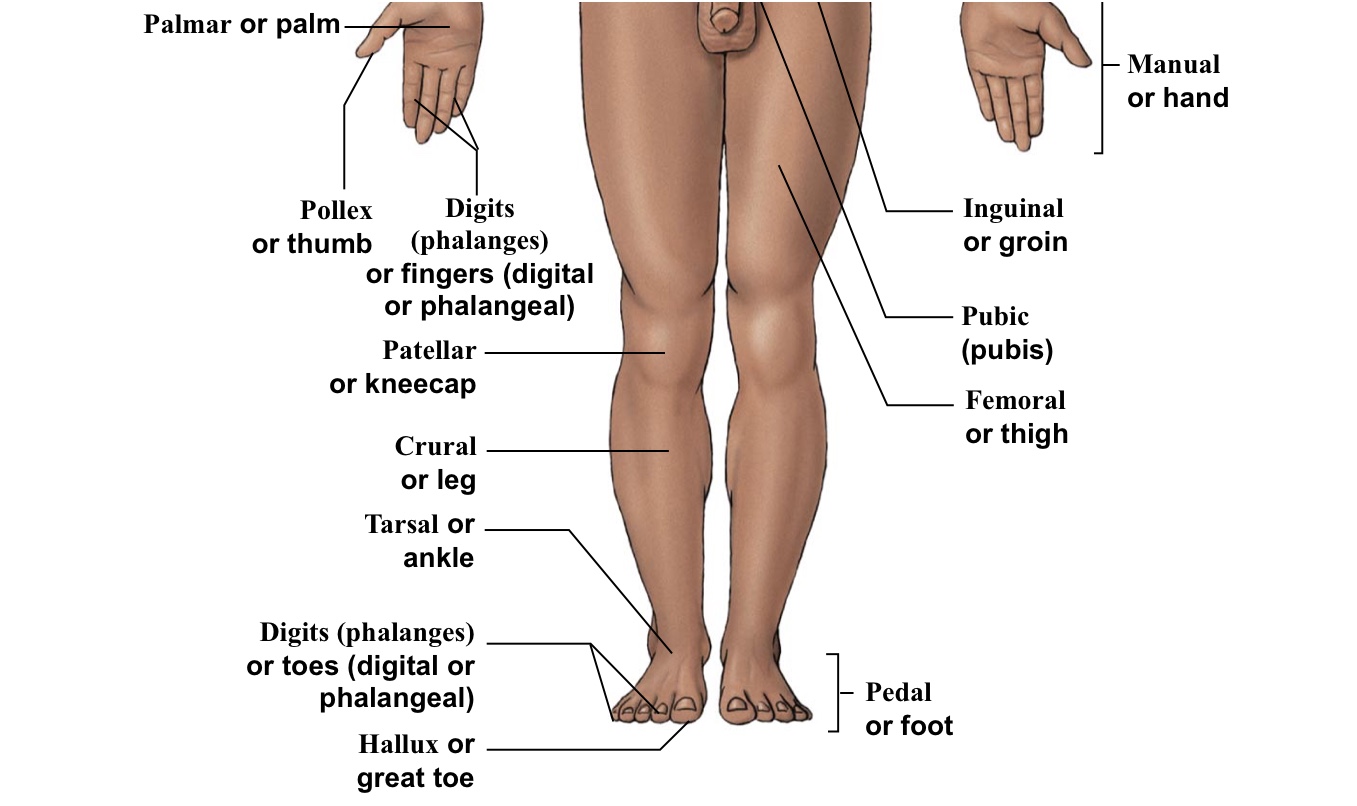
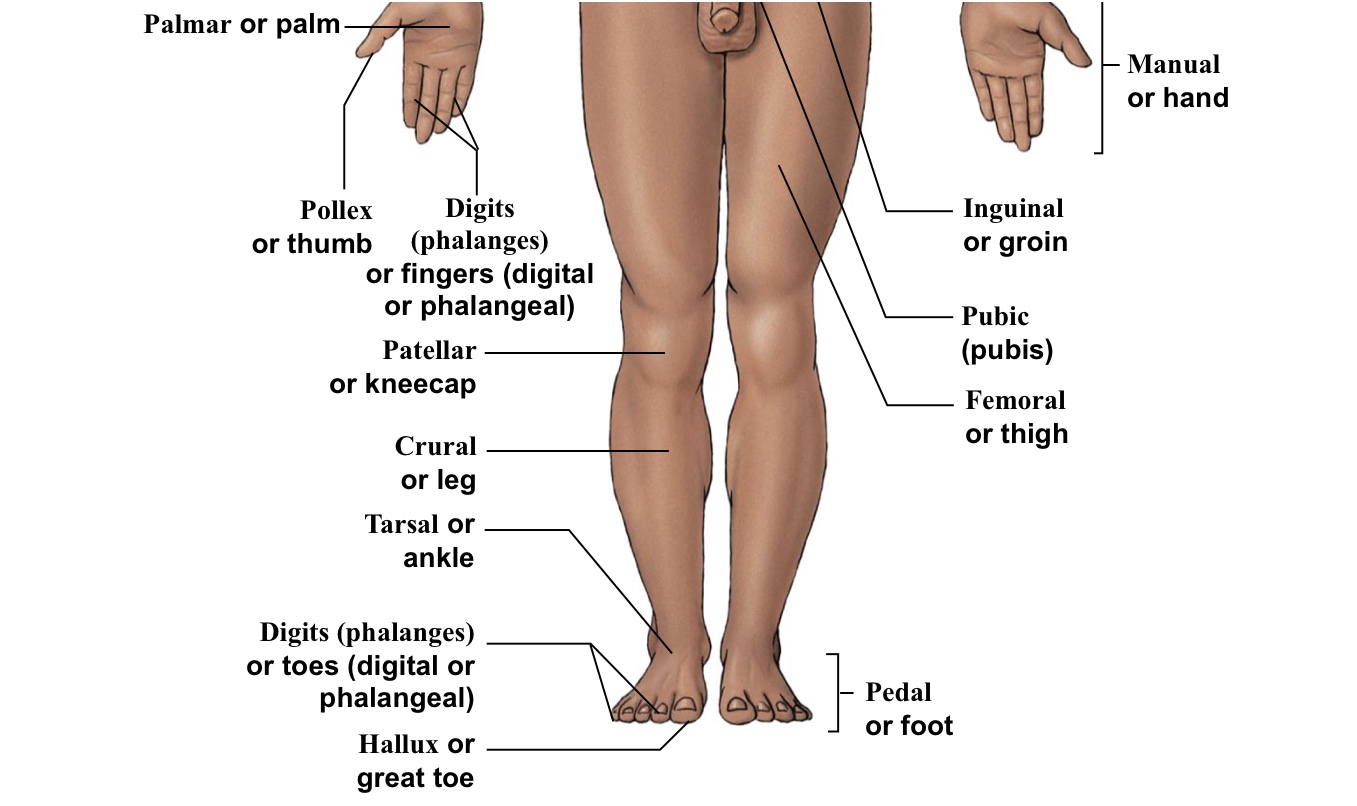
Femoral
Thigh (arrow points to the middle of the quad)
Gluteal
Buttox
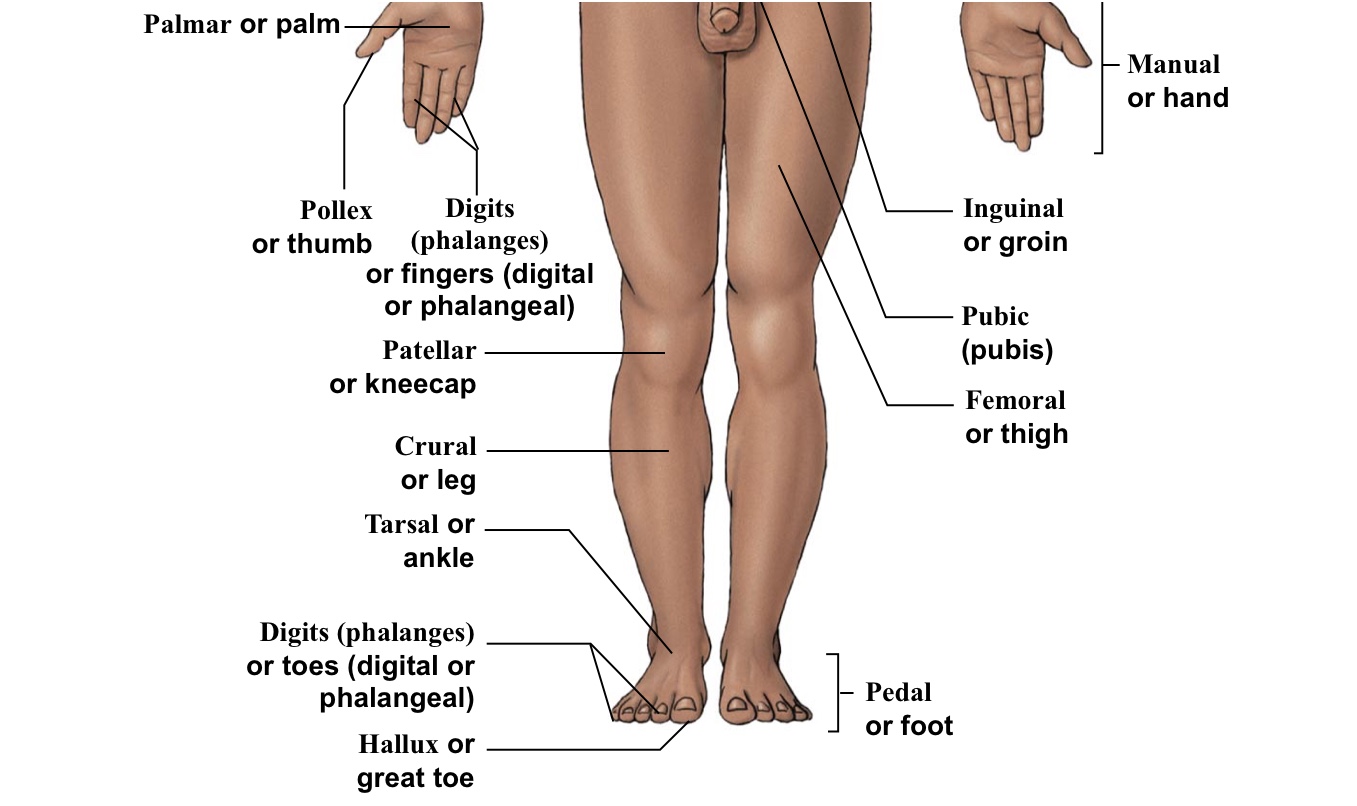
