Water Pollution and Treatment
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Chromium Defnition
a heavy metal that can contaminate water through industrial activities, particularly from electroplating, leather tanning, and stainless steel manufacturing.
Which form of Chromium (Cr) is less toxic and less soluble?
Cr3+
Fe3O4-activated C removes which heavy metal and at what pH?
Chromium at pH of 3
How does Cadmium effect enzyme functions?
Alters enzyme functions by replacing zinc, impairing catalytic activity
Summer stagnation definition
Cadmium precipitates as insoluble CdS via microbial sulfate reduction.
Winter Mixing Definition
Aerobic bay water desorbs cadmium, dispersing it into the aquatic system.
Which disease does Cd cause?
Itai Itai
What does Itai-Ital disease cause?
softening of bone marrow, osteoporosis, and renal failure
What can EDTA do to Cd?
can work as a catalyst to remove Cd
Mercury Definition
a heavy-metal pollutant with significant environmental and health risks, including neurotoxicity and birth defects
Where is Mercury (Hg) found?
continental rocks, coal, lignite, emissions, and goal extraction; often exceeding 100ppb
what are the industrial use of Hg
Chlorine gas production and pesiticde and fungicides
Which heavy metal cuased the Minamata Bay, Japan tragedy and what did it cause?
Mercury posioning by contaminated seafood, leading to 43 dead and severe congenital defects
What does Hg toxicitiy cause?
neurological damage and phychological symptoms
What is the aquatic methylation process in Hg
•Anaerobic bacteria convert inorganic mercury to methylmercury compounds (CH₃Hg⁺ and (CH₃)₂Hg).
•Methylcobalamin (vitamin B12 analog) facilitates methylation.
•Bioaccumulation in fish lipid tissues with concentration factors > 10³.
Nanomaterials definition
thermal stability, conductivity strength and 1-100um in size
Siloxanes Definition
used in many commercial and industrial applications due to the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility
What are the health impacts of siloxanes
D4, D5, and D6 included significant endocrine disruption, reproductive toxicity, and liver toxicity
Disinfection By-Products (DBPs) Definition
are compounds formed by reactions between water disinfectants (e.g., chlorine, hypochlorite) and naturally occurring substances in water.
What are some examples of DBPs?
Trihalomethanes (THMs): Chloroform (CHCl₃), Dibromochloromethane (CHClBr₂), Bromodichloromethane (CHCl₂Br), Tribromomethane (CHBr₃)
What are the exposure pathways of DBPs?
Drinking, skin contact, and inhalation
What is an example of Pesticide degradation products: glyphosate
Aminomethyl phosphonic acid; highly toxic pesticide breakdown product
Organochlorine Mode of Action
Cause sodium/potassium imbalance, preventing normal nerve transmission and GABA Receptor Inhibition
What is another banned organochlorines?
endosulfan
What is the chemical structure of endosulfan?
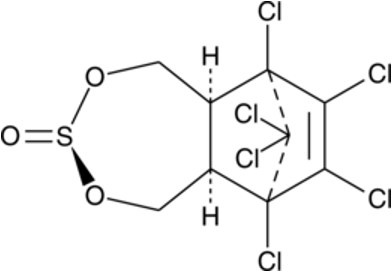
What is the mode of action for endosulfan?
Gaba-gated chloride channel blockers
What does endosulfan inhibit?
endocrine disruptor - weak estrogenic inhibitor
What does endosulfan effect; epigenome effects?
Methylates DNA and aerially transported at high temps and continuously ciculates throught environment
How long does endosulfan stay air-born half-life
3-12 months
Organophosphates definition
Organic compounds containing phosphorus.
What are some examples of organophosphates
Malathion and Chlorpyrifos
What enzyme does organophosphate inhibit?
Inhibits acetylcholinesterase: Critical enzyme for nerve function.
What is the toxic effect of Malathion?
Hydrolyzed by carboxylase enzymes in mammals into nontoxic products.
What is the toxic effect of chlorpyrifos?
A broad-spectrum insecticide -corn, soybeans, citrus, tree nuts, alfalfa, and many other crops.
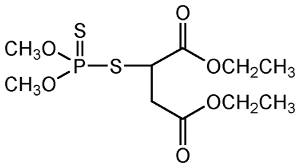
Malathion Chemical Structure
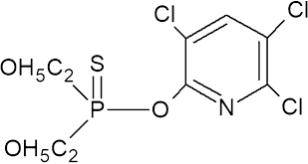
Chlorpyrifos Chemical Structure
How does Organophosphate insecticides bind to Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)?
It binds covalently to the active site of the enzyme
How does the binding inhibit AChE from breaking down acetylcholine (ACh) at synaptic clefs result for postsynaptic cells?