Inguinal
Groin (points to hip area-refer to picture)
Hallux
Big toe
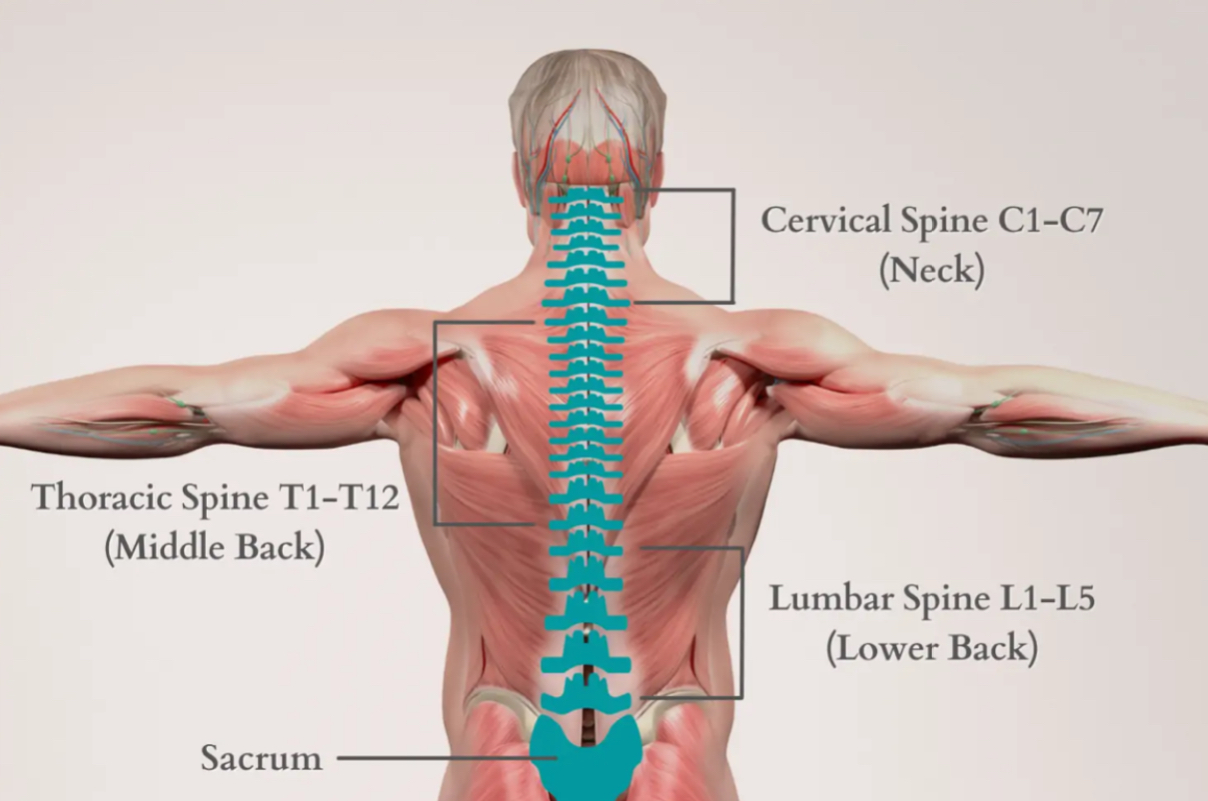
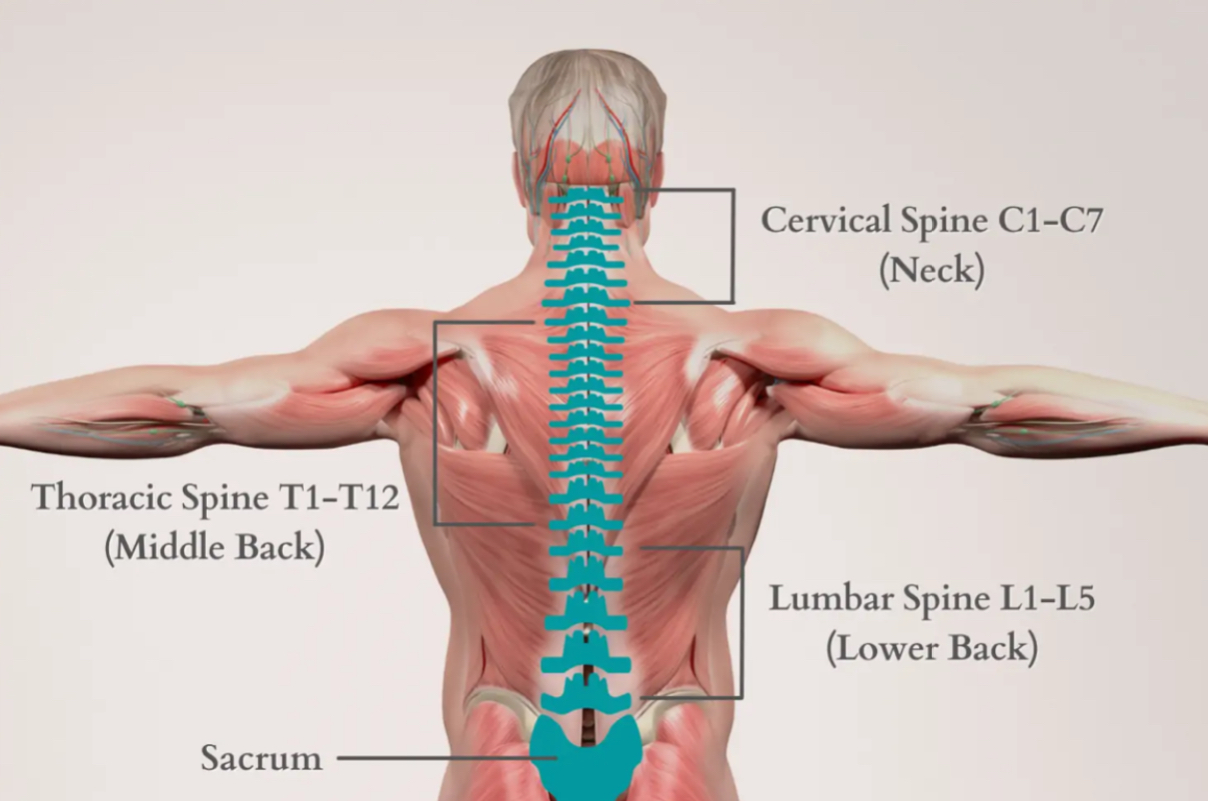
Lumbar
Lower back (lumbar spine - includes 5 vertebrae)