Accumulation of ACh at synapses, leading to overstimulation of acetylcholine receptors (AChR
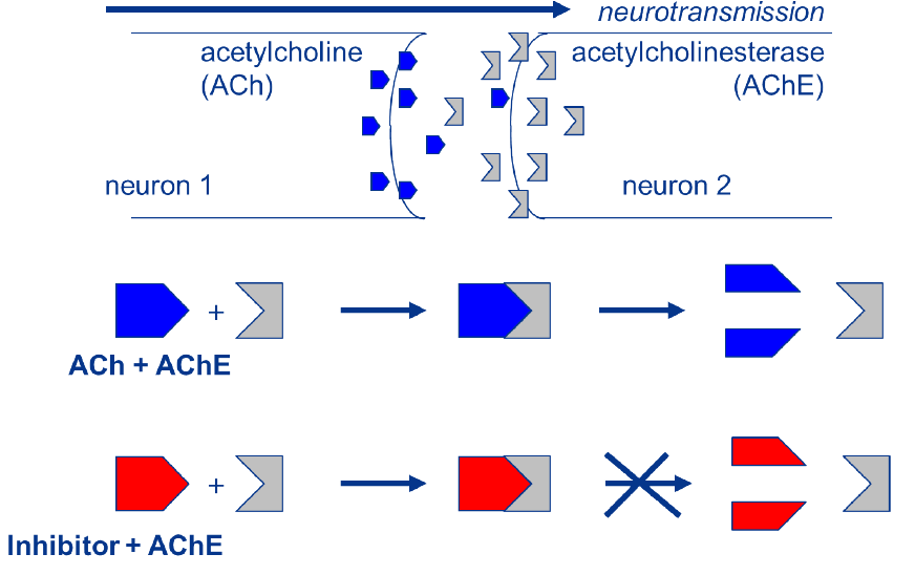
The Mechanism of Action of the neurotoxicity from organophosate insecticides
ACh (blue) is released from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse where it
merges to and activates the AChR present on membrane of the postsynaptic cell (not
shown). Meanwhile, AChE (grey) present in the synaptic cleft hydrolyses the ACh
neurotransmitter to avoid overstimulation of the postsynaptic membrane. Organophosphate
insecticides (red) bind to the AChE and prevent its reaction with ACh, causing accumulation
of ACh
Carbamates Definition
Organic derivatives of carbamic acid
what is an example of carbamates?
Aldicarb
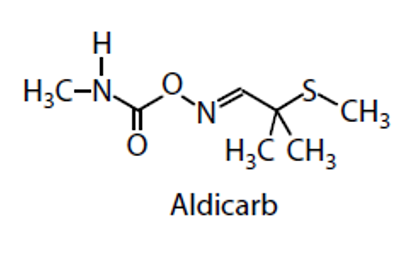
What does Organophosphates and Carbamates inhibit?
Acetylcholinesterase
Why is Carbamates less toxic than many organophosphates?
to transient cholinesterase inhibition and rapid reactivation of AChE enzymatic activity.
Herbicides: cell membrane disruptors Defintion
Destroy cell membranes, contents leak out, plant dessicates
What are examples of cell membrane disruptors
Diquat and paraquat
Herbicides: Photosynthesis inhibitors definition
interupt one or more steps of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis inhibitors example
Atrazine
Herbicides: Pigment Synthesis inhibitors definition
inhibit formation of chlorophyll, plants cannot photosyntehsize
Pigment Synthesis inhibitors example
zorial
Herbicides: Growth regulator Definition
affect several plant process-cell division, protein synthesis, respiration and upset normal hormonal balance
Growth regulator example
Dicamba
Herbicides: Seedling growth inhibitor (Root inhibitor) definition
inhibit cell division (mitosis) of developing roots
Herbicides: Seedling growth inhibitor (Shoot inhibitor) definition
MOA is related to photosynthesis, light required, inhibits key enzyme in chlorophyll synthesis, toxic radicals formed, disrupts cell membranes
Seedling growth inhibitor (Shoot inhibitor) example
Oxadization
Seedling growth inhibitor (Root inhibitor) example
Balan
Herbicides: Lipid synthesis inhibitors definition
disrupt lipid biosynthesis in grasses, turning the leaves reddish
Herbicides: Lipid synthesis inhibitors example
Poast
Herbicides-Amino Acid Inhibitors example
glyphosphate
Glyphosate Definition
Inhibit the production of amino acids, resulting in inhibition of plant proteins
What does Glyphosphate disrupt
Shikimate pathway pathway by competing with the EPSP synthase enzyme
What does glyphosphate prevent which amino acid productions?
tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine in plant cells.