Mammary (pectoral)
Breast (boob area)
Manual
The WHOLE hand
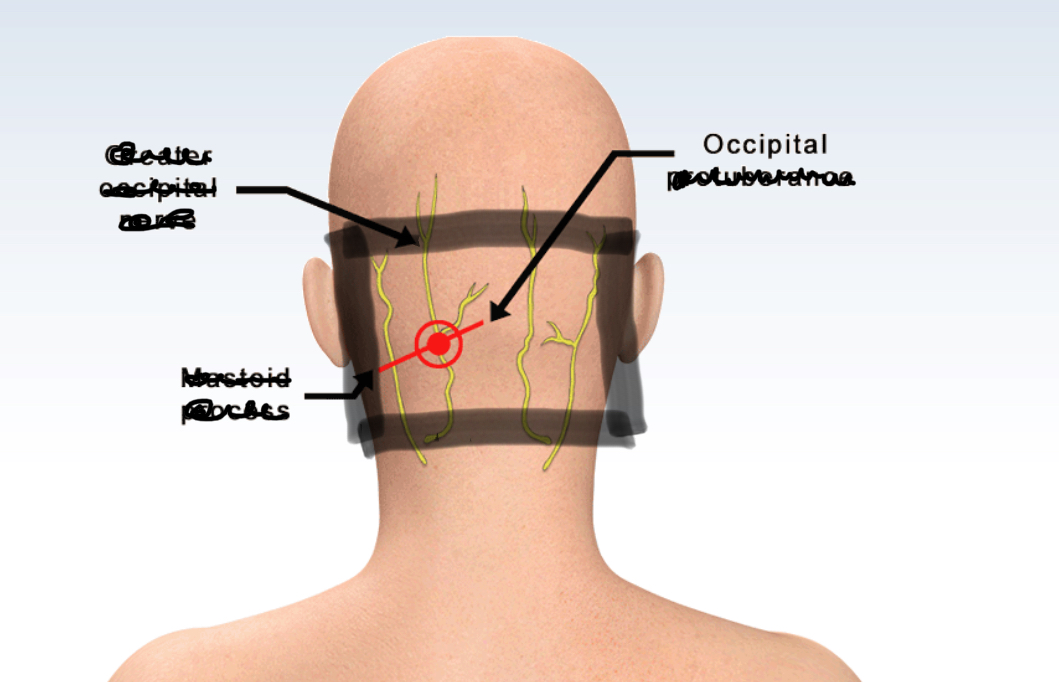
Occipital
ONLY the back of the head
Ocular (optic, ophthalmic, orbital)
Eye (arrow points to orbital socket)
Olecranal (=cubital)
The elbow
Otic
Ear
Palmar
The palm of the hand
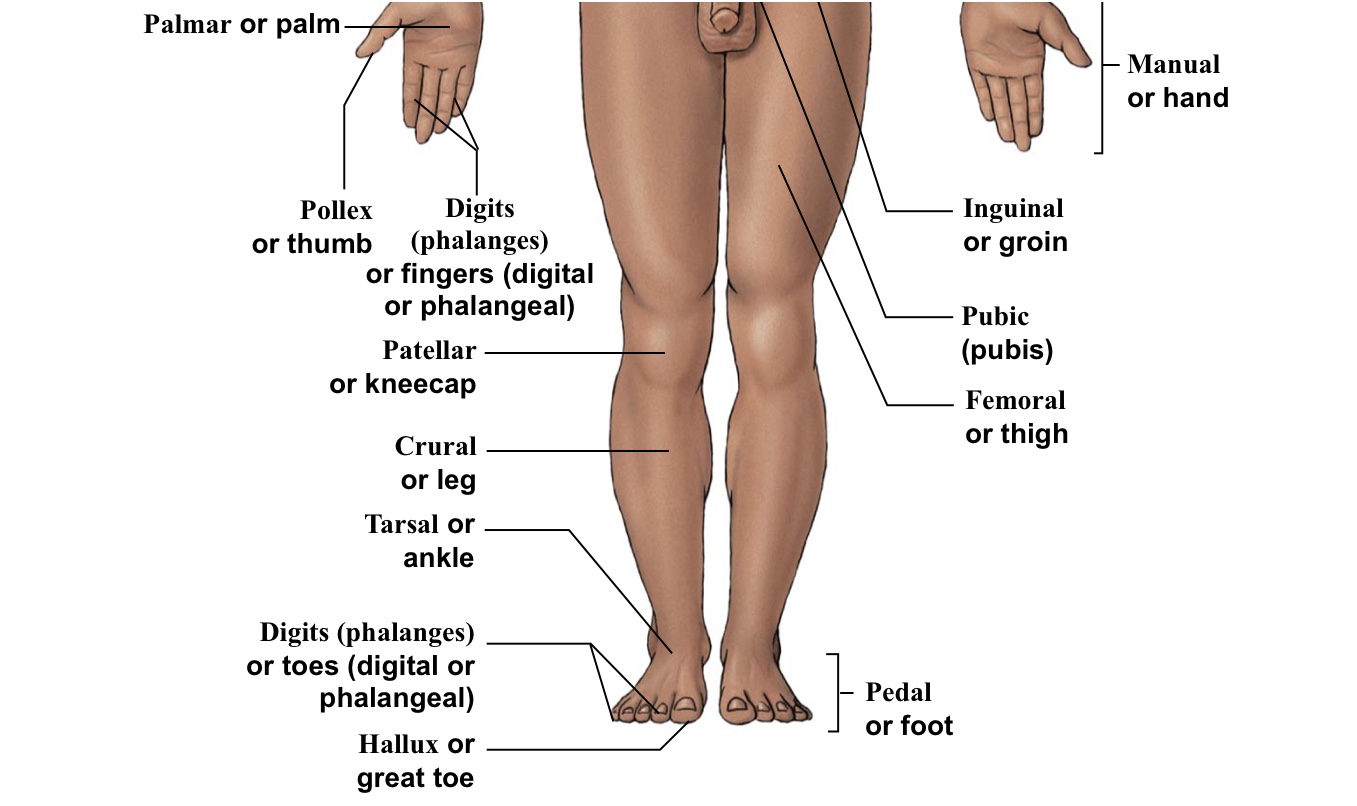
Patellar
Kneecaps
Pedal (pes)
The WHOLE foot
Pelvic