What enzyme does Glyphosate disrupt
endocrine disruptor that can interfere with hormone functions and aromatse inhibitor
What does glyphosphate effect?
Cardiovascular, digestive, and potentially cause cancer
What are some natural insecticides?
Nicotine, pyrethrins, and neem
What is pyrethrins?
They are extracted from certian chrysanthemums and are used as natural insecticides due to their effectiveness against pests.
Why are Nicotine, pyrethrins and neem good?
they are biodegradable and easily degraded by enzymes and are quickly paralyze flying insects
What are pyrethroids?
Synthetic analogs of pyrethrins, produced for widespread insecticidal use
Which pyrethroid is more frequently used?
Permethrin
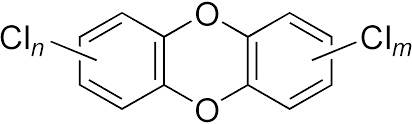
What is the by-product of organochlorine pesticides?
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), commonly known as "dioxins.“
What does Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs) cause in humans
chlorance and is linked to hazardous wast incidents
what was the most notbale case of contamination of PCDDs?
Times beach, Missouri and Hopewell, Virginia (Kepone Incident)
What is the chemical structure of PCDDs?
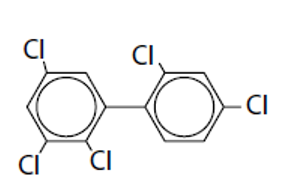
What are Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) uses
High chemical, thermal, and biological stability so its good for coolant-insulatnt fluids, plasticizsers, epoxy paint additives
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) are found where?
found in water, sediments, fish, and bird tissues
Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Chemical structure
what are the environmental impacts of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
persistent pollutant that accumulates in sediments, limiting biodegradtion and is promident in the Hudson river sediments
What causes the Decreased Thyroid Hormone (T4) Levels?
Organohalogenated Phenols causes the decrease
What protein does Organohalogenated Phenols bind to inhibit T4?
The protein binds to transthyretin (TTR), a protein that transports thyroid hormone T4.
What are the effects on T4 levels caused by organohalogenated Phenols?
increases levels of unbound T4 in bloodstream, enhancing clearance of T4 from the body via liver metabolism and urinary excretion. This leads to an overall lower levels of T4 in the blood, disrupting thyroid function
what does pharmaceuticals in water do?
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), β-blockers ad psychoactive compounds, analgesics, antibiotics, endocrine disruptors, antiretroviral drugs, and drugs to treat cancer.