Pelvis area (directly above genitalia)
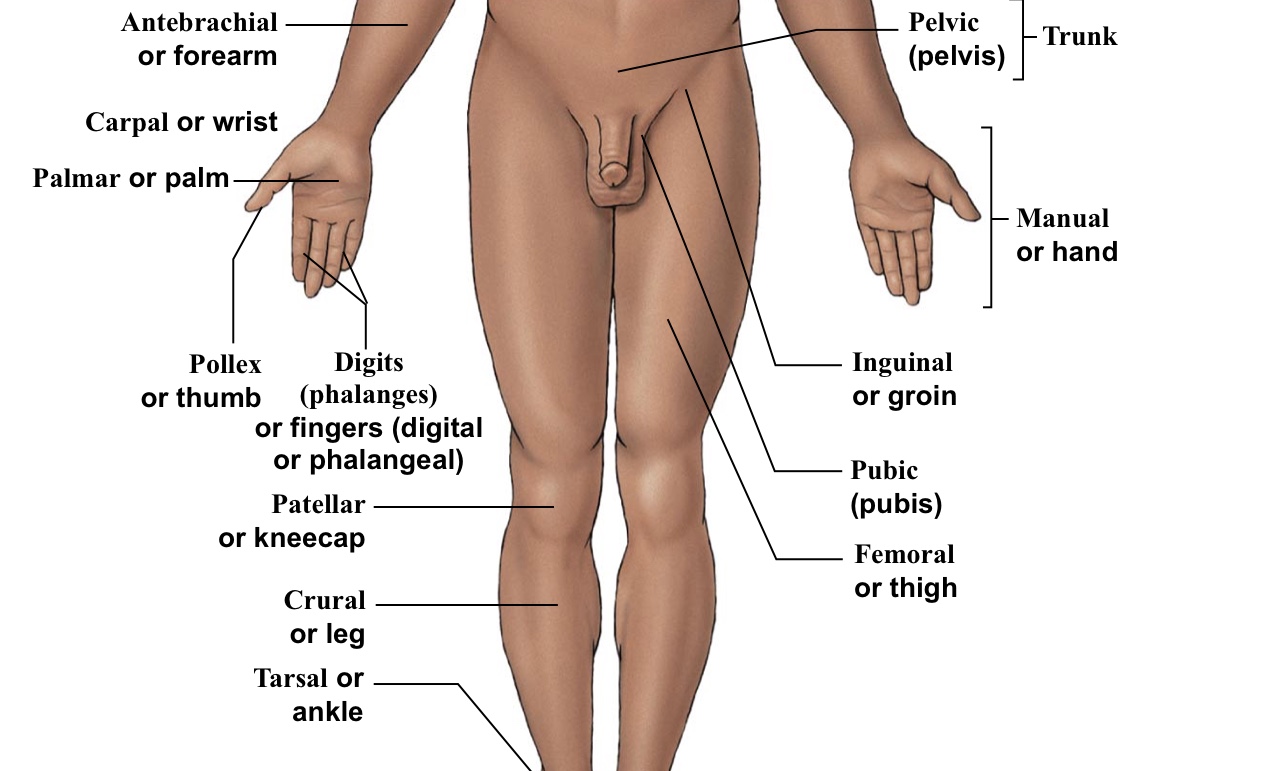
Plantar
The WHOLE bottom of the foot
Pollex
The thumb
Popliteal
BACK of the knee
Pubic
Points directly/very close to the genitalia