Triclosan and its derivatives are bacteridides in water, where are they found?
found in antibacterial soaps, shampoos, deodorants, lotions, and even consumer items like sportswear and carpets
What are some sources of radionuclides?
Cosmic reactions, uranium decay series (e.g., Radium-226, Potassium-40).
What are some artifical sources of radionuclides?
•Nuclear fission in reactors and weapons (e.g., Strontium-90, Cesium-137).
•Non-fission neutron reactions in reactors (e.g., Cobalt-60).
What are some transuranic elements of radionuclides?
Neptunium, Plutonium, Americium, Curium.
What are some characteristics of raditation?
•Alpha particles: High ionization, low penetration.
•Beta particles: Moderate penetration, lower ionization.
•Gamma rays: High penetration, lower ionization.
Radionuclides in the Aquatic Environment chemical formula
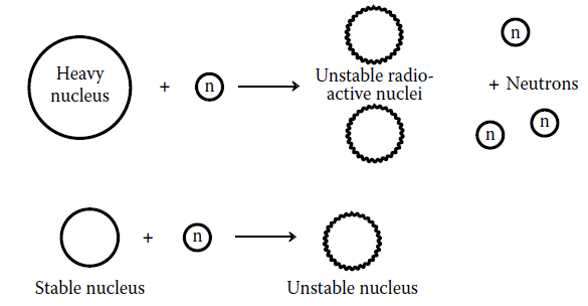
chemical formula to get Th and alpha particles
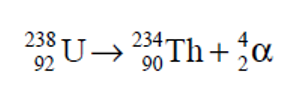
chemical formula to get Cl and gamma rays
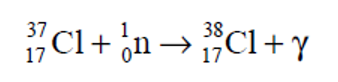
chemical formula to get Ar and beta particles
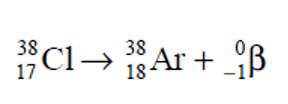
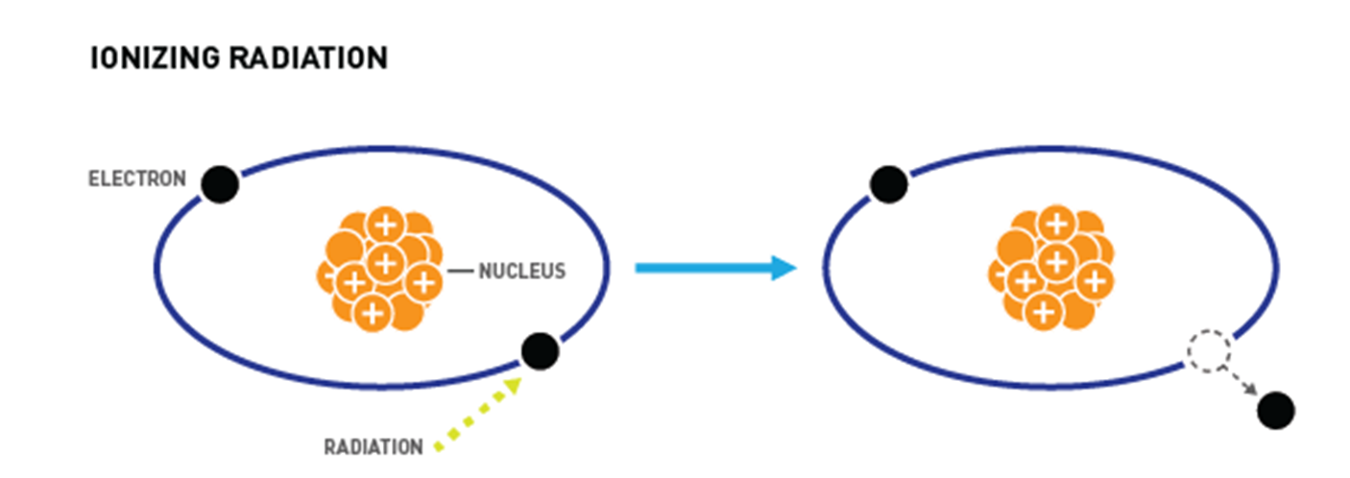
What is ionizing radiations?
radiation with enough energy so that during an interaction with an atom, it can remove tightly bound electrons from the orbit of an atom, causing the atom to become charged or ionized.
What are some examples fo ionizing radtiation?
Alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons gamma and x-rays
What are background ionizing raditations?
constant source of ionizing radiation present in the environment and emitted from a variety of sources.
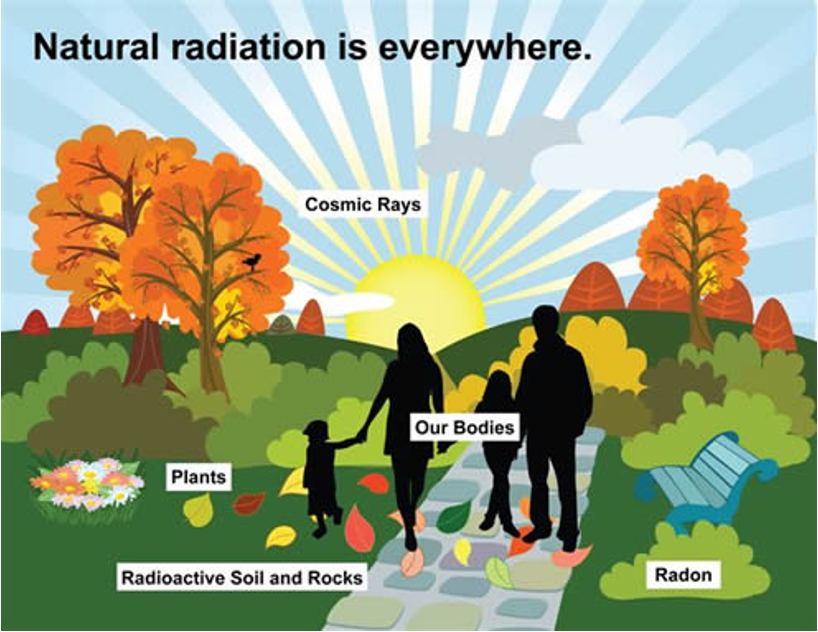
How long is the half life of radon gas?
3.8 days
What happens to our lungs when we breath in radon gas
it gets into the lungs where they decay further and emit alpha particles
what does alpha particles cause?
•greatest amount of ionization and are therefore potentially the most dangerous type of radiation. results in lung cell death/damage
what are the top 2 nuclear accidents
Chernobyl and Fukushima
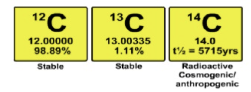
what are radioactive isotopes?
•Different isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but differing numbers of neutrons.
What does Uranium-238 undero to become lead-206
14 radioactive decays
What is alpha raditation
•Made up of two protons and two neutrons and is positively charged. greatest exposure for an average person is inhalation of radon
What is Beta radiation
stream of electrons and has a negative charge. can damage skin and is hazardous if ingested