Sacral
Coccyx (only 1 vertebra - directly under lumbar spine)
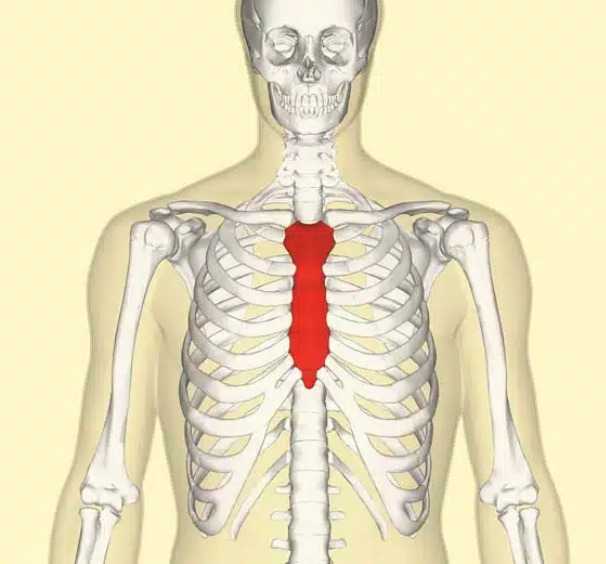
Sternal
The sternum (pointing directly to the middle of the chest)
Sural
Calf (the back portion of the leg below the kneecap)
Tarsal
Ankle bones
Umbilical
Belly button
Thoracic spine
Middle of spine (12 vertebrae shown by bracket in middle of back)
Cell Membrane (where and what is it?)
Separates inside organelles from extra cellular materials
Cytosol (where and what is it?)
Liquid inside of a cell
Nucleus (where and what is it?)
Responsible for holding DNA, centrally located inside the cell
Nuclear membrane/envelope (where and what is it?)
Allows the DNA that belongs inside the cell to stay and the other stuff like waste to go
Nucleolus (where and what is it?)
Responsible for making Ribosomes (Ribosome synthesis)
Chromatin (where is it and what does it do?)
Loosely coiled DNA in cells not dividing (surrounds the nucleus)
Golgi Apparatus (where is it and what does it do?)
Flattened membrane in the cytosol
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (where is it and what does it do?)
“Smooth ER” has no ribosomes (responsible for detox)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (where is it and what does it do?)
Rough ER HAS ribosomes (the ribosomes is what makes it “rough”)
Ribosomes (where is it and what does it do?)
Protein, responsible for protein synthesis
Mitochondrion (where is it and what does it do?)
Makes ATP (or energy) for cells and muscles
Centrosome (where is it and what does it do?)
Has 2 parts (2 paired centrioles) needed for mitosis
Vesicle (where is it and what does it do?)
Take the crap inside the cell do exocytosis (gets rid of waste)
Cilium (where is it and what does it do?)
Found in the trachea, main job is to get rid of stuff (long projection on the outside)
Flagellum
Found in male sperm ONLY
Microvillus (where is it and what does it do?)
“Finger like” projections for absorption
Microfilaments/microtubules (where is it and what does it do?)
Structural proteins for shape (little sticks on the inside of the cell)
Integral protein (where is it and what does it do?)
Within the membrane (through the entire cell)(communicate with inside and outside)
Peripheral Protein (where is it and what does it do?)
Bound to inner OR outer surface of membrane but CANNOT BE BOTH
What type of cell shape is this?
Squamous cell shape
What type of cell shape is this?
Cuboidal cell shape
What type of cell shape is this?
Columnar cell shape
What type of cell shape is this?
Goblet cell
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Simple squamous epithelium - one layer of flat cells (not a lot of protection)found around heart and lungs. Function = reduce friction and allow permeability
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Simple columnar, ciliated - one layer of rectangle shaped cells covered in cilia (lines stomach & intestines. Function = protection)
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Simple cuboidal epithelium - one layer of cube shaped cells (found around the glands, ducts and kidneys)
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Simple columnar, non ciliated - one layer of rectangle shaped cells NOT covered in cilia (just regular)(lines stomach & intestines. Function = protection)
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Pseudostratified, ciliated columnar epithelium - NOT nice and neat, columnar with NOT nearly arranged nuclei (found in nasal cavity, trachea and lungs)
What type of tissue is this? And briefly describe
Stratified squamous epithelial - multiple layers of flat cells (provides protection) (found in surface of skin, lining of mouth and esophagus. Function = protection